Abstract
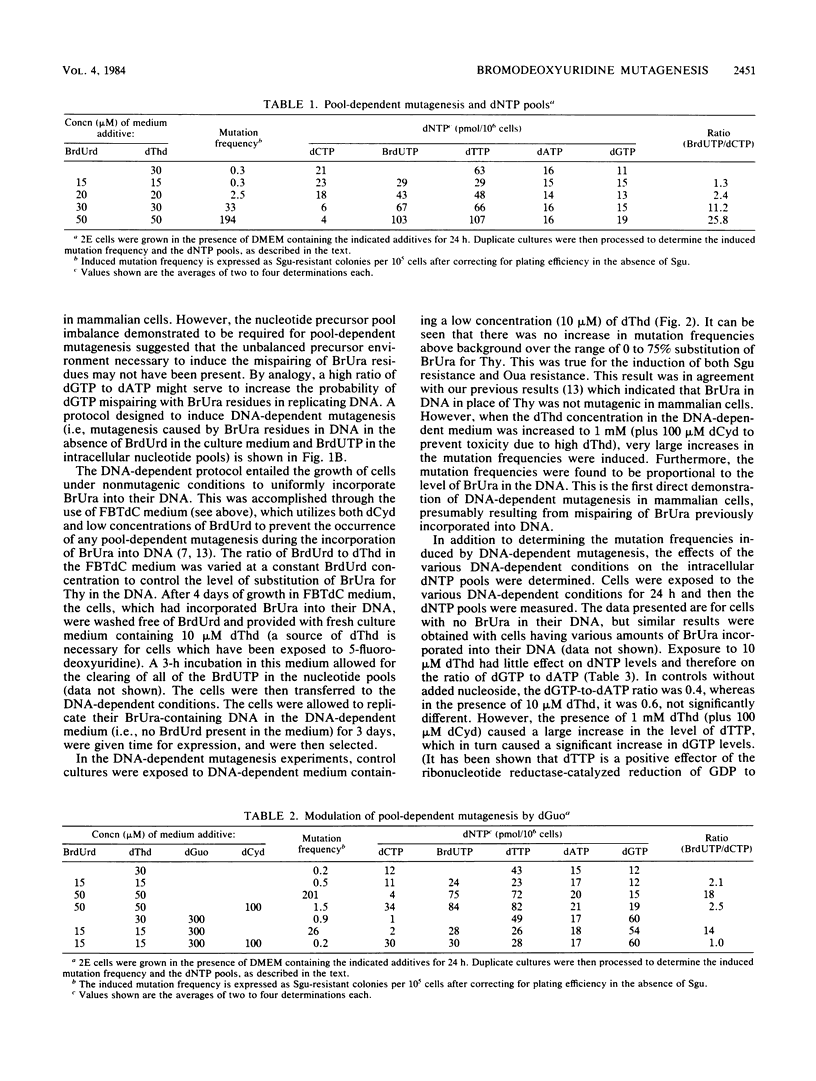
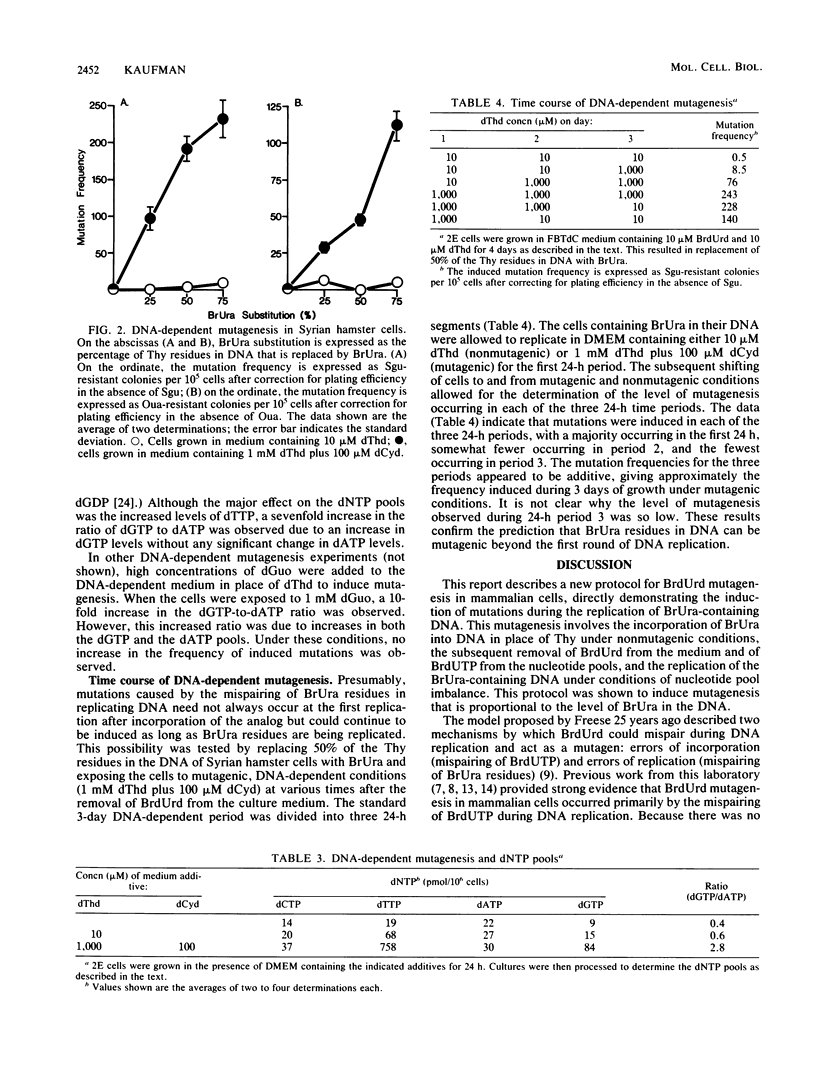
A new protocol for inducing mutations in mammalian cells in culture by exposure to the thymidine analog 5-bromodeoxyuridine (BrdUrd) was established. This protocol, called "DNA-dependent" mutagenesis, involved the incorporation of BrdUrd into DNA under nonmutagenic conditions and the subsequent replication of the 5-bromouracil (BrUra)-containing DNA under mutagenic conditions but with no BrdUrd present in the culture medium. The mutagenic conditions were induced by allowing BrUra-containing DNA to replicate in the presence of high concentrations of thymidine. This generated high intracellular levels of dTTP and dGTP, causing nucleotide pool imbalance. The mutagenesis induced by this protocol was found to correlate with the level of BrUra substituted for thymine in DNA.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aebersold P. M. Mutagenic mechanism of 5-bromodeoxyuridine in Chinese hamster cells. Mutat Res. 1976 Sep;36(3):357–362. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(76)90245-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashman C. R., Davidson R. L. Bromodeoxyuridine mutagenesis in mammalian cells is related to deoxyribonucleotide pool imbalance. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;1(3):254–260. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.3.254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benzer S., Freese E. INDUCTION OF SPECIFIC MUTATIONS WITH 5-BROMOURACIL. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1958 Feb;44(2):112–119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.44.2.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bick M. D., Davidson R. L. Total substitution of bromodeoxyuridine for thymidine in the DNA of a bromodeoxyuridine-dependent cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):2082–2086. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.2082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAMPE S. P., BENZER S. Reversal of mutant phenotypes by 5-fluorouracil: an approach to nucleotide sequences in messenger-RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Apr 15;48:532–546. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.4.532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. S., Flaks J. G., Barner H. D., Loeb M. R., Lichtenstein J. THE MODE OF ACTION OF 5-FLUOROURACIL AND ITS DERIVATIVES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1958 Oct 15;44(10):1004–1012. doi: 10.1073/pnas.44.10.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson R. L., Kaufman E. R. Bromodeoxyuridine mutagenesis in mammalian cells is stimulated by thymidine and suppressed by deoxycytidine. Nature. 1978 Dec 14;276(5689):722–723. doi: 10.1038/276722a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson R. L., Kaufman E. R. Resistance to bromodeoxyuridine mutagenesis and toxicity in mammalian cells selected for resistance to hydroxyurea. Somatic Cell Genet. 1979 Nov;5(6):873–885. doi: 10.1007/BF01542647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett C., Santi D. V. A rapid and sensitive high pressure liquid chromatography assay for deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates in cell extracts. Anal Biochem. 1979 Nov 1;99(2):268–273. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(79)80005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWARD B. D., TESSMAN I. IDENTIFICATION OF THE ALTERED BASES IN MUTATED SINGLE-STRANDED DNA. II. IN VIVO MUTAGENESIS BY 5-BROMODEOXYURIDINE AND 2-AMINOPURINE. J Mol Biol. 1964 Aug;9:364–371. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80213-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman E., Heidelberger C. The mutagenicity to mammalian cells of pyrimidine nucleoside analogs. Mutat Res. 1972 Jan;14(1):130–132. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(72)90117-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman E. R., Davidson R. L. Bromodeoxyuridine mutagenesis in mammalian cells is stimulated by purine deoxyribonucleosides. Somatic Cell Genet. 1979 Sep;5(5):653–663. doi: 10.1007/BF01542701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman E. R., Davidson R. L. Bromodeoxyuridine mutagenesis in mammalian cells: mutagenesis is independent of the amount of bromouracil in DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4982–4986. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khym J. X. An analytical system for rapid separation of tissue nucleotides at low pressures on conventional anion exchangers. Clin Chem. 1975 Aug;21(9):1245–1252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITMAN R. M., PARDEE A. B. Production of bacteriophage mutants by a disturbance of deoxyribonucleic acid metabolism. Nature. 1956 Sep 8;178(4532):529–531. doi: 10.1038/178529b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORE G. E. IN VITRO CULTURES OF A PIGMENTED HAMSTER MELANOMA CELL LINE. Exp Cell Res. 1964 Nov;36:422–423. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(64)90224-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore E. C., Hurlbert R. B. Regulation of mammalian deoxyribonucleotide biosynthesis by nucleotides as activators and inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1966 Oct 25;241(20):4802–4809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUDNER R. Mutation as an error in base pairing. I. The mutagenicity of base analogues and their incorporation into the DNA of Salmonella typhimurium. Z Vererbungsl. 1961;92:336–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronen A., Rahat A. Mutagen specificity and position effects on mutation in T4rII nonsense sites. Mutat Res. 1976 Jan;34(1):21–34. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(76)90258-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skopek T. R., Hutchinson F. DNA base sequence changes induced by bromouracil mutagenesis of lambda phage. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jul 25;159(1):19–33. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90029-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark R. M., Littlefield J. W. Mutagenic effect of BUdR in diploid human fibroblasts. Mutat Res. 1974 Mar;22(3):281–286. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(74)90029-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelander L., Reichard P. Reduction of ribonucleotides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:133–158. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



