Abstract
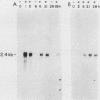
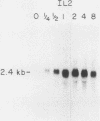
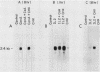
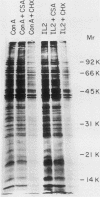
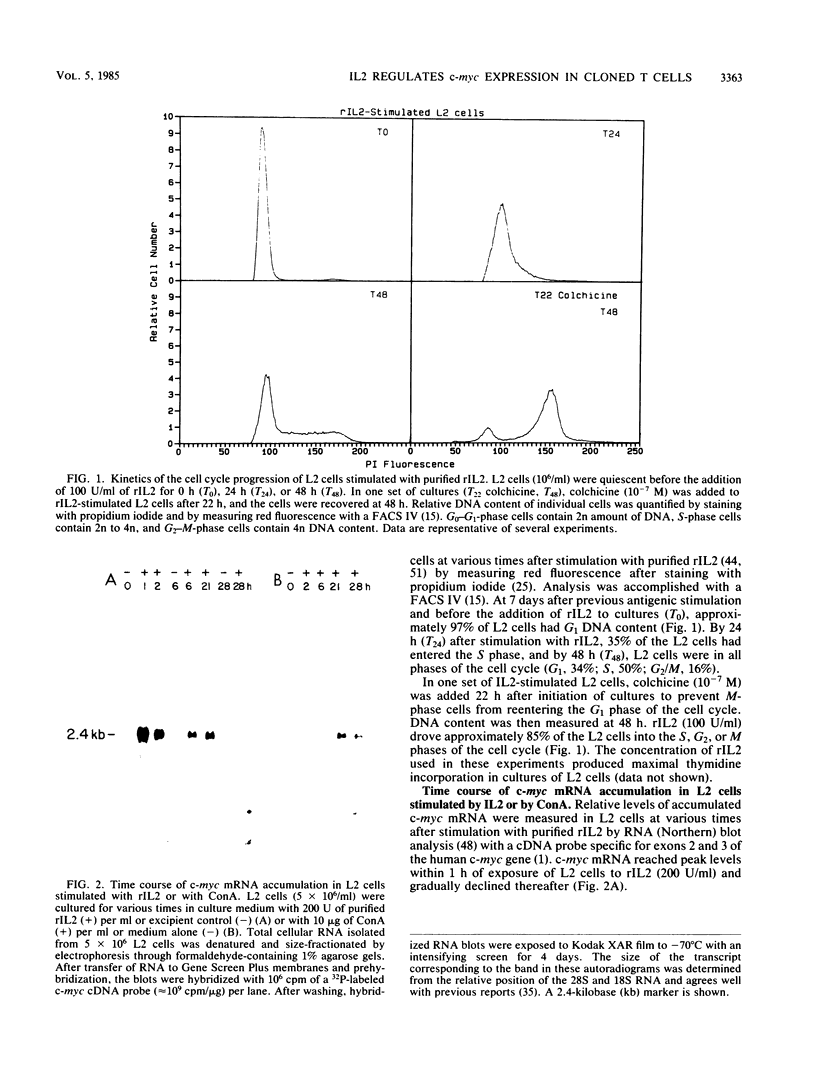
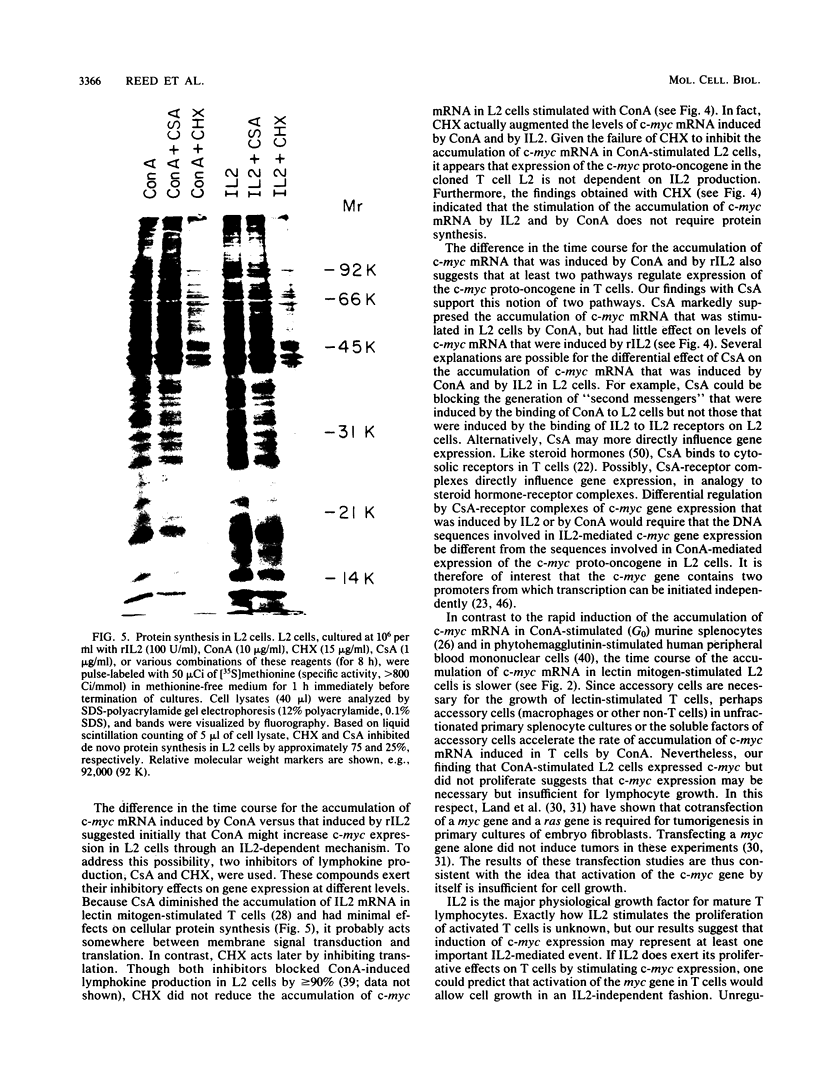
The cellular oncogene c-myc has been implicated in the regulation of growth of normal and neoplastic cells. Recently, it was suggested that c-myc gene expression may control the G0----G1-phase transition in normal lymphocytes that were stimulated to enter the cell cycle by the lectin concanavalin A (ConA). Here we describe the effects of purified recombinant interleukin 2 (rIL2) and of ConA on levels of c-myc mRNA in the noncytolytic murine T-cell clone L2. In contrast to resting (G0) primary cultures of lymphocytes, quiescent L2 cells have a higher RNA content than resting splenocytes and express receptors for interleukin 2 (IL2). Resting L2 cells are therefore best regarded as early G1-phase cells. Purified rIL2 was found to stimulate the rapid accumulation of c-myc mRNA in L2 cells. Levels of c-myc mRNA became maximal within 1 h and declined gradually thereafter. In contrast, ConA induced slower accumulation of c-myc mRNA in L2 cells, with increased levels of c-myc mRNA becoming detectable 4 to 8 h after stimulation. Experiments with the protein synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide demonstrated that the increase in levels of c-myc mRNA that were induced by ConA was a direct effect of this lectin and not secondary to IL2 production. Cyclosporin A, an immunosuppressive agent, markedly reduced the accumulation of c-myc mRNA that was induced by ConA but only slightly diminished the accumulation of c-myc mRNA that was induced by rIL2. Taken together, these data provide evidence that (i) c-myc gene expression can be regulated by at least two distinct pathways in T lymphocytes, only one of which is sensitive to cyclosporine A, and (ii) the accumulation of c-myc mRNA can be induced in T cells by IL2 during the G1 phase of the cell cycle.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishop J. M. Cellular oncogenes and retroviruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:301–354. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.001505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campisi J., Gray H. E., Pardee A. B., Dean M., Sonenshein G. E. Cell-cycle control of c-myc but not c-ras expression is lost following chemical transformation. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):241–247. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90217-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantrell D. A., Smith K. A. The interleukin-2 T-cell system: a new cell growth model. Science. 1984 Jun 22;224(4655):1312–1316. doi: 10.1126/science.6427923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochran B. H., Zullo J., Verma I. M., Stiles C. D. Expression of the c-fos gene and of an fos-related gene is stimulated by platelet-derived growth factor. Science. 1984 Nov 30;226(4678):1080–1082. doi: 10.1126/science.6093261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper G. M. Cellular transforming genes. Science. 1982 Aug 27;217(4562):801–806. doi: 10.1126/science.6285471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson W. F., Parish C. R. A procedure for removing red cells and dead cells from lymphoid cell suspensions. J Immunol Methods. 1975 Jun;7(2-3):291–300. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(75)90026-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einat M., Resnitzky D., Kimchi A. Close link between reduction of c-myc expression by interferon and, G0/G1 arrest. Nature. 1985 Feb 14;313(6003):597–600. doi: 10.1038/313597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ely J. M., Fitch F. W. Alloreactive cloned T cell lines. VII. Comparison of the kinetics of IL 2 release stimulated by alloantigen or Con A. J Immunol. 1983 Sep;131(3):1274–1279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ely J. M., Prystowsky M. B., Eisenberg L., Quintans J., Goldwasser E., Glasebrook A. L., Fitch F. W. Alloreactive cloned T cell lines. V. Differential kinetics of IL 2, CSF, and BCSF release by a cloned T amplifier cell and its variant. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2345–2349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried J. Analysis of deoxyribonucleic acid histograms from flow cytofluorometry. Estimation of the distribution of cells within S phase. J Histochem Cytochem. 1977 Jul;25(7):942–951. doi: 10.1177/25.7.894010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasebrook A. L., Fitch F. W. Alloreactive cloned T cell lines. I. Interactions between cloned amplifier and cytolytic T cell lines. J Exp Med. 1980 Apr 1;151(4):876–895. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.4.876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda T. J., Metcalf D. Expression of myb, myc and fos proto-oncogenes during the differentiation of a murine myeloid leukaemia. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):249–251. doi: 10.1038/310249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyette M., Petropoulos C. J., Shank P. R., Fausto N. Regulated transcription of c-Ki-ras and c-myc during compensatory growth of rat liver. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1493–1498. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handschumacher R. E., Harding M. W., Rice J., Drugge R. J., Speicher D. W. Cyclophilin: a specific cytosolic binding protein for cyclosporin A. Science. 1984 Nov 2;226(4674):544–547. doi: 10.1126/science.6238408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann S. R., Eisenman R. N. Proteins encoded by the human c-myc oncogene: differential expression in neoplastic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2486–2497. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keath E. J., Kelekar A., Cole M. D. Transcriptional activation of the translocated c-myc oncogene in mouse plasmacytomas: similar RNA levels in tumor and proliferating normal cells. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):521–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90382-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehrl J. H., Muraguchi A., Fauci A. S. Human B cell activation and cell cycle progression: stimulation with anti-mu and Staphylococcus aureus Cowan strain I. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Feb;14(2):115–121. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koretzky G. A., Daniele R. P., Nowell P. C. A phorbol ester (TPA) can replace macrophages in human lymphocyte cultures stimulated with a mitogen but not with an antigen. J Immunol. 1982 Apr;128(4):1776–1780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruijer W., Cooper J. A., Hunter T., Verma I. M. Platelet-derived growth factor induces rapid but transient expression of the c-fos gene and protein. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):711–716. doi: 10.1038/312711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krönke M., Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Arya S. K., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C., Waldmann T. A., Greene W. C. Cyclosporin A inhibits T-cell growth factor gene expression at the level of mRNA transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5214–5218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Parada L. F., Weinberg R. A. Cellular oncogenes and multistep carcinogenesis. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):771–778. doi: 10.1126/science.6356358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Parada L. F., Weinberg R. A. Tumorigenic conversion of primary embryo fibroblasts requires at least two cooperating oncogenes. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):596–602. doi: 10.1038/304596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillehoj H. S., Malek T. R., Shevach E. M. Differential effect of cyclosporin A on the expression of T and B lymphocyte activation antigens. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):244–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malek T. R., Ortega G., Jakway J. P., Chan C., Shevach E. M. The murine IL 2 receptor. II. Monoclonal anti-IL 2 receptor antibodies as specific inhibitors of T cell function in vitro. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):1976–1982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Bravo R., Burckhardt J., Curran T. Induction of c-fos gene and protein by growth factors precedes activation of c-myc. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):716–720. doi: 10.1038/312716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orosz C. G., Fidelus R. K., Roopenian D. C., Widmer M. B., Ferguson R. M., Bach F. H. Analysis of cloned T cell function. I. Dissection of cloned T cell proliferative responses using cyclosporin A. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):1865–1868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. C., Nowell P. C., Hoover R. G. Regulation of c-myc mRNA levels in normal human lymphocytes by modulators of cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4221–4224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitsma P. H., Rothberg P. G., Astrin S. M., Trial J., Bar-Shavit Z., Hall A., Teitelbaum S. L., Kahn A. J. Regulation of myc gene expression in HL-60 leukaemia cells by a vitamin D metabolite. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):492–494. doi: 10.1038/306492a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D. P. Lymphocyte cell-cycle analysis by flow cytometry. Evidence for a specific postmitotic phase before return to G0. J Cell Biol. 1980 May;85(2):459–465. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Grimm E. A., McGrogan M., Doyle M., Kawasaki E., Koths K., Mark D. F. Biological activity of recombinant human interleukin-2 produced in Escherichia coli. Science. 1984 Mar 30;223(4643):1412–1414. doi: 10.1126/science.6367046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadler B. M., Kristensen F., de Weck A. L. Thymocyte activation by cytokines: direct assessment of G0-G1 transition by flow-cytometry. Cell Immunol. 1980 Oct;55(2):436–443. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90174-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart T. A., Bellvé A. R., Leder P. Transcription and promoter usage of the myc gene in normal somatic and spermatogenic cells. Science. 1984 Nov 9;226(4675):707–710. doi: 10.1126/science.6494906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taub R., Moulding C., Battey J., Murphy W., Vasicek T., Lenoir G. M., Leder P. Activation and somatic mutation of the translocated c-myc gene in burkitt lymphoma cells. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):339–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90227-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. B., Challoner P. B., Neiman P. E., Groudine M. Levels of c-myc oncogene mRNA are invariant throughout the cell cycle. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):363–366. doi: 10.1038/314363a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A., Lu S. D., Mark D. F. Site-specific mutagenesis of the human interleukin-2 gene: structure-function analysis of the cysteine residues. Science. 1984 Jun 29;224(4656):1431–1433. doi: 10.1126/science.6427925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang B. S., Heacock E. H., Collins K. H., Hutchinson I. F., Tilney N. L., Mannick J. A. Suppressive effects of cyclosporin A on the induction of alloreactivity in vitro and in vivo. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):89–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ar-Rushdi A., Nishikura K., Erikson J., Watt R., Rovera G., Croce C. M. Differential expression of the translocated and the untranslocated c-myc oncogene in Burkitt lymphoma. Science. 1983 Oct 28;222(4622):390–393. doi: 10.1126/science.6414084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]