Abstract
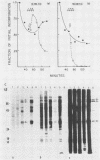
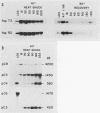
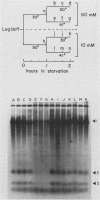
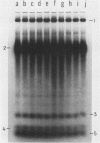
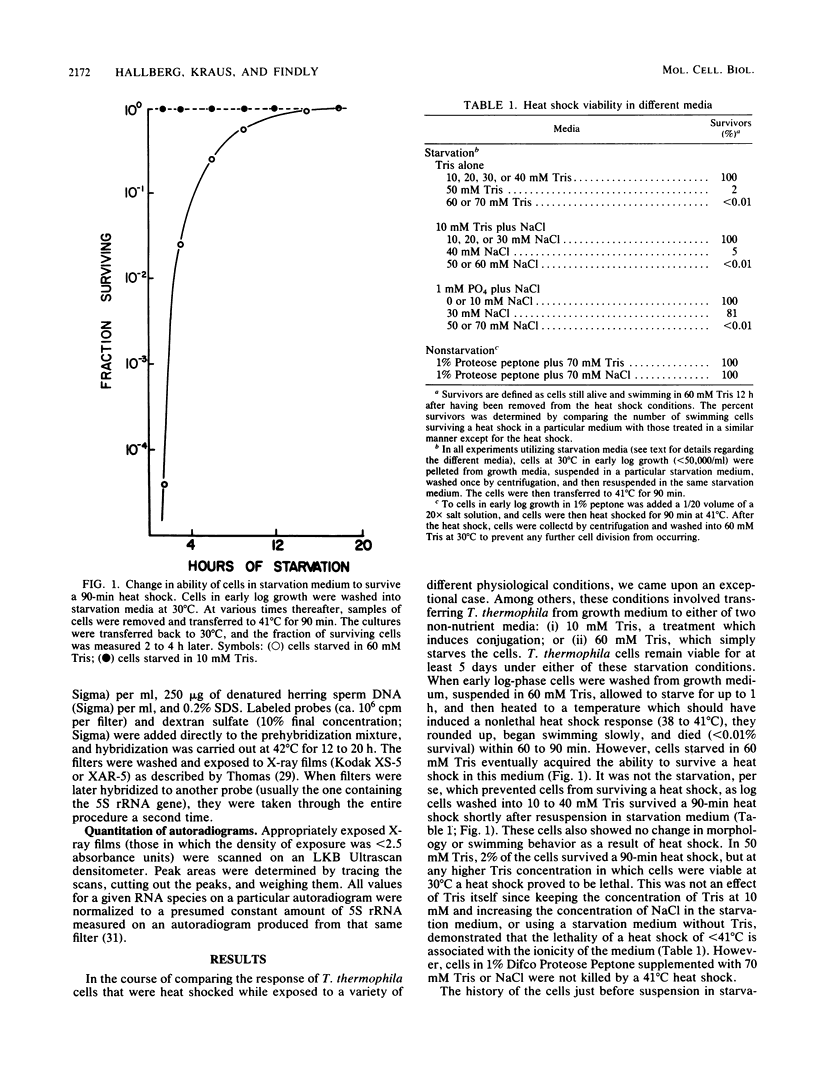
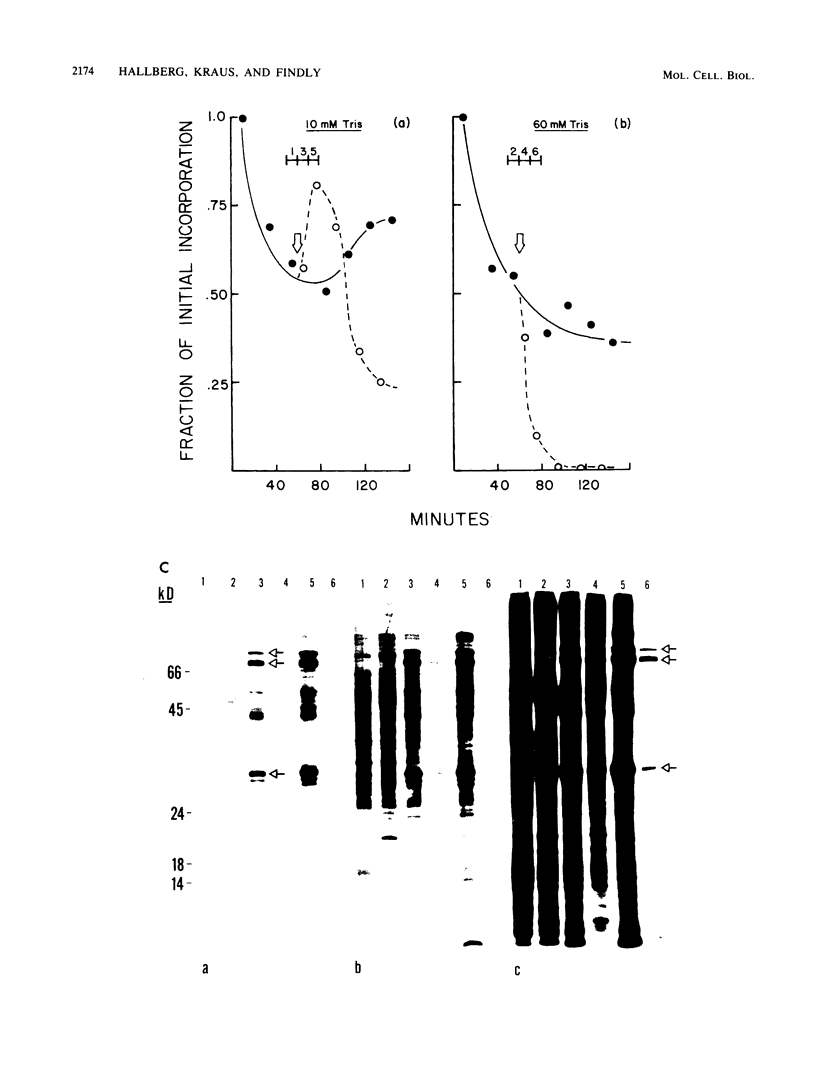
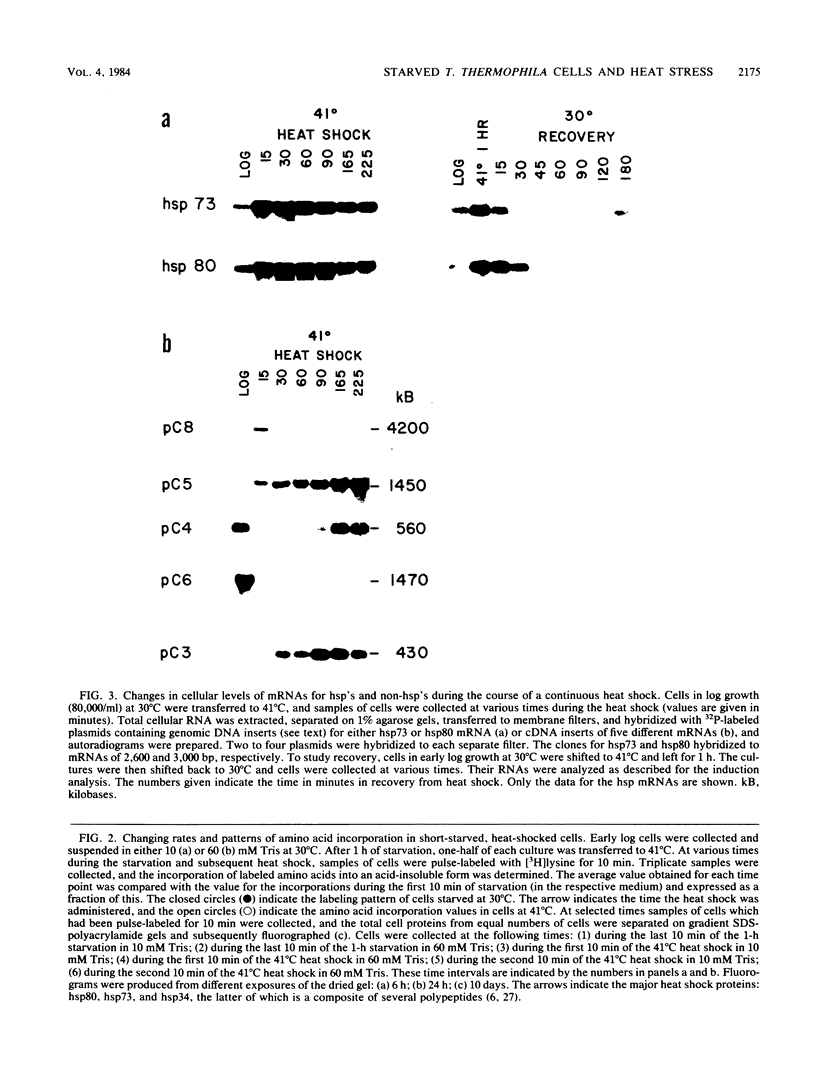
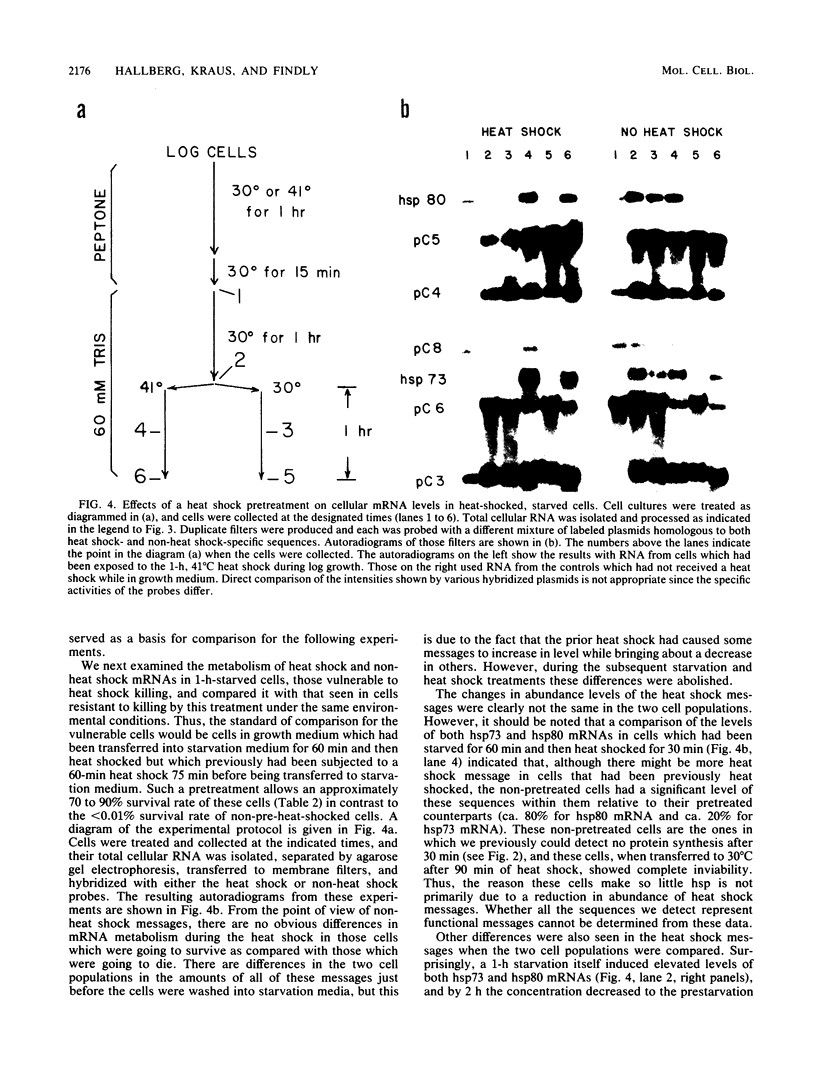
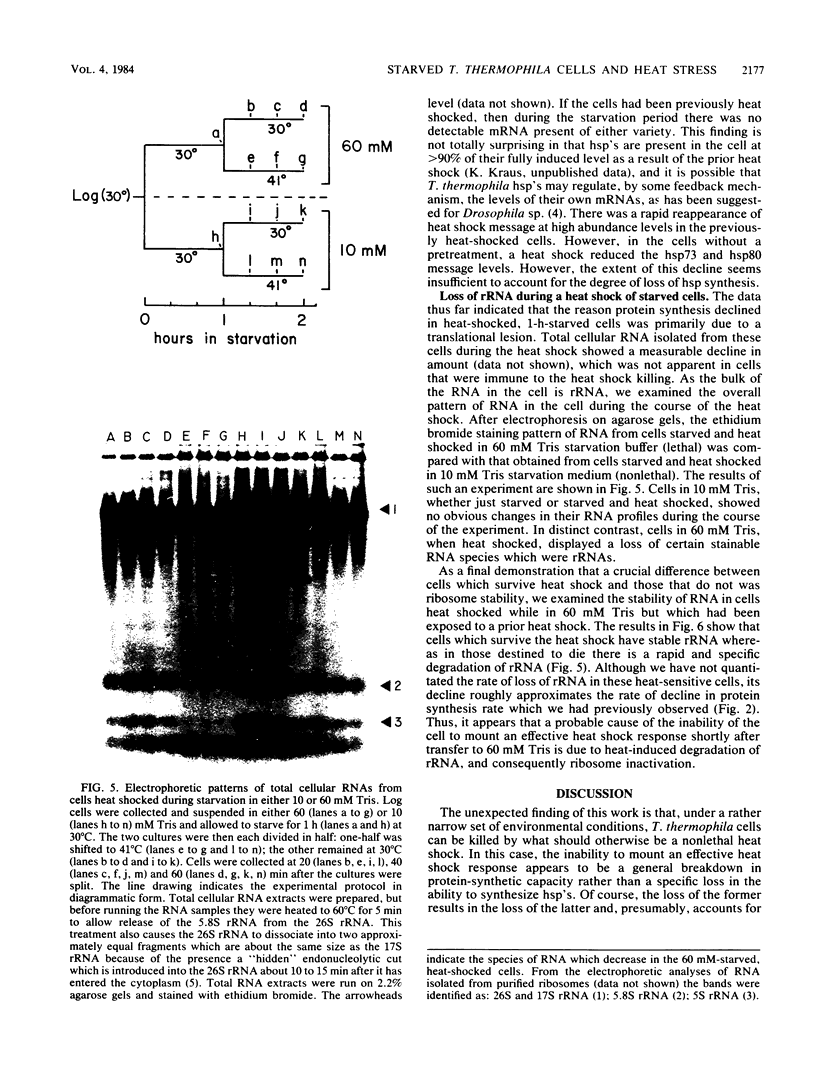
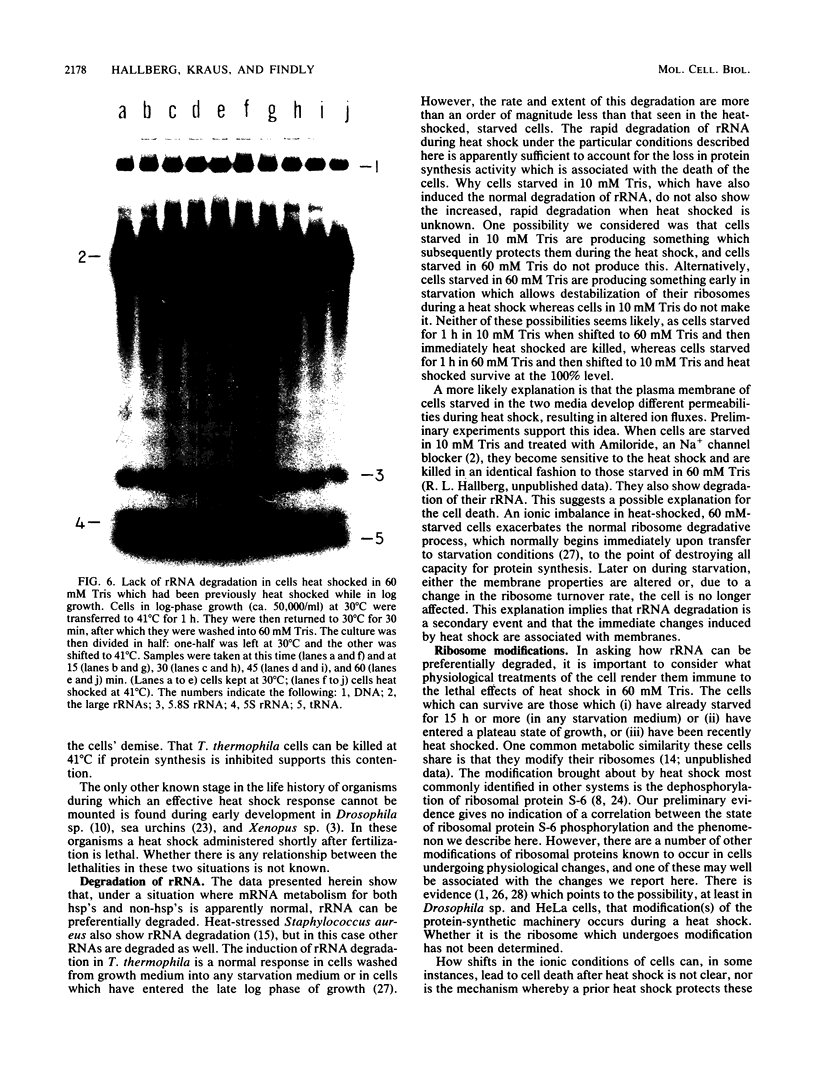
Tetrahymena thermophila cells that had been shifted from log growth to a non-nutrient medium (60 mM Tris) were unable, during the first few hours of starvation, to mount a successful heat shock response and were killed by what should normally have been a nonlethal heat shock. An examination of the protein synthetic response of these short-starved cells during heat shock revealed that whereas they were able to initiate the synthesis of heat shock proteins, it was at a much reduced rate relative to controls and they quickly lost all capacity to synthesize any proteins. Certain pretreatments of cells, including a prior heat shock, abolished the heat shock inviability of these starved cells. Also, if cells were transferred to 10 mM Tris rather than 60 mM Tris, they were not killed by the same heat treatment. We found no abnormalities in either heat shock or non-heat shock mRNA metabolism in starved cells unable to survive a sublethal heat shock when compared with the response of those cells which can survive such a treatment. However, selective rRNA degradation occurred in the nonsurviving cells during the heat shock and this presumably accounted for their inviability. A prior heat shock administered to growing cells not only immunized them against the lethality of a heat shock while starved, but also prevented rRNA degradation from occurring.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballinger D. G., Pardue M. L. The control of protein synthesis during heat shock in Drosophila cells involves altered polypeptide elongation rates. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90339-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benos D. J. Amiloride: a molecular probe of sodium transport in tissues and cells. Am J Physiol. 1982 Mar;242(3):C131–C145. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1982.242.3.C131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz M. Developmental control of the heat shock response in Xenopus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3138–3142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiDomenico B. J., Bugaisky G. E., Lindquist S. The heat shock response is self-regulated at both the transcriptional and posttranscriptional levels. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):593–603. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90315-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert W. A., Kaffenberger W., Krohne G., Franke W. W. Introduction of hidden breaks during rRNA maturation and ageing in Tetrahymena pyriformis. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jul 3;87(3):607–616. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12413.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findly R. C., Gillies R. J., Shulman R. G. In vivo phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance reveals lowered ATP during heat shock of Tetrahymena. Science. 1983 Mar 11;219(4589):1223–1225. doi: 10.1126/science.6828852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink K., Zeuthen E. Heat shock proteins in Tetrahymena studied under growth conditions. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Jul;128(1):23–30. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90382-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glover C. V. Heat shock induces rapid dephosphorylation of a ribosomal protein in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1781–1785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godson G. N., Vapnek D. A simple method of preparing large amounts of phiX174 RF 1 supercoiled DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 11;299(4):516–520. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90223-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guttman S. D., Glover C. V., Allis C. D., Gorovsky M. A. Heat shock, deciliation and release from anoxia induce the synthesis of the same set of polypeptides in starved T. pyriformis. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):299–307. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90177-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallberg R. L., Bruns P. J. Ribosome biosynthesis in Tetrahymena pyriformis. Regulation in response to nutritional changes. J Cell Biol. 1976 Nov;71(2):383–394. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.2.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallberg R. L., Sutton C. A. Nonidentity of ribosomal structural proteins in growing and starved Tetrahymena. J Cell Biol. 1977 Oct;75(1):268–276. doi: 10.1083/jcb.75.1.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallberg R. L., Wilson P. G., Sutton C. Regulation of ribosome phosphorylation and antibiotic sensitivity in Tetrahymena thermophila: A correlation. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(1 Pt 1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90032-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S. Varying patterns of protein synthesis in Drosophila during heat shock: implications for regulation. Dev Biol. 1980 Jun 15;77(2):463–479. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90488-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loomis W. F., Wheeler S. Heat shock response of Dictyostelium. Dev Biol. 1980 Oct;79(2):399–408. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90125-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martindale D. W., Bruns P. J. Cloning of abundant mRNA species present during conjugation of Tetrahymena thermophila: identification of mRNA species present exclusively during meiosis. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;3(10):1857–1865. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.10.1857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAlister L., Finkelstein D. B. Heat shock proteins and thermal resistance in yeast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Apr 14;93(3):819–824. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91150-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roccheri M. C., Di Bernardo M. G., Giudice G. Synthesis of heat-shock proteins in developing sea urchins. Dev Biol. 1981 Apr 15;83(1):173–177. doi: 10.1016/s0012-1606(81)80020-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharf K. D., Nover L. Heat-shock-induced alterations of ribosomal protein phosphorylation in plant cell cultures. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):427–437. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90240-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. P., Pardue M. L. Translational control in lysates of Drosophila melanogaster cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3353–3357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton C. A., Hallberg R. L. Ribosome biosynthesis in Tetrahymena thermophila. III. Regulation of ribosomal RNA degradation in growing and growth arrested cells. J Cell Physiol. 1979 Nov;101(2):349–358. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041010214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman J. L., Petri W., Meselson M. Accumulation of a specific subset of D. melanogaster heat shock mRNAs in normal development without heat shock. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1161–1170. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90299-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]