Abstract
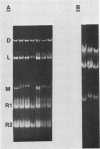
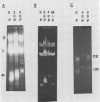
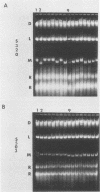
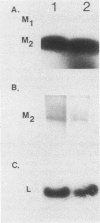
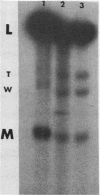
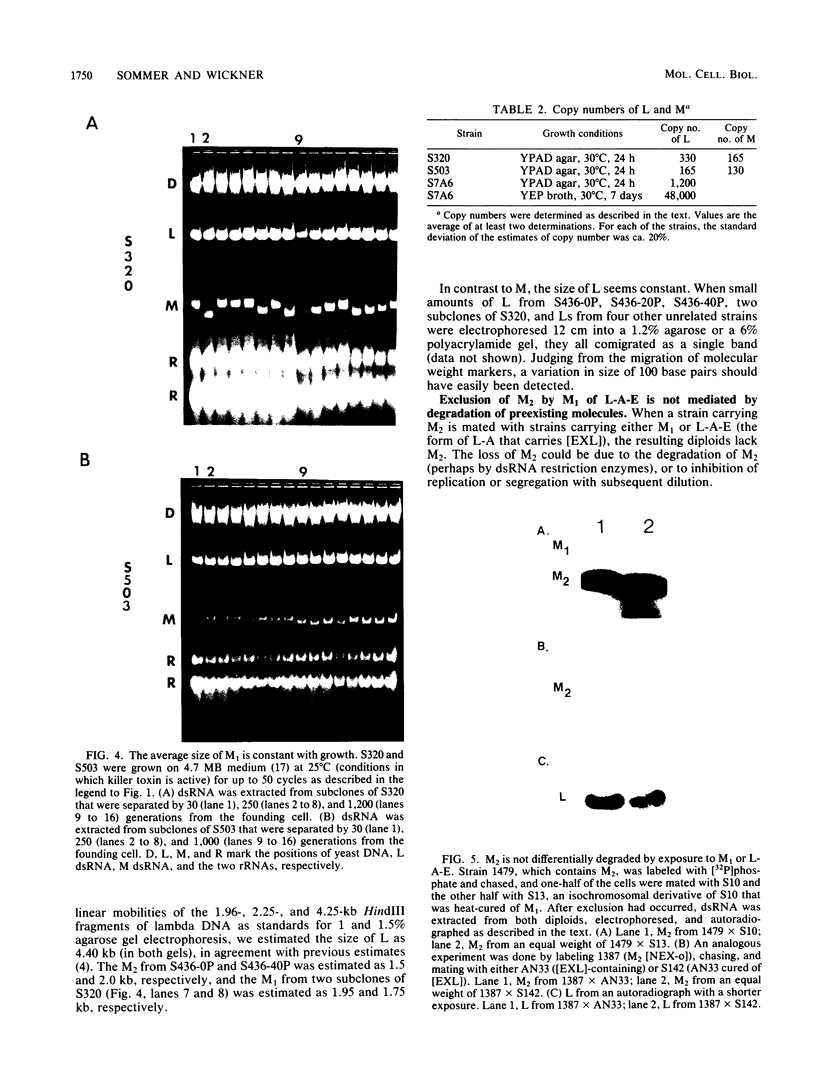
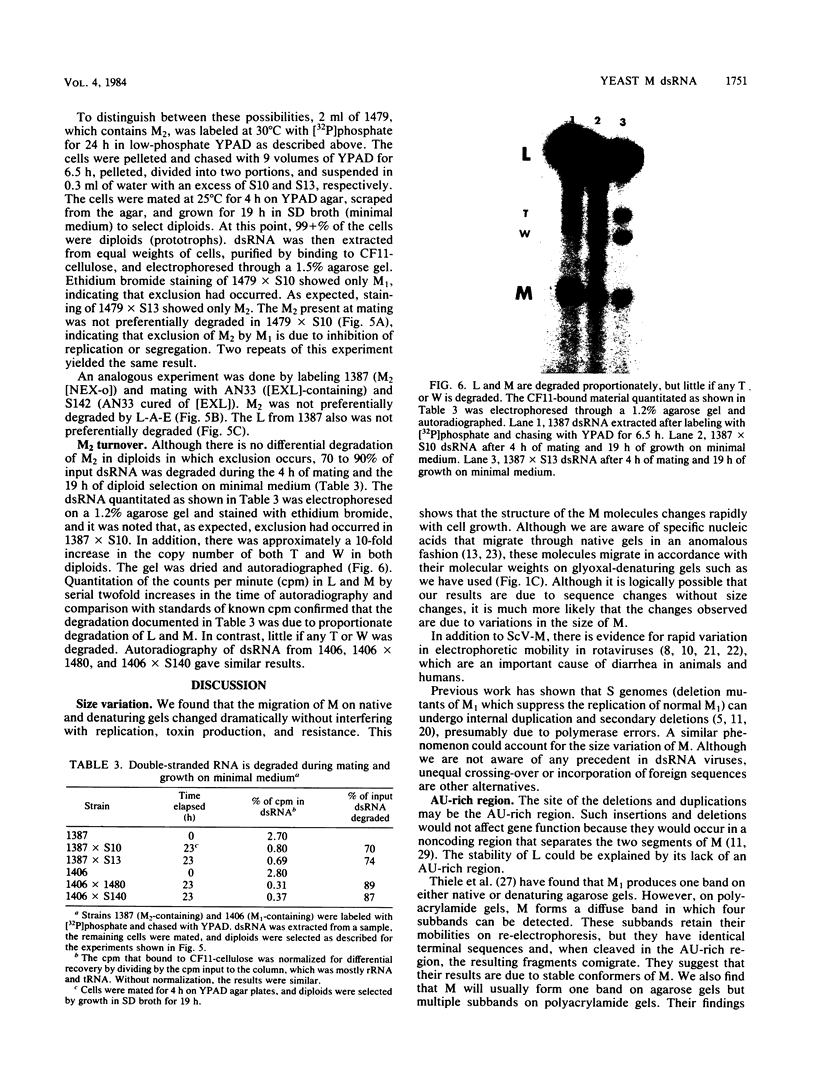
The sizes of M1 and M2 (but not L) change rapidly with growth, varying by perhaps as much as 33%. Size variation is seen within 76 generations. In addition, the exclusion of M2 by M1 or L-A-E [( EXL]) is mediated by inhibition of replication or segregation, not by enhanced degradation of preexisting molecules.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bevan E. A., Herring A. J., Mitchell D. J. Preliminary characterization of two species of dsRNA in yeast and their relationship to the "killer" character. Nature. 1973 Sep 14;245(5420):81–86. doi: 10.1038/245081b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bostian K. A., Hopper J. E., Rogers D. T., Tipper D. J. Translational analysis of the killer-associated virus-like particle dsRNA genome of S. cerevisiae: M dsRNA encodes toxin. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):403–414. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90514-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer B. J., Fangman W. L. Preferential inclusion of extrachromosomal genetic elements in yeast meiotic spores. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5380–5384. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruenn J. A. Virus-like particles of yeast. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:49–68. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.000405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruenn J., Kane W. Relatedness of the double-stranded RNAs present in yeast virus-like particles. J Virol. 1978 Jun;26(3):762–772. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.3.762-772.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussey H. Physiology of killer factor in yeast. Adv Microb Physiol. 1981;22:93–122. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60326-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clare J. J., Oliver S. G. The regulation of RNA synthesis in yeast IV. Synthesis of double-stranded RNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Mar 20;171(2):161–166. doi: 10.1007/BF00270002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espejo R. T., Muñz O., Serafin F., Romero P. Shift in the prevalent human rotavirus detected by ribonucleic acid segment differences. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):351–354. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.351-354.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink G. R., Styles C. A. Curing of a killer factor in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2846–2849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Perez I., White L., Perez M., Kalica A. R., Marquina R., Wyatt R. G., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Genetic relatedness among human rotaviruses as determined by RNA hybridization. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):648–655. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.648-655.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried H. M., Fink G. R. Electron microscopic heteroduplex analysis of "killer" double-stranded RNA species from yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4224–4228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii K., Hashimoto-Gotoh T., Matsubara K. Random replication and random assortment model for plasmid incompatibility in bacteria. Plasmid. 1978 Sep;1(4):435–445. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90002-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marini J. C., Levene S. D., Crothers D. M., Englund P. T. Bent helical structure in kinetoplast DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7664–7668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead D. J., Oliver S. G. Purification and properties of a double-stranded ribonuclease from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Dec 15;137(3):501–507. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07854.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumova G. I., Naumova T. I. Sravitel'naia genetika drozhzhei. Soobshchenie XIII. Sravitel'noe izuchenie sakharomitsetov-ubiits iz razlichnykh kollektsii. Genetika. 1973 Nov;9(11):140–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P., Hoppensteadt F. C. On plasmid incompatibility. Plasmid. 1978 Sep;1(4):421–434. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90001-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver S. G., McCREADY S. J., Holm C., Sutherland P. A., McLaughlin C. S., Cox B. S. Biochemical and physiological studies of the yeast virus-like particle. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;130(3):1303–1309. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.3.1303-1309.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palfree R. G., Bussey H. Yeast killer toxin: purification and characterisation of the protein toxin from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Feb 1;93(3):487–493. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12847.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley S. P., Sommer S. S., Wickner R. B. Superkiller mutations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae suppress exclusion of M2 double-stranded RNA by L-A-HN and confer cold sensitivity in the presence of M and L-A-HN. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;4(4):761–770. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.4.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley S. P., Wickner R. B. Defective Interference in the Killer System of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):800–812. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.800-812.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodger S. M., Bishop R. F., Birch C., McLean B., Holmes I. H. Molecular epidemiology of human rotaviruses in Melbourne, Australia, from 1973 to 1979, as determined by electrophoresis of genome ribonucleic acid. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Feb;13(2):272–278. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.2.272-278.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodger S. M., Holmes I. H. Comparison of the genomes of simian, bovine, and human rotaviruses by gel electrophoresis and detection of genomic variation among bovine isolates. J Virol. 1979 Jun;30(3):839–846. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.3.839-846.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Shulman M., Landy A. Biochemical analysis of att-defective mutants of the phage lambda site-specific recombination system. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 15;156(3):505–522. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90263-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somers J. M., Bevan E. A. The inheritance of the killer character in yeast. Genet Res. 1969 Feb;13(1):71–83. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300002743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer S. S., Wickner R. B. Co-curing of plasmids affecting killer double-stranded RNAs of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: [HOK], [NEX], and the abundance of L are related and further evidence that M1 requires L. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):545–551. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.545-551.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer S. S., Wickner R. B. Yeast L dsRNA consists of at least three distinct RNAs; evidence that the non-Mendelian genes [HOK], [NEX] and [EXL] are on one of these dsRNAs. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):429–441. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90136-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiele D. J., Wang R. W., Leibowitz M. J. Separation and sequence of the 3' termini of M double-stranded RNA from killer yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 11;10(5):1661–1678. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.5.1661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vodkin M., Katterman F., Fink G. R. Yeast killer mutants with altered double-stranded ribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):681–686. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.681-686.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh D., Leibowitz M. J. Transcription of killer virion double-stranded RNA in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jun 11;8(11):2365–2375. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.11.2365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wesolowski M., Wickner R. B. Two new double-stranded RNA molecules showing non-mendelian inheritance and heat inducibility in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;4(1):181–187. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.1.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner R. B. Genetic control of replication of the double-stranded RNA segments of the killer systems in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Apr 1;222(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90496-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner R. B. Killer systems in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: three distinct modes of exclusion of M2 double-stranded RNA by three species of double-stranded RNA, M1, L-A-E, and L-A-HN. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;3(4):654–661. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.4.654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner R. B. Plasmids controlled exclusion of the K2 killer double-stranded RNA plasmid of yeast. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):217–226. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90129-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner R. B., Toh-e A. [HOK], a new yeast non-Mendelian trait, enables a replication-defective killer plasmid to be maintained. Genetics. 1982 Feb;100(2):159–174. doi: 10.1093/genetics/100.2.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young T. W., Yagiu M. A comparison of the killer character in different yeasts and its classification. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1978;44(1):59–77. doi: 10.1007/BF00400077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]