Abstract
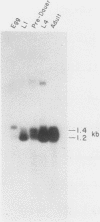
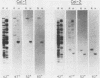
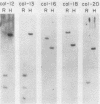
We analyzed the number and organization of collagen genes in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Genomic Southern blot hybridization experiments and recombinant phage library screenings indicated that C. elegans has between 40 and 150 distinct collagen genes. A large number of recombinant phages containing collagen genes were isolated from C. elegans DNA libraries. Physical mapping studies indicated that most phage contained a single small collagen gene less than 3 kilobases in size. A few phage contained multiple collagen hybridizing regions and may contain a larger collagen gene or several tightly linked small collagen genes. No overlaps were observed between phages containing different collagen genes, implying that the genes are dispersed in the C. elegans genome. Consistent with the small size of most collagen genes, we found that the predominant class of collagen mRNA in C. elegans is 1.2 to 1.4 kilobases in length. Genomic Southern blot experiments under stringent hybridization conditions revealed considerable sequence diversity among collagen genes. Our data suggest that most collagen genes are unique or are present in only a few copies.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams E. Invertebrate collagens. Science. 1978 Nov 10;202(4368):591–598. doi: 10.1126/science.212833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentz H., Morris N. P., Murray L. W., Sakai L. Y., Hollister D. W., Burgeson R. E. Isolation and partial characterization of a new human collagen with an extended triple-helical structural domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3168–3172. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein P., Sage H. Structurally distinct collagen types. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:957–1003. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.004521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner S. The genetics of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1974 May;77(1):71–94. doi: 10.1093/genetics/77.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassada R. C., Russell R. L. The dauerlarva, a post-embryonic developmental variant of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev Biol. 1975 Oct;46(2):326–342. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(75)90109-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B. Nature of Col E 1 plasmid replication in Escherichia coli in the presence of the chloramphenicol. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):667–676. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.667-676.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox G. N., Laufer J. S., Kusch M., Edgar R. S. Genetic and Phenotypic Characterization of Roller Mutants of CAENORHABDITIS ELEGANS. Genetics. 1980 Jun;95(2):317–339. doi: 10.1093/genetics/95.2.317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox G. N., Staprans S., Edgar R. S. The cuticle of Caenorhabditis elegans. II. Stage-specific changes in ultrastructure and protein composition during postembryonic development. Dev Biol. 1981 Sep;86(2):456–470. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90204-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards M. K., Wood W. B. Location of specific messenger RNAs in Caenorhabditis elegans by cytological hybridization. Dev Biol. 1983 Jun;97(2):375–390. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90094-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eickbush T. H., Kafatos F. C. A walk in the chorion locus of Bombyx mori. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):633–643. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90179-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmons S. W., Klass M. R., Hirsh D. Analysis of the constancy of DNA sequences during development and evolution of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1333–1337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre D. R. Collagen: molecular diversity in the body's protein scaffold. Science. 1980 Mar 21;207(4437):1315–1322. doi: 10.1126/science.7355290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Files J. G., Carr S., Hirsh D. Actin gene family of Caenorhabditis elegans. J Mol Biol. 1983 Mar 5;164(3):355–375. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins B. J., Hirsh D. Roller mutants of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Jan 7;150(1):63–72. doi: 10.1007/BF02425326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huerre C., Junien C., Weil D., Chu M. L., Morabito M., Van Cong N., Myers J. C., Foubert C., Gross M. S., Prockop D. J. Human type I procollagen genes are located on different chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6627–6630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn J., Brenner S., Barnett L., Cesareni G. Novel bacteriophage lambda cloning vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5172–5176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer J. M., Cox G. N., Hirsh D. Comparisons of the complete sequences of two collagen genes from Caenorhabditis elegans. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):599–606. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90256-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Frischauf A. M., Hanahan D., Wozney J., Fuller F., Crkvenjakov R., Boedtker H., Doty P. Construction and characterization of a 2.5-kilobase procollagen clone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5417–5421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monson J. M., Natzle J., Friedman J., McCarthy B. J. Expression and novel structure of a collagen gene in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1761–1765. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natzle J. E., Monson J. M., McCarthy B. J. Cytogenetic location and expression of collagen-like genes in Drosophila. Nature. 1982 Mar 25;296(5855):368–371. doi: 10.1038/296368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkubo H., Vogeli G., Mudryj M., Avvedimento V. E., Sullivan M., Pastan I., de Crombrugghe B. Isolation and characterization of overlapping genomic clones covering the chicken alpha 2 (type I) collagen gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7059–7063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachat F., Garcea R. L., Epstein H. F. Myosins exist as homodimers of heavy chains: demonstration with specific antibody purified by nematode mutant myosin affinity chromatography. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):405–411. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90009-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Winoto A., Minard K., Hood L. Clusters of genes encoding mouse transplantation antigens. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):489–498. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90203-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulston J. E., Brenner S. The DNA of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1974 May;77(1):95–104. doi: 10.1093/genetics/77.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson M. M., Riddle D. L. Critical periods in the development of the Caenorhabditis elegans dauer larva. Dev Biol. 1981 May;84(1):27–40. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90367-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vande Woude G. F., Oskarsson M., Enquist L. W., Nomura S., Sullivan M., Fischinger P. J. Cloning of integrated Moloney sarcoma proviral DNA sequences in bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4464–4468. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozney J., Hanahan D., Tate V., Boedtker H., Doty P. Structure of the pro alpha 2 (I) collagen gene. Nature. 1981 Nov 12;294(5837):129–135. doi: 10.1038/294129a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada Y., Avvedimento V. E., Mudryj M., Ohkubo H., Vogeli G., Irani M., Pastan I., de Crombrugghe B. The collagen gene: evidence for its evolutinary assembly by amplification of a DNA segment containing an exon of 54 bp. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):887–892. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90565-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R., Alberts B. M., Benzinger R., Lawhorne L., Treiber G. Rapid bacteriophage sedimentation in the presence of polyethylene glycol and its application to large-scale virus purification. Virology. 1970 Mar;40(3):734–744. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90218-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]