Background: The epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) is a substrate for the endoplasmic reticulum associated degradation (ERAD) quality control system.
Results: The chaperone Lhs1/GRP170 selects the nonglycosylated form of the α subunit for ERAD.
Conclusion: This study is the first to show a role for Lhs1/GRP170 in ERAD substrate selection.
Significance: Mutations in ENaC are associated with human disease; therefore, Lhs1/GRP170, as a modulator of ENaC expression, may be a target for new therapeutic agents.
Keywords: ENaC, Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER), ER-associated Degradation, Molecular Chaperone, Proteasome, Sodium Channels
Abstract
The epithelial sodium channel, ENaC, plays a critical role in maintaining salt and water homeostasis, and not surprisingly defects in ENaC function are associated with disease. Like many other membrane-spanning proteins, this trimeric protein complex folds and assembles inefficiently in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), which results in a substantial percentage of the channel being targeted for ER-associated degradation (ERAD). Because the spectrum of factors that facilitates the degradation of ENaC is incomplete, we developed yeast expression systems for each ENaC subunit. We discovered that a conserved Hsp70-like chaperone, Lhs1, is required for maximal turnover of the ENaC α subunit. By expressing Lhs1 ATP binding mutants, we also found that the nucleotide exchange properties of this chaperone are dispensable for ENaC degradation. Consistent with the precipitation of an Lhs1-αENaC complex, Lhs1 holdase activity was instead most likely required to support the ERAD of αENaC. Moreover, a complex containing the mammalian Lhs1 homolog GRP170 and αENaC co-precipitated, and GRP170 also facilitated ENaC degradation in human, HEK293 cells, and in a Xenopus oocyte expression system. In both yeast and higher cell types, the effect of Lhs1 on the ERAD of αENaC was selective for the unglycosylated form of the protein. These data establish the first evidence that Lhs1/Grp170 chaperones can act as mediators of ERAD substrate selection.
Introduction
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)3-associated degradation (ERAD) targets defective secreted and integral membrane proteins for destruction (1–3). After being selected for ERAD, substrates are delivered to the cytosolic proteasome. ERAD substrates include proteins containing mutations that lead to folding defects, proteins that fail to assemble with specific partners, and proteins whose activities are regulated by degradation. Because protein folding is inherently error-prone, even a significant percentage of some wild-type proteins is also targeted for ERAD.
Proteins that transit through the secretory pathway play essential roles in cellular homeostasis, so it is not surprising that many prominent diseases are also linked to ERAD substrates. Some of these diseases include cystic fibrosis (the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR)), antitrypsin deficiency (α1-antitrypsin Z), nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (AQP2), and atherosclerosis (apolipoprotein B) (4). The epithelial Na+ channel (ENaC) is another protein that folds inefficiently in the ER and is associated with several diseases.
ENaC is a heterotrimeric protein composed of α, β, and γ subunits that is required for the reabsorption of sodium in the kidney collecting duct. Each subunit contains two transmembrane domains, a large extracellular loop, and a short N and C terminus that reside within the cytoplasm (5). It is generally assumed that the trimeric holochannel assembles in the ER before it traffics through the secretory pathway and functions at the apical membrane of several epithelia. Here, ENaC plays a critical role in the regulation of blood pressure and extracellular fluid balance within the body, and not surprisingly ENaC levels and activity are highly regulated (6–9). Gain of function mutations in ENaC that prolong its residency at the plasma membrane result in high blood pressure associated with Liddle's syndrome (10). In turn, loss of function mutations result in low blood pressure, salt-wasting, and pseudohypoaldosteronism type I (11).
The regulation and trafficking itinerary of ENaC at the cell surface have been extensively studied. In contrast, the early steps during ENaC biogenesis and quality control are not well characterized. However, it is clear that a significant proportion of each subunit is targeted for ERAD either when expressed alone or when coexpressed with the other subunits (12–14). These data are consistent with the notion that the ENaC subunits and holochannel are inherently unstable.
The ERAD pathway can be divided into distinct steps (3, 15, 16). First, proteins are recognized and targeted for degradation by molecular chaperones and chaperone-like lectins (17, 18). Second, ERAD substrates are ubiquitinated and retrotranslocated from the ER to the cytosol. A specialized set of E2 (ubiquitin conjugating) and E3 (ubiquitin ligase) enzymes modifies ERAD substrates (19), which facilitates interaction with a AAA-ATPase, Cdc48-p97, and its ubiquitin binding partners. The Cdc48-p97 complex then drives the ATP-dependent retrotranslocation of substrate into the cytoplasm (20–23). Finally, the cytosolic 26 S proteasome complex degrades ubiquitinated ERAD substrates, most likely with the aid of associated factors (24).
The molecular chaperone network housed within the ER not only helps select ERAD substrates but directly facilitates protein folding. Like other Hsp70s, the ER lumenal Hsp70, known as BiP (or Kar2 in yeast), recognizes substrates when bound to ATP. BiP/Kar2 specificity and function depend on cochaperones that assist in substrate binding, ATP hydrolysis (which traps the substrate), and nucleotide exchange (which helps release the substrate). One class of BiP/Kar2 cochaperones is the J-domain containing Hsp40s, which stimulate ATP hydrolysis. In yeast, the ER lumenal Hsp40s Jem1 and Scj1 function redundantly during BiP/Kar2-dependent ERAD substrate selection (25), and in mammals a select group of ER Hsp40s, the ERdjs, probably acts similarly (26–28). Hsp40s can also bind substrates independent of Hsp70 and may deliver these polypeptides to Hsp70s (29–32). To release bound substrates, nucleotide exchange factors (NEFs) stimulate the release of ADP, thus allowing the Hsp70 cycle to restart upon ATP binding. In yeast, there are two ER lumenal NEFs that act on BiP, Lhs1 and Sil1, and the mammalian homologs are known as GRP170 and SIL1, respectively. Lhs1 and Sil1 act as BiP cochaperones during protein translocation, or import, into the ER (33–37). However, there is no evidence linking the function of any of the ER NEFs to ERAD. This may be because Lhs1 and Sil1 are functionally redundant, and because the deletion of both Lhs1 and Sil1 is lethal in yeast (36) the role of these chaperones in ERAD cannot easily be investigated. Alternatively, the modest increase in the overall chaperone cycle facilitated by NEFs, in contrast to the profound stimulation by Hsp40s (38, 39), may indicate that their function is dispensable for ERAD.
To better define the pathway by which ENaC is targeted for ERAD, we established a yeast expression system for each subunit and as expected found that degradation was ubiquitin ligase, Cdc48, and proteasome-dependent; in addition, we discovered that cytoplasmic small heat shock proteins (Hsps) facilitated the degradation of the ENaC subunits in both yeast and in a Xenopus oocyte expression system (40, 41). By further employment of the yeast ENaC expression system, we then found that the ER lumenal Hsp40s, Jem1 and Scj1, help target all three ENaC subunits for degradation, which was again confirmed in the oocyte expression system. Specifically, overexpression of the human Hsp40 homologs, ERdj3 and ERdj4, augmented the proteasome dependent degradation of ENaC (40).
In this study we show for the first time a requirement for an ER lumenal NEF for ERAD. We discovered that yeast lacking Lhs1 exhibit a degradation defect for the ENaC α subunit. By examining the effect of an Lhs1 mutant on the turnover of αENaC, we found that NEF activity was dispensable, consistent with previous data that αENaC degradation was BiP/Kar2-independent (40) and suggesting that the chaperone “holdase” activity (i.e. the ability to prevent aggregation of a misfolded protein) is vital. Importantly, the effect of this chaperone on the stability of the ENaC α subunit was conserved; when levels of the Lhs1 homolog, GRP170, were modulated in either Xenopus oocytes or in HEK293 cells, αENaC turnover was impacted. Moreover, both Lhs1 and GRP170 co-precipitated with the ENaC α subunit in yeast and mammalian cells, respectively. These data provide further support for the notion that the ERAD of ENaC exhibits unique requirements and provide the first demonstration that the Lhs1/Grp170 family of chaperones is involved in ERAD.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Yeast Strains and Growth Conditions
Yeast strains were propagated at 26 °C using established methods, and media preparation and transformation were performed as published unless otherwise noted (42).
The wild-type (WT) yeast strain was BY4742 unless otherwise noted. BY4742, Δsil1, and Δlhs1 strains were from Open Biosystems (Thermo Scientific). The Δjem1Δscj1Δlhs1 strain was generated by mating the appropriate yeast strains using standard genetic techniques (42). In brief, a MATa lhs1Δ (ura, leu, TRP, his, lys, lhs1::KANMX, Open Biosystems) strain was mated with a MATα jem1Δscj1Δ (ura, leu, trp, his, lys, suc, jem1::LEU2, scj1::TRP1 (25)) strain to produce heterozygous diploids, which were patched onto solid rich medium at 30 °C for 2–3 days. Cells were then transferred to liquid sporulation media (1% potassium acetate; 0.005% zinc acetate) at 26 °C, tetrads were dissected and screened on selective medium, and deletions were confirmed using PCR. The resulting strain was back-crossed twice into the WT background, and a JEM1/SCJ1/LHS1 strain as well as Δjem1Δscj1Δlhs1 with identical genetic backgrounds were isolated.
Yeast growth assays were performed as follows. The Δlhs1 yeast strain was transformed with pRS313-LHS1, pRS313-lhs1D26A, or pRS313 (see below) as a vector control. Yeast cultures were grown overnight in selective media to log phase, serially diluted, and pinned onto selective media. The plates were incubated at 26 °C.
Mammalian Cell Growth and Transfection Conditions
HEK-293T cells were cultured at 37 °C in high glucose Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum, l-glutamine, and penicillin/streptomycin. Cells were transiently transfected using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen) following the manufacturer's instructions. Cells were analyzed 24 h after transfection.
Plasmid Construction and Molecular Techniques
The constitutive expression of a C-terminal HA epitope tagged form of the ENaC subunits (40) or CPY* (43) was previously described. The CFTR expression plasmid was also previously described (44). pRS313-LHS1 and pRS313-lhs1D26A expression plasmids were generously supplied by the Stirling laboratory (45). A higher level of Lhs1 expression was achieved by inserting the Lhs1 coding sequence into plasmid, pRS423GPD (46), to generate pRS423GPD-myc-LHS1. In brief, the LHS1 gene was amplified and epitope-tagged by PCR using pRS313-LHS1 as a template, and the PCR product was digested with BamHI and SalI and ligated into the same sites in pRS423GPD.
To express non-glycosylated forms of the ENaC subunits, a pRS426GPD-ΔGαENaC-HA construct was created by PCR amplification of pBluescript (SK−)-ΔGαENaC (Kleyman laboratory) that lacked N-linked glycosylation sites, and the product was digested with EcoRI and ClaI and ligated into the corresponding sites in pRS426GPD (46). pRS426GPD-ΔGβENaC-HA and pRS426GPD-ΔGγENaC-HA were constructed using PCR overlap extension (47) to mutate the Asn residue (AAT or AAC) within each of the glycosylation consensus sites (Asn-X-Ser/Thr) to Gln (CAG). Five consensus sites were mutated to create ΔGγENaC, and 13 sites were mutated to create ΔGβENaC. pRS426GPD-βENaC-HA and pRS426GPD-γENaC-HA were used as template DNAs, and the final PCR products were digested with EcoRI and BamHI for ΔGβENaC-HA or SpeI and HindIII for ΔGγENaC-HA and ligated into the appropriate sites in pRS426GPD (46).
The pcDNA3.1-αENaC-HA mammalian expression vector was described previously (48) and a pcDNA3.1-GRP170 mammalian expression plasmid was created by PCR using pBacPAK-His1 GRP170 (49) as a template (a gift from the Subjeck laboratory, Roswell Park Medical Institute). PCR products were digested with XbaI and BamHI and ligated into the same sites in pCDNA3.1(−) (Invitrogen). All constructs generated for this study were confirmed by restriction digest and DNA sequence analysis. Primer sequences are available upon request.
Protein Degradation and Other Biochemical Assays
Cycloheximide chase analyses of the ENaC subunits, CPY* and CFTR, in yeast were performed as previously described (40). Cell lysates from chase samples were generated using alkaline lysis followed by trichloroacetic acid precipitation (50), and proteins were immediately resolved by SDS-PAGE before Western blot analysis. The ENaC subunits, CPY* and CFTR, were detected using anti-HA-HRP (clone 3F10; Roche Applied Science) at a dilution of 1:5000. Western blots were also probed with anti-glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6P; Sigma) antisera, which served as a loading control. The G6P primary antibody was detected with a donkey horseradish peroxidase conjugated anti-rabbit IgG secondary (GE Healthcare). The Western blot signals were imaged using enhanced chemiluminescence (Pierce) and visualized on a Kodak 440CF Image Station. Quantitation was carried out using the imager-associated Kodak 1D software (Roche Applied Science). p values for all quantitative experiments were calculated using Student's t test.
For cycloheximide chase studies in HEK293 cells, cells transiently expressing the ENaC α subunit were assayed 24 h post-transfection. To stop protein translation, cells were placed in fresh high glucose DMEM containing 10% FBS, l-glutamine, and cycloheximide (Sigma) at a final concentration of 100 μg/ml. The cells were chased in a 37 °C 5% CO2 incubator for the indicated times. The cycloheximide-containing medium was aspirated; cells were washed twice with ice-cold Dulbecco's phosphate-buffered saline, scraped, collected, and isolated by centrifugation at 1000 × g for 5 min. Cell pellets were lysed using detergent solution (50 mm Tris-HCl, pH 8.5, 1% Nonidet P-40, 0.4% sodium deoxycholate, and 62.5 mm EDTA supplemented with one Roche Applied Science mini EDTA-free complete protease inhibitor tablet per 7 ml of buffer, 1 mm PMSF, and 1 mm pepstatin (Sigma)). The samples were then incubated on ice for 20 min and centrifuged at 16,000 × g for 5 min to remove insoluble material. Protein concentrations were determined using the Bradford assay (Bio-Rad). For samples subjected to SDS-PAGE, lysates were denatured in Laemmli buffer for 20 min at room temperature or heated to 90 °C for 5 min, loaded onto 10% polyacrylamide gels, and resolved by SDS-PAGE as described previously (51). Other antibodies used for this study include anti-(mammalian) Sec61 (AbCam), and anti-GRP170 (a kind gift from the Hendershot Laboratory, St. Jude Children's Research Hospital).
For digestion of proteins from yeast with endoglycosidase H (EndoH; New England Biolabs), samples were prepared as described above except before SDS-PAGE, EndoH was added according to the manufacturer's instructions (Roche Applied Science) for 3 h at 37 °C. For deglycosylation studies using mammalian cell lysates, 100 μg of lysate diluted to a total of 300 μl was precleared with 50 μl of Sepharose 6B (Sigma) by end-over-end rotation for 2 h at 4 °C. Precleared lysate was added to 20 μl of anti-HA-agarose (Sigma) and rotated end-over-end at 4 °C overnight. The samples were centrifuged at low speed, and the beads were washed 4 times in 1 ml of ice-cold PBS. The immunoprecipitated proteins were then eluted with glycoprotein denaturing buffer (New England Biolabs) by incubating the beads at 90 °C for 2 min. G5 buffer and Endoglycosidase H were added to the eluate (10 μg of lysate), and the sample was incubated at 37 °C for 3 h.
For peptide-N-glycosidase F digestions, immunoprecipitated proteins were eluted with glycoprotein denaturing buffer by incubating the beads at 90 °C for 2 min. G7 Buffer, Nonidet P-40, and peptide-N-glycosidase F (New England Biolabs) were added to the eluate, and the sample was incubated at 37 °C for 1 h. A total of 10 μg of lysate was used.
To separate yeast cellular membrane and cytosolic fractions, a total of ∼1 A600 of cells in log phase were pelleted in a microcentrifuge. The pellet was resuspended in 200 μl of lysis buffer (20 mm HEPES, pH 7.4, 0.1 m sorbitol, 50 mm potassium acetate, 2 mm EDTA, 1 mm DTT, 1 mm PMSF, 2 μg/ml leupeptin, 0.1 μg/ml pepstatin A), and cells were disrupted by the addition of glass beads and agitation on a Vortex mixer 4 times for 1 min with incubations of 1 min on ice in between each step. After the supernatant was removed, unbroken cells were pelleted by centrifugation at 3000 rpm for 3 min in a microcentrifuge, and the supernatant was retained. An aliquot was removed for Western blot analysis for total (T) protein, and the remaining lysate was centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 20 min. An aliquot of the supernatant was saved (S1), and the pellet (P1) was resuspended in 100 μl of lysis buffer. A second 13,000 rpm 20 min spin was carried-out to obtain a second supernatant fraction (S2) and pellet fraction (P2). Aliquots from each fraction were mixed with SDS sample buffer, and proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting as described above. For the integral membrane protein control, anti-Sec61 antiserum (52) was used.
Lhs1 and Grp170 coimmunoprecipitation assays were performed in yeast and in αENaC transfected HEK293 cells, respectively. In yeast, Δlhs1 yeast were transformed with pRS423GPD-myc-LHS1 and either pRS426GPD-αENaC-HA or a vector control, pRS316. A 25-ml overnight culture of each strain was grown to log phase (A600 = 1.0), and cells were pelleted and resuspended in 500 μl of lysis buffer (150 mm NaCl 50 mm Tris, pH 7.5, 0.1% Nonidet P-40, 1 mm DTT, 1 mm PMSF, 2 μg/ml leupeptin, 0.1 μg/ml pepstatin A) and then disrupted by the addition of glass beads and agitation on a Vortex mixer 4 times for 1 min with incubations of 1 min on ice in between each step. The cell debris was removed from the resulting lysate by centrifugation at 8000 rpm for 8 min. The lysate was then incubated with 18 μl of anti-HA affinity matrix (Roche Applied Science) for 3 h at 4 °C on a rotator. The affinity beads were washed 3 times with lysis buffer and resuspended in SDS sample buffer, heated at 70 °C for 10 min, and subject to analysis by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting. Western blots were probed with either anti-HA antibody (Roche Applied Science) or anti-Lhs1 antibody (a kind gift from the E. Craig laboratory, University of Wisconsin) and detected as described above.
To detect co-immunoprecipitation of HA-tagged αENaC with GRP170 in HEK293 cells, 100 μg of lysate diluted to a total volume of 300 μl was precleared with 30 μl of protein A/G-agarose slurry (Calbiochem) by end-over-end rotation overnight at 4 °C. A 1-μl aliquot of GRP170 antibody was added to the precleared lysate with 30 μl of fresh protein A/G beads, and the solution was rotated end-over-end at room temperature for 1 h. The samples were centrifuged at low speed, and the beads were washed 4 times in 1 ml of PBS containing 0.1% Triton X-100 and 100 mm KCl. Immunoprecipitated proteins were eluted by incubating the beads at room temperature for 20 min in SDS sample buffer. For reciprocal co-immunoprecipitation of GRP170 with αENaC-HA, a total of 200 μg of lysate diluted to 300 μl was precleared with 50 μl of Sepharose 6B (Sigma) by end-over-end rotation overnight at 4 °C. Precleared lysate was added to 30 μl of anti-HA-agarose (Sigma) and rotated end-over-end at room temperature for 1 h. The samples were centrifuged at low speed, and the beads were washed 4 times in 1 ml of PBS containing 0.1% Triton X-100 and 100 mm KCl. Immunoprecipitated proteins were eluted by incubating the beads at room temperature for 20 min with SDS sample buffer.
Functional Analysis of αENaC Channel Activity in Xenopus Oocytes
αENaC function was analyzed in Xenopus oocytes using two-electrode voltage clamp (41). The cDNA encoding the murine αENaC subunit was previously described (40), and the cDNA encoding GRP170 from pGEM4Z-GRP170 was made by PCR amplifying GRP170 from pBacPAK-His1-GRP170 (49). The PCR product was digested with BamHI and SacI and ligated into pGEM4Z (Promega). For αENaC the cRNA was prepared from linearized DNA templates using T3 RNA polymerase according to the manufacturer's instructions (Ambion). For GRP170 the cRNA was prepared from linearized DNA using T7 polymerase according to manufacturer's instructions (Promega). Stage V and VI oocytes were injected with cRNAs encoding αENaC (1 or 5 ng) and 5 ng of GRP170 cRNA.
After injection the oocytes were incubated at 18 °C in modified Barth's saline (15 mm HEPES, pH 7.4, 88 mm NaCl, 1 mm KCl, 2.4 mm NaHCO3, 0.3 mm Ca(NO3)2, 0.41 mm CaCl2, 0.82 mm MgSO4, 10 μg/ml sodium penicillin, 10 μg/ml streptomycin sulfate, and 100 μg/ml gentamycin sulfate). A two-electrode voltage clamp assay was performed 48 h after injection using a DigiData 1320A interface and a GeneClamp 500B voltage clamp amplifier (Axon Instruments). Data acquisition and analyses were performed using pClamp software, Version 8.2 (Axon Instruments). Glass pipettes were pulled from borosilicate glass capillaries (World Precision Instruments, Inc.) with a Micropipette Puller (Sutter Instrument Co.) and had a resistance of 0.3–5 megaohms when filled with 3 m KCl and inserted into the bath solution. During the recording oocytes were placed in a recording chamber (Automate Scientific) and perfused continuously at a flow rate of 3 ml/min with bath solution (10 mm HEPES, pH 7.4, 110 mm NaCl, 2 mm KCl, 2 mm CaCl2), and subsequently with this solution supplemented with 10 μm amiloride.
RESULTS
Lhs1 Facilitates the Degradation of αENaC
By developing and then employing a yeast expression system for each ENaC subunit, we showed that the ERAD of the ENaC subunits does not require the ER lumenal Hsp70, BiP/Kar2, but depends on two ER lumenal Hsp40s, Jem1 and Scj1 (40). This result was unexpected because the requirement for Hsp40s during ERAD is usually accompanied by Hsp70 dependence (25, 26, 53–57). Because ENaC degradation was BiP/Kar2P-independent, we hypothesized that ENaC degradation might be facilitated by another Hsp70-like molecule in the ER, Lhs1. Lhs1 is an ER resident, ∼116-kDa glycoprotein that contains an ER retention signal. The mammalian homolog, GRP170, is also an ER retained glycoprotein (58, 59). Lhs1/GRP170 have an extended loop domain (60) and exhibit holdase activity (45, 61), which prevents the aggregation of protein substrates until they are delivered to other chaperone systems. Lhs1/GRP170 are also NEFs (35, 45, 59, 62, 63) and triggers nucleotide exchange by affecting the Hsp70 structure in a very similar manner to another class of NEFs, the Hsp110s, (62) but in a mechanistically distinct fashion from Sil1 (63).
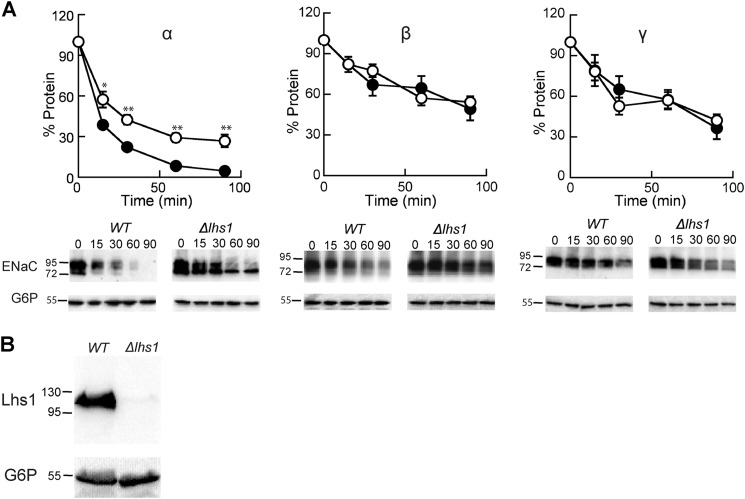
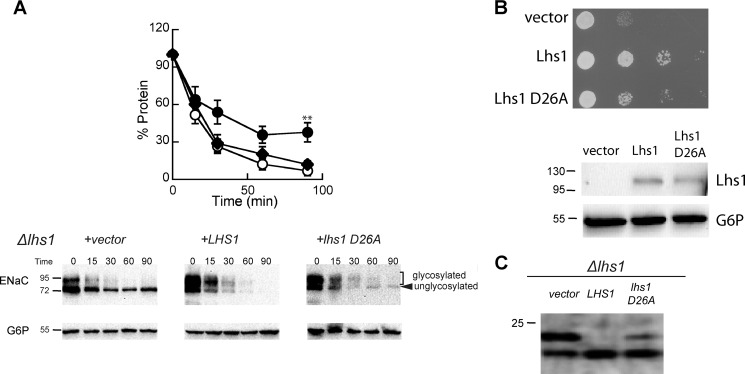
To test whether Lhs1 affects ENaC subunit stability, cycloheximide chase experiments were performed in either a WT yeast strain or a Δlhs1 strain expressing α, β, or γENaC over a 90-min time period (Fig. 1A). As observed previously (40), the turnover of the α subunit was more extensive than the β or γ subunits in the WT strain (40). As hypothesized, we found that αENaC degradation was significantly less efficient in the Δlhs1 strain in comparison to the WT strain. In contrast, the degradation of the β- and γENaC subunits was unaffected. To confirm that the Lhs1 protein was absent in the Δlhs1 strain, a Western blot was performed on cell lysates from LHS1 and Δlhs1 yeast, and the blot was probed with anti-Lhs1 antisera (Fig. 1B). The Lhs1 antibody detected a prominent species at the expected molecular weight in the LHS1 strain that was absent in the Δlhs1 strain, thus confirming that the Lhs1 gene was deleted.
FIGURE 1.
The ER-associated degradation of αENaC but not β- or γENaC is facilitated by the ER resident molecular chaperone Lhs1. A, cycloheximide chase reactions were performed as described under “Experimental Procedures” in LHS1 (filled circles) or Δlhs1 (open circles) yeast strains expressing a C-terminally HA epitope-tagged form of α-, β-, or γENaC. Chase reactions were performed at 37 °C, and lysates were immunoblotted with anti-HA antisera (ENaC) and with anti-G6P as a loading control. Data represent the means of 3–7 experiments, ±S.E. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.001. B, LHS1 and Δlhs1 yeast were grown to log phase, and proteins were precipitated as described under “Experimental Procedures” and immunoblotted with both anti-Lhs1 and anti-G6P antisera.
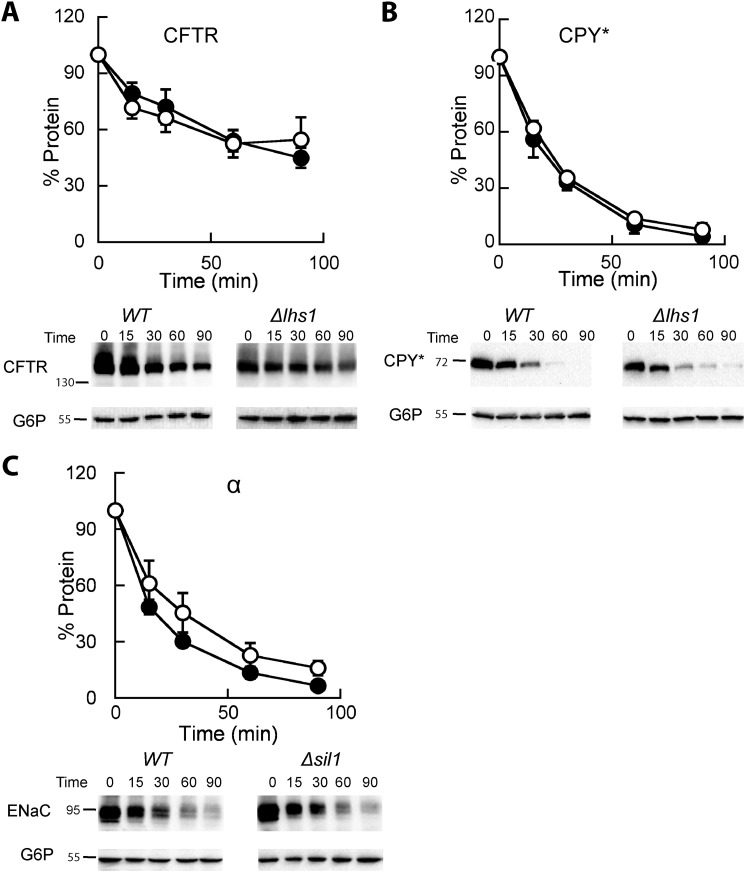
To determine whether Lhs1 only affects αENaC or plays a more general role in selecting misfolded proteins for degradation, we assayed the degradation of two other well characterized ERAD substrates, the inefficiently folded transmembrane protein CFTR and the misfolded soluble protein, CPY*; yeast expression systems for both of these ERAD substrates have been used extensively (50, 54, 64–67). Deletion of Lhs1 had no effect on the degradation of either protein (Fig. 2, A and B). These results are also consistent with a pulse-chase degradation assay showing that the deletion of Lhs1 had essentially no effect on CPY* degradation (25).
FIGURE 2.
The ERAD of CFTR and CPY* is Lhs1-independent, and the nucleotide exchange factor Sil1 is dispensable for αENaC degradation. A and B, cycloheximide chase reactions were performed as described under “Experimental Procedures” in LHS1 wild-type (filled circles) or Δlhs1 (open circles) yeast strains expressing a C-terminally 3HA epitope-tagged form of CFTR or a C-terminally 3HA-tagged form of CPY*. C, cycloheximide chase reactions were performed as described above in SIL1 (filled circles) or Δsil1 (open circles) yeast strains expressing a C-terminally HA epitope tagged form of αENaC. All chase reactions were performed at 37 °C, and lysates were immunoblotted with anti-HA antisera (ENaC, CFTR, and CPY*) and with anti-G6P as a loading control. Data represent the means of 4–7 experiments, ±S.E.
The best-characterized role for Lhs1 is as a NEF for BiP/Kar2 (35, 45, 63). To determine whether the degradation defect is Lhs1-specific we assayed αENaC degradation in yeast deleted for the gene that encodes another ER lumenal NEF, Sil1. Lhs1 and Sil1 exhibit overlapping functions, and both catalyze nucleotide exchange on BiP/Kar2 and facilitate protein translocation (36). In fact, Sil1 is the only gene that rescues the synthetic lethal effect of an Δlhs1Δire1 strain, which besides lacking Lhs1 is unable to mount an unfolded protein response. However, we found that αENaC degradation was not significantly altered in a Δsil1 strain when compared with WT yeast (Fig. 2C). In contrast, the Weissman laboratory observed a minor effect on the ERAD of CPY* when a pulse-chase assay was performed in a Δsil1 strain (68). Together, these data suggest that Lhs1 and Sil1 play unique roles in ER physiology. The data are also consistent with the lack of structural similarity between these chaperones and with the fact that select functions are associated with only one of the two NEFS (i.e. only Lhs1 exhibits holdase activity (45)).
Nonglycosylated αENaC Is Preferentially Stabilized in the Absence of Lhs1
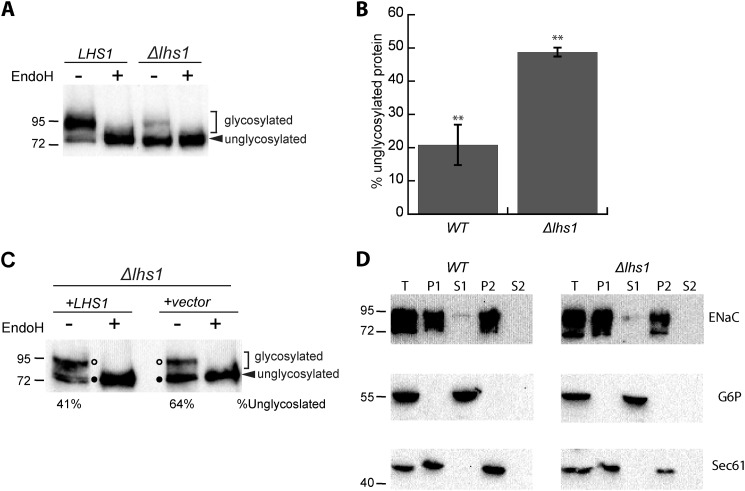
Close inspection of αENaC degradation in Δlhs1 yeast suggested that a lower molecular weight band was preferentially stabilized (see the Fig. 1A gel). αENaC contains six consensus sites for N-linked glycosylation (5, 69) that are modified with variable efficiencies in divergent systems (40, 70–72). To confirm that the lower molecular weight band represents the unglycosylated protein rather than a truncated form of the protein, we treated samples from both WT and Δlhs1 yeast expressing αENaC with EndoH to remove N-linked oligosaccharides. EndoH treatment collapsed the higher molecular weight species to a single lower molecular weight species in both the WT and Δlhs1 samples (Fig. 3A). This result confirms that the preferentially stabilized protein is unglycosylated and is not a truncated or proteolytically cleaved form of αENaC. We compared the relative ratio of these two forms of αENaC in WT and Δlhs1 strains at time 0 (from Fig. 1A) and found that significantly less unglycosylated material was present in WT strains (Fig. 3B). To confirm these data, the Lhs1 mutant was transformed with either an empty vector or with an Lhs1 expression vector. Lhs1 reduced the proportion of unglycosylated αENaC compared with the empty vector (Fig. 3C, compare the ratio of glycosylated to unglycosylated protein in the +LHS1 versus +vector conditions), suggesting Lhs1 specifically facilitates the degradation of unglycosylated αENaC.
FIGURE 3.
The unglycosylated form of αENaC accumulates in the absence of Lhs1. A, lysates were prepared from LHS1 WT or Δlhs1 yeast expressing a C-terminal HA-tagged form of αENaC and were incubated at 37 °C in the presence or absence of EndoH before performing an immunoblot analysis with anti-HA antiserum to detect ENaC. B, the relative percent of unglycosylated protein was quantitated using the zero time point in Fig. 1A (αENaC). Data represent the means of four experiments ± S.E.; **, p < 0.01 C, lysates were prepared from Δlhs1 yeast expressing a C-terminal, HA-tagged form of αENaC and a plasmid containing Lhs1 or a vector control and were treated with EndoH and analyzed as above. D, lysates were prepared from WT or Δlhs1 yeast expressing a C-terminal HA-tagged form of αENaC and membrane (P1 and P2) and supernatant fractions (S1 and S2) were isolated as described under “Experimental Procedures.” These fractions and an aliquot of the total cell lysate (T) were immunoblotted with anti-HA antisera (ENaC) or anti-G6P as a cytosolic control or anti-Sec61 as an integral ER membrane protein control.
The addition of N-linked sugars occurs during and after protein translocation into the ER lumen (73–75). Because Lhs1 aids in the translocation of some proteins (33, 34, 36), we investigated whether the unglycosylated protein observed in the Δlhs1 strain was untranslocated, which would leave a portion of the protein in the cytosol and inaccessible to the glycosylation machinery. To rule this scenario out, we isolated supernatant and pellet (ER membrane containing) fractions from WT and Δlhs1 yeast cell extracts and immunoblotted for αENaC (HA), a cytosolic protein, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6P), or an integral ER membrane protein, Sec61 (Fig. 3D). All three proteins were present in the total cell lysates (T), whereas only the soluble, cytosolic protein, G6P, was present in the supernatant (S1) fraction. Sec61 and αENaC were present in the pellet fraction (P1) in both WT and Δlhs1 strains. After the initial spin the supernatant (S1) was removed, and the pellet was resuspended in buffer and subject to a second centrifugation. The resulting supernatant fraction (S2) lacked G6P because the cytosol was completely removed with the S1 fraction, whereas the integral membrane proteins αENaC and Sec61 were observed in the P2 fractions. Importantly, we observed no differences between the residence of αENaC in the WT and Δlhs1 strains. These results suggest that αENaC is both efficiently translocated and membrane-associated. We also examined whether the conformation of αENaC was significantly altered when Lhs1 was deleted, which might occur if the protein was inefficiently translocated. We performed a protease digestion assay using increasing concentrations of trypsin. However, we failed to identify any major differences in the αENaC proteolytic patterns when using lysates from the Δlhs1 strain in comparison to the WT strain (data not shown).
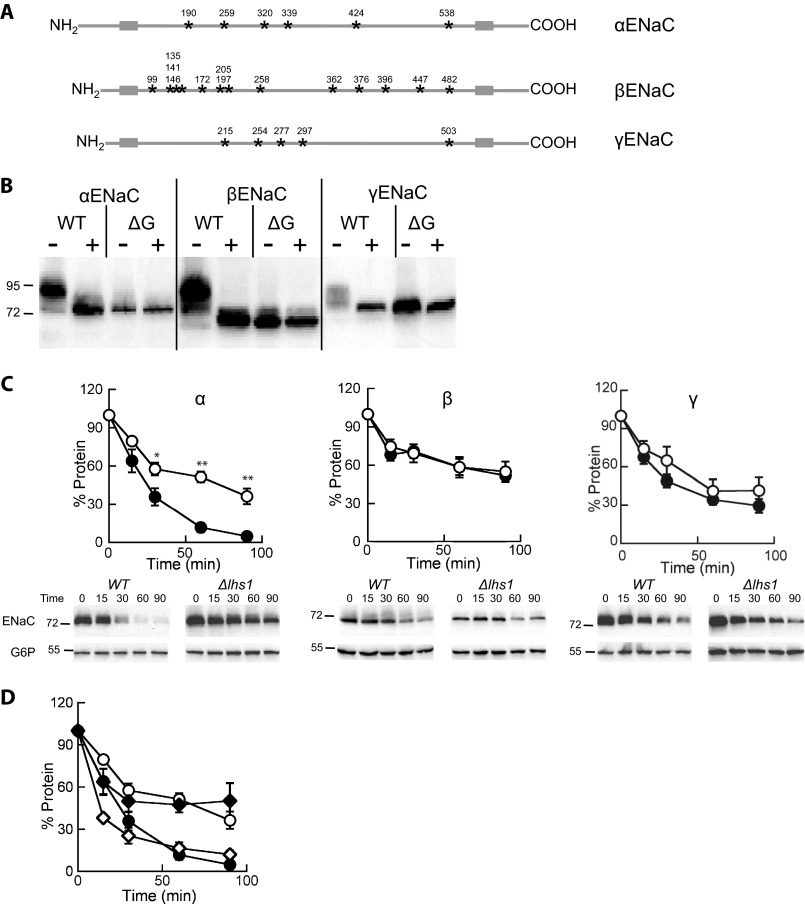
Based on the data presented above we next wished to investigate if the presence of N-linked sugars altered the Lhs1-dependent degradation of the ENaC subunits. We generated ENaC expression constructs that lacked recognition sites for N-linked glycosylation (ΔG constructs) (Fig. 4A). The Asn within the glycan acceptor consensus sequence, Asn-X-Ser/Thr, was mutated to a Gln at six sites in αENaC, 13 sites in βENaC, and 5 sites in γENaC. EndoH digestion of all three native constructs collapsed the bands to a single, lower, molecular weight species, which co-migrated with the corresponding ΔG ENaC construct regardless of whether EndoH was added (Fig. 4B). This confirms that the ΔG ENaC subunits are not glycosylated.
FIGURE 4.
Lhs1 is critical for the degradation of the unglycosylated form of αENaC but is dispensable for the turnover of the unglycosylated versions of β- or γENaC. A, shown is a schematic representation of the ENaC subunits demonstrating the transmembrane segments (gray boxes) and N-linked glycosylation sites (stars) with the amino acid positions noted above each site. B, lysates were prepared from LHS1 WT yeast expressing a C-terminal HA-tagged form of α-, β-, γ-, ΔGα-, ΔGβ-, or ΔGγENaC and were incubated at 37 °C in the presence or absence of EndoH before an immunoblot analysis was performed with anti-HA antiserum to detect ENaC. C, cycloheximide chase reactions were performed as described under “Experimental Procedures” in LHS1 (filled circles) or Δlhs1 (open circles) yeast strains expressing C-terminal HA epitope-tagged ΔGα-, ΔGβ-, or ΔGγENaC. Chase reactions were performed at 37 °C, and lysates were immunoblotted with anti-HA antiserum (ENaC) and with anti-G6P as a loading control. Data represent the means of 7–13 experiments ±S.E.; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.001. D, the glycosylated (open diamonds) and unglycosylated (closed diamonds) species from the Δlhs1 αENaC data from Fig. 1A were quantified and compared with the ΔGαENaC data from C. Note that the symbols used in this panel as the same as those used in C.
We then individually transformed the ΔG α, β, and γENaC constructs into WT and Δlhs1 yeast and assessed degradation as described above. Interestingly, deletion of the glycosylation sites had no measurable effect on the degradation rates of α, β, or γENaC in WT yeast (compare Fig. 4C, WT, to Fig. 1A, WT, degradation rates) despite data suggesting glycans are important for degradation, folding, and maturation (17, 18, 76). Deletion of the glycan acceptor sites also had no effect on the Lhs1-dependent degradation of the β- or γENaC subunit, as neither subunit showed any Lhs1 dependence. In contrast, the ERAD of the ΔG version of αENaC was clearly Lhs1-dependent (Fig. 4C). We compared the quantified signals corresponding to the unglycosylated αENaC species in Δlhs1 yeast from Fig. 1A to the ΔG-αENaC signals in WT and Δlhs1 cells (Fig. 4C) and found them indistinguishable (Fig. 4D). These data confirm that Lhs1 selectively facilitates the degradation of the unglycosylated form of αENaC.
Lhs1 Nucleotide Exchange Activity Is Dispensable for αENaC Degradation
Lhs1 mutants that are unable to bind ATP no longer associate with or stimulate BiP/Kar2 ATPase activity (45) but are still able to act as holdases, preventing the aggregation of a misfolded protein in vitro. Because the degradation of αENaC is BiP/Kar2-independent (40), we hypothesized that the holdase, but not the NEF activity, is important during the ERAD of αENaC. To examine this hypothesis, Δlhs1 yeast expressing αENaC were transformed with a vector engineered to express Lhs1 or Lhs1 with a mutation in the ATP binding domain that prevents NEF activity (Lhs1 D26A; Ref. 45) or with a vector control. We found that both Lhs1 and Lhs1 D26A rescued αENaC degradation, in agreement with our hypothesis (Fig. 5A). It is noteworthy that both Lhs1 and Lhs1 D26A specifically accelerated the degradation of the unglycosylated αENaC species, which was quite stable in the Δlhs1 background. This result also supports our previous finding that αENaC degradation is BiP/Kar2-independent (40), as Lhs1 D26A is unable to associate with or stimulate the ATPase activity of BiP/Kar2.
FIGURE 5.
The ATP binding activity of Lhs1 is not required to support the degradation of αENaC. A, cycloheximide chase reactions were performed as described under “Experimental Procedures” in an Δlhs1 yeast strain expressing a C-terminal HA epitope-tagged form of αENaC and either wild-type Lhs1 (open circles), Lhs1 D26A (diamonds), or a vector control (filled circles). Chase reactions were performed at 37 °C, and lysates were immunoblotted with anti-HA antiserum (αENaC) and with anti-G6P as a loading control. Data represent the means of 6–8 experiments ±S.E.; **, p < 0.02, vector versus lhs1 D26A. B, Δlhs1 yeast strains expressing the indicated protein or containing a vector control were serial-diluted and plated on selective medium and incubated at 26 °C. Cells from the plates were resuspended in lysis buffer and lysed, and the total protein was subjected to immunoblot analysis with anti-Lhs1 antisera and anti-G6P as a loading control. C, Δlhs1 yeast strains expressing ΔGppαF-HA and containing a vector engineered for the expression of either wild-type Lhs1 or Lhs1 D26A or a vector control were grown to log phase, and proteins were precipitated as described under “Experimental Procedures” and immunoblotted with anti-HA antisera.
Although Lhs1 D26A enhanced αENaC degradation, the expression of this mutant does impair other Lhs1-dependent activities (45). We performed two experiments to confirm that Lhs1 D26A-expressing yeast exhibit the anticipated mutant phenotype. First, we tested whether Lhs1 and Lhs1 D26A could rescue the growth defect of the Δlhs1 strain. Growth of Δlhs1 yeast expressing Lhs1 D26A was more robust than that of the vector control but less so than Δlhs1 yeast expressing Lhs1 (Fig. 5B). Western blots of lysates from these yeast suggested similar levels of Lhs1 expression (Fig. 5B). Second, we tested whether Lhs1 and Lhs1 D26A restored efficient translocation of a model yeast preprotein, prepro-α-factor, into the ER of Δlhs1 yeast (34, 35). Lhs1 can rescue this defect of Δlhs1 yeast, but Lhs1 D26A cannot (45). Therefore, we transformed Δlhs1 yeast with a plasmid that encodes a version of prepro-α-factor that has had the glycosylation sites mutated and contains a C-terminal HA epitope tag (ΔGppαF-HA) (77) and monitored translocation into the ER by a decrease in molecular weight caused by signal sequence cleavage. In the absence of Lhs1 (Fig. 5C, vector), a significant population of the ΔGppαF-HA remained untranslocated (upper species), whereas yeast expressing the wild-type version of Lhs1 completely translocated the substrate (i.e. only the faster migrating species is evident). In contrast, the Lhs1 D26A mutant partially rescued the translocation defect, implying that the holdase function of Lhs1 helps facilitate the action of Lhs1 during protein translocation. To some extent, these data are in contrast to previous work in which translocation was suggested to exclusively require Lhs1 NEF activity (36, 45). In any event, our results indicate that the Lhs1 D26A version of Lhs1 facilitates αENaC degradation while exhibiting other, expected cellular defects.
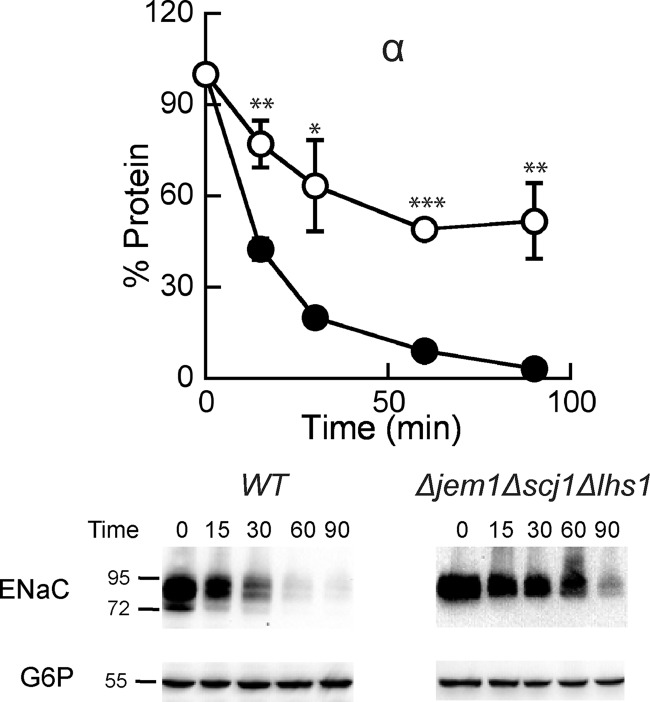
We previously reported that two ER lumenal Hsp40s, Jem1 and Scj1, are also required to support maximal rates of αENaC degradation (40). To determine whether Lhs1 functions in the same degradation pathway with these Hsp40s, we constructed a yeast strain in which all three chaperones were deleted (Δjem1Δscj1Δlhs1). We found that αENaC degradation was slower in the Δjem1Δscj1Δlhs1 (Fig. 6) strain than in either the Δlhs1 (Fig. 1A) or Δjem1Δscj1 (Ref. 40; see Fig. 4A) strains. In the triple mutant 52% of the protein escaped degradation at the 90-min time point versus only 27% for the Δlhs1 strain and 36% for the Δjem1Δscj1 strain. Because the degradation defect was greater in the triple mutant than in the single or double mutants, we suggest that Lhs1 functions in an independent degradation pathway from Jem1 and Scj1 or that these proteins bind to unique regions in αENaC and maintain the protein in a soluble state before retrotranslocation and degradation.
FIGURE 6.
The degradation defect on αENaC is additive when yeast lack both the ER lumenal Hsp40s and Lhs1. Cycloheximide chase reactions were performed as described under “Experimental Procedures” in WT (filled circles) or Δjem1Δscj1Δlhs1 (open circles) yeast strains expressing a C-terminal HA epitope-tagged form of αENaC. Chase reactions were performed at 37 °C, and lysates were immunoblotted with anti-HA antisera (ENaC) and with anti-G6P as a loading control. Data represent the means of 4–5 experiments ± S.E.; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.
Lhs1 and GRP170 Coprecipitate with αENaC
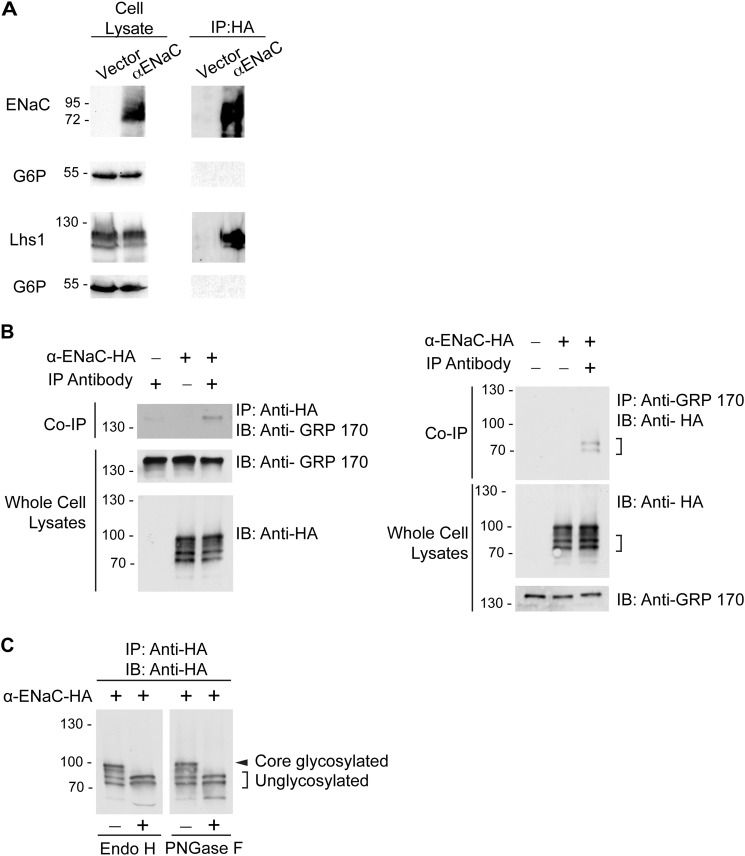
Our data suggest that Lhs1 selects unglycosylated αENaC for ERAD. Therefore, we tested whether Lhs1 co-precipitates with αENaC in yeast. Yeast expressing αENaC or containing a vector control were lysed, and the protein was precipitated. As shown in Fig. 7A, we found Lhs1 but not an abundant cytoplasmic protein (G6P) in the precipitate.
FIGURE 7.
Lhs1 and its mammalian homolog, GRP170, co-immunoprecipitate with αENaC in yeast and mammalian cells, respectively. A, right, cell lysates from Δlhs1 yeast expressing pRS423GPD myc-LHS1 and C-terminal HA-tagged αENaC or containing a vector control were subject to immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-HA-agarose resin and immunoblotted for anti-HA (αENaC), anti-Lhs1, or anti-G6P to serve as both a loading and an immunoprecipitation control. Left, 5% whole cell lysate inputs for immunoprecipitation were immunoblotted as indicated. B, top left, whole cell lysates from HEK293T cells transfected with either HA-tagged αENaC (+) cDNA or an empty vector (−) were immunoprecipitated with anti-HA agarose resin and immunoblotted (IB) with anti-GRP170 antibody to detect the co-immunoprecipitation of endogenous GRP170. Bottom left, 10% of the whole cell lysate inputs for the immunoprecipitation were immunoblotted for αENaC-HA or GRP170 with the indicated antibodies. The experiment is representative of four experiments. Top right, whole cell lysates from HEK293T cells transfected with either αENaC-HA (+) cDNA or empty pcDNA3.1 vector (−) were subjected to immunoprecipitation with polyclonal anti-GRP-170 antibody, and the immunoprecipitates were immunoblotted with anti-HA antibodies. Two lower molecular weight αENaC species that specifically co-immunoprecipitate with the anti-GRP170 antibodies are indicated with brackets. Bottom right, 10% inputs of the whole cell lysates used in the immunoprecipitation were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. Data are representative of three experiments. C, deglycosylation of αENaC in lysates from HEK293T cells is shown. Whole cell lysates were prepared from HEK293T cells transiently expressing HA-tagged αENaC and were subject to an immunoprecipitation analysis with anti-HA agarose resin. The immunoprecipitates were then examined in deglycosylation reactions with EndoH or peptide-N-glycosidase F (PNGaseF) as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The samples were fractionated by SDS-PAGE, and αENaC subunits were detected with HRP-conjugated anti-HA antibodies. Core-glycosylated αENaC is indicated with an asterisk, and unglycosylated αENaC is indicated with brackets.
The mammalian ortholog of Lhs1 is GRP170, which has similarly been shown to act as a NEF for BiP (59). To assess whether GRP170 interacts with αENaC, we performed co-immunoprecipitation experiments in HEK-293T cells. As demonstrated in Fig. 7B, anti-HA-agarose resin immunoprecipitated endogenously expressed GRP170 from lysates of cells expressing HA-tagged αENaC. We observed almost no background binding of the chaperone to resin lacking the anti-HA antibody conjugate. We also observed co-immunoprecipitation of GRP170 and αENaC in the reciprocal direction. In these experiments anti-GRP170 antibody specifically immunoprecipitated two lower molecular mass forms of αENaC that migrated at ∼70 kDa (Fig. 7B). We suspected that these lower molecular weight bands represented the immature, unglycosylated channel based on our yeast experiments. Therefore, we next performed deglycosylation studies. We digested αENaC-HA from whole cell lysates with Endo H (which cleaves high mannose core-N-glycans) or peptide-N-glycosidase F (which removes all types of N-linked oligosaccharides), both of which resulted in the collapse of the anti-HA immunoreactive signal to two bands (Fig. 7C). These bands were identical in molecular weight to the species that selectively co-immunoprecipitated with GRP170. Collectively, these data strongly suggest that αENaC and Lhs1/GRP170 selectively interact and that this interaction appears to favor the unglycosylated α subunit.
GRP170 Promotes αENaC Degradation in Human and Vertebrate Cells
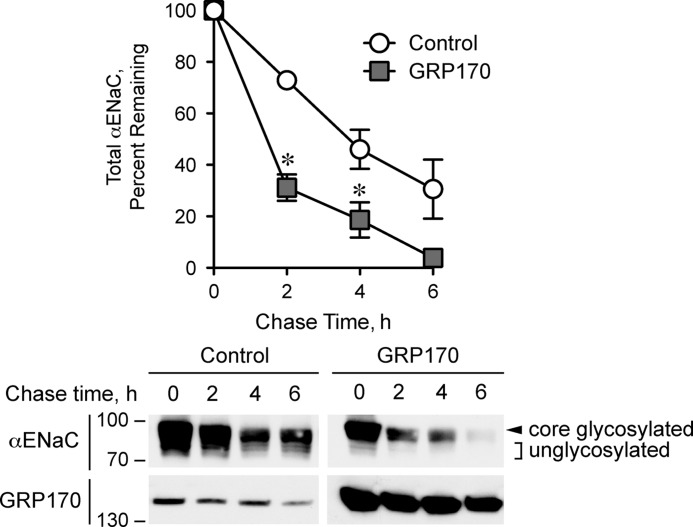
Because Lhs1 promotes the ERAD of αENaC in yeast, we reasoned that overexpression of GRP170 in human cells should have a similar effect on the channel stability. To test this hypothesis, we cotransfected HEK293 cells with HA-tagged αENaC and either a cDNA encoding human GRP170 or an empty vector control. We performed cycloheximide chase assays to monitor αENaC turnover. As predicted, and consistent with stabilization of αENaC in the absence of Lhs1 in yeast, GRP170 overexpression significantly increased the rate of αENaC degradation (Fig. 8). GRP170 overexpression was also evident by Western blot with anti-GRP170 anti-serum. Of note, overexpression of the GRP170 chaperone accelerated the turnover of both core and unglycosylated αENaC. Because GRP170 selectively interacts with unglycosylated αENaC (Fig. 7), these results are consistent with our other data indicating that GRP170 enhances the clearance of unglycosylated αENaC subunits from the ER. This, in turn, would decrease the number of channels that advance along the biosynthetic pathway, resulting in destabilization of the core-glycosylated αENaC pool.
FIGURE 8.
GRP170 targets αENaC for degradation in HEK293T cells. HEK293T cells transfected with HA-tagged αENaC cDNA and with either a human GRP170 expression vector or a vector control were subjected to cycloheximide chase reactions as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Whole cell lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. Top, shown is quantification of the progressive decay in αENaC abundance during the 6-h chase period, expressed as a percentage of αENaC abundance at time zero. Representative immunoblots for both experimental groups are shown below the graph. Core-glycosylated αENaC is indicated with an arrowhead. Unglycosylated αENaC species are indicated with brackets. Data represent the means of three experiments ±S.E.; *, p < 0.02.
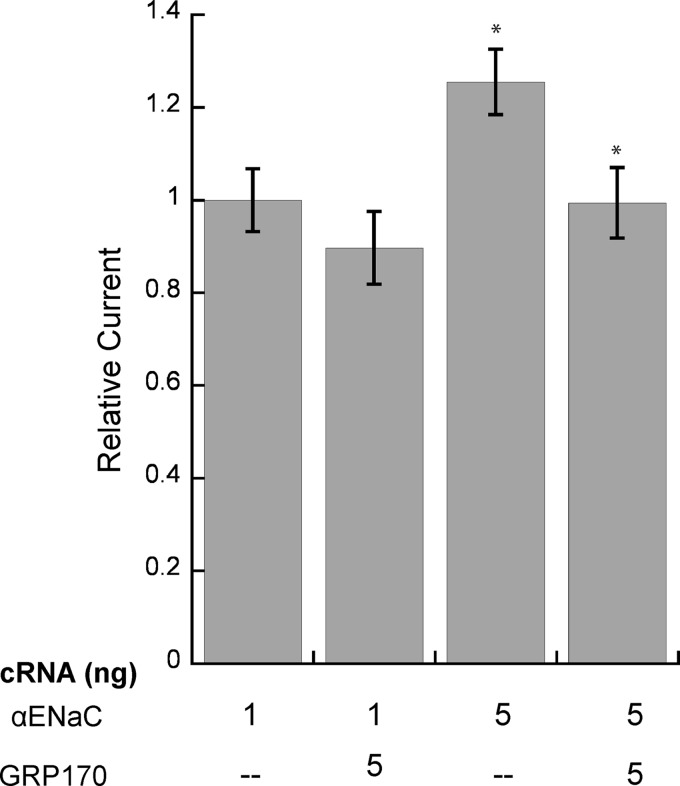
To confirm that GRP170 facilitates the ERAD of the α subunit of ENaC, we assayed the functional effect of GRP170 overexpression on αENaC. In Xenopus oocytes, the α subunit of ENaC is capable of forming a Na+ conducting channel in the absence of the β and γ subunits (78), albeit with significantly reduced Na+ currents. We previously established that the current mediated by the α subunit correlates inversely with proteasome activity in the oocyte system and thus provides a read-out for ERAD; moreover, we used this model to verify that homologs of yeast chaperones function analogously in vertebrate cells (40, 41). We injected cRNA for αENaC into Xenopus oocytes with or without GRP170 cRNA and measured amiloride-sensitive Na+ (ENaC-specific) current 48 h later. We predicted that if GRP170 promotes the degradation of αENaC, then co-injection of GRP170 cRNA would increase αENaC degradation and decrease the amiloride-sensitive Na+ current. Consistent with our prediction, co-injection of GRP170 cRNA reduced the amiloride-sensitive Na+ current by ∼14–20% when either 1 or 5 ng of cRNA corresponding to αENaC was introduced (Fig. 9). Although the reduction of αENaC current was not as substantial as the results seen in HEK293 and yeast experiments, this may be due to very low currents (∼30–100 nA) produced by expressing the α subunit alone and perhaps the inability of the oocyte ER to translocate substantial amounts of both αENaC and GRP170 into the ER. Nonetheless these data are consistent with results in both the yeast and mammalian cell systems that the chaperones play an important role in αENaC quality control. More broadly, our results provide the first evidence that GRP170 facilitates the degradation of an established ERAD substrate.
FIGURE 9.
GRP170 overexpression reduces αENaC Na+ current in Xenopus oocytes. Oocytes were injected with αENaC cRNA (1 or 5 ng) and in the presence or absence of 5 ng GRP170 cRNA. Amiloride-sensitive currents were measured 48 h post-injection by two-electrode voltage clamp. Data represent the means of 21–25 oocytes from three frogs ±S.E.; *, p < 0.02. Amiloride-sensitive Na+ currents were normalized to the average amiloride-sensitive current of wild-type ENaC (1 ng) from the same batch of oocytes assayed on the same day. The average current in oocytes injected with wild-type ENaC (1 ng) varied between 30 and 100 nA.
DISCUSSION
We present three novel findings in this study. First, members of the Lhs1 family of chaperones play a role in ERAD. Second, the mechanism of Lhs1 action during ERAD is BiP/Kar2-independent and appears to require the chaperones' holdase activity. Third, Lhs1 selectively targets the unglycosylated form of αENaC for degradation, suggesting that Lhs1 exhibits substrate specificity for ERAD substrates that are unglycosylated.
Our discovery that the human Lhs1 ortholog, GRP170, contributes to the ERAD of αENaC in higher cell types once more validates our yeast genetics approach to identifying factors that affect quality control decisions for mammalian ERAD substrates. We have successfully applied our approach to varied substrates including: CFTR (50, 54, 66, 79), apolipoprotein B (80, 81), antitrypsin-Z (82–84), and the sodium chloride cotransporter (51). In each case yeast model studies have led us to identify conserved, human homologs of chaperones and chaperone-like proteins that impact the ERAD of these substrates in higher eukaryotes.
Previous work demonstrated that Lhs1 helps repair a heat-denatured, synthetic protein substrate in the ER (85). Specifically, yeast lacking Lhs1 were unable to refold Hsp105Δ-β-lactamase after denaturation, which led to its degradation. Furthermore, Lhs1 precipitated with the heat-denatured protein as well as with pro-CPY, another secretory pathway protein, after cells were heated. However, Lhs1 was dispensable for the folding and secretion of Hsp105Δ-β-lactamase and pro-CPY under standard cellular conditions. GRP170 has also been shown to coprecipitate with misfolded and incompletely folded proteins (58, 86, 87). The contribution of Lhs1/GRP170 to the degradation of these substrates was unexplored. These data are consistent with our finding that Lhs1/GRP170 associates with αENaC.
We also found that Lhs1 is not required for the degradation of a variety of other ERAD substrates. A dual role for a chaperone or cochaperone in both preventing the degradation of a misfolded protein and promoting the degradation of another substrate is not without precedent. For example, BiP/Kar2 is required to traffic the yeast secretory protein, CPY (88), but targets a mutated version of the same protein, CPY*, for ERAD (89, 90). Similarly, Hsp90 can act as either a pro-folding or pro-degradative chaperone during ERAD, depending on the substrate (see for example Refs. 91–94).
Perhaps the best-known role of the Lhs1/GRP170 chaperones is that they act as NEFs for BiP/Kar2. The exchange activities of Lhs1 and Sil1, the other NEF in the ER, facilitate the translocation of nascent-secreted proteins into the ER in cooperation with BiP/Kar2 (33–37). Sil1 lacks sequence similarity with Lhs1/GRP170 but shows some similarity to a cytosolic yeast NEF, Fes1, and a homologous cytoplasmic mammalian NEF, HspBP1 (33, 37, 95). Unlike Sil1, Lhs1 contains an Hsp70-like domain and is 25% identical and shares 50% similarity with Kar2 (85, 96) but is structurally more similar to the cytosolic Hsp110 chaperone family (97). Both Lhs1/GRP170 and the Hsp110 proteins possess an extended loop that separates the α-helical region within the substrate binding domain from a series of β-sheets (60, 98, 99). Although the function of this loop is largely uncharacterized, Lhs1/GRP170 triggers nucleotide exchange by affecting the Hsp70 structure in a very similar manner to the Hsp110, Sse1 (62), but in a mechanistically distinct fashion from Sil1 (63). We initially reasoned that Lhs1 NEF activity would be critical for its action during the ERAD of αENaC. This was not the case, as a mutant form of the protein defective in NEF activity and BiP/Kar2 binding completely rescued the Δlhs1 degradation defect. These data are consistent with a previous study from our laboratory showing that the degradation of αENaC is BiP/Kar2-independent (40). Thus, Hsp70 cochaperones can exhibit Hsp70 (BiP)-independent activities in cells and can be considered bona fide chaperones. This is also consistent with our conclusion that the Lhs1/GRP170 holdase activity is instead required for the ERAD of unglycosylated αENaC. Because unglycosylated substrates are aggregation-prone (100, 101), we envision that the Lhs1/GRP170 holdase activity maintains αENaC in a soluble, retrotranslocation-competent state.
One question that arises from our work is why Lhs1 specifically targets unglycosylated αENaC, but not β- or γENaC, for ERAD. We hypothesize several non-mutually exclusive sources for these differences. First, although 30–40% identical, the three subunits are regulated and modified differently (7, 102). For example, in the kidney the β and γ subunits are constitutively expressed at much higher levels than the α subunit and are subject to degradation by the proteasome (6, 13, 14) until α subunit expression is induced by aldosterone (103, 104). When all three subunits are present, channel assembly and trafficking to the cell surface can occur. In contrast the α subunit can assemble and traffic to the plasma membrane in the absence of the β and γ subunits, albeit with low efficiency (78), whereas the orphaned β and γ subunits do not form a functional sodium channel and may be retained within the ER. This is most likely evident because αENaC contains a C-terminal ER-exit signal (105), which the other subunits apparently lack. It is possible that the ability to assemble and exit the ER may alter the complement of chaperones involved in the quality control of the α subunit. Second, α subunit folding in yeast is less efficient than the β or γ subunits, which may cause it to be recognized by Lhs1 (40). Third, the three subunits exhibit differences in post-translational modification that may be recognized by Lhs1 (7, 102). For example, only the β and γ subunits are modified by Cys palmitoylation (106).
Our findings further suggest that unique degradation pathways exist for the unglycosylated and glycosylated protein. Importantly, the inefficient glycosylation as well as the degradation differences we observed for the glycosylated versus unglycosylated forms of αENaC are not merely an artifact of the yeast expression system; a study by Snyder et al. (71) found that both the glycosylated and unglycosylated species of αENaC were present in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells and migrated distinctly after centrifugation on a sucrose gradient. These results imply that each species associates with a different cohort of protein partners. Another study by Prince and Welsh (72) found that a mixed population of glycosylated and unglycosylated α- and βENaC exists in COS-7 cells, and over time the levels of the soluble/glycosylated species decreased as the insoluble-unglycosylated protein increased.
One class of ER chaperones, the lectins, binds to N-linked glycans and assists in both protein folding and degradation pathways in the ER (77, 107–111). We reasoned that the lectins target the glycosylated protein for degradation but were unable to recognize the unglycosylated protein, making the unglycosylated species dependent on a distinct degradation pathway. Contrary to our predictions, deletion of the ER lectins (calnexin, Yos9, or Mnl1) had no effect on the degradation rate of glycosylated or unglycosylated αENaC (data not shown). Alternatively, it is possible that there is redundancy among the ER lectins and that deletion of multiple lectins may be required to reveal a phenotype. A study by Schmidt and Perlmutter (86) found that GRP170 associates with α1-antitrypsin Z, which is similarly an ERAD substrate in both yeast and mammalian cells (82, 112, 113). Interestingly, the amount of GRP170 associated with α1-antitrypsin Z increased in the presence of tunicamycin, which blocks glycosylation. The authors reasoned that this was due to an increase in the amount of GRP170 due to induction of the unfolded protein response. Alternatively, an increase in association with the non-glycosylated protein is consistent with our result that Lhs1/GRP170 is more important for the quality control of unglycosylated αENaC.
Finally, our results add to the growing list of chaperones that act on ENaC during its biogenesis; we and others reported that the small heat shock proteins and ER lumenal Hsp40s contribute to the ERAD of ENaC subunits (40, 41), and cytosolic Hsp70 promotes ENaC trafficking to the cell surface, whereas the cytosolic Hsp70s and Hsp40s were dispensable for ENaC ERAD (114, 115). Because several ERAD-linked diseases arise from specific mutations and because polymorphisms in the ENaC-encoding genes may predispose individuals to other maladies (116), it will be important to continue to define potential therapeutic targets that can be modulated to alter ENaC biogenesis.
Acknowledgments
We thank all the members of the Kleyman and Brodsky laboratories and Drs. Rebecca Hughey, Michael Grabe, Linda Hendershot, Davis Ng, Elizabeth Craig, Colin Stirling, John Subjeck, Jonathan Weissman, and Allison O'Donnell for helpful discussions, reagents, and/or technical assistance.
This work was supported, in whole or in part, by National Institutes of Health Grants K01DK090195 (to T. M. B.), DK65161 (to T. K.), GM75061 (to J. L. B.), and DK79307 (to the University of Pittsburgh George O'Brien Kidney Research Center).
- ER
- endoplasmic reticulum
- ERAD
- ER-associated degradation
- CFTR
- cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator
- ENaC
- epithelial Na+ channel
- NEF
- nucleotide exchange factor
- Hsp
- heat shock protein
- EndoH
- endoglycosidase H
- G6P
- glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase.
REFERENCES
- 1. Smith M. H., Ploegh H. L., Weissman J. S. (2011) Road to ruin. Targeting proteins for degradation in the endoplasmic reticulum. Science 334, 1086–1090 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Brodsky J. L. (2012) Cleaning up. ER-associated degradation to the rescue. Cell 151, 1163–1167 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Vembar S. S., Brodsky J. L. (2008) One step at a time. endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 9, 944–957 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Guerriero C. J., Brodsky J. L. (2012) The delicate balance between secreted protein folding and endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation in human physiology. Physiol. Rev. 92, 537–576 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Canessa C. M., Merillat A. M., Rossier B. C. (1994) Membrane topology of the epithelial sodium channel in intact cells. Am. J. Physiol. 267, C1682–C1690 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Snyder P. M. (2005) Minireview. Regulation of epithelial Na+ channel trafficking. Endocrinology 146, 5079–5085 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Bhalla V., Hallows K. R. (2008) Mechanisms of ENaC regulation and clinical implications. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 19, 1845–1854 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Soundararajan R., Pearce D., Ziera T. (2012) The role of the ENaC-regulatory complex in aldosterone-mediated sodium transport. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 350, 242–247 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Kashlan O. B., Kleyman T. R. (2012) Epithelial Na+ channel regulation by cytoplasmic and extracellular factors. Exp. Cell Res. 318, 1011–1019 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Staub O., Dho S., Henry P., Correa J., Ishikawa T., McGlade J., Rotin D. (1996) WW domains of Nedd4 bind to the proline-rich PY motifs in the epithelial Na+ channel deleted in Liddle's syndrome. EMBO J. 15, 2371–2380 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Gründer S., Firsov D., Chang S. S., Jaeger N. F., Gautschi I., Schild L., Lifton R. P., Rossier B. C. (1997) A mutation causing pseudohypoaldosteronism type 1 identifies a conserved glycine that is involved in the gating of the epithelial sodium channel. EMBO J. 16, 899–907 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Malik B., Schlanger L., Al-Khalili O., Bao H. F., Yue G., Price S. R., Mitch W. E., Eaton D. C. (2001) Enac degradation in A6 cells by the ubiquitin-proteosome proteolytic pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 12903–12910 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Staub O., Gautschi I., Ishikawa T., Breitschopf K., Ciechanover A., Schild L., Rotin D. (1997) Regulation of stability and function of the epithelial Na+ channel (ENaC) by ubiquitination. EMBO J. 16, 6325–6336 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Valentijn J. A., Fyfe G. K., Canessa C. M. (1998) Biosynthesis and processing of epithelial sodium channels in Xenopus oocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 30344–30351 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Meusser B., Hirsch C., Jarosch E., Sommer T. (2005) ERAD. The long road to destruction. Nat. Cell Biol. 7, 766–772 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Ismail N., Ng D. T. (2006) Have you HRD? Understanding ERAD is DOAble! Cell 126, 237–239 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Rutkevich L. A., Williams D. B. (2011) Participation of lectin chaperones and thiol oxidoreductases in protein folding within the endoplasmic reticulum. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 23, 157–166 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Hebert D. N., Molinari M. (2012) Flagging and docking. dual roles for N-glycans in protein quality control and cellular proteostasis. Trends Biochem. Sci 37, 404–410 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Claessen J. H., Kundrat L., Ploegh H. L. (2012) Protein quality control in the ER. Balancing the ubiquitin checkbook. Trends Cell Biol. 22, 22–32 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Ye Y., Meyer H. H., Rapoport T. A. (2001) The AAA ATPase Cdc48/p97 and its partners transport proteins from the ER into the cytosol. Nature 414, 652–656 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Rabinovich E., Kerem A., Fröhlich K. U., Diamant N., Bar-Nun S. (2002) AAA-ATPase p97/Cdc48p, a cytosolic chaperone required for endoplasmic reticulum-associated protein degradation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 22, 626–634 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Hitchcock A. L., Krebber H., Frietze S., Lin A., Latterich M., Silver P. A. (2001) The conserved npl4 protein complex mediates proteasome-dependent membrane-bound transcription factor activation. Mol. Biol. Cell 12, 3226–3241 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Bays N. W., Wilhovsky S. K., Goradia A., Hodgkiss-Harlow K., Hampton R. Y. (2001) HRD4/NPL4 is required for the proteasomal processing of ubiquitinated ER proteins. Mol. Biol. Cell 12, 4114–4128 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Raasi S., Wolf D. H. (2007) Ubiquitin receptors and ERAD. A network of pathways to the proteasome. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 18, 780–791 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Nishikawa S. I., Fewell S. W., Kato Y., Brodsky J. L., Endo T. (2001) Molecular chaperones in the yeast endoplasmic reticulum maintain the solubility of proteins for retrotranslocation and degradation. J. Cell Biol. 153, 1061–1070 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Dong M., Bridges J. P., Apsley K., Xu Y., Weaver T. E. (2008) ERdj4 and ERdj5 are required for endoplasmic reticulum-associated protein degradation of misfolded surfactant protein C. Mol. Biol. Cell 19, 2620–2630 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Shen Y., Hendershot L. M. (2005) ERdj3, a stress-inducible endoplasmic reticulum DnaJ homologue, serves as a cofactor for BiP's interactions with unfolded substrates. Mol. Biol. Cell 16, 40–50 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Shen Y., Meunier L., Hendershot L. M. (2002) Identification and characterization of a novel endoplasmic reticulum (ER) DnaJ homologue, which stimulates ATPase activity of BiP in vitro and is induced by ER stress. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 15947–15956 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Buck T. M., Wright C. M., Brodsky J. L. (2007) The activities and function of molecular chaperones in the endoplasmic reticulum. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 18, 751–761 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Hennessy F., Nicoll W. S., Zimmermann R., Cheetham M. E., Blatch G. L. (2005) Not all J domains are created equal. Implications for the specificity of Hsp40-Hsp70 interactions. Protein Sci 14, 1697–1709 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Qiu X. B., Shao Y. M., Miao S., Wang L. (2006) The diversity of the DnaJ/Hsp40 family, the crucial partners for Hsp70 chaperones. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 63, 2560–2570 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Kampinga H. H., Craig E. A. (2010) The HSP70 chaperone machinery. J proteins as drivers of functional specificity. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 11, 579–592 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Craven R. A., Egerton M., Stirling C. J. (1996) A novel Hsp70 of the yeast ER lumen is required for the efficient translocation of a number of protein precursors. EMBO J. 15, 2640–2650 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Baxter B. K., James P., Evans T., Craig E. A. (1996) SSI1 encodes a novel Hsp70 of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae endoplasmic reticulum. Mol. Cell. Biol. 16, 6444–6456 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Steel G. J., Fullerton D. M., Tyson J. R., Stirling C. J. (2004) Coordinated activation of Hsp70 chaperones. Science 303, 98–101 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Tyson J. R., Stirling C. J. (2000) LHS1 and SIL1 provide a lumenal function that is essential for protein translocation into the endoplasmic reticulum. EMBO J. 19, 6440–6452 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Yan M., Li J., Sha B. (2011) Structural analysis of the Sil1-Bip complex reveals the mechanism for Sil1 to function as a nucleotide-exchange factor. Biochem. J. 438, 447–455 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Liberek K., Wall D., Georgopoulos C. (1995) The DnaJ chaperone catalytically activates the DnaK chaperone to preferentially bind the δ32 heat shock transcriptional regulator. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 92, 6224–6228 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Jordan R., McMacken R. (1995) Modulation of the ATPase activity of the molecular chaperone DnaK by peptides and the DnaJ and GrpE heat shock proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 4563–4569 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Buck T. M., Kolb A. R., Boyd C. R., Kleyman T. R., Brodsky J. L. (2010) The endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation of the epithelial sodium channel requires a unique complement of molecular chaperones. Mol. Biol. Cell 21, 1047–1058 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Kashlan O. B., Mueller G. M., Qamar M. Z., Poland P. A., Ahner A., Rubenstein R. C., Hughey R. P., Brodsky J. L., Kleyman T. R. (2007) Small heat shock protein αA-crystallin regulates epithelial sodium channel expression. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 28149–28156 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Adams A., Gottschling D. E., Kaiser C. A., Stearns T. (1997) A Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Course Manual, 1997 Ed., Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY [Google Scholar]
- 43. Bhamidipati A., Denic V., Quan E. M., Weissman J. S. (2005) Exploration of the topological requirements of ERAD identifies Yos9p as a lectin sensor of misfolded glycoproteins in the ER lumen. Mol. Cell 19, 741–751 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Zhang Y., Michaelis S., Brodsky J. L. (2002) CFTR expression and ER-associated degradation in yeast. Methods Mol. Med. 70, 257–265 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. de Keyzer J., Steel G. J., Hale S. J., Humphries D., Stirling C. J. (2009) Nucleotide binding by Lhs1p is essential for its nucleotide exchange activity and for function in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 31564–31571 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Mumberg D., Müller R., Funk M. (1995) Yeast vectors for the controlled expression of heterologous proteins in different genetic backgrounds. Gene 156, 119–122 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Ho S. N., Hunt H. D., Horton R. M., Pullen J. K., Pease L. R. (1989) Site-directed mutagenesis by overlap extension using the polymerase chain reaction. Gene 77, 51–59 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Hughey R. P., Mueller G. M., Bruns J. B., Kinlough C. L., Poland P. A., Harkleroad K. L., Carattino M. D., Kleyman T. R. (2003) Maturation of the epithelial Na+ channel involves proteolytic processing of the α- and γ-subunits. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 37073–37082 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Park J. E., Facciponte J., Chen X., MacDonald I., Repasky E. A., Manjili M. H., Wang X. Y., Subjeck J. R. (2006) Chaperoning function of stress protein grp170, a member of the hsp70 superfamily, is responsible for its immunoadjuvant activity. Cancer Res. 66, 1161–1168 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Zhang Y., Nijbroek G., Sullivan M. L., McCracken A. A., Watkins S. C., Michaelis S., Brodsky J. L. (2001) Hsp70 molecular chaperone facilitates endoplasmic reticulum-associated protein degradation of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator in yeast. Mol. Biol. Cell 12, 1303–1314 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Needham P. G., Mikoluk K., Dhakarwal P., Khadem S., Snyder A. C., Subramanya A. R., Brodsky J. L. (2011) The thiazide-sensitive NaCl cotransporter is targeted for chaperone-dependent endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 43611–43621 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Stirling C. J., Rothblatt J., Hosobuchi M., Deshaies R., Schekman R. (1992) Protein translocation mutants defective in the insertion of integral membrane proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum. Mol. Biol. Cell 3, 129–142 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Meacham G. C., Lu Z., King S., Sorscher E., Tousson A., Cyr D. M. (1999) The Hdj-2/Hsc70 chaperone pair facilitates early steps in CFTR biogenesis. EMBO J. 18, 1492–1505 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Youker R. T., Walsh P., Beilharz T., Lithgow T., Brodsky J. L. (2004) Distinct roles for the Hsp40 and Hsp90 molecular chaperones during cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator degradation in yeast. Mol. Biol. Cell 15, 4787–4797 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Nakatsukasa K., Huyer G., Michaelis S., Brodsky J. L. (2008) Dissecting the ER-associated degradation of a misfolded polytopic membrane protein. Cell 132, 101–112 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Han S., Liu Y., Chang A. (2007) Cytoplasmic Hsp70 promotes ubiquitination for endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation of a misfolded mutant of the yeast plasma membrane ATPase, PMA1. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 26140–26149 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Hill K., Cooper A. A. (2000) Degradation of unassembled Vph1p reveals novel aspects of the yeast ER quality control system. EMBO J. 19, 550–561 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Lin H. Y., Masso-Welch P., Di Y. P., Cai J. W., Shen J. W., Subjeck J. R. (1993) The 170-kDa glucose-regulated stress protein is an endoplasmic reticulum protein that binds immunoglobulin. Mol. Biol. Cell 4, 1109–1119 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Weitzmann A., Volkmer J., Zimmermann R. (2006) The nucleotide exchange factor activity of Grp170 may explain the non-lethal phenotype of loss of Sil1 function in man and mouse. FEBS Lett. 580, 5237–5240 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Easton D. P., Kaneko Y., Subjeck J. R. (2000) The hsp110 and Grp1 70 stress proteins. Newly recognized relatives of the Hsp70s. Cell Stress Chaperones 5, 276–290 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Park J., Easton D. P., Chen X., MacDonald I. J., Wang X. Y., Subjeck J. R. (2003) The chaperoning properties of mouse grp170, a member of the third family of hsp70 related proteins. Biochemistry 42, 14893–14902 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Andréasson C., Rampelt H., Fiaux J., Druffel-Augustin S., Bukau B. (2010) The endoplasmic reticulum Grp170 acts as a nucleotide exchange factor of Hsp70 via a mechanism similar to that of the cytosolic Hsp110. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 12445–12453 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Hale S. J., Lovell S. C., de Keyzer J., Stirling C. J. (2010) Interactions between Kar2p and its nucleotide exchange factors Sil1p and Lhs1p are mechanistically distinct. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 21600–21606 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Wolf D. H., Schäfer A. (2005) CPY* and the power of yeast genetics in the elucidation of quality control and associated protein degradation of the endoplasmic reticulum. Curr. Top Microbiol. Immunol. 300, 41–56 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Lukacs G. L., Verkman A. S. (2012) CFTR. folding, misfolding and correcting the ΔF508 conformational defect. Trends Mol. Med. 18, 81–91 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Ahner A., Nakatsukasa K., Zhang H., Frizzell R. A., Brodsky J. L. (2007) Small heat-shock proteins select δF508-CFTR for endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation. Mol. Biol. Cell 18, 806–814 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Gnann A., Riordan J. R., Wolf D. H. (2004) Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator degradation depends on the lectins Htm1p/EDEM and the Cdc48 protein complex in yeast. Mol. Biol. Cell 15, 4125–4135 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68. Travers K. J., Patil C. K., Wodicka L., Lockhart D. J., Weissman J. S., Walter P. (2000) Functional and genomic analyses reveal an essential coordination between the unfolded protein response and ER-associated degradation. Cell 101, 249–258 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. Snyder P. M., McDonald F. J., Stokes J. B., Welsh M. J. (1994) Membrane topology of the amiloride-sensitive epithelial sodium channel. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 24379–24383 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70. Adams C. M., Snyder P. M., Welsh M. J. (1997) Interactions between subunits of the human epithelial sodium channel. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 27295–27300 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71. Snyder P. M., Cheng C., Prince L. S., Rogers J. C., Welsh M. J. (1998) Electrophysiological and biochemical evidence that DEG/ENaC cation channels are composed of nine subunits. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 681–684 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72. Prince L. S., Welsh M. J. (1999) Effect of subunit composition and Liddle's syndrome mutations on biosynthesis of ENaC. Am. J. Physiol. 276, C1346–C1351 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73. Nilsson I., Kelleher D. J., Miao Y., Shao Y., Kreibich G., Gilmore R., von Heijne G., Johnson A. E. (2003) Photocross-linking of nascent chains to the STT3 subunit of the oligosaccharyltransferase complex. J. Cell Biol. 161, 715–725 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74. Trueman S. F., Mandon E. C., Gilmore R. (2012) A gating motif in the translocation channel sets the hydrophobicity threshold for signal sequence function. J. Cell Biol. 199, 907–918 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75. Ruiz-Canada C., Kelleher D. J., Gilmore R. (2009) Cotranslational and posttranslational N-glycosylation of polypeptides by distinct mammalian OST isoforms. Cell 136, 272–283 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76. Aebi M., Bernasconi R., Clerc S., Molinari M. (2010) N-glycan structures. Recognition and processing in the ER. Trends Biochem. Sci 35, 74–82 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77. Kim W., Spear E. D., Ng D. T. (2005) Yos9p detects and targets misfolded glycoproteins for ER-associated degradation. Mol. Cell 19, 753–764 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78. Canessa C. M., Schild L., Buell G., Thorens B., Gautschi I., Horisberger J. D., Rossier B. C. (1994) Amiloride-sensitive epithelial Na+ channel is made of three homologous subunits. Nature 367, 463–467 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79. Hutt D. M., Roth D. M., Chalfant M. A., Youker R. T., Matteson J., Brodsky J. L., Balch W. E. (2012) FK506 binding protein 8 peptidylprolyl isomerase activity manages a late stage of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) folding and stability. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 21914–21925 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80. Grubb S., Guo L., Fisher E. A., Brodsky J. L. (2012) Protein disulfide isomerases contribute differentially to the endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation of apolipoprotein B and other substrates. Mol. Biol. Cell 23, 520–532 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81. Hrizo S. L., Gusarova V., Habiel D. M., Goeckeler J. L., Fisher E. A., Brodsky J. L. (2007) The Hsp110 molecular chaperone stabilizes apolipoprotein B from endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation (ERAD). J. Biol. Chem. 282, 32665–32675 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82. Werner E. D., Brodsky J. L., McCracken A. A. (1996) Proteasome-dependent endoplasmic reticulum-associated protein degradation. An unconventional route to a familiar fate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 93, 13797–13801 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83. Scott C. M., Kruse K. B., Schmidt B. Z., Perlmutter D. H., McCracken A. A., Brodsky J. L. (2007) ADD66, a gene involved in the endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation of α-1-antitrypsin-Z in yeast, facilitates proteasome activity and assembly. Mol. Biol. Cell 18, 3776–3787 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84. Gelling C. L., Dawes I. W., Perlmutter D. H., Fisher E. A., Brodsky J. L. (2012) The endosomal protein-sorting receptor sortilin has a role in trafficking α-1 antitrypsin. Genetics 192, 889–903 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85. Saris N., Holkeri H., Craven R. A., Stirling C. J., Makarow M. (1997) The Hsp70 homologue Lhs1p is involved in a novel function of the yeast endoplasmic reticulum, refolding, and stabilization of heat-denatured protein aggregates. J. Cell Biol. 137, 813–824 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86. Schmidt B. Z., Perlmutter D. H. (2005) Grp78, Grp94, and Grp170 interact with α1-antitrypsin mutants that are retained in the endoplasmic reticulum. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 289, G444–G455 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87. Meunier L., Usherwood Y. K., Chung K. T., Hendershot L. M. (2002) A subset of chaperones and folding enzymes form multiprotein complexes in endoplasmic reticulum to bind nascent proteins. Mol. Biol. Cell 13, 4456–4469 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88. Simons J. F., Ferro-Novick S., Rose M. D., Helenius A. (1995) BiP/Kar2p serves as a molecular chaperone during carboxypeptidase Y folding in yeast. J. Cell Biol. 130, 41–49 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89. Brodsky J. L., Werner E. D., Dubas M. E., Goeckeler J. L., Kruse K. B., McCracken A. A. (1999) The requirement for molecular chaperones during endoplasmic reticulum-associated protein degradation demonstrates that protein export and import are mechanistically distinct. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 3453–3460 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90. Plemper R. K., Böhmler S., Bordallo J., Sommer T., Wolf D. H. (1997) Mutant analysis links the translocon and BiP to retrograde protein transport for ER degradation. Nature 388, 891–895 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91. Gusarova V., Caplan A. J., Brodsky J. L., Fisher E. A. (2001) Apoprotein B degradation is promoted by the molecular chaperones hsp90 and hsp70. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 24891–24900 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92. Loo M. A., Jensen T. J., Cui L., Hou Y., Chang X. B., Riordan J. R. (1998) Perturbation of Hsp90 interaction with nascent CFTR prevents its maturation and accelerates its degradation by the proteasome. EMBO J. 17, 6879–6887 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93. Giodini A., Cresswell P. (2008) Hsp90-mediated cytosolic refolding of exogenous proteins internalized by dendritic cells. EMBO J. 27, 201–211 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94. Taylor M., Navarro-Garcia F., Huerta J., Burress H., Massey S., Ireton K., Teter K. (2010) Hsp90 is required for transfer of the cholera toxin A1 subunit from the endoplasmic reticulum to the cytosol. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 31261–31267 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95. Kabani M., McLellan C., Raynes D. A., Guerriero V., Brodsky J. L. (2002) HspBP1, a homologue of the yeast Fes1 and Sls1 proteins, is an Hsc70 nucleotide exchange factor. FEBS Lett. 531, 339–342 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96. Rasmussen S. W. (1994) Sequence of a 20.7-kb region of yeast chromosome XI includes the NUP100 gene, an open reading frame (ORF) possibly representing a nucleoside diphosphate kinase gene, and tRNAs for His, Val, and Trp in addition to seven ORFs with weak or no significant similarity to known proteins. Yeast 10, S69–S74 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97. Shaner L., Morano K. A. (2007) All in the family. Atypical Hsp70 chaperones are conserved modulators of Hsp70 activity. Cell Stress Chaperones 12, 1–8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98. Polier S., Dragovic Z., Hartl F. U., Bracher A. (2008) Structural basis for the cooperation of Hsp70 and Hsp110 chaperones in protein folding. Cell 133, 1068–1079 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99. Liu Q., Hendrickson W. A. (2007) Insights into Hsp70 chaperone activity from a crystal structure of the yeast Hsp110 Sse1. Cell 131, 106–120 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100. Tams J. W., Vind J., Welinder K. G. (1999) Adapting protein solubility by glycosylation. N-Glycosylation mutants of Coprinus cinereus peroxidase in salt and organic solutions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1432, 214–221 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101. Wang C., Eufemi M., Turano C., Giartosio A. (1996) Influence of the carbohydrate moiety on the stability of glycoproteins. Biochemistry 35, 7299–7307 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102. Weisz O. A., Wang J. M., Edinger R. S., Johnson J. P. (2000) Non-coordinate regulation of endogenous epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) subunit expression at the apical membrane of A6 cells in response to various transporting conditions. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 39886–39893 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103. Asher C., Wald H., Rossier B. C., Garty H. (1996) Aldosterone-induced increase in the abundance of Na+ channel subunits. Am. J. Physiol. 271, C605–C611 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104. Masilamani S., Kim G. H., Mitchell C., Wade J. B., Knepper M. A. (1999) Aldosterone-mediated regulation of ENaCα, -β, and -γ subunit proteins in rat kidney. J. Clin. Invest. 104, R19–R23 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105. Mueller G. M., Kashlan O. B., Bruns J. B., Maarouf A. B., Aridor M., Kleyman T. R., Hughey R. P. (2007) Epithelial sodium channel exit from the endoplasmic reticulum is regulated by a signal within the carboxyl cytoplasmic domain of the α subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 33475–33483 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106. Mueller G. M., Maarouf A. B., Kinlough C. L., Sheng N., Kashlan O. B., Okumura S., Luthy S., Kleyman T. R., Hughey R. P. (2010) Cys palmitoylation of the β subunit modulates gating of the epithelial sodium channel. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 30453–30462 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107. Clerc S., Hirsch C., Oggier D. M., Deprez P., Jakob C., Sommer T., Aebi M. (2009) Htm1 protein generates the N-glycan signal for glycoprotein degradation in the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Cell Biol. 184, 159–172 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108. Denic V., Quan E. M., Weissman J. S. (2006) A luminal surveillance complex that selects misfolded glycoproteins for ER-associated degradation. Cell 126, 349–359 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109. Helenius A., Aebi M. (2004) Roles of N-linked glycans in the endoplasmic reticulum. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 73, 1019–1049 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110. Quan E. M., Kamiya Y., Kamiya D., Denic V., Weibezahn J., Kato K., Weissman J. S. (2008) Defining the glycan destruction signal for endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation. Mol. Cell 32, 870–877 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111. Szathmary R., Bielmann R., Nita-Lazar M., Burda P., Jakob C. A. (2005) Yos9 protein is essential for degradation of misfolded glycoproteins and may function as lectin in ERAD. Mol. Cell 19, 765–775 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112. Qu D., Teckman J. H., Omura S., Perlmutter D. H. (1996) Degradation of a mutant secretory protein, α1-antitrypsin Z, in the endoplasmic reticulum requires proteasome activity. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 22791–22795 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113. Teckman J. H., Perlmutter D. H. (1996) The endoplasmic reticulum degradation pathway for mutant secretory proteins α1-antitrypsin Z and S is distinct from that for an unassembled membrane protein. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 13215–13220 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114. Chanoux R. A., Robay A., Shubin C. B., Kebler C., Suaud L., Rubenstein R. C. (2012) Hsp70 promotes epithelial sodium channel functional expression by increasing its association with coat complex II and its exit from endoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 19255–19265 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115. Goldfarb S. B., Kashlan O. B., Watkins J. N., Suaud L., Yan W., Kleyman T. R., Rubenstein R. C. (2006) Differential effects of Hsc70 and Hsp70 on the intracellular trafficking and functional expression of epithelial sodium channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103, 5817–5822 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116. Soundararajan R., Pearce D., Hughey R. P., Kleyman T. R. (2010) Role of epithelial sodium channels and their regulators in hypertension. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 30363–30369 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]