Abstract
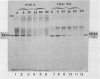
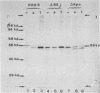
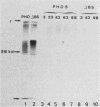
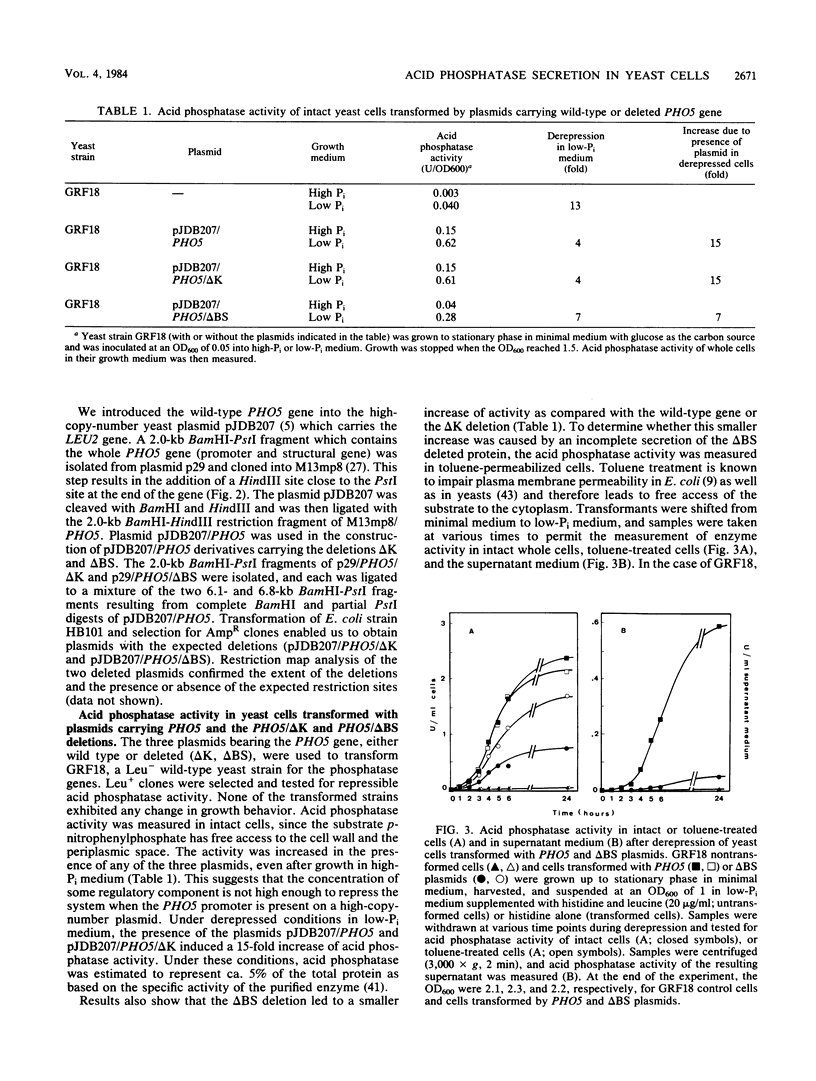
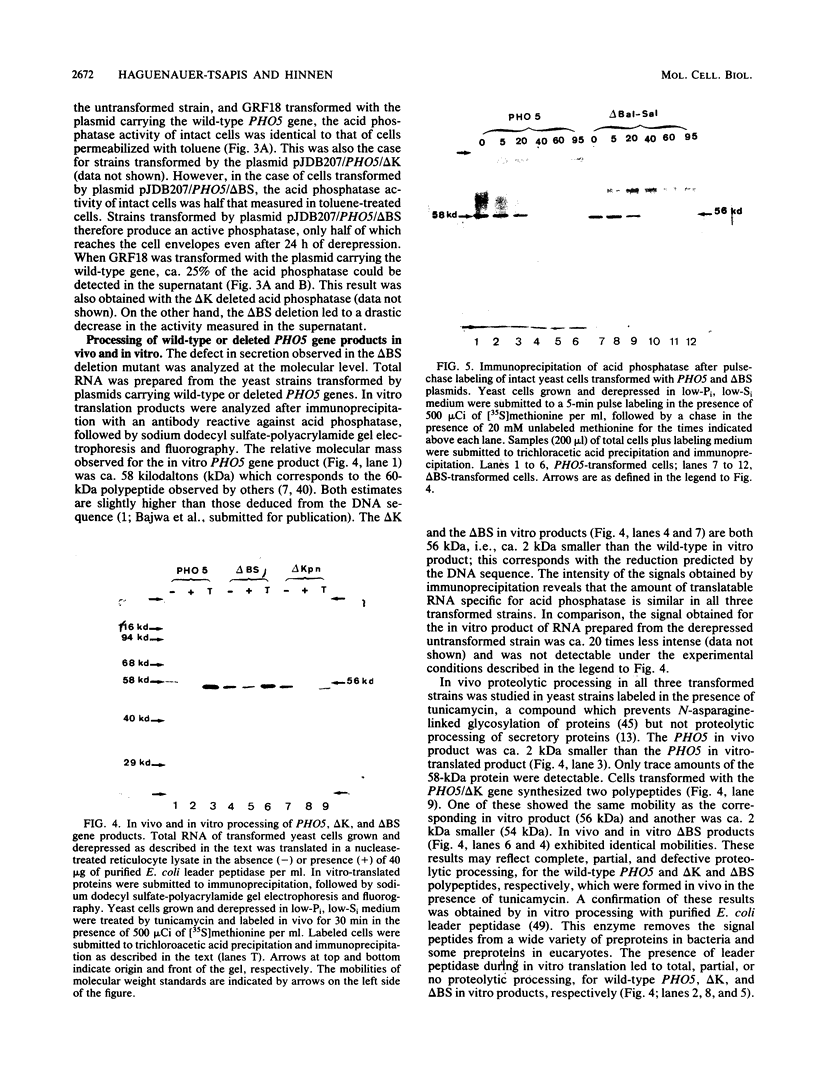
We transformed Saccharomyces cerevisiae with a high-copy-number plasmid carrying either the wild-type gene coding for a repressible cell surface acid phosphatase or two modified genes whose products lack a 13- or 14-amino-acid segment spanning or immediately adjacent to the signal peptidase cleavage site. The wild-type gene product underwent proteolytic cleavage of the signal peptide, core glycosylation, and outer chain glycosylation. The deletion spanning the signal peptidase cleavage site led to an unprocessed protein. This modified protein exhibited core glycosylation, whereas its outer chain glycosylation was severely inhibited. Secretion of the deleted protein was impaired, and active enzyme accumulated within the cell. The deletion immediately adjacent to the signal peptidase cleavage site exhibited only a small decrease in the efficiency of processing and had no effect on the efficiency of secretion.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arima K., Oshima T., Kubota I., Nakamura N., Mizunaga T., Toh-e A. The nucleotide sequence of the yeast PHO5 gene: a putative precursor of repressible acid phosphatase contains a signal peptide. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1657–1672. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold W. N. Location of acid phosphatase and -fructofuranosidase within yeast cell envelopes. J Bacteriol. 1972 Dec;112(3):1346–1352. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.3.1346-1352.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTTIN G. M'ECANISMES R'EGULATEURS DANS LA BIOSYNTH'ESE DES ENZYMES DU M'ETABOLISME DU GALACTOSE CHEZ ESCHERICHIA COLI K12. I. LA BIOSYNTH'ESE INDUITE DE LA GALACTOKINASE ET L'INDUCTION SIMULTAN'EE DE LA S'EQUENCE ENZYMATIQUE. J Mol Biol. 1963 Aug;7:164–182. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80044-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballou C. Structure and biosynthesis of the mannan component of the yeast cell envelope. Adv Microb Physiol. 1976;14(11):93–158. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60227-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Dobberstein B. Transfer of proteins across membranes. I. Presence of proteolytically processed and unprocessed nascent immunoglobulin light chains on membrane-bound ribosomes of murine myeloma. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):835–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bostian K. A., Lemire J. M., Cannon L. E., Halvorson H. O. In vitro synthesis of repressible yeast acid phosphatase: identification of multiple mRNAs and products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4504–4508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bostian K. A., Lemire J. M., Halvorson H. O. Physiological control of repressible acid phosphatase gene transcripts in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):839–853. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Taussig R., Kustu S., Botstein D. The secreted form of invertase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is synthesized from mRNA encoding a signal sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;3(3):439–447. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.3.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. P. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):132–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90716-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B. Nature of Col E 1 plasmid replication in Escherichia coli in the presence of the chloramphenicol. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):667–676. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.667-676.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobberstein B., Garoff H., Warren G., Robinson P. J. Cell-free synthesis and membrane insertion of mouse H-2Dd histocompatibility antigen and beta 2-microglobulin. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):759–769. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90316-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas M. G., Butow R. A. Variant forms of mitochondrial translation products in yeast: evidence for location of determinants on mitochondrial DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1083–1086. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon B., Novick P., Schekman R. Compartmentalized assembly of oligosaccharides on exported glycoproteins in yeast. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):451–460. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90063-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., Sambrook J. Construction of influenza haemagglutinin genes that code for intracellular and secreted forms of the protein. Nature. 1982 Dec 16;300(5893):598–603. doi: 10.1038/300598a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. N., Silhavy T. J. Genetic analysis of the major outer membrane proteins of Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:91–142. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.000515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnen A., Hicks J. B., Fink G. R. Transformation of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1929–1933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz F. N., Rothman J. E., Lingappa V. R., Blobel G., Lodish H. F. Membrane assembly in vitro: synthesis, glycosylation, and asymmetric insertion of a transmembrane protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3278–3282. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreil G., Mollay C., Kaschnitz R., Haiml L., Vilas U. Prepromelittin: specific cleavage of the pre- and the propeptide in vitro. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;343:338–346. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb47262.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreil G. Transfer of proteins across membranes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:317–348. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.001533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. J., Kanazawa H., Ozols J., Wu H. C. An Escherichia coli mutant with an amino acid alteration within the signal sequence of outer membrane prolipoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4891–4895. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. J., Kanazawa H., Wu H. C. Assembly of outer membrane lipoprotein in an Escherichia coli mutant with a single amino acid replacement within the signal sequence of prolipoprotein. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):550–557. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.550-557.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linnemans W. A., Boer P., Elbers P. F. Localization of acid phosphatase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a clue to cell wall formation. J Bacteriol. 1977 Aug;131(2):638–644. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.2.638-644.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D. I., Krause E., Dobberstein B. Secretory protein translocation across membranes-the role of the "docking protein'. Nature. 1982 Jun 24;297(5868):647–650. doi: 10.1038/297647a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyhack B., Bajwa W., Rudolph H., Hinnen A. Two yeast acid phosphatase structural genes are the result of a tandem duplication and show different degrees of homology in their promoter and coding sequences. EMBO J. 1982;1(6):675–680. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01229.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis S., Beckwith J. Mechanism of incorporation of cell envelope proteins in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982;36:435–465. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.002251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstein C., Brownlee G. G., Harrison T. M., Mathews M. B. A possible precursor of immunoglobulin light chains. Nat New Biol. 1972 Sep 27;239(91):117–120. doi: 10.1038/newbio239117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick P., Ferro S., Schekman R. Order of events in the yeast secretory pathway. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):461–469. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick P., Field C., Schekman R. Identification of 23 complementation groups required for post-translational events in the yeast secretory pathway. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):205–215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90128-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi A., Gibson J., Gregor I., Schatz G. Import of proteins into mitochondria. The precursor of cytochrome c1 is processed in two steps, one of them heme-dependent. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):13042–13047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palade G. Intracellular aspects of the process of protein synthesis. Science. 1975 Aug 1;189(4200):347–358. doi: 10.1126/science.1096303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman D., Halvorson H. O. Distinct repressible mRNAs for cytoplasmic and secreted yeast invertase are encoded by a single gene. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):525–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90071-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid G. A., Yonetani T., Schatz G. Import of proteins into mitochondria. Import and maturation of the mitochondrial intermembrane space enzymes cytochrome b2 and cytochrome c peroxidase in intact yeast cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):13068–13074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riezman H., Hase T., van Loon A. P., Grivell L. A., Suda K., Schatz G. Import of proteins into mitochondria: a 70 kilodalton outer membrane protein with a large carboxy-terminal deletion is still transported to the outer membrane. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2161–2168. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01717.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers D. T., Lemire J. M., Bostian K. A. Acid phosphatase polypeptides in Saccharomyces cerevisiae are encoded by a differentially regulated multigene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2157–2161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweingruber A. M., Schweingruber M. E. Differential regulation of the active and inactive forms of Saccharomyces cerevisiae acid phosphatase. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;187(1):107–111. doi: 10.1007/BF00384391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekikawa K., Lai C. J. Defects in functional expression of an influenza virus hemagglutinin lacking the signal peptide sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3563–3567. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano R., Gancedo J. M., Gancedo C. Assay of yeast enzymes in situ. A potential tool in regulation studies. Eur J Biochem. 1973 May 2;34(3):479–482. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02783.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider M. D., Robbins P. W. Transmembrane organization of protein glycosylation. Mature oligosaccharide-lipid is located on the luminal side of microsomes from Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):6796–6801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thill G. P., Kramer R. A., Turner K. J., Bostian K. A. Comparative analysis of the 5'-end regions of two repressible acid phosphatase genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;3(4):570–579. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.4.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- To-E A., Ueda Y., Kakimoto S. I., Oshima Y. Isolation and characterization of acid phosphatase mutants in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):727–738. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.727-738.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Translocation of proteins across the endoplasmic reticulum. II. Signal recognition protein (SRP) mediates the selective binding to microsomal membranes of in-vitro-assembled polysomes synthesizing secretory protein. J Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;91(2 Pt 1):551–556. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.2.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe P. B., Silver P., Wickner W. The isolation of homogeneous leader peptidase from a strain of Escherichia coli which overproduces the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7898–7902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]