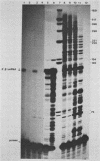
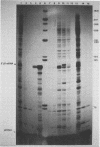
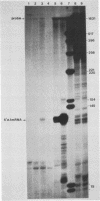
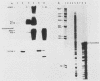
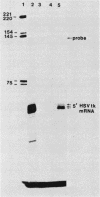
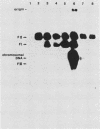
Abstract
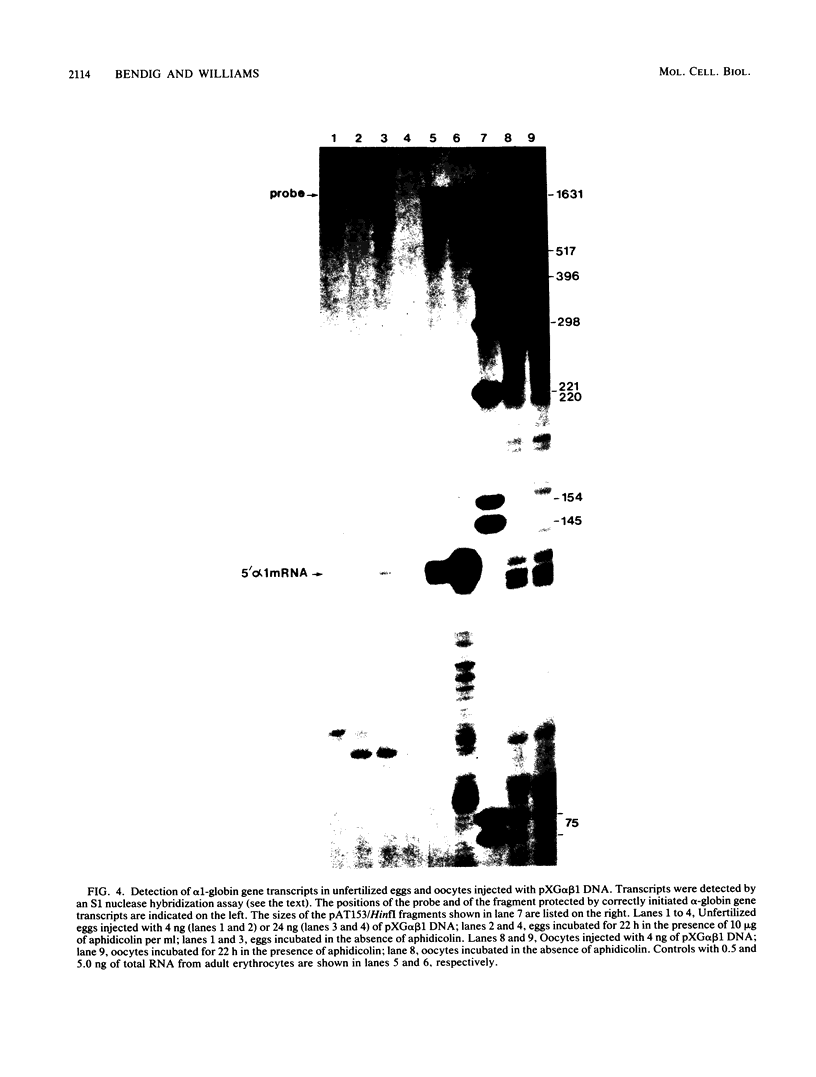
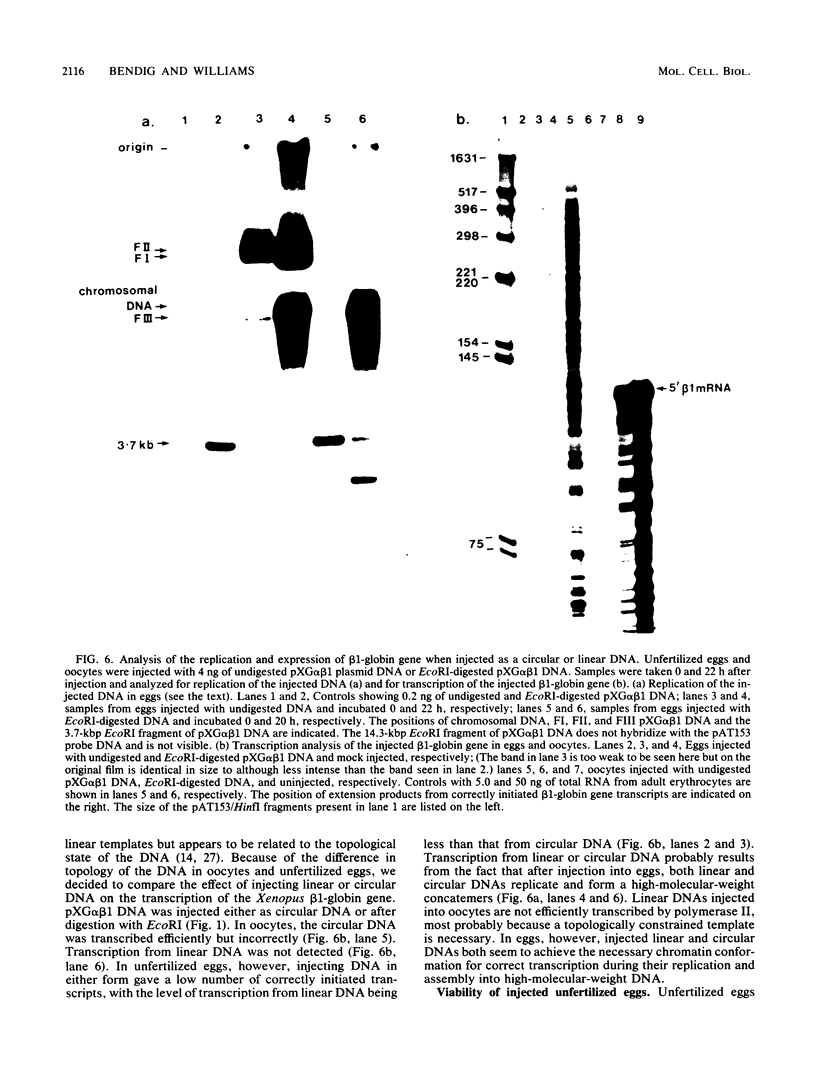
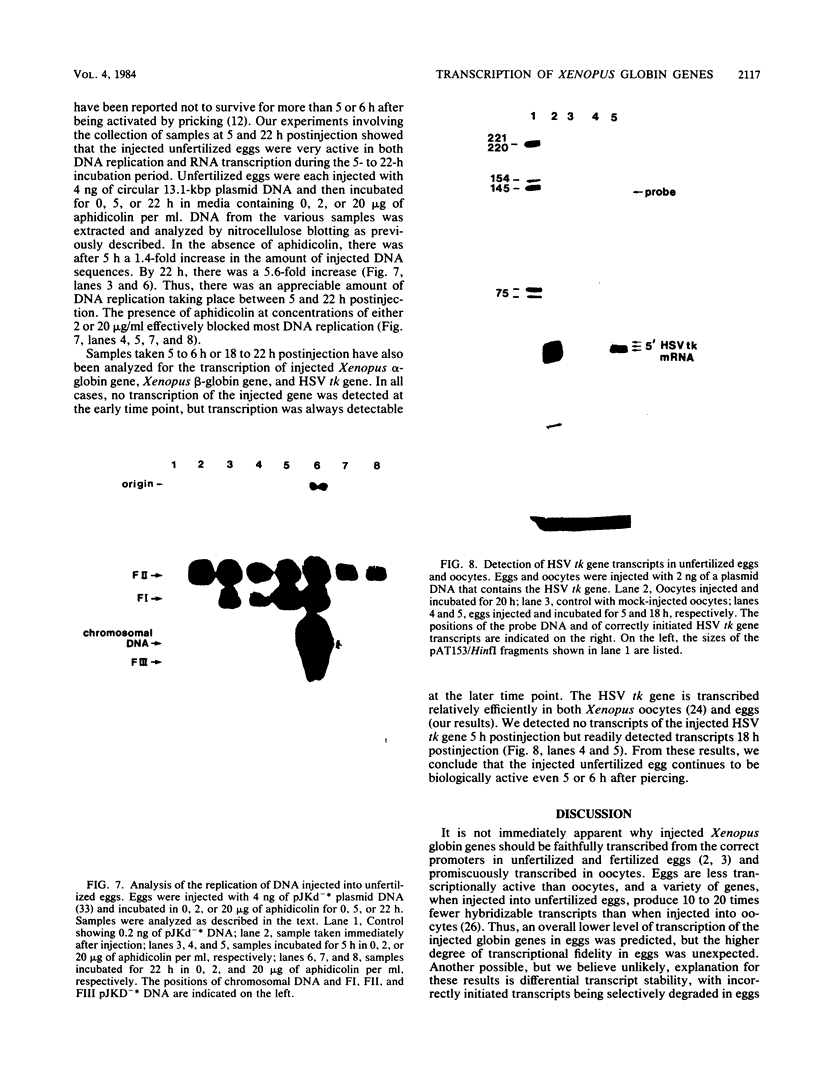
The Xenopus laevis alpha 1- and beta 1-globin genes were injected into oocytes and unfertilized eggs of X. laevis. In oocytes, the injected globin genes were actively transcribed, but the majority of the transcripts were incorrectly initiated. In unfertilized eggs, the injected genes were transcribed at a low level but only from the correct start sites. In oocytes, the injected circular plasmid DNA containing the cloned globin genes persisted but did not replicate. In contrast, DNA injected into unfertilized eggs replicated up to 15-fold within a 22-h period. We suggest that the ability of the egg to selectively transcribe the injected X. laevis globin genes from the correct promoter sites may be related to differences in chromatin structure between the oocyte and the unfertilized egg.
Full text
PDF

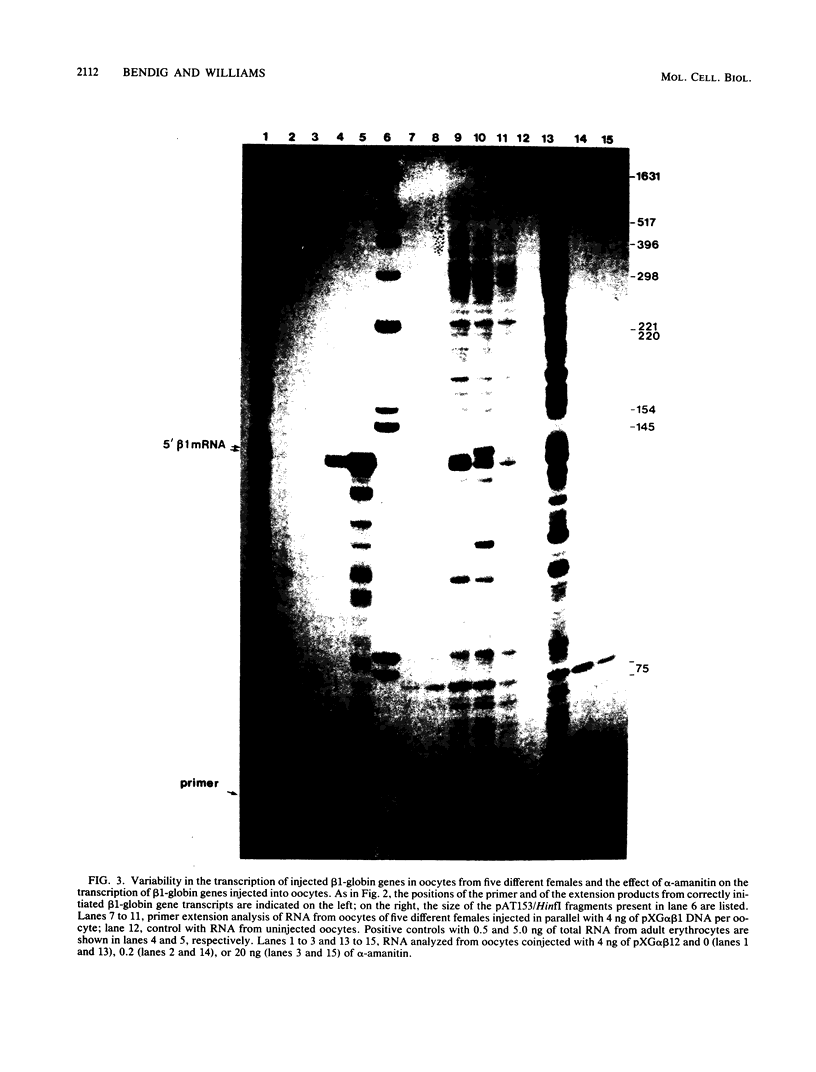




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bendig M. M. Persistence and expression of histone genes injected into Xenopus eggs in early development. Nature. 1981 Jul 2;292(5818):65–67. doi: 10.1038/292065a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendig M. M., Williams J. G. Differential expression of the Xenopus laevis tadpole and adult beta-globin genes when injected into fertilized Xenopus laevis eggs. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):567–570. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendig M. M., Williams J. G. Replication and expression of Xenopus laevis globin genes injected into fertilized Xenopus eggs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6197–6201. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busby S. J., Reeder R. H. Fate of amplified nucleoli in Xenopus laevis embryos. Dev Biol. 1982 Jun;91(2):458–467. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90052-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont J. N. Oogenesis in Xenopus laevis (Daudin). I. Stages of oocyte development in laboratory maintained animals. J Morphol. 1972 Feb;136(2):153–179. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051360203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etkin L. D., Maxson R. E., Jr The synthesis of authentic sea urchin transcriptional and translational products by sea urchin histone genes injected into Xenopus laevis oocytes. Dev Biol. 1980 Mar;75(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90140-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford C. C., Woodland H. R. DNA synthesis in ocytes and eggs of Xenopus laevis injected with DNA. Dev Biol. 1975 Mar;43(1):189–199. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(75)90140-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gargiulo G., Wasserman W., Worcel A. Properties of the chromatin assembled on DNA injected into Xenopus oocytes and eggs. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):549–556. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B., Birnstiel M. L., Speight V. A. The replication of purified DNA introduced into living egg cytoplasm. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Feb 18;174(2):614–628. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90291-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B., Melton D. A. Gene transfer in amphibian eggs and oocytes. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:189–218. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.001201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harland R. M., Laskey R. A. Regulated replication of DNA microinjected into eggs of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):761–771. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90439-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harland R. M., Weintraub H., McKnight S. L. Transcription of DNA injected into Xenopus oocytes is influenced by template topology. Nature. 1983 Mar 3;302(5903):38–43. doi: 10.1038/302038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igo-Kemenes T., Hörz W., Zachau H. G. Chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:89–121. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.000513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikegami S., Taguchi T., Ohashi M., Oguro M., Nagano H., Mano Y. Aphidicolin prevents mitotic cell division by interfering with the activity of DNA polymerase-alpha. Nature. 1978 Oct 5;275(5679):458–460. doi: 10.1038/275458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Wilson V., Wood D., Simons J. P., Kay R. M., Williams J. G. Linkage of adult alpha- and beta-globin genes in X. laevis and gene duplication by tetraploidization. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):555–564. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90493-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. C., Richter J. D., Weeks D. L., Smith L. D. Regulation of adenovirus transcription by an E1a gene in microinjected Xenopus laevis oocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2131–2142. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn L. J., Gurdon J. B., Price J. Oocyte extracts reactivate developmentally inert Xenopus 5S genes in somatic nuclei. Nature. 1982 Nov 25;300(5890):354–355. doi: 10.1038/300354a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Gurdon J. B. Induction of polyoma DNA synthesis by injection into frog-egg cytoplasm. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Sep 3;37(3):467–471. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03007.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Harland R. M., Méchali M. Induction of chromosome replication during maturation of amphibian oocytes. Ciba Found Symp. 1983;98:25–43. doi: 10.1002/9780470720790.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Honda B. M., Mills A. D., Morris N. R., Wyllie A. H., Mertz J. E., De Roberts E. M., Gurdon J. B. Chromatin assembly and transcription in eggs and oocytes of Xenopus laevis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 1):171–178. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Gavis E. R., Kingsbury R., Axel R. Analysis of transcriptional regulatory signals of the HSV thymidine kinase gene: identification of an upstream control region. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):385–398. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertz J. E., Gurdon J. B. Purified DNAs are transcribed after microinjection into Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1502–1506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. J., Mertz J. E. Template structural requirements for transcription in vivo by RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;2(12):1595–1607. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.12.1595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Méchali M., Harland R. M. DNA synthesis in a cell-free system from Xenopus eggs: priming and elongation on single-stranded DNA in vitro. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):93–101. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newport J., Kirschner M. A major developmental transition in early Xenopus embryos: I. characterization and timing of cellular changes at the midblastula stage. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):675–686. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newport J., Kirschner M. A major developmental transition in early Xenopus embryos: II. Control of the onset of transcription. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):687–696. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90273-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patient R. K., Elkington J. A., Kay R. M., Williams J. G. Internal organization of the major adult alpha- and beta-globin genes of X. laevis. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):565–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90494-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patient R. K., Harris R., Walmsley M. E., Williams J. G. The complete nucleotide sequence of the major adult beta globin gene of Xenopus laevis. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):8521–8523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusconi S., Schaffner W. Transformation of frog embryos with a rabbit beta-globin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5051–5055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryoji M., Worcel A. Chromatin assembly in Xenopus oocytes: in vivo studies. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):21–32. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90297-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twigg A. J., Sherratt D. Trans-complementable copy-number mutants of plasmid ColE1. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):216–218. doi: 10.1038/283216a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. A., Jared D. W., Dumont J. N., Sega M. W. Protein incorporation by isolated amphibian oocytes. 3. Optimum incubation conditions. J Exp Zool. 1973 Jun;184(3):321–333. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401840305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickens M. P., Woo S., O'Malley B. W., Gurdon J. B. Expression of a chicken chromosomal ovalbumin gene injected into frog oocyte nuclei. Nature. 1980 Jun 26;285(5767):628–634. doi: 10.1038/285628a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H., Laskey R. A., Finch J., Gurdon J. B. Selective DNA conservation and chromatin assembly after injection of SV40 DNA into Xenopus oocytes. Dev Biol. 1978 May;64(1):178–188. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]