Abstract
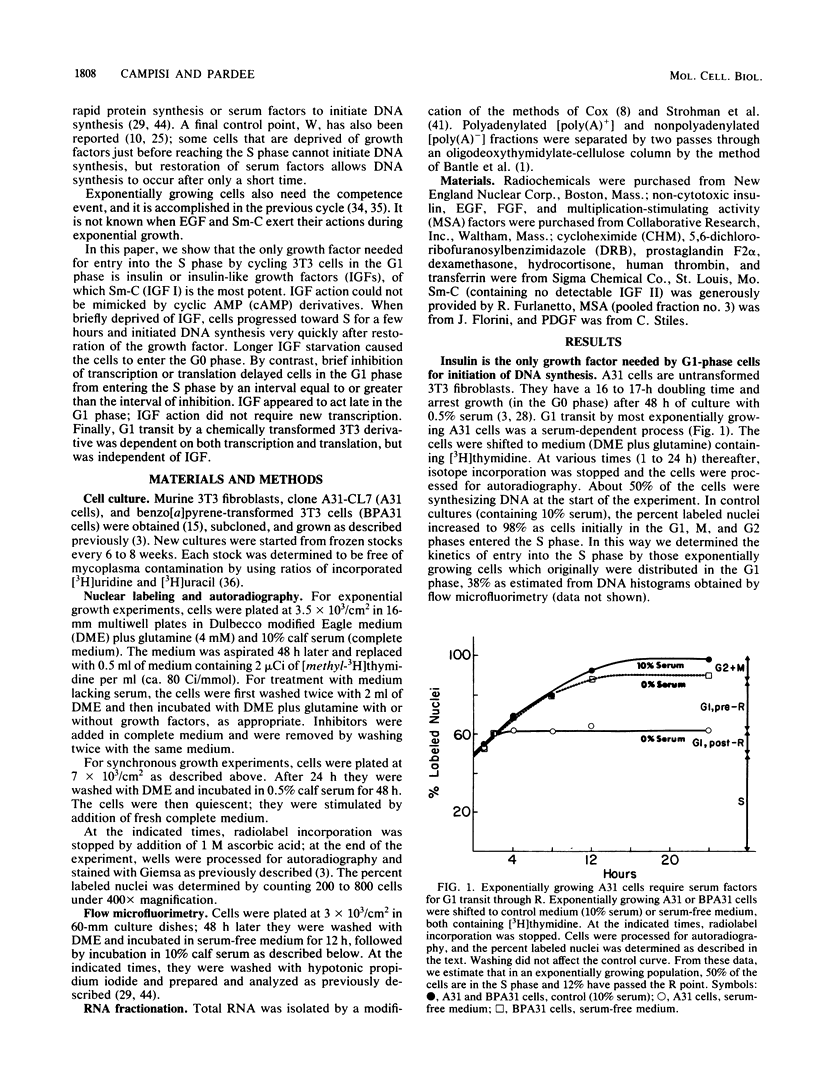
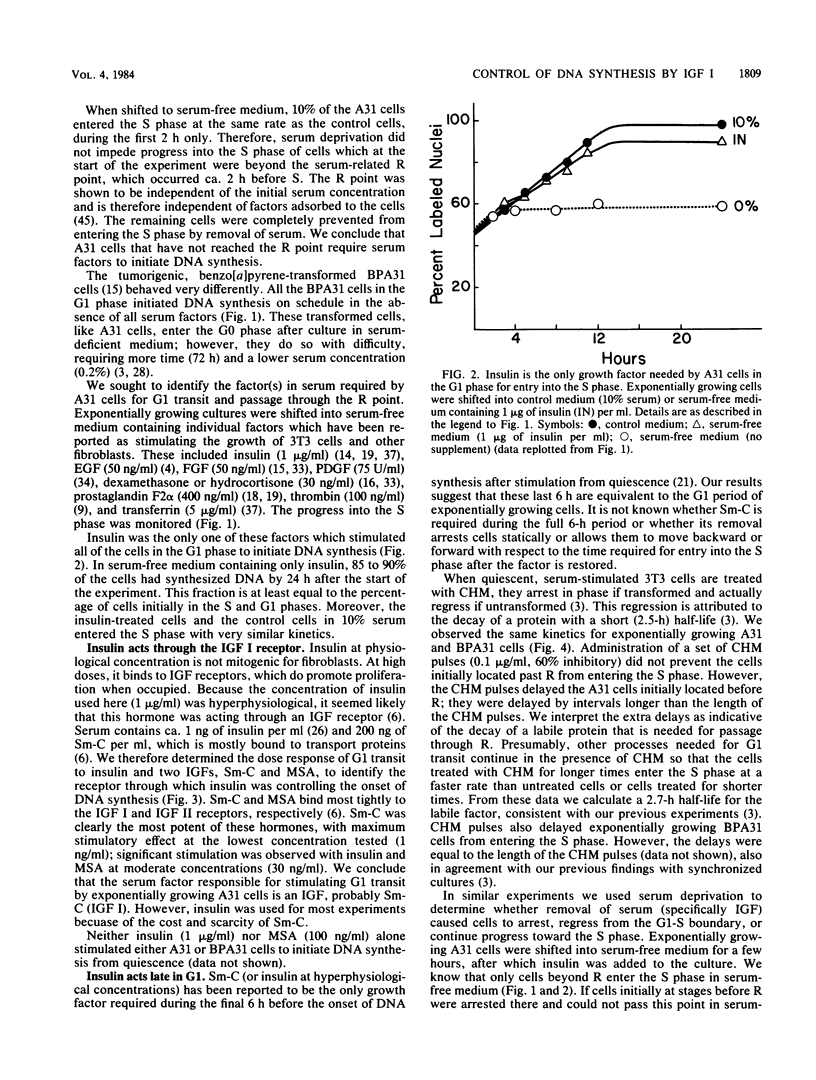
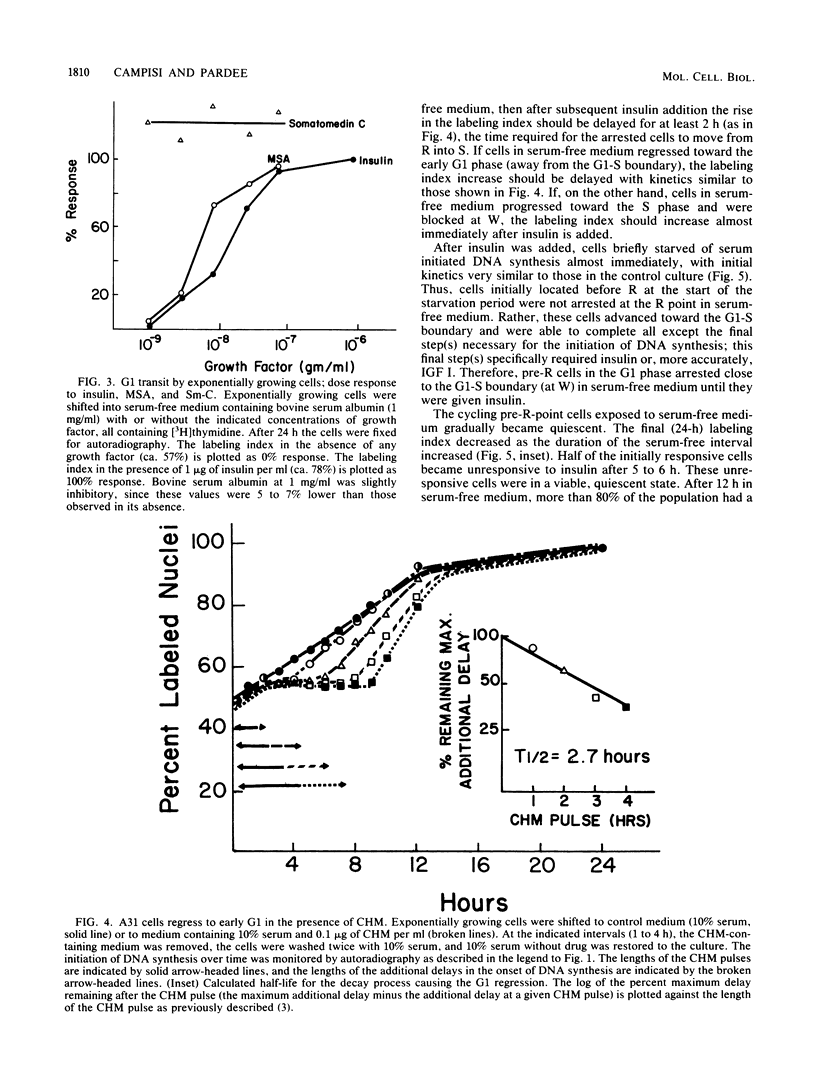
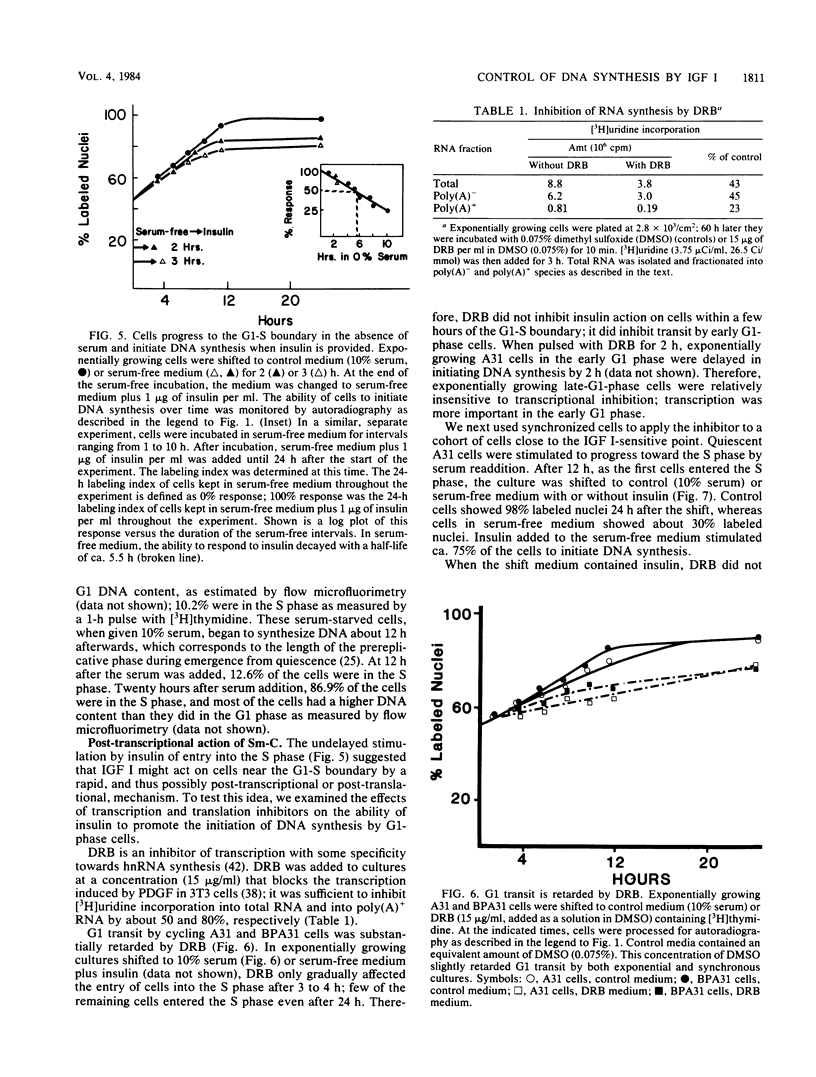
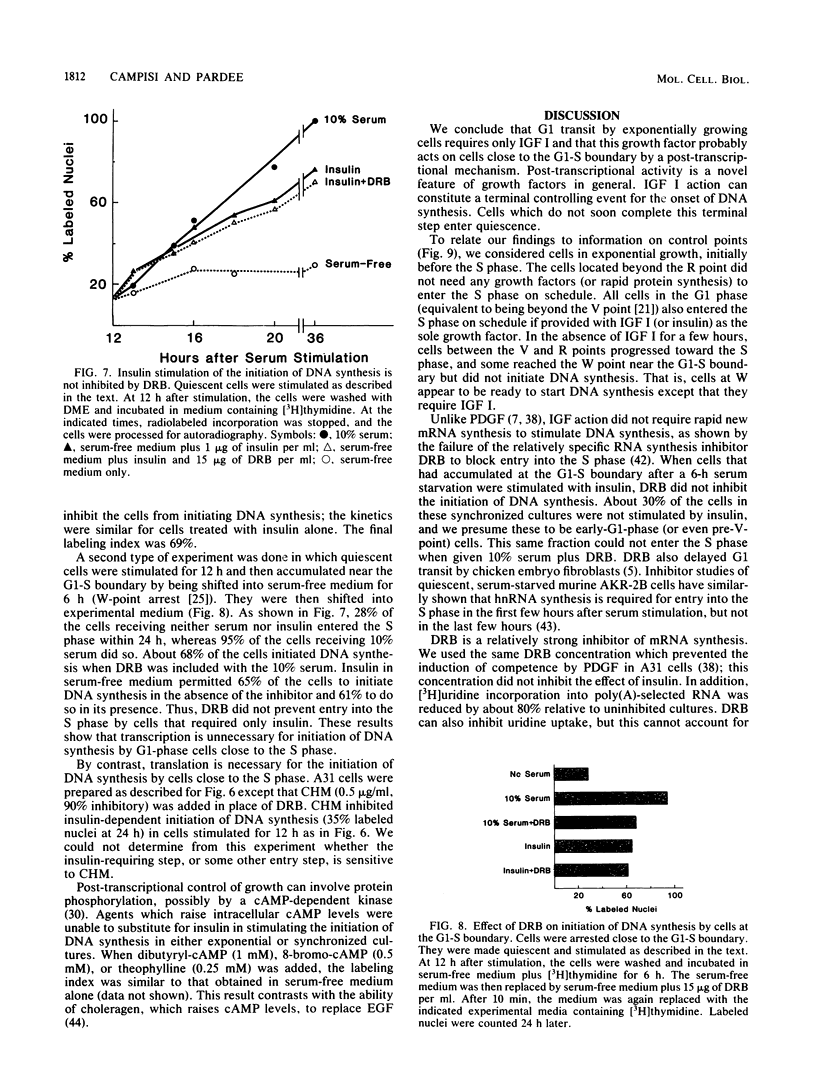
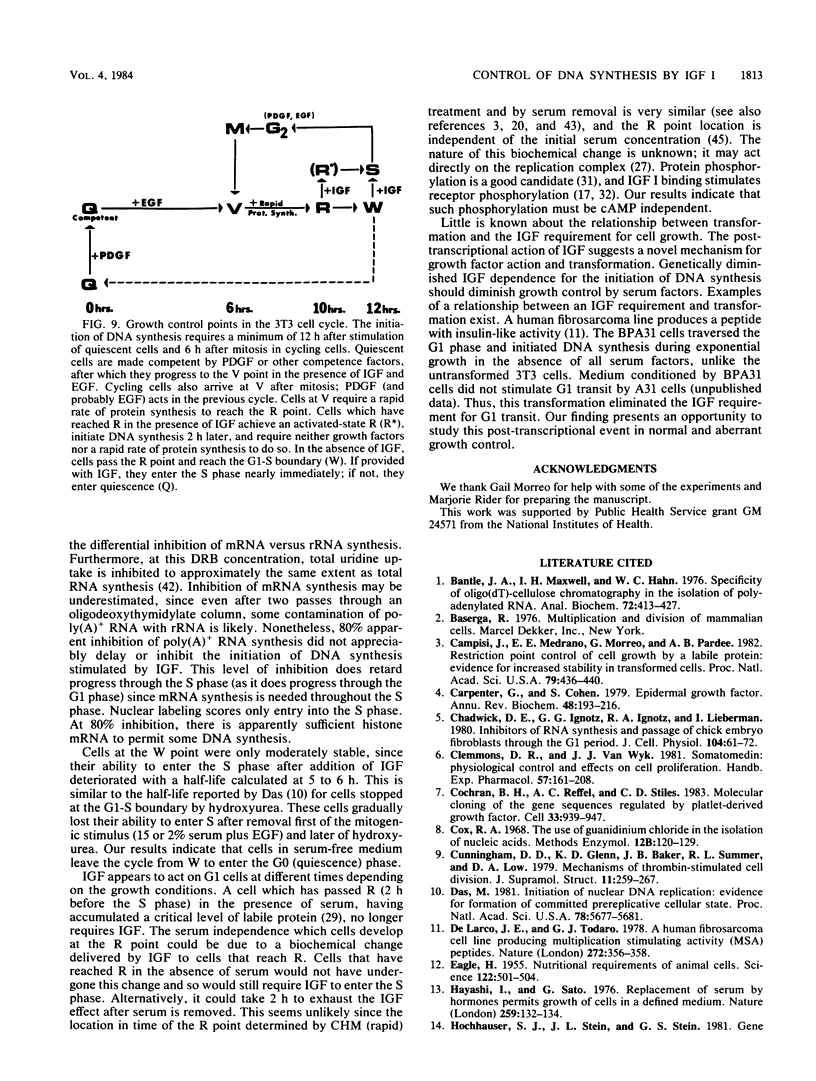
The control of eucaryotic cell proliferation is governed largely by a series of regulatory events which occur in the G1 phase of the cell cycle. When stimulated to proliferate, quiescent (G0) 3T3 fibroblasts require transcription, rapid translation, and three growth factors for the growth state transition. We examined exponentially growing 3T3 cells to relate the requirements for G1 transit to those necessary for the transition from the G0 to the S phase. Cycling cells in the G1 phase required transcription, rapid translation, and a single growth factor (insulin-like growth factor [IGF] I) to initiate DNA synthesis. IGF I acted post-transcriptionally at a late G1 step. All cells in the G1 phase entered the S phase on schedule if either insulin (hyperphysiological concentration) or IGF I (subnanomolar concentration) was provided as the sole growth factor. In medium lacking all growth factors, only cells within 2 to 3 h of the S phase were able to initiate DNA synthesis. Similarly, cells within 2 to 3 h of the S phase were less dependent on transcription and translation for entry into the S phase. Cells responded very differently to inhibited translation than to growth factor deprivation. Cells in the early and mid-G1 phases did not progress toward the S phase during transcriptional or translational inhibition, and during translational inhibition they actually regressed from the S phase. In the absence of growth factors, however, these cells continued progressing toward the S phase, but still required IGF at a terminal step before initiating DNA synthesis. We conclude that a suboptimal condition causes cells to either progress or regress in the cell cycle rather than freezing them at their initial position. By using synchronized cultures, we also show that in contrast to earlier events, this final, IGF-dependent step did not require new transcription. This result is in contrast to findings that other growth factors induce new transcription. We examined the requirements for G1 transit by using a chemically transformed 3T3 cell line (BPA31 cells) which has lost some but not all ability to regulate its growth. Early- and mid-G1-phase BPA31 cells required transcription and translation to initiate DNA synthesis, although they did not regress from the S phase during translational inhibition. However, these cells did not need IGF for entry into the S phase.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bantle J. A., Maxwell I. H., Hahn W. E. Specificity of oligo (dT)-cellulose chromatography in the isolation of polyadenylated RNA. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:413–427. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90549-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campisi J., Medrano E. E., Morreo G., Pardee A. B. Restriction point control of cell growth by a labile protein: evidence for increased stability in transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):436–440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:193–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chadwick D. E., Ignotz G. G., Ignotz R. A., Lieberman I. Inhibitors of RNA synthesis and passage of chick embryo fibroblasts through the G1 period. J Cell Physiol. 1980 Jul;104(1):61–72. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041040110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochran B. H., Reffel A. C., Stiles C. D. Molecular cloning of gene sequences regulated by platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):939–947. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90037-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham D. D., Glenn K. C., Baker J. B., Simmer R. L., Low D. A. Mechanisms of thrombin-stimulated cell division. J Supramol Struct. 1979;11(2):259–267. doi: 10.1002/jss.400110215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das M. Initiation of nuclear DNA replication: evidence for formation of committed prereplicative cellular state. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5677–5681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Larco J. E., Tadaro G. J. A human fibrosarcoma cell line producing multiplication stimulating activity (MSA)-related peptides. Nature. 1978 Mar 23;272(5651):356–358. doi: 10.1038/272356a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Nutrition needs of mammalian cells in tissue culture. Science. 1955 Sep 16;122(3168):501–514. doi: 10.1126/science.122.3168.501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi I., Sato G. H. Replacement of serum by hormones permits growth of cells in a defined medium. Nature. 1976 Jan 15;259(5539):132–134. doi: 10.1038/259132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holley R. W., Baldwin J. H., Kiernan J. A., Messmer T. O. Control of growth of benzo(a)pyrene-transformed 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3229–3232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollwy R. W., Kiernan J. A. Control of the initiation of DNA synthesis in 3T3 cells: serum factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2908–2911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S., Kull F. C., Jr, Earp H. S., Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J., Cuatrecasas P. Somatomedin-C stimulates the phosphorylation of the beta-subunit of its own receptor. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9581–9584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez de Asua L., Richmond K. M., Otto A. M. Two growth factors and two hormones regulate initiation of DNA synthesis in cultured mouse cells through different pathways of events. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1004–1008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leof E. B., Van Wyk J. J., O'Keefe E. J., Pledger W. J. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) is required only during the traverse of early G1 in PDGF stimulated density-arrested BALB/c-3T3 cells. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Aug;147(1):202–208. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90285-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leof E. B., Wharton W., van Wyk J. J., Pledger W. J. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) and somatomedin C regulate G1 progression in competent BALB/c-3T3 cells. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Sep;141(1):107–115. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B. A restriction point for control of normal animal cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1286–1290. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B., Dubrow R., Hamlin J. L., Kletzien R. F. Animal cell cycle. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:715–750. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.003435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pledger W. J., Stiles C. D., Antoniades H. N., Scher C. D. An ordered sequence of events is required before BALB/c-3T3 cells become committed to DNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2839–2843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pledger W. J., Stiles C. D., Antoniades H. N., Scher C. D. Induction of DNA synthesis in BALB/c 3T3 cells by serum components: reevaluation of the commitment process. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4481–4485. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prem veer Reddy G., Pardee A. B. Multienzyme complex for metabolic channeling in mammalian DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3312–3316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price P. J., Gregory E. A. Relationship between in vitro growth promotion and biophysical and biochemical properties of the serum supplement. In Vitro. 1982 Jun;18(6):576–584. doi: 10.1007/BF02810081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddle V. G., Lehtomaki D. M. Growth arrest states of RNA virus- and chemically transformed mouse cells. Cancer Res. 1981 May;41(5):1778–1783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossow P. W., Riddle V. G., Pardee A. B. Synthesis of labile, serum-dependent protein in early G1 controls animal cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4446–4450. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Legg A., Strang G., Courtenay-Luck N. Cyclic AMP: a mitogenic signal for Swiss 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4392–4396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. S., Rosen O. M. Protein phosphorylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:831–887. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.004151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin J. B., Shia M. A., Pilch P. F. Stimulation of tyrosine-specific phosphorylation in vitro by insulin-like growth factor I. 1983 Sep 29-Oct 5Nature. 305(5933):438–440. doi: 10.1038/305438a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudland P. S., Seifert W., Gospodarowicz D. Growth control in cultured mouse fibroblasts: induction of the pleiotypic and mitogenic responses by a purified growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2600–2604. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher C. D., Shepard R. C., Antoniades H. N., Stiles C. D. Platelet-derived growth factor and the regulation of the mammalian fibroblast cell cycle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Aug 10;560(2):217–241. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(79)90020-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher C. D., Stone M. E., Stiles C. D. Platelet-derived growth factor prevents G0 growth arrest. Nature. 1979 Oct 4;281(5730):390–392. doi: 10.1038/281390a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider E. L., Stanbridge E. J., Epstein C. J. Incorporation of 3H-uridine and 3H-uracil into RNA: a simple technique for the detection of mycoplasma contamination of cultured cells. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Mar 15;84(1):311–318. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90411-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. C., Stiles C. D. Cytoplasmic transfer of the mitogenic response to platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4363–4367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles C. D., Capone G. T., Scher C. D., Antoniades H. N., Van Wyk J. J., Pledger W. J. Dual control of cell growth by somatomedins and platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1279–1283. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles C. D., Isberg R. R., Pledger W. J., Antoniades H. N., Scher C. D. Control of the Balb/c-3T3 cell cycle by nutrients and serum factors: analysis using platelet-derived growth factor and platelet-poor plasma. J Cell Physiol. 1979 Jun;99(3):395–405. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040990314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strohman R. C., Moss P. S., Micou-Eastwood J., Spector D., Przybyla A., Paterson B. Messenger RNA for myosin polypeptides: isolation from single myogenic cell cultures. Cell. 1977 Feb;10(2):265–273. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90220-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamm I., Hand R., Caliguiri L. A. Action of dichlorobenzimidazole riboside on RNA synthesis in L-929 and HeLa cells. J Cell Biol. 1976 May;69(2):229–240. doi: 10.1083/jcb.69.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells D. J., Stoddard L. S., Getz M. J., Moses H. L. alpha-Amanitin and 5-fluorouridine inhibition of serum-stimulated DNA synthesis in quiescent AKR-2B mouse embryo cells. J Cell Physiol. 1979 Aug;100(2):199–214. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041000202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton W., Leof E., Pledger W. J., O'Keefe E. J. Modulation of the epidermal growth factor receptor by platelet-derived growth factor and choleragen: effects on mitogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5567–5571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen A., Pardee A. B. Exponential 3T3 cells escape in mid-G1 from their high serum requirement. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Oct 1;116(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



