Abstract
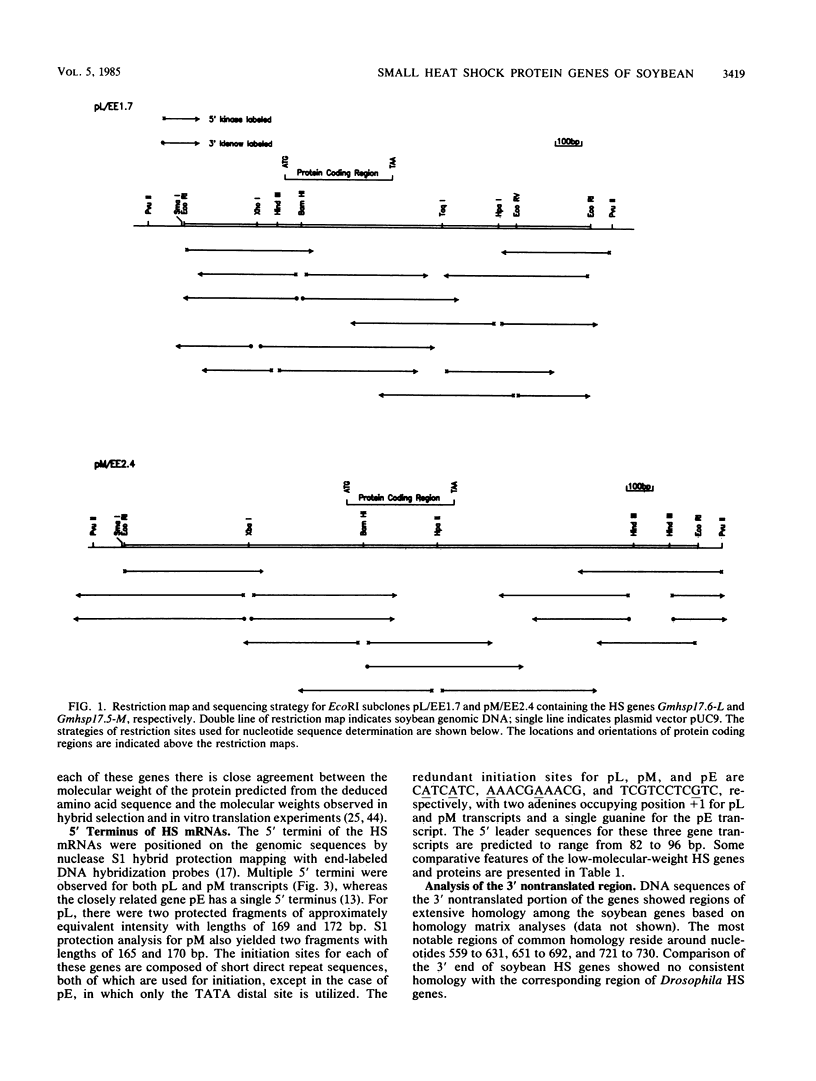
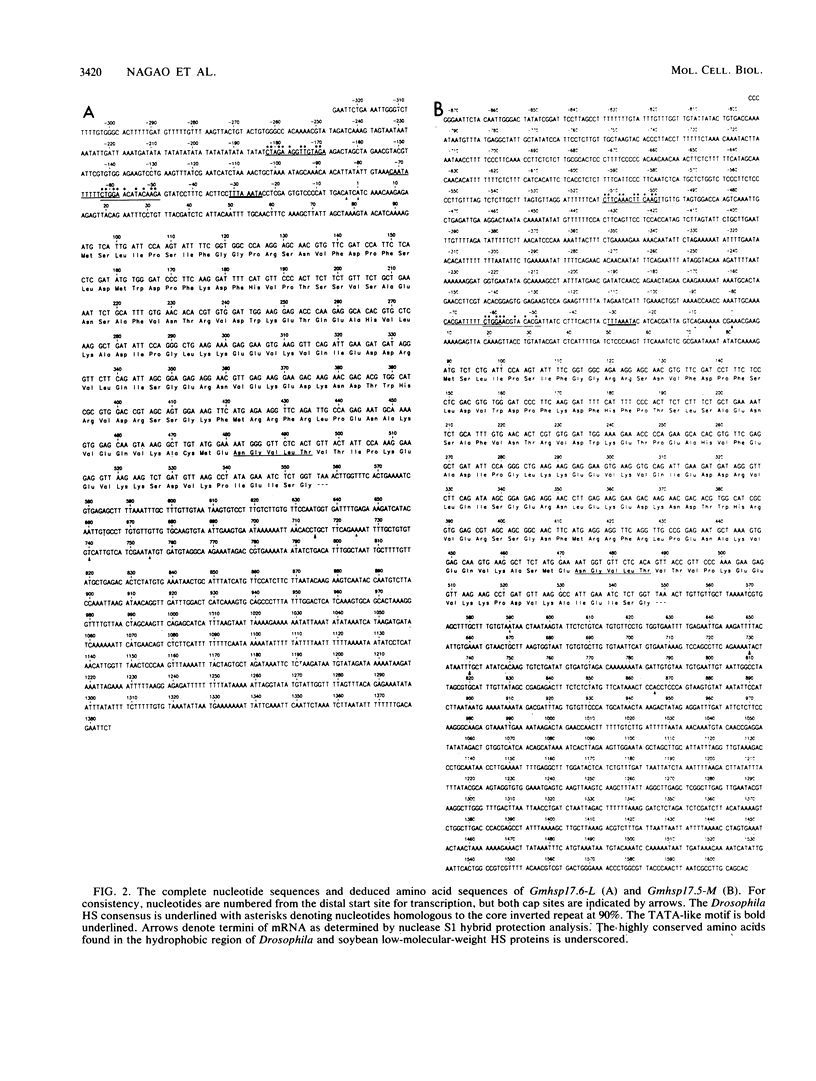
Soybeans, Glycine max, synthesize a family of low-molecular-weight heat shock (HS) proteins in response to HS. The DNA sequences of two genes encoding 17.5- and 17.6-kilodalton HS proteins were determined. Nuclease S1 mapping of the corresponding mRNA indicated multiple start termini at the 5' end and multiple stop termini at the 3' end. These two genes were compared with two other soybean HS genes of similar size. A comparison among the 5' flanking regions encompassing the presumptive HS promoter of the soybean HS-protein genes demonstrated this region to be extremely homologous. Analysis of the DNA sequences in the 5' flanking regions of the soybean genes with the corresponding regions of Drosophila melanogaster HS-protein genes revealed striking similarity between plants and animals in the presumptive promoter structure of thermoinducible genes. Sequences related to the Drosophila HS consensus regulatory element were found 57 to 62 base pairs 5' to the start of transcription in addition to secondary HS consensus elements located further upstream. Comparative analysis of the deduced amino acid sequences of four soybean HS proteins illustrated that these proteins were greater than 90% homologous. Comparison of the amino acid sequence for soybean HS proteins with other organisms showed much lower homology (less than 20%). Hydropathy profiles for Drosophila, Xenopus, Caenorhabditis elegans, and G. max HS proteins showed a similarity of major hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions, which suggests conservation of functional domains for these proteins among widely dispersed organisms.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arrigo A. P., Ahmad-Zadeh C. Immunofluorescence localization of a small heat shock protein (hsp 23) in salivary gland cells of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(1):73–79. doi: 10.1007/BF00271198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrigo A. P., Fakan S., Tissières A. Localization of the heat shock-induced proteins in Drosophila melanogaster tissue culture cells. Dev Biol. 1980 Jul;78(1):86–103. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90320-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M., Bonner J. J. The induction of gene activity in drosophilia by heat shock. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):241–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90150-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayme A., Southgate R., Tissières A. Nucleotide sequences responsible for the thermal inducibility of the Drosophila small heat-shock protein genes in monkey COS cells. J Mol Biol. 1985 Apr 20;182(4):469–475. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90233-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., O'Hare K., Breathnach R., Chambon P. The ovalbumin gene-sequence of putative control regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):127–142. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz M. Developmental control of the heat shock response in Xenopus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3138–3142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz M., Pelham H. R. Expression of a Drosophila heat-shock protein in Xenopus oocytes: conserved and divergent regulatory signals. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1583–1588. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01359.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Blechl A. E., Denniston-Thompson K., Faber H. E., Richards J. E., Slightom J. L., Tucker P. W., Smithies O. Cloning human fetal gamma globin and mouse alpha-type globin DNA: preparation and screening of shotgun collections. Science. 1978 Dec 22;202(4374):1279–1284. doi: 10.1126/science.725603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corces V., Pellicer A., Axel R., Meselson M. Integration, transcription, and control of a Drosophila heat shock gene in mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7038–7042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
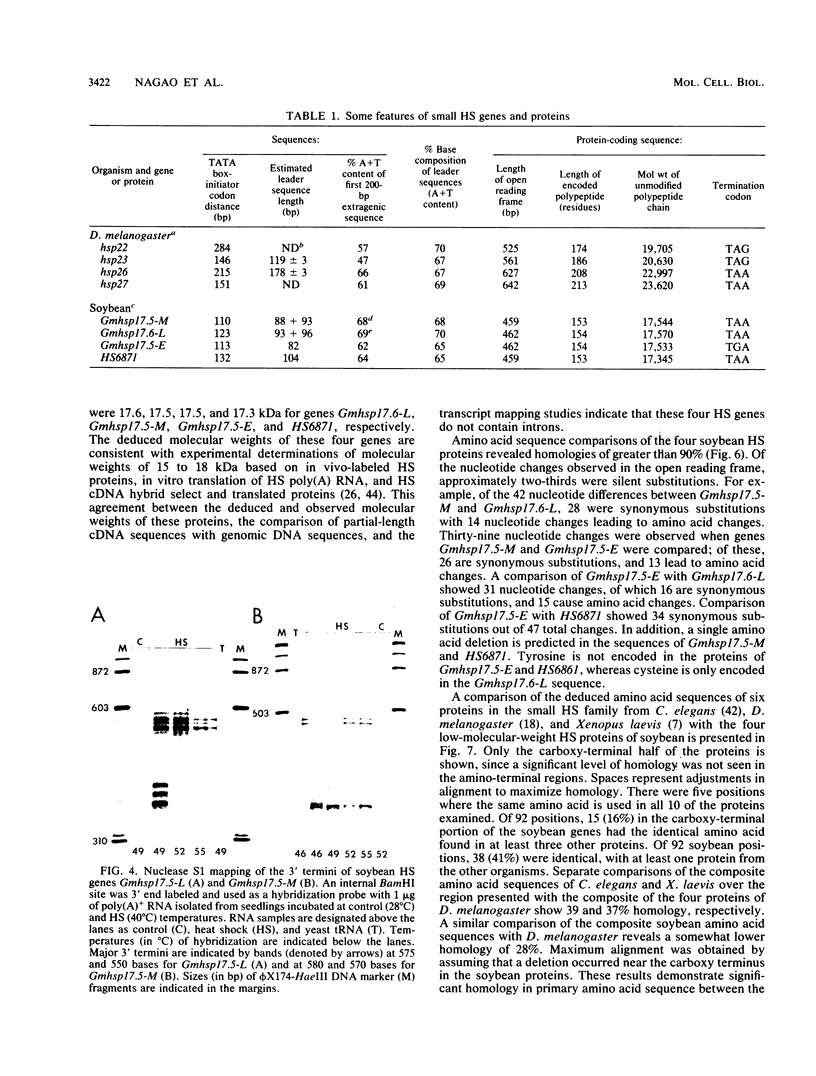
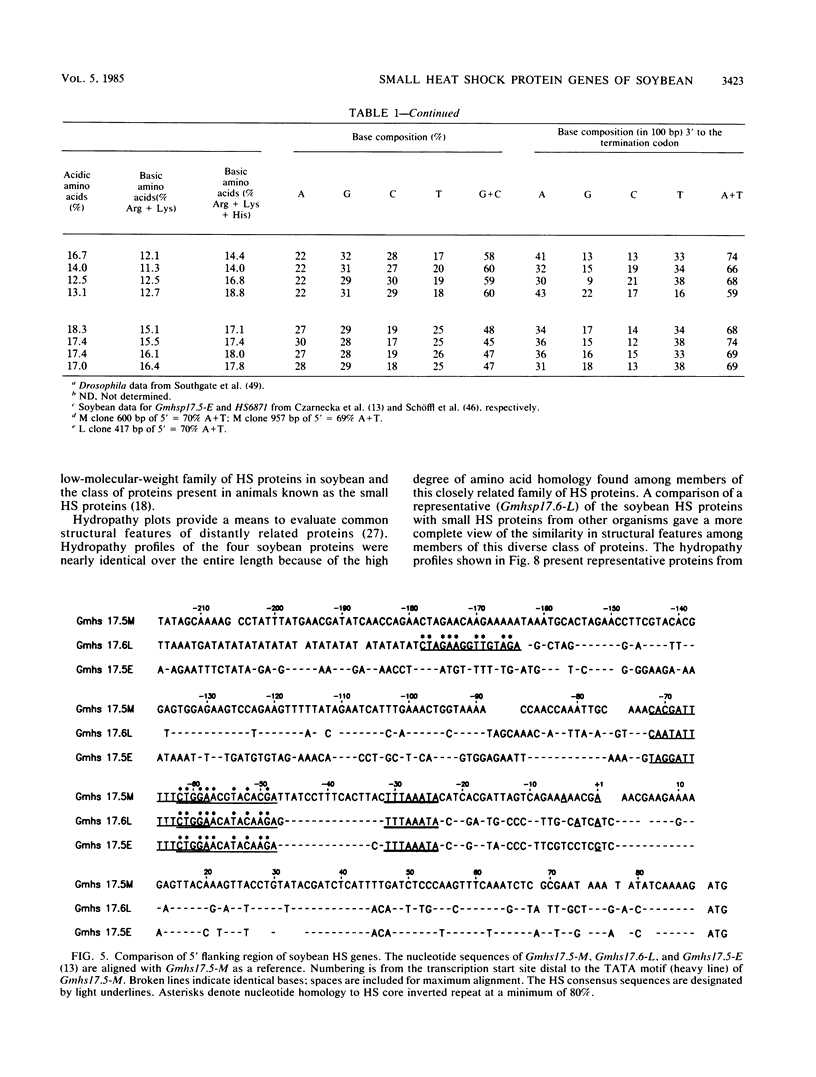
- Czarnecka E., Gurley W. B., Nagao R. T., Mosquera L. A., Key J. L. DNA sequence and transcript mapping of a soybean gene encoding a small heat shock protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3726–3730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiDomenico B. J., Bugaisky G. E., Lindquist S. Heat shock and recovery are mediated by different translational mechanisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6181–6185. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiDomenico B. J., Bugaisky G. E., Lindquist S. The heat shock response is self-regulated at both the transcriptional and posttranscriptional levels. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):593–603. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90315-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudler R., Travers A. A. Upstream elements necessary for optimal function of the hsp 70 promoter in transformed flies. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):391–398. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90494-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro J., Treisman R., Kamen R. Transcription maps of polyoma virus-specific RNA: analysis by two-dimensional nuclease S1 gel mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):718–749. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingolia T. D., Craig E. A. Four small Drosophila heat shock proteins are related to each other and to mammalian alpha-crystallin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2360–2364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Haslinger A., Holtgreve H., Richards R. I., Krauter P., Westphal H. M., Beato M. Characterization of DNA sequences through which cadmium and glucocorticoid hormones induce human metallothionein-IIA gene. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):513–519. doi: 10.1038/308513a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn J., Brenner S., Barnett L., Cesareni G. Novel bacteriophage lambda cloning vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5172–5176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley P. M., Schlesinger M. J. Antibodies to two major chicken heat shock proteins cross-react with similar proteins in widely divergent species. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;2(3):267–274. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.3.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Key J. L., Lin C. Y., Chen Y. M. Heat shock proteins of higher plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3526–3530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
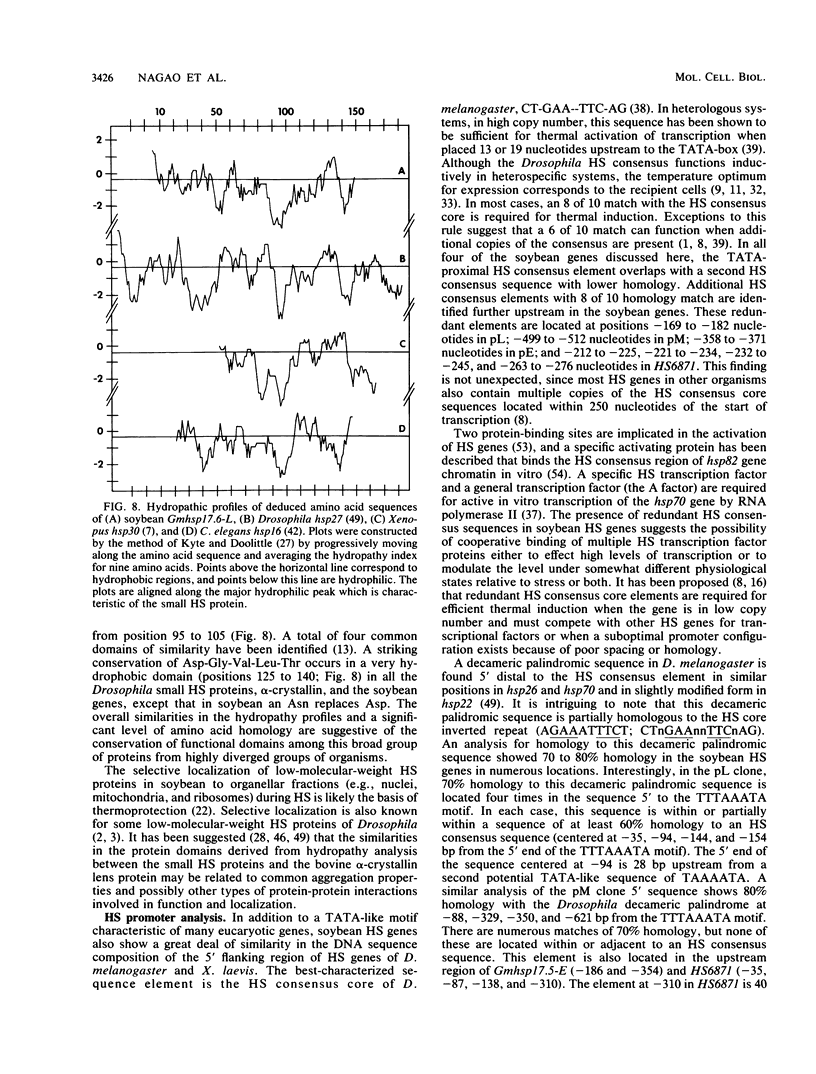
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. Y., Roberts J. K., Key J. L. Acquisition of Thermotolerance in Soybean Seedlings : Synthesis and Accumulation of Heat Shock Proteins and their Cellular Localization. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jan;74(1):152–160. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.1.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon A. P., Novak T. J., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Inducible expression of a cloned heat shock fusion gene in sea urchin embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7490–7494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirault M. E., Southgate R., Delwart E. Regulation of heat-shock genes: a DNA sequence upstream of Drosophila hsp70 genes is essential for their induction in monkey cells. EMBO J. 1982;1(10):1279–1285. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb00025.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagao R. T., Shah D. M., Eckenrode V. K., Meagher R. B. Multigene family of actin-related sequences isolated from a soybean genomic library. DNA. 1981;1(1):1–9. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1981.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordheim A., Rich A. Negatively supercoiled simian virus 40 DNA contains Z-DNA segments within transcriptional enhancer sequences. Nature. 1983 Jun 23;303(5919):674–679. doi: 10.1038/303674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor D., Lis J. T. Two closely linked transcription units within the 63B heat shock puff locus of D. melanogaster display strikingly different regulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 10;9(19):5075–5092. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.19.5075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Topol J. A Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription factor binds to the regulatory site of an hsp 70 gene. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):273–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90323-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. A regulatory upstream promoter element in the Drosophila hsp 70 heat-shock gene. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):517–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90249-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Bienz M. A synthetic heat-shock promoter element confers heat-inducibility on the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1473–1477. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01340.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pustell J., Kafatos F. C. A convenient and adaptable package of DNA sequence analysis programs for microcomputers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):51–59. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russnak R. H., Jones D., Candido E. P. Cloning and analysis of cDNA sequences coding for two 16 kilodalton heat shock proteins (hsps) in Caenorhabditis elegans: homology with the small hsps of Drosophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 25;11(10):3187–3205. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.10.3187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöffl F., Key J. L. An analysis of mRNAs for a group of heat shock proteins of soybean using cloned cDNAs. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):301–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöffl F., Raschke E., Nagao R. T. The DNA sequence analysis of soybean heat-shock genes and identification of possible regulatory promoter elements. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2491–2497. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02161.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slightom J. L., Blechl A. E., Smithies O. Human fetal G gamma- and A gamma-globin genes: complete nucleotide sequences suggest that DNA can be exchanged between these duplicated genes. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):627–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90426-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southgate R., Ayme A., Voellmy R. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the Drosophila small heat shock gene cluster at locus 67B. J Mol Biol. 1983 Mar 25;165(1):35–57. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80241-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vierling E., Key J. L. Ribulose 1,5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase Synthesis during Heat Shock. Plant Physiol. 1985 May;78(1):155–162. doi: 10.1104/pp.78.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. Activating protein factor binds in vitro to upstream control sequences in heat shock gene chromatin. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):81–84. doi: 10.1038/311081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. Two protein-binding sites in chromatin implicated in the activation of heat-shock genes. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):229–234. doi: 10.1038/309229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]