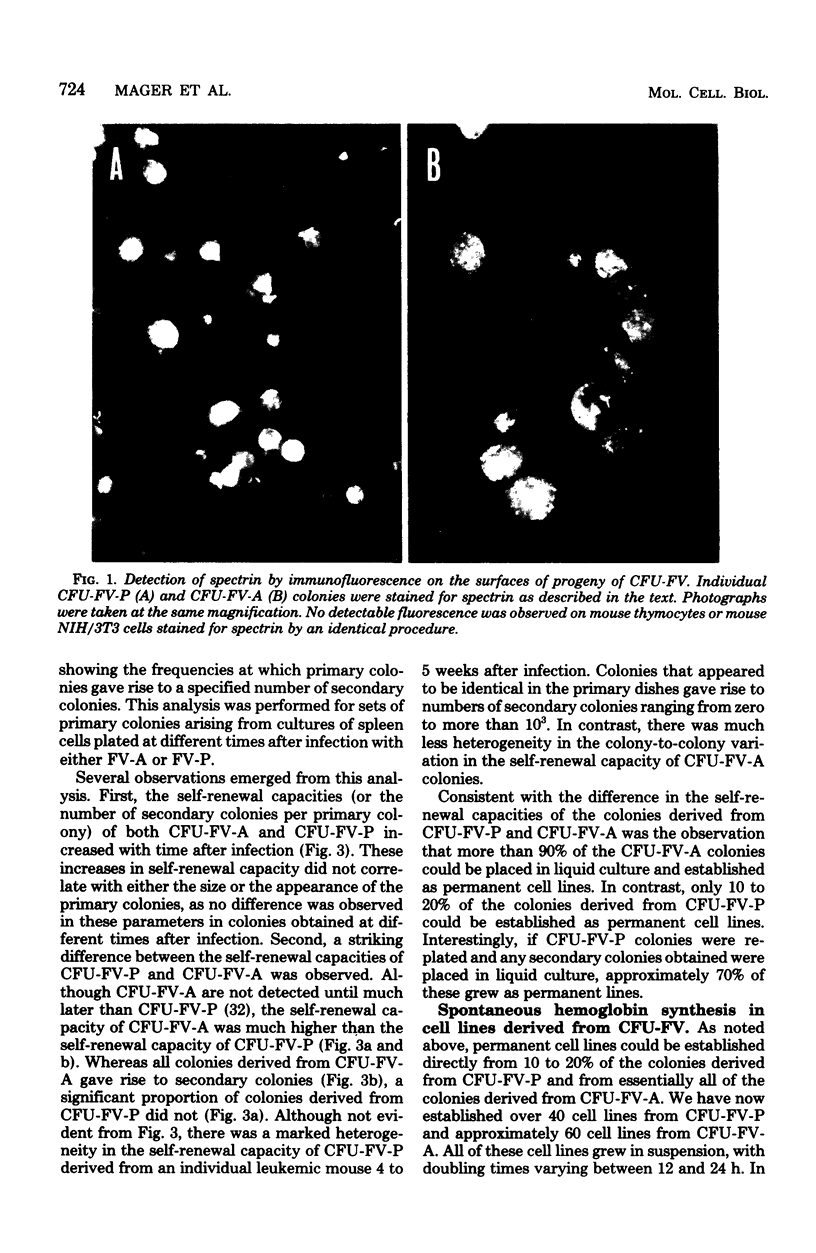
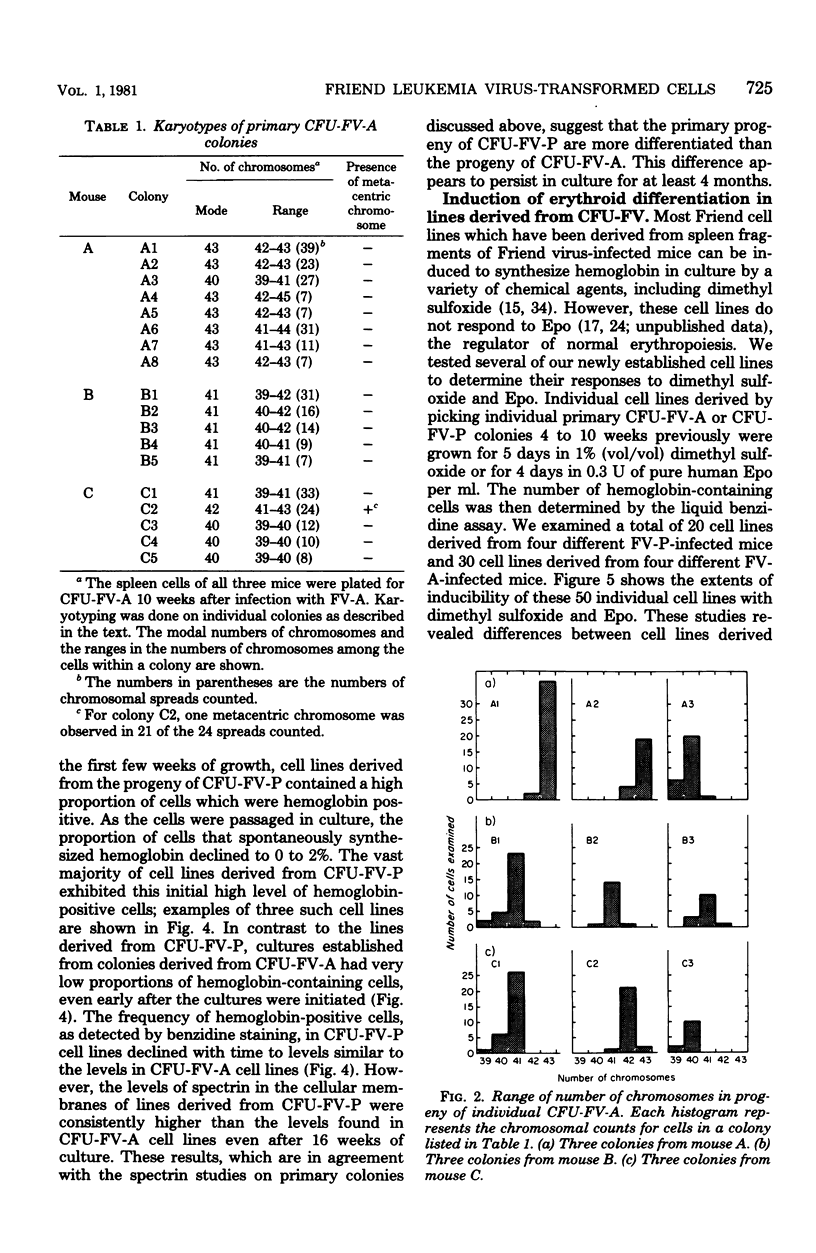
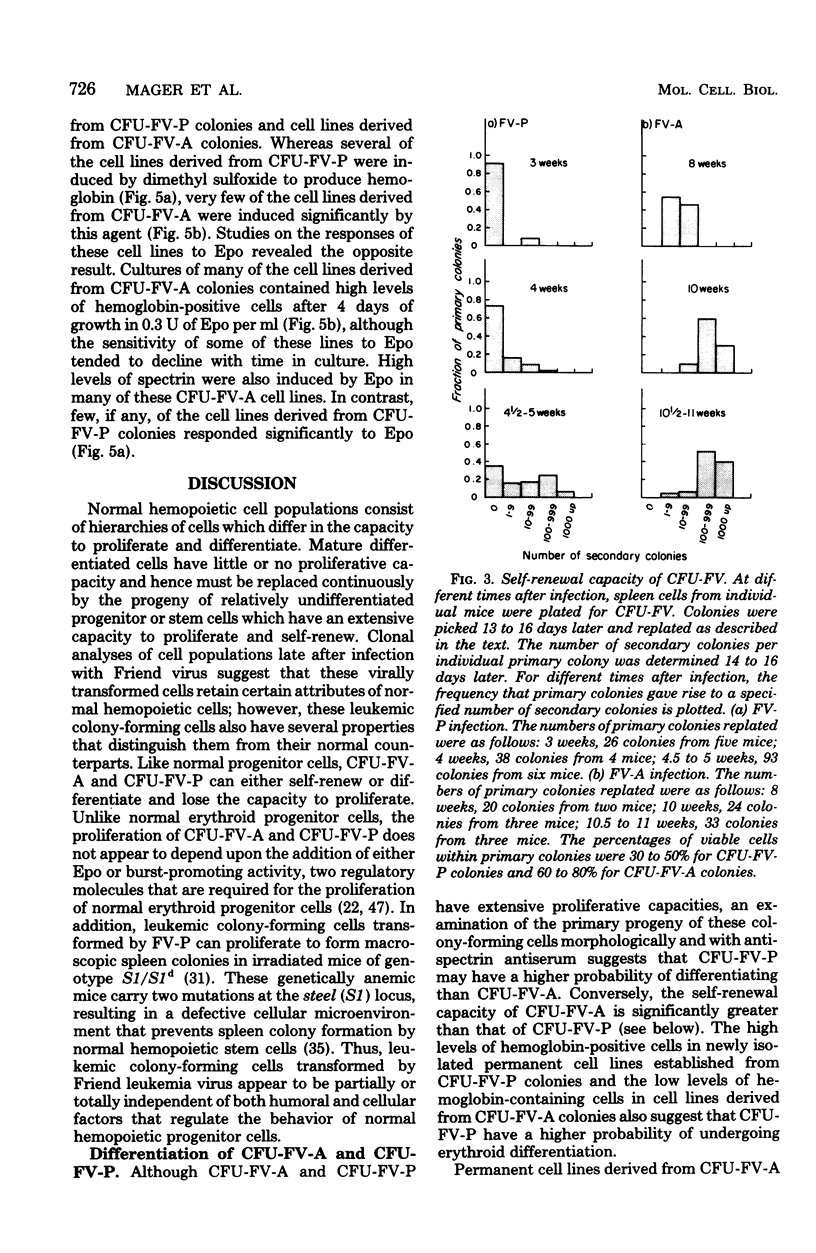
Abstract
We observed striking differences between the tumorigenic colony-forming cells present in the spleens of mice late after infection with the anemia-inducing strain of Friend leukemia virus (strain FV-A) and those present after infection with the polycythemia-inducing strain (strain FV-P). Cells within primary colonies derived from FV-A- and FV-P-transformed cells (CFU-FV-A and CFU-FV-P, respectively) contained hemoglobin and spectrin, indicating that the CFU-FV-A and CFU-FV-P were transformed erythroid progenitor cells. The proportion of cells containing hemoglobin was relatively high (> 25%) in newly isolated cell lines derived from CFU-FV-P colonies, whereas cell lines derived from CFU-FV-A colonies had only low levels (0 to 2%) of hemoglobin-containing cells. A high proportion of the cell lines derived from CFU-FV-A colonies responded to pure erythropoietin and accumulated spectrin and hemoglobin, whereas the cell lines derived from CFU-FV-P colonies did not. A cytogenetic analysis indicated that primary CFU-FV-P colony cells were diploid, whereas chromosomal aberrations were observed in the immediate progeny of CFU-FV-A. The presence of unique chromosomal markers in the majority of the cells within individual colonies derived from CFU-FV-A suggested that these colonies originated from single cells. Finally, leukemic progenitor cells transformed by strain FV-A appeared to have an extensive capacity to self-renew (i.e., form secondary colonies in methylcellulose), whereas a significant proportion of the corresponding cells transformed by strain FV-P did not. In addition, the self-renewal capacity of both CFU-FV-A and CFU-FV-P increased as the disease progressed. From these observations, we propose a model for the multistage nature of Friend disease; this model involves clonal evolution and expansion from a differentiating population with limited proliferative capacity to a population with a high capacity for self-renewal and proliferation.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AXELRAD A. A., STEEVES R. A. ASSAY FOR FRIEND LEUKEMIA VIRUS: RAPID QUANTITATIVE METHOD BASED ON ENUMERATION OF MACROSCOPIC SPLEEN FOCI IN MICE. Virology. 1964 Nov;24:513–518. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90199-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUFFETT R. F., FURTH J. A transplantable reticulum-cell sarcoma variant of Friend's viral leukemia. Cancer Res. 1959 Nov;19:1063–1069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein A., Mak T. W., Stephenson J. R. The Friend virus genome: evidence for the stable association of MuLV sequences and sequences involved in erythroleukemic transformation. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):287–294. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90206-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON P. J., FIELDSTEEL A. H., BOSTICK W. L. Pathologic studies of Friend virus leukemia and the development of a transplantable tumor in BALB/c mice. Cancer Res. 1963 Mar;23:349–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dexter T. M., Allen T. D., Scott D., Teich N. M. Isolation and characterisation of a bipotential haematopoietic cell line. Nature. 1979 Feb 8;277(5696):471–474. doi: 10.1038/277471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen H., Bach R., Emery R. Induction of spectrin in erythroleukemic cells transformed by Friend virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3898–3902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEND C. Cell-free transmission in adult Swiss mice of a disease having the character of a leukemia. J Exp Med. 1957 Apr 1;105(4):307–318. doi: 10.1084/jem.105.4.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEND C., HADDAD J. R. Tumor formation with transplants of spleen or liver from mice with virus-induced leukemia. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1960 Dec;25:1279–1285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fioritoni G., Bertolini L., Torlontano G., Revoltella R. Cytochemical characteristics of leukopoietic differentiation in murine erythroleukemic (Friend) cells. Cancer Res. 1980 Mar;40(3):866–872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend C., Patuleia M. C., De Harven E. Erythrocytic maturation in vitro of murine (Friend) virus-induced leukemic cells. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1966 Sep;22:505–522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend C., Scher W., Holland J. G., Sato T. Hemoglobin synthesis in murine virus-induced leukemic cells in vitro: stimulation of erythroid differentiation by dimethyl sulfoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):378–382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend C. The phenomenon of differentiation in murine erythroleukemic cells. Harvey Lect. 1978;72:253–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golde D. W., Bersch N., Friend C., Tsuei D., Marovitz W. Transformation of DBA/2 mouse fetal liver cells infected in vitro by the anemic strain of Friend leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):962–966. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein K., Preisler H. D., Lutton J. D., Zanjani E. D. Erythroid colony formation in vitro by dimethylsulfoxide-treated erythroleukemic cells. Blood. 1974 Dec;44(6):831–836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hankins W. D., Troxler D. Polycythemia- and anemia-inducing erythroleukemia viruses exhibit differential erythroid transforming effects in vitro. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):693–699. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90545-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harnden D. G., Taylor A. M. Chromosomes and neoplasia. Adv Hum Genet. 1979;9:1-70, 355-60. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-8276-2_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasthorpe S., Bol S. Erythropoietin responses and physical characterization of erythroid progenitor cells in Rauscher virus infected BALB/c mice. J Cell Physiol. 1979 Jul;100(1):77–86. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041000108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horoszewicz J. S., Leong S. S., Carter W. A. Friend leukemia: rapid development of erythropoietin-independent hematopoietic precursors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Jan;54(1):265–267. doi: 10.1093/jnci/54.1.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G. Lymphoma development in mice and humans: diversity of initiation is followed by convergent cytogenetic evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2442–2446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kluge N., Gaedicke G., Steinheider G., Dube S., Ostertag W. Globin synthesis in Friend-erythroleukemia mouse cells in protein- and lipid-free medium. Effects of dimethyl-sulfoxide, iron and erythropoietin. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Oct;88(2):257–262. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90239-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao S. K., Axelrad A. A. Erythropoietin-independent erythroid colony formation in vitro by hemopoietic cells of mice infected with friend virus. Int J Cancer. 1975 Mar 15;15(3):467–482. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910150313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIRAND E. A., PRENTICE T., HOFFMAN J. G., GRACE J. T., Jr Effect of Friend virus in Swiss and DBA/1 mice on Fe59 uptake. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 Feb;106:423–426. doi: 10.3181/00379727-106-26358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald M. E., Johnson G. R., Bernstein A. Different pseudotypes of Friend spleen focus-forming virus induce polycythemia and erythropoietin-independent colony formation in serum-free medium. Virology. 1981 Apr 15;110(1):231–236. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald M. E., Mak T. W., Bernstein A. Erythroleukemia induction by replication-competent type C viruses cloned from the anemia- and polycythemia-inducing isolates of Friend leukemia virus. J Exp Med. 1980 Jun 1;151(6):1493–1503. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.6.1493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald M. E., Reynolds F. H., Jr, Van de Ven W. J., Stephenson J. R., Mak T. W., Bernstein A. Anemia- and polycythemia-inducing isolates of Friend spleen focus-forming virus. Biological and molecular evidence for two distinct viral genomes. J Exp Med. 1980 Jun 1;151(6):1477–1492. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.6.1477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mager D. L., Mak T. W., Bernstein A. Quantitative colony method for tumorigenic cells transformed by two distinct strains of Friend leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1703–1707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mager D., Mak T. W., Bernstein A. Friend leukaemia virus-transformed cells, unlike normal stem cells, form spleen colonies in Sl/sld mice. Nature. 1980 Dec 11;288(5791):592–594. doi: 10.1038/288592a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesi V. T., Steers E., Jr Selective solubilization of a protein component of the red cell membrane. Science. 1968 Jan 12;159(3811):203–204. doi: 10.1126/science.159.3811.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks P. A., Rifkind R. A. Erythroleukemic differentiation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:419–448. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.002223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCulloch E. A., Siminovitch L., Till J. E., Russell E. S., Bernstein S. E. The cellular basis of the genetically determined hemopoietic defect in anemic mice of genotype Sl-Sld. Blood. 1965 Oct;26(4):399–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirand E. A., Steeves R. A., Lange R. D., Grace J. T., Jr Virus-induced polycythemia in mice: erythropoiesis without erythropoietin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Jul;128(3):844–849. doi: 10.3181/00379727-128-33139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake T., Kung C. K., Goldwasser E. Purification of human erythropoietin. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 10;252(15):5558–5564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowell P. C. The clonal evolution of tumor cell populations. Science. 1976 Oct 1;194(4260):23–28. doi: 10.1126/science.959840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H., Harosi F. I., Leder P. Differentiation in erythroleukemic cells and their somatic hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):98–102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostertag W., Melderis H., Steinheider G., Kluge N., Dube S. Synthesis of mouse haemoglobin and globin mRNA in leukaemic cell cultures. Nat New Biol. 1972 Oct 25;239(95):231–234. doi: 10.1038/newbio239231a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Painter R. G., Sheetz M., Singer S. J. Detection and ultrastructural localization of human smooth muscle myosin-like molecules in human non-muscle cells by specific antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1359–1363. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preisler H. D., Shiraishi Y., Mori M., Sandberg A. A. Clones of Friend leukemia cells: differences in karyotypes and responsiveness to inducers of differentiation. Cell Differ. 1976 Oct;5(3):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(76)90022-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revoltella R., Bertolini L., Friend C. In vitro transformation of mouse bone marrow cells by the polycythemic strain of Friend leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1464–1468. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson J. R., Axelrad A. A., McLeod D. L., Shreeve M. M. Induction of colonies of hemoglobin-synthesizing cells by erythropoietin in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jul;68(7):1542–1546. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.7.1542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSUCHIDA R., RICH M. A. CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATIONS IN VIRAL LEUKEMOGENESIS. I. FRIEND AND RAUSCHER LEUKEMIA. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1964 Jul;33:33–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tambourin P. E., Wendling F., Jasmin C., Smadja-Joffe F. The physiopathology of Friend leukemia. Leuk Res. 1979;3(3):117–129. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(79)90009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Till J. E., McCulloch E. A. Hemopoietic stem cell differentiation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 26;605(4):431–459. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(80)90009-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Both N. J., Vermey M., van't Hull E., Klootwijk-van-Dijke E., van Griensven L. J., Mol J. N., Stoof T. J. A new erythroid cell line induced by Rauscher murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1978 Apr 13;272(5654):626–628. doi: 10.1038/272626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]