Abstract
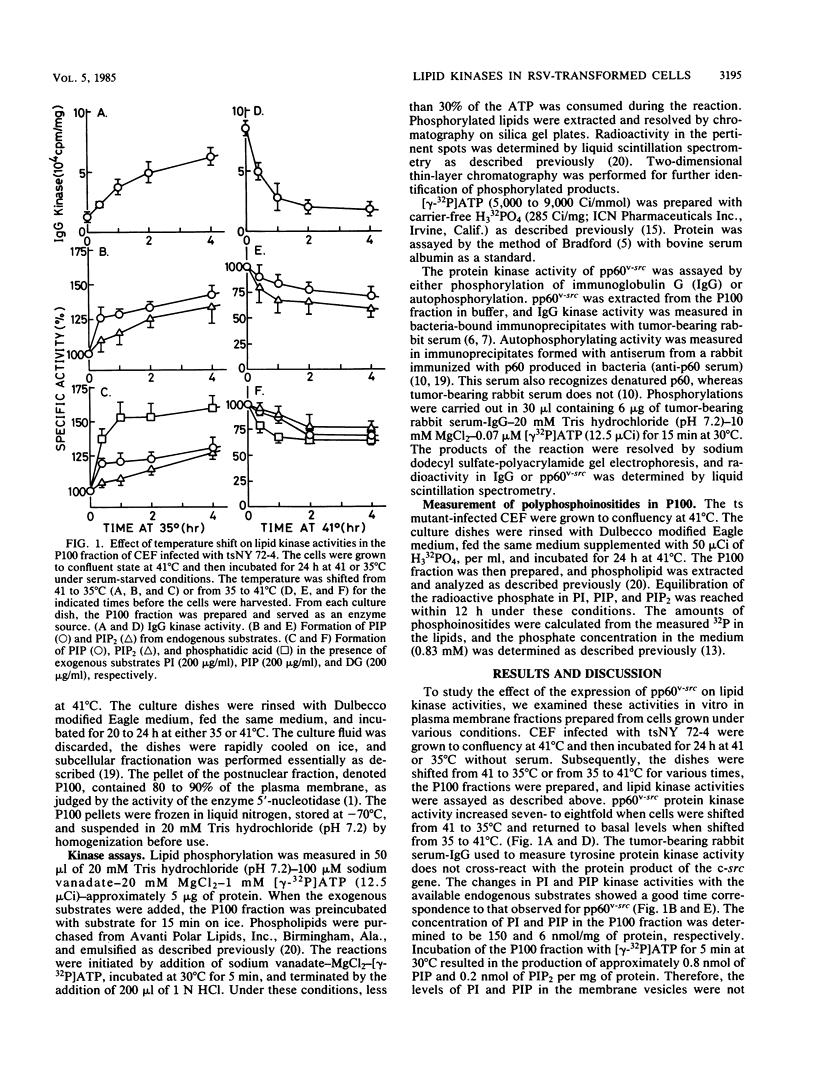
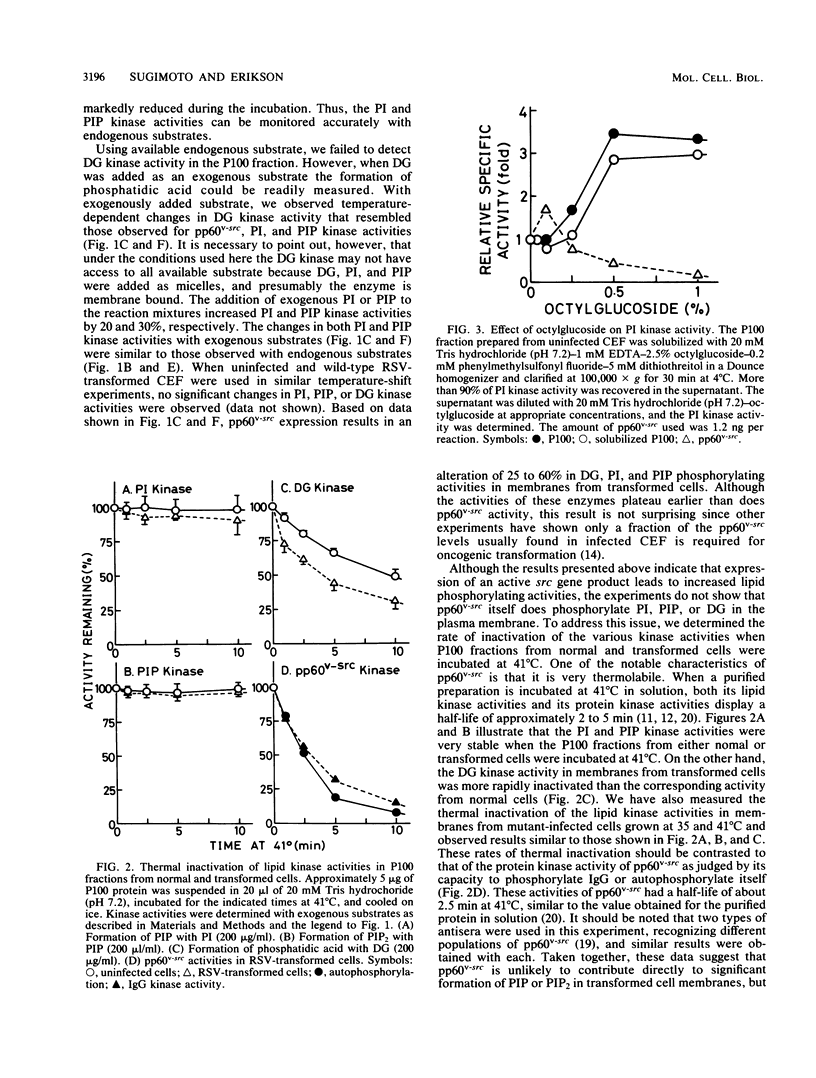
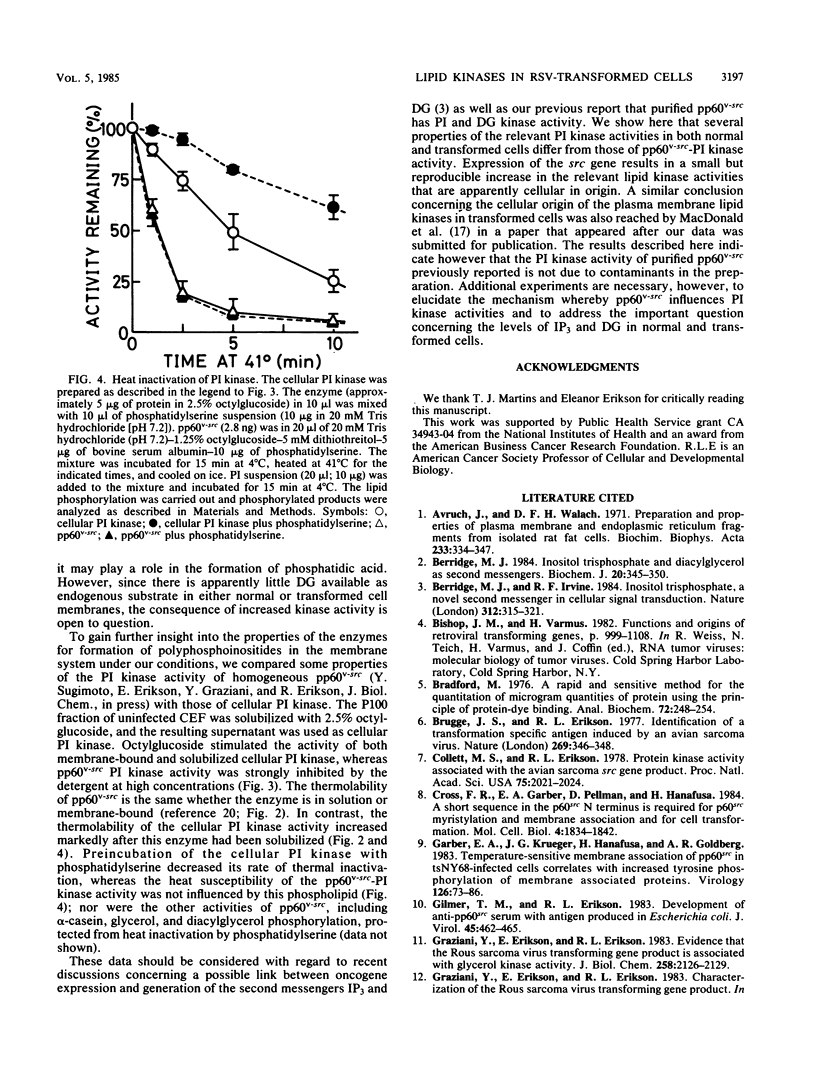
The phosphatidylinositol (PI), phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate (PIP), and diacylglycerol kinase activities in the plasma membrane-rich fraction of chicken embryo fibroblasts infected with a temperature-sensitive mutant of Rous sarcoma virus increased when the cells were shifted from the nonpermissive temperature, 41 degrees C, to the permissive temperature, 35 degrees C. Temperature shift from 35 to 41 degrees C decreased the lipid kinase activities in the membrane vesicles. These changes accompanied the changes observed in pp60v-src protein kinase activity. Thermal inactivation at 41 degrees C did not appreciably reduce PI and PIP kinase activities in membrane vesicles prepared from uninfected or Rous sarcoma virus-transformed cells, whereas pp60v-src protein kinase activity in the membrane vesicles was rapidly inactivated under the same conditions. These data suggest that pp60v-src may indirectly enhance PI and PIP phosphorylation but not directly contribute to this pathway.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avruch J., Wallach D. F. Preparation and properties of plasma membrane and endoplasmic reticulum fragments from isolated rat fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Apr 13;233(2):334–347. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90331-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2200345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Erikson R. L. Identification of a transformation-specific antigen induced by an avian sarcoma virus. Nature. 1977 Sep 22;269(5626):346–348. doi: 10.1038/269346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Erikson R. L. Protein kinase activity associated with the avian sarcoma virus src gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):2021–2024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R., Garber E. A., Pellman D., Hanafusa H. A short sequence in the p60src N terminus is required for p60src myristylation and membrane association and for cell transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1834–1842. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber E. A., Krueger J. G., Hanafusa H., Goldberg A. R. Temperature-sensitive membrane association of pp60src in tsNY68-infected cells correlates with increased tyrosine phosphorylation of membrane-associated proteins. Virology. 1983 Apr 15;126(1):73–86. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90462-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmer T. M., Erikson R. L. Development of anti-pp60src serum with antigen produced in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):462–465. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.462-465.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziani Y., Erikson E., Erikson R. L. Evidence that the Rous sarcoma virus transforming gene product is associated with glycerol kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2126–2129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess H. H., Derr J. E. Assay of inorganic and organic phosphorus in the 0.1-5 nanomole range. Anal Biochem. 1975 Feb;63(2):607–613. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90388-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobovits E. B., Majors J. E., Varmus H. E. Hormonal regulation of the Rous sarcoma virus src gene via a heterologous promoter defines a threshold dose for cellular transformation. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):757–765. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90271-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. A., Walseth T. F. The enzymatic preparation of [alpha-32P]ATP, [alpha-32P]GTP, [32P]cAMP, and [32P]cGMP, and their use in the assay of adenylate and guanylate cyclases and cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;10:135–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald M. L., Kuenzel E. A., Glomset J. A., Krebs E. G. Evidence from two transformed cell lines that the phosphorylations of peptide tyrosine and phosphatidylinositol are catalyzed by different proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):3993–3997. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.3993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macara I. G., Marinetti G. V., Balduzzi P. C. Transforming protein of avian sarcoma virus UR2 is associated with phosphatidylinositol kinase activity: possible role in tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2728–2732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poirier F., Calothy G., Karess R. E., Erikson E., Hanafusa H. Role of p60src kinase activity in the induction of neuroretinal cell proliferation by rous sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):780–789. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.780-789.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resh M. D., Erikson R. L. Highly specific antibody to Rous sarcoma virus src gene product recognizes a novel population of pp60v-src and pp60c-src molecules. J Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;100(2):409–417. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto Y., Whitman M., Cantley L. C., Erikson R. L. Evidence that the Rous sarcoma virus transforming gene product phosphorylates phosphatidylinositol and diacylglycerol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2117–2121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



