Abstract
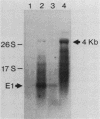
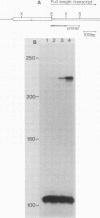
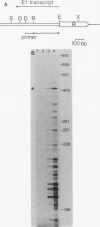
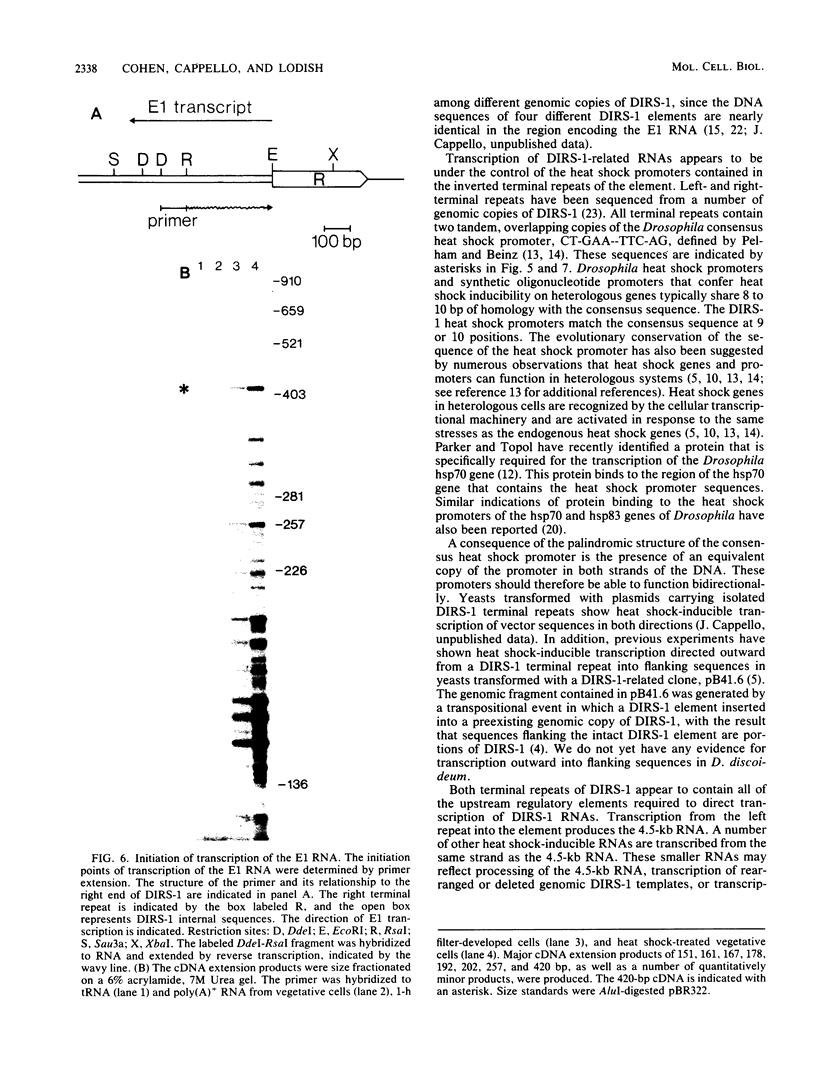
DIRS-1 is a Dictyostelium discoideum transposable element that contains heat shock promoter sequences in the inverted terminal repeats. We showed that transcription of a 4.5-kilobase polyadenylated RNA initiates at a discrete site within the left-terminal repeat of DIRS-1, downstream from heat shock promoter and TATA box sequences. This RNA represents a full-length transcript of DIRS-1. We describe a cDNA clone that contains the 4.1 kilobases of internal sequence of DIRS-1, a cDNA clone that spans the junction between the internal sequences and the right-terminal repeat, and a cDNA clone that appears to have been transcribed from a rearranged genomic copy of DIRS-1. A second DIRS-1 RNA, named E1, is transcribed on the opposite strand of DIRS-1 from the 4.5-kilobase RNA and is under control of the heat shock promoter in the right-terminal repeat. E1 transcription initiates at multiple positions both within and downstream from the right-terminal repeat. The same transcriptional initiation sites are used during normal development and during heat shock, suggesting that in all cases DIRS-1 transcription is regulated by the heat shock promoters contained within the two terminal repeats.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alton T. H., Lodish H. F. Developmental changes in messenger RNAs and protein synthesis in Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Biol. 1977 Oct 1;60(1):180–206. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg D. D., Lodish H. F. Complexity of nuclear and polysomal RNAs in growing Dictyostelium discoideum cells. Dev Biol. 1980 Aug;78(2):268–284. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90336-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cappello J., Cohen S. M., Lodish H. F. Dictyostelium transposable element DIRS-1 preferentially inserts into DIRS-1 sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):2207–2213. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.2207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cappello J., Zuker C., Lodish H. F. Repetitive Dictyostelium heat-shock promotor functions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;4(4):591–598. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.4.591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S., Zuker C., Lodish H. F. A repetitive and apparently transposable DNA sequence in Dictyostelium discoideum associated with developmentally regulated RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jul 25;11(14):4835–4852. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.14.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstratiadis A., Kafatos F. C., Maxam A. M., Maniatis T. Enzymatic in vitro synthesis of globin genes. Cell. 1976 Feb;7(2):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90027-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel A. R., Firtel R. A. Sequence organization in Dictyostelium: unique structure at the 5'-ends of protein coding genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 25;11(2):541–552. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.2.541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Topol J. A Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription factor binds to the regulatory site of an hsp 70 gene. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):273–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90323-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. A regulatory upstream promoter element in the Drosophila hsp 70 heat-shock gene. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):517–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90249-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Bienz M. A synthetic heat-shock promoter element confers heat-inducibility on the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1473–1477. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01340.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen E., Sivertsen A., Firtel R. A. An unusual transposon encoding heat shock inducible and developmentally regulated transcripts in Dictyostelium. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):243–251. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90227-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. The use of thin acrylamide gels for DNA sequencing. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 1;87(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scalenghe F., Turco E., Edström J. E., Pirrotta V., Melli M. Microdissection and cloning of DNA from a specific region of Drosophila melanogaster polytene chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1981;82(2):205–216. doi: 10.1007/BF00286105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Proudfoot N. J., Shander M., Maniatis T. A single-base change at a splice site in a beta 0-thalassemic gene causes abnormal RNA splicing. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):903–911. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90452-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. Two protein-binding sites in chromatin implicated in the activation of heat-shock genes. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):229–234. doi: 10.1038/309229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker C., Cappello J., Chisholm R. L., Lodish H. F. A repetitive Dictyostelium gene family that is induced during differentiation and by heat shock. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):997–1005. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90557-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker C., Cappello J., Lodish H. F., George P., Chung S. Dictyostelium transposable element DIRS-1 has 350-base-pair inverted terminal repeats that contain a heat shock promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2660–2664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker C., Lodish H. F. Repetitive DNA sequences cotranscribed with developmentally regulated Dictyostelium discoideum mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5386–5390. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]