Abstract
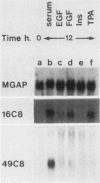
We obtained eight cDNA clones that define five genes whose expression (appearance of transcripts in the cytoplasm) is enhanced when quiescent mouse fibroblasts are stimulated with serum to divide. Two of these clones (designated 49C8 and 16C8) correspond to RNA species that are present in the cytoplasm of quiescent cells at very low levels. After serum stimulation, the level of 16C8 mRNA rose more rapidly than that of 49C8 RNA, reaching a maximum around 6 to 12 h. The data suggest that 49C8 and 16C8 RNAs are induced as a result of independent stimuli. Either fibroblast growth factor or 12-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate alone could induce 16C8 expression almost as effectively as serum; in contrast, 49C8 was not efficiently induced by epidermal growth factor, fibroblast growth factor, insulin, or 12-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate. Inhibitors of transcription and translation diminished the induction of 16C8, while 49C8 expression was sensitive to actinomycin D but not cycloheximide or 5,6-dichloro-1-beta-D-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole. In vitro transcription experiments with isolated nuclei revealed a peak in transcriptional activity of the 16C8 gene at around 3 h after serum stimulation. Sequence analysis of the 49C8 cDNA clone showed greater than 90% homology of a large portion to a consensus rodent B2 repetitive element.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berger S. L., Birkenmeier C. S. Inhibition of intractable nucleases with ribonucleoside--vanadyl complexes: isolation of messenger ribonucleic acid from resting lymphocytes. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 13;18(23):5143–5149. doi: 10.1021/bi00590a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brickell P. M., Latchman D. S., Murphy D., Willison K., Rigby P. W. Activation of a Qa/Tla class I major histocompatibility antigen gene is a general feature of oncogenesis in the mouse. Nature. 1983 Dec 22;306(5945):756–760. doi: 10.1038/306756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks R. F. Continuous protein synthesis is required to maintain the probability of entry into S phase. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):311–317. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90209-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campisi J., Pardee A. B. Post-transcriptional control of the onset of DNA synthesis by an insulin-like growth factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1807–1814. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Lopata M. A., MacDonald R. J., Cowan N. J., Rutter W. J., Kirschner M. W. Number and evolutionary conservation of alpha- and beta-tubulin and cytoplasmic beta- and gamma-actin genes using specific cloned cDNA probes. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90238-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochran B. H., Reffel A. C., Stiles C. D. Molecular cloning of gene sequences regulated by platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):939–947. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90037-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochran B. H., Zullo J., Verma I. M., Stiles C. D. Expression of the c-fos gene and of an fos-related gene is stimulated by platelet-derived growth factor. Science. 1984 Nov 30;226(4678):1080–1082. doi: 10.1126/science.6093261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Jr Variety in the level of gene control in eukaryotic cells. Nature. 1982 Jun 3;297(5865):365–371. doi: 10.1038/297365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards D. R., Denhardt D. T. A study of mitochondrial and nuclear transcription with cloned cDNA probes. Changes in the relative abundance of mitochondrial transcripts after stimulation of quiescent mouse fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Mar;157(1):127–143. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(85)90157-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Peretz M., Weintraub H. Transcriptional regulation of hemoglobin switching in chicken embryos. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;1(3):281–288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.3.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschhorn R. R., Aller P., Yuan Z. A., Gibson C. W., Baserga R. Cell-cycle-specific cDNAs from mammalian cells temperature sensitive for growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6004–6008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson C. P., Elder P. K., Ono T., Foster D. N., Getz M. J. Structure and expression of mouse VL30 genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2221–2231. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafatos F. C., Jones C. W., Efstratiadis A. Determination of nucleic acid sequence homologies and relative concentrations by a dot hybridization procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1541–1552. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston R. E., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Regulation of heat shock protein 70 gene expression by c-myc. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):280–282. doi: 10.1038/312280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramerov D. A., Tillib S. V., Lekakh I. V., Ryskov A. P., Georgiev G. P. Biosynthesis and cytoplasmic distribution of small poly(A)-containing B2 RNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Feb 20;824(2):85–98. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(85)90084-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krayev A. S., Markusheva T. V., Kramerov D. A., Ryskov A. P., Skryabin K. G., Bayev A. A., Georgiev G. P. Ubiquitous transposon-like repeats B1 and B2 of the mouse genome: B2 sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7461–7475. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruijer W., Cooper J. A., Hunter T., Verma I. M. Platelet-derived growth factor induces rapid but transient expression of the c-fos gene and protein. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):711–716. doi: 10.1038/312711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leof E. B., Wharton W., van Wyk J. J., Pledger W. J. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) and somatomedin C regulate G1 progression in competent BALB/c-3T3 cells. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Sep;141(1):107–115. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Nathans D. Growth-related changes in specific mRNAs of cultured mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4271–4275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Nathans D. Nucleotide sequence of a growth-related mRNA encoding a member of the prolactin-growth hormone family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4255–4259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer W. E., Avignolo C., Baserga R. Role of the p53 protein in cell proliferation as studied by microinjection of monoclonal antibodies. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;4(2):276–281. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.2.276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulcahy L. S., Smith M. R., Stacey D. W. Requirement for ras proto-oncogene function during serum-stimulated growth of NIH 3T3 cells. Nature. 1985 Jan 17;313(5999):241–243. doi: 10.1038/313241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D., Brickell P. M., Latchman D. S., Willison K., Rigby P. W. Transcripts regulated during normal embryonic development and oncogenic transformation share a repetitive element. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):865–871. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Bravo R., Burckhardt J., Curran T. Induction of c-fos gene and protein by growth factors precedes activation of c-myc. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):716–720. doi: 10.1038/312716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen-Hamilton M., Shapiro J. M., Massoglia S. L., Hamilton R. T. Selective stimulation by mitogens of incorporation of 35S-methionine into a family of proteins released into the medium by 3T3 cells. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):19–28. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parfett C. L., Hamilton R. T., Howell B. W., Edwards D. R., Nilsen-Hamilton M., Denhardt D. T. Characterization of a cDNA clone encoding murine mitogen-regulated protein: regulation of mRNA levels in mortal and immortal cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3289–3292. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pledger W. J., Stiles C. D., Antoniades H. N., Scher C. D. An ordered sequence of events is required before BALB/c-3T3 cells become committed to DNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2839–2843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich N. C., Levine A. J. Growth regulation of a cellular tumour antigen, p53, in nontransformed cells. Nature. 1984 Mar 8;308(5955):199–201. doi: 10.1038/308199a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddle V. G., Pardee A. B. Quiescent cells but not cycling cells exhibit enhanced actin synthesis before they synthesize DNA. J Cell Physiol. 1980 Apr;103(1):11–15. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041030103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryskov A. P., Ivanov P. L., Kramerov D. A., Georgiev G. P. Mouse ubiquitous B2 repeat in polysomal and cytoplasmic poly(A)+RNAs: uniderectional orientation and 3'-end localization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6541–6558. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salditt-Georgieff M., Darnell J. E., Jr Further evidence that the majority of primary nuclear RNA transcripts in mammalian cells do not contribute to mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jun;2(6):701–707. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.6.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salditt-Georgieff M., Harpold M. M., Wilson M. C., Darnell J. E., Jr Large heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleic acid has three times as many 5' caps as polyadenylic acid segments, and most caps do not enter polyribosomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;1(2):179–187. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.2.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. R., Westphal K. H., Rigby P. W. Activation of mouse genes in transformed cells. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):557–567. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90388-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh K., Carey M., Saragosti S., Botchan M. Expression of enhanced levels of small RNA polymerase III transcripts encoded by the B2 repeats in simian virus 40-transformed mouse cells. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):553–556. doi: 10.1038/314553a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles C. D., Capone G. T., Scher C. D., Antoniades H. N., Van Wyk J. J., Pledger W. J. Dual control of cell growth by somatomedins and platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1279–1283. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waechter D. E., Avignolo C., Freund E., Riggenbach C. M., Mercer W. E., McGuire P. M., Baserga R. Microinjection of RNA polymerase II corrects the temperature-sensitive defect of tsAF8 cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 1984;60(1):77–82. doi: 10.1007/BF00226301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]