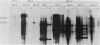Abstract
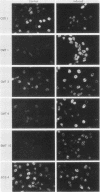
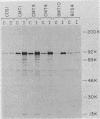
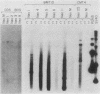
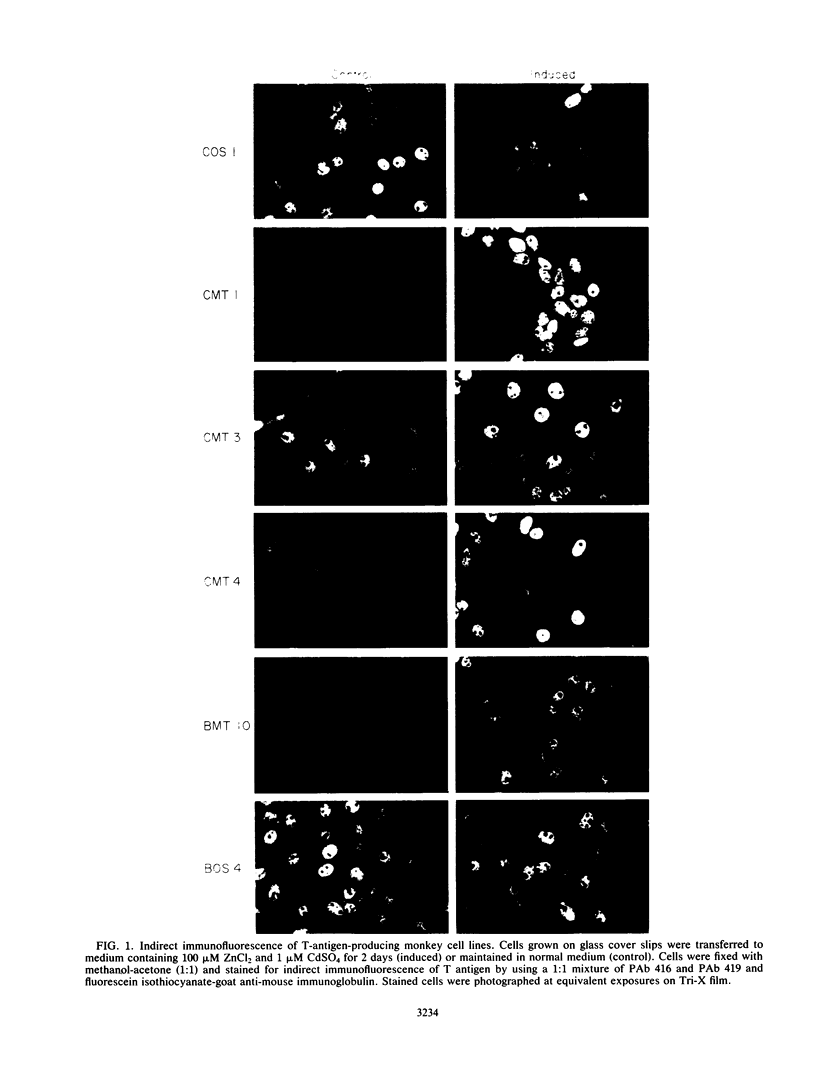
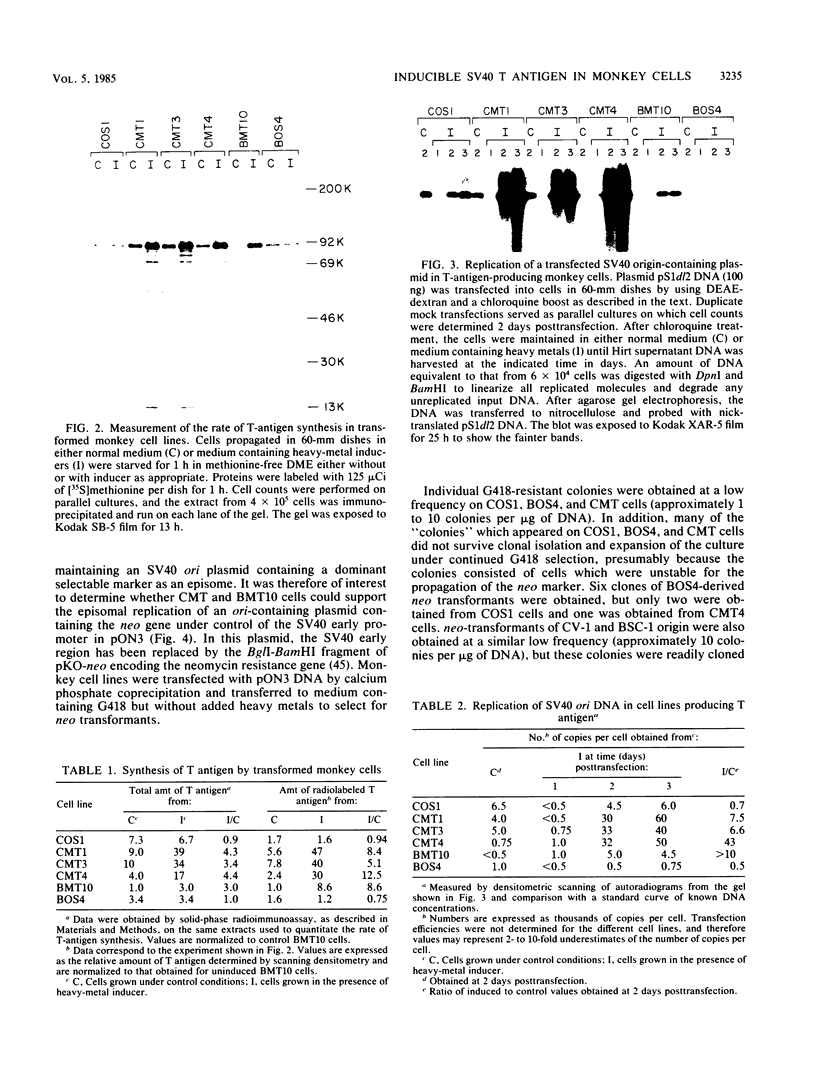
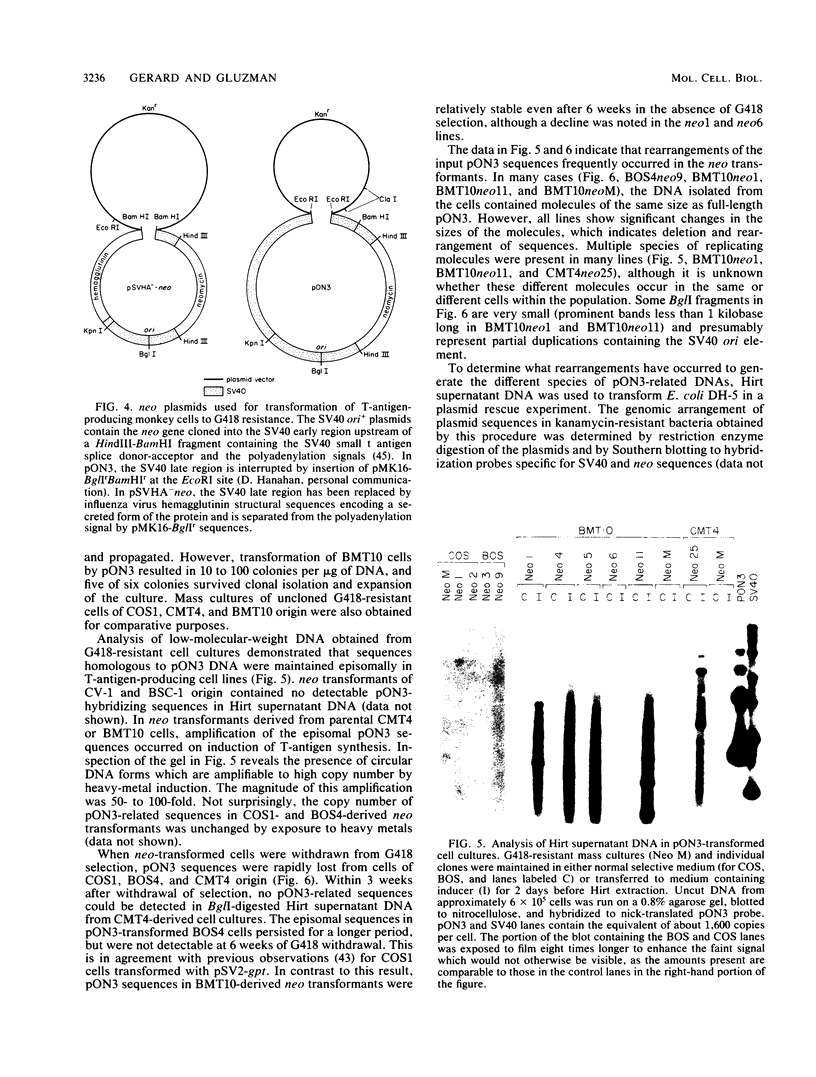
Transformed monkey cell lines (CMT and BMT) that inducible express simian virus 40 (SV40) T antigen from the metallothionein promoter have been isolated and characterized. Immunoprecipitation of pulse-labeled T antigen demonstrates a 5- to 12-fold increase in the rate of synthesis on addition of heavy-metal inducers to the culture medium. Radioimmunoassay of cell extracts indicates the accumulation of three- to fourfold more total T antigen after 2 days of induction by comparison with uninduced controls. A direct correlation was found between the level of T-antigen synthesis and the extent of SV40 DNA replication in inducible cells. Inducible BMT cells expressing a low basal level of T antigen were efficiently transformed by a vector carrying the neomycin resistance marker and an SV40 origin of replication. These vector sequences were maintained in an episomal form in most G418-resistant cell lines examined and persisted even in the absence of biochemical selection. Extensive rearrangements were observed only if the vector contained bacterial plasmid sequences. Expression of a protein product under the control of the SV40 late promoter in such vectors was increased after heavy-metal-dependent amplification of the template. These results demonstrate the ability of BMT cells to maintain a cloned eucaryotic gene in an amplifiable episomal state.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benchimol S., Pim D., Crawford L. Radioimmunoassay of the cellular protein p53 in mouse and human cell lines. EMBO J. 1982;1(9):1055–1062. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01296.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergsma D. J., Olive D. M., Hartzell S. W., Subramanian K. N. Territorial limits and functional anatomy of the simian virus 40 replication origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):381–385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J., Bolen J. B., Radonovich M., Salzman N., Khoury G. Stimulation of simian virus 40 late gene expression by simian virus 40 tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2040–2044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMaio D., Nathans D. Regulatory mutants of simian virus 40. Effect of mutations at a T antigen binding site on DNA replication and expression of viral genes. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 15;156(3):531–548. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90265-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm M., Berg P. Simian virus 40 early- and late-region promoter functions are enhanced by the 72-base-pair repeat inserted at distant locations and inverted orientations. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):991–999. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard R. D., Montelone B. A., Walter C. F., Innis J. W., Scott W. A. Role of specific simian virus 40 sequences in the nuclease-sensitive structure in viral chromatin. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):52–58. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard R. D., Woodworth-Gutai M., Scott W. A. Deletion mutants which affect the nuclease-sensitive site in simian virus 40 chromatin. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jul;2(7):782–788. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.7.782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., Sambrook J. Cell-surface expression of influenza haemagglutinin from a cloned DNA copy of the RNA gene. Nature. 1981 Oct 22;293(5834):620–625. doi: 10.1038/293620a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., Sambrook J. Construction of influenza haemagglutinin genes that code for intracellular and secreted forms of the protein. Nature. 1982 Dec 16;300(5893):598–603. doi: 10.1038/300598a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glanville N., Durnam D. M., Palmiter R. D. Structure of mouse metallothionein-I gene and its mRNA. Nature. 1981 Jul 16;292(5820):267–269. doi: 10.1038/292267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y., Ahrens B. SV40 early mutants that are defective for viral DNA synthesis but competent for transformation of cultured rat and simian cells. Virology. 1982 Nov;123(1):78–92. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90296-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y., Frisque R. J., Sambrook J. Origin-defective mutants of SV40. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):293–300. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss P., Khoury G. Expression of simian virus 40-rat preproinsulin recombinants in monkey kidney cells: use of preproinsulin RNA processing signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):133–137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamer D. H., Kaehler M., Leder P. A mouse globin gene promoter is functional in SV40. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):697–708. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90433-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamer D. H., Leder P. Expression of the chromosomal mouse Beta maj-globin gene cloned in SV40. Nature. 1979 Sep 6;281(5726):35–40. doi: 10.1038/281035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamer D. H., Walling M. Regulation in vivo of a cloned mammalian gene: cadmium induces the transcription of a mouse metallothionein gene in SV40 vectors. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):273–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E., Crawford L. V., Pim D. C., Williamson N. M. Monoclonal antibodies specific for simian virus 40 tumor antigens. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):861–869. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.861-869.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E., Pim D. C., Crawford L. V. Complex of simian virus 40 large-T antigen and host 53,000-molecular-weight protein in monkey cells. J Virol. 1981 Feb;37(2):564–573. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.2.564-573.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innis J. W., Scott W. A. DNA replication and chromatin structure of simian virus 40 insertion mutants. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1499–1507. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jongstra J., Reudelhuber T. L., Oudet P., Benoist C., Chae C. B., Jeltsch J. M., Mathis D. J., Chambon P. Induction of altered chromatin structures by simian virus 40 enhancer and promoter elements. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):708–714. doi: 10.1038/307708a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller J. M., Alwine J. C. Activation of the SV40 late promoter: direct effects of T antigen in the absence of viral DNA replication. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):381–389. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90231-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klessig D. F., Brough D. E., Cleghon V. Introduction, stable integration, and controlled expression of a chimeric adenovirus gene whose product is toxic to the recipient human cell. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;4(7):1354–1362. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.7.1354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Hamer D. H., Roeder R. G. Stable transcription complex on a class III gene in a minichromosome. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):40–45. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. Inhibition of SV40 replication in simian cells by specific pBR322 DNA sequences. Nature. 1981 Sep 3;293(5827):79–81. doi: 10.1038/293079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luthman H., Magnusson G. High efficiency polyoma DNA transfection of chloroquine treated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1295–1308. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo K. E., Warren R., Palmiter R. D. The mouse metallothionein-I gene is transcriptionally regulated by cadmium following transfection into human or mouse cells. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):99–108. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90094-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan J. H., Pagano J. S. Enchancement of the infectivity of simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid with diethylaminoethyl-dextran. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 Aug;41(2):351–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon P., Parker V., Gluzman Y., Maniatis T. Identification of DNA sequences required for transcription of the human alpha 1-globin gene in a new SV40 host-vector system. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90411-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriarty A. M., Hoyer B. H., Shih J. W., Gerin J. L., Hamer D. H. Expression of the hepatitis B virus surface antigen gene in cell culture by using a simian virus 40 vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2606–2610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan R. C., Howard B. H., Berg P. Synthesis of rabbit beta-globin in cultured monkey kidney cells following infection with a SV40 beta-globin recombinant genome. Nature. 1979 Jan 11;277(5692):108–114. doi: 10.1038/277108a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Rio D. C., Robbins A. K., Tjian R. SV40 gene expression is modulated by the cooperative binding of T antigen to DNA. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):373–384. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peden K. W., Pipas J. M., Pearson-White S., Nathans D. Isolation of mutants of an animal virus in bacteria. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1392–1396. doi: 10.1126/science.6251547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rio D. C., Clark S. G., Tjian R. A mammalian host-vector system that regulates expression and amplification of transfected genes by temperature induction. Science. 1985 Jan 4;227(4682):23–28. doi: 10.1126/science.2981116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sveda M. M., Lai C. J. Functional expression in primate cells of cloned DNA coding for the hemagglutinin surface glycoprotein of influenza virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5488–5492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsui L. C., Breitman M. L. Replication of pSV2-gpt in COS-1 cells: stability of plasmid DNA in the presence and absence of biochemical selection. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1985 Mar;11(2):167–176. doi: 10.1007/BF01534705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsui L. C., Breitman M. L., Siminovitch L., Buchwald M. Persistence of freely replicating SV40 recombinant molecules carrying a selectable marker in permissive simian cells. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):499–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90247-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Doren K., Hanahan D., Gluzman Y. Infection of eucaryotic cells by helper-independent recombinant adenoviruses: early region 1 is not obligatory for integration of viral DNA. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):606–614. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.606-614.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R. Biochemical transfer of single-copy eucaryotic genes using total cellular DNA as donor. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):725–731. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90254-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigmore D. J., Eaton R. W., Scott W. A. Endonuclease-sensitive regions in SV40 chromatin from cells infected with duplicated mutants. Virology. 1980 Jul 30;104(2):462–473. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90348-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]