Abstract
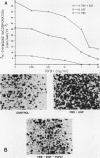
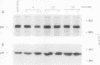
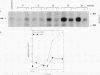
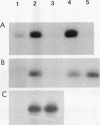
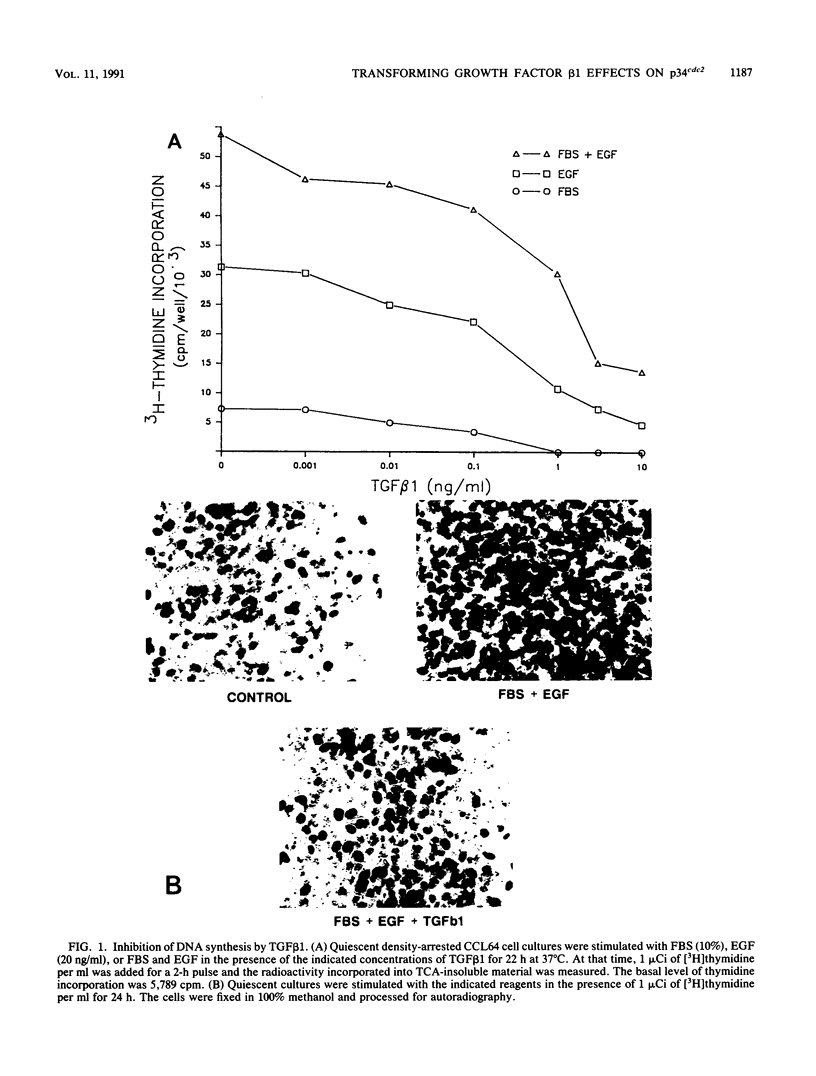
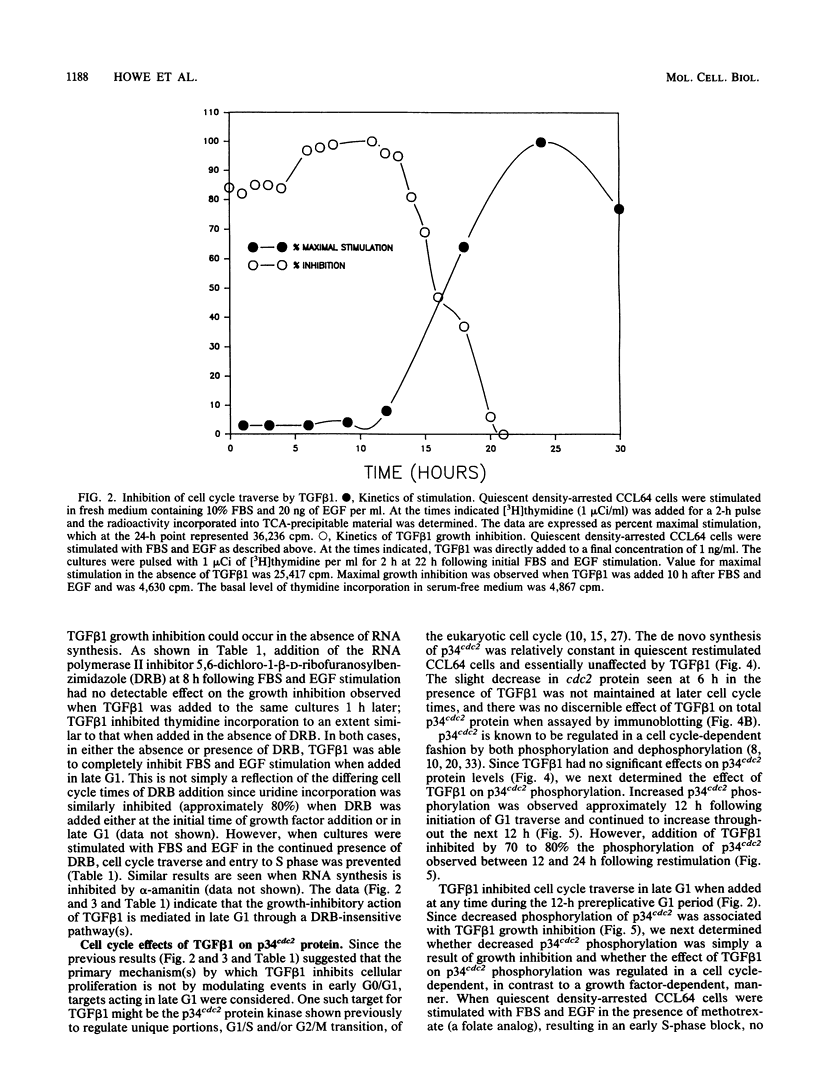
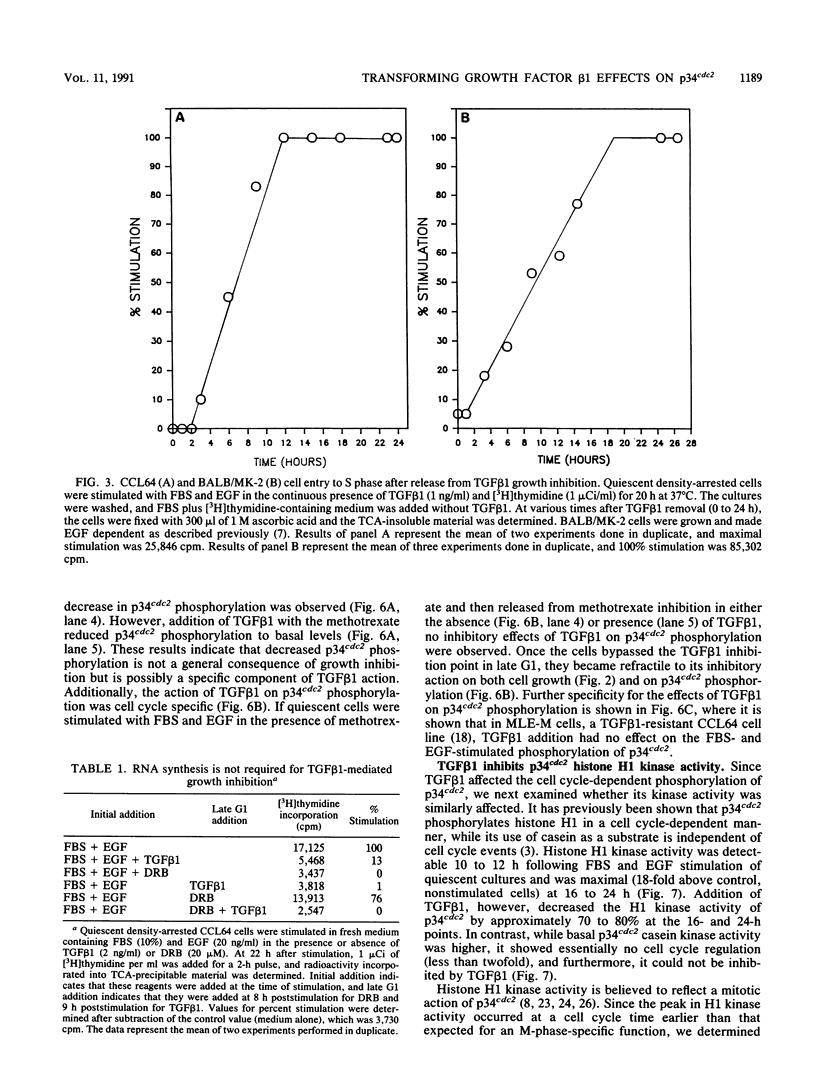
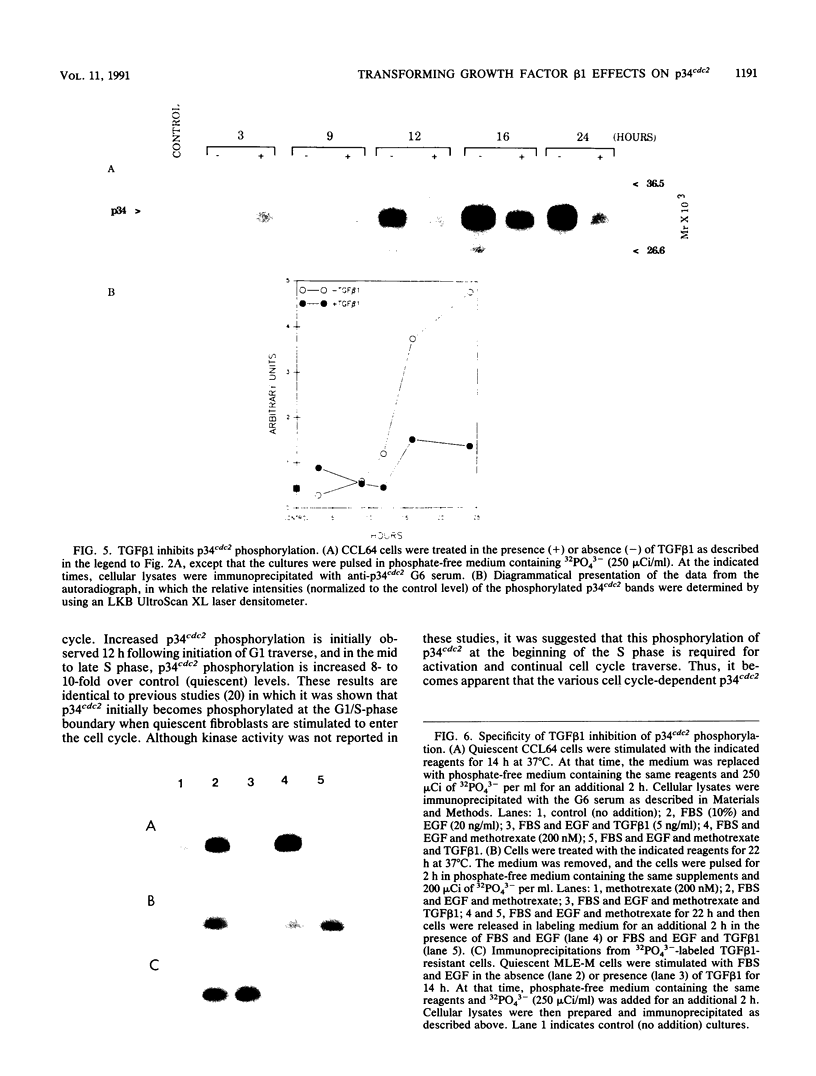
Transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF beta 1) is a potent inhibitor of epithelial cell proliferation. We present data which indicate that epithelial cell proliferation is inhibited when TGF beta 1 is added throughout the prereplicative G1 phase. Cultures become reversibly blocked in late G1 at the G1/S-phase boundary. The inhibitory effects of TGF beta 1 on cell growth occur in the presence of the RNA synthesis inhibitor 5,6-dichloro-1-beta-D-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole. Associated with this inhibitory effect is a decrease in the phosphorylation and histone H1 kinase activity of the p34cdc2 protein kinase. These data suggest that TGF beta 1 growth inhibition in epithelial cells involves the regulation of p34cdc2 activity at the G1/S transition.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arion D., Meijer L., Brizuela L., Beach D. cdc2 is a component of the M phase-specific histone H1 kinase: evidence for identity with MPF. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):371–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90060-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brizuela L., Draetta G., Beach D. Activation of human CDC2 protein as a histone H1 kinase is associated with complex formation with the p62 subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4362–4366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campisi J., Medrano E. E., Morreo G., Pardee A. B. Restriction point control of cell growth by a labile protein: evidence for increased stability in transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):436–440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campisi J., Morreo G., Pardee A. B. Kinetics of G1 transit following brief starvation for serum factors. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Jun;152(2):459–466. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90647-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambard J. C., Pouysségur J. TGF-beta inhibits growth factor-induced DNA synthesis in hamster fibroblasts without affecting the early mitogenic events. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Apr;135(1):101–107. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041350114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffey R. J., Jr, Bascom C. C., Sipes N. J., Graves-Deal R., Weissman B. E., Moses H. L. Selective inhibition of growth-related gene expression in murine keratinocytes by transforming growth factor beta. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3088–3093. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Beach D. Activation of cdc2 protein kinase during mitosis in human cells: cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation and subunit rearrangement. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90175-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Piwnica-Worms H., Morrison D., Druker B., Roberts T., Beach D. Human cdc2 protein kinase is a major cell-cycle regulated tyrosine kinase substrate. Nature. 1988 Dec 22;336(6201):738–744. doi: 10.1038/336738a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Brizuela L., Beach D., Newport J. The Xenopus cdc2 protein is a component of MPF, a cytoplasmic regulator of mitosis. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):423–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90205-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Newport J. W. Fission yeast p13 blocks mitotic activation and tyrosine dephosphorylation of the Xenopus cdc2 protein kinase. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):181–191. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90414-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Norbury C., Lohka M., Nurse P., Maller J. Purified maturation-promoting factor contains the product of a Xenopus homolog of the fission yeast cell cycle control gene cdc2+. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):433–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90206-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gewirtz A. M., Anfossi G., Venturelli D., Valpreda S., Sims R., Calabretta B. G1/S transition in normal human T-lymphocytes requires the nuclear protein encoded by c-myb. Science. 1989 Jul 14;245(4914):180–183. doi: 10.1126/science.2665077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giordano A., Whyte P., Harlow E., Franza B. R., Jr, Beach D., Draetta G. A 60 kd cdc2-associated polypeptide complexes with the E1A proteins in adenovirus-infected cells. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):981–990. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90949-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goustin A. S., Leof E. B., Shipley G. D., Moses H. L. Growth factors and cancer. Cancer Res. 1986 Mar;46(3):1015–1029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe P. H., Cunningham M. R., Leof E. B. Inhibition of mink lung epithelial cell proliferation by transforming growth factor-beta is coupled through a pertussis-toxin-sensitive substrate. Biochem J. 1990 Mar 1;266(2):537–543. doi: 10.1042/bj2660537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe P. H., Leof E. B. Transforming growth factor beta 1 treatment of AKR-2B cells is coupled through a pertussis-toxin-sensitive G-protein(s). Biochem J. 1989 Aug 1;261(3):879–886. doi: 10.1042/bj2610879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labbe J. C., Lee M. G., Nurse P., Picard A., Doree M. Activation at M-phase of a protein kinase encoded by a starfish homologue of the cell cycle control gene cdc2+. Nature. 1988 Sep 15;335(6187):251–254. doi: 10.1038/335251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. G., Norbury C. J., Spurr N. K., Nurse P. Regulated expression and phosphorylation of a possible mammalian cell-cycle control protein. Nature. 1988 Jun 16;333(6174):676–679. doi: 10.1038/333676a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leof E. B., Van Wyk J. J., O'Keefe E. J., Pledger W. J. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) is required only during the traverse of early G1 in PDGF stimulated density-arrested BALB/c-3T3 cells. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Aug;147(1):202–208. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90285-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Like B., Massagué J. The antiproliferative effect of type beta transforming growth factor occurs at a level distal from receptors for growth-activating factors. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 15;261(29):13426–13429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno S., Hayles J., Nurse P. Regulation of p34cdc2 protein kinase during mitosis. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):361–372. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90850-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. O., Kaplan J. M., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Mitosis-specific phosphorylation of p60c-src by p34cdc2-associated protein kinase. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):775–786. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90792-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morla A. O., Draetta G., Beach D., Wang J. Y. Reversible tyrosine phosphorylation of cdc2: dephosphorylation accompanies activation during entry into mitosis. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):193–203. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90415-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P., Bissett Y. Gene required in G1 for commitment to cell cycle and in G2 for control of mitosis in fission yeast. Nature. 1981 Aug 6;292(5823):558–560. doi: 10.1038/292558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P. Universal control mechanism regulating onset of M-phase. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):503–508. doi: 10.1038/344503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B. G1 events and regulation of cell proliferation. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):603–608. doi: 10.1126/science.2683075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. Isolation of a human cyclin cDNA: evidence for cyclin mRNA and protein regulation in the cell cycle and for interaction with p34cdc2. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):833–846. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90936-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pledger W. J., Stiles C. D., Antoniades H. N., Scher C. D. An ordered sequence of events is required before BALB/c-3T3 cells become committed to DNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2839–2843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittling S. R., Brooks K. M., Cristofalo V. J., Baserga R. Expression of cell cycle-dependent genes in young and senescent WI-38 fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3316–3320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenoy S., Choi J. K., Bagrodia S., Copeland T. D., Maller J. L., Shalloway D. Purified maturation promoting factor phosphorylates pp60c-src at the sites phosphorylated during fibroblast mitosis. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):763–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90791-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simanis V., Nurse P. The cell cycle control gene cdc2+ of fission yeast encodes a protein kinase potentially regulated by phosphorylation. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):261–268. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90390-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells D. J., Stoddard L. S., Getz M. J., Moses H. L. alpha-Amanitin and 5-fluorouridine inhibition of serum-stimulated DNA synthesis in quiescent AKR-2B mouse embryo cells. J Cell Physiol. 1979 Aug;100(2):199–214. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041000202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang H. C., Pardee A. B. Insulin-like growth factor I regulation of transcription and replicating enzyme induction necessary for DNA synthesis. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Jun;127(3):410–416. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041270309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]