Abstract
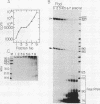
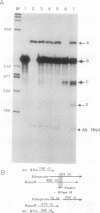
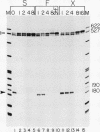
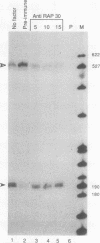
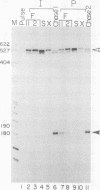
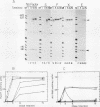
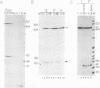
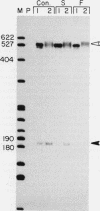
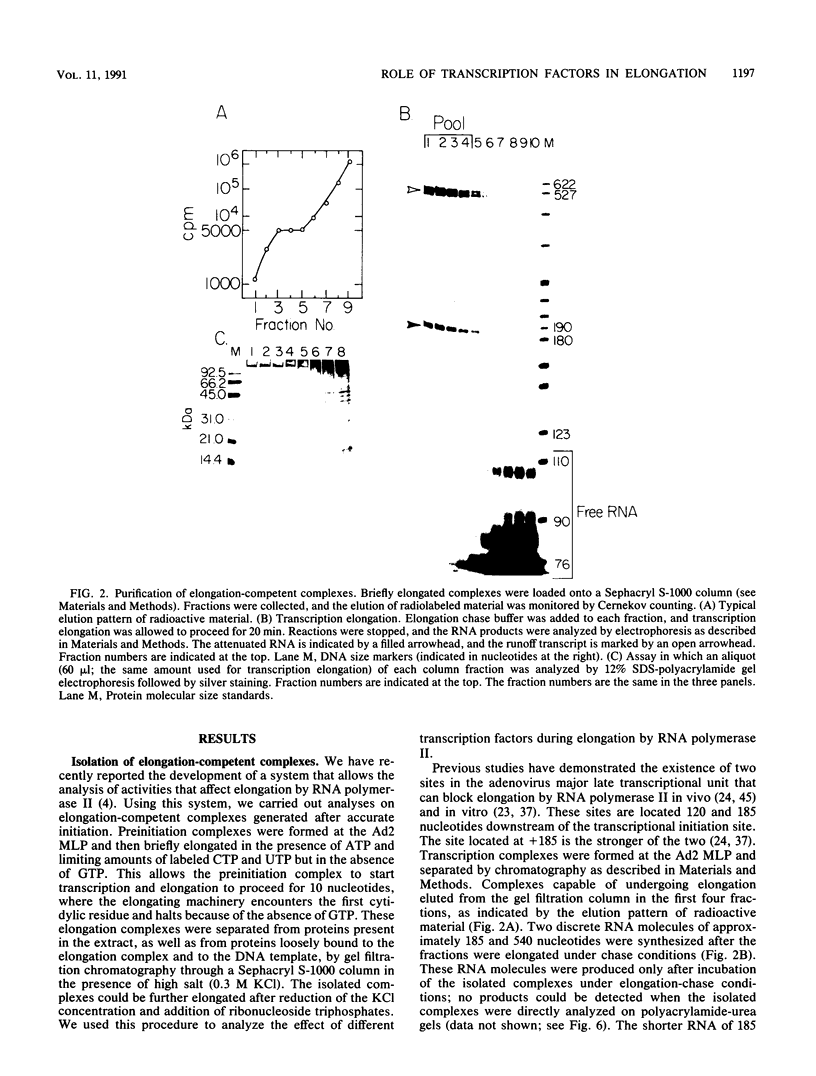
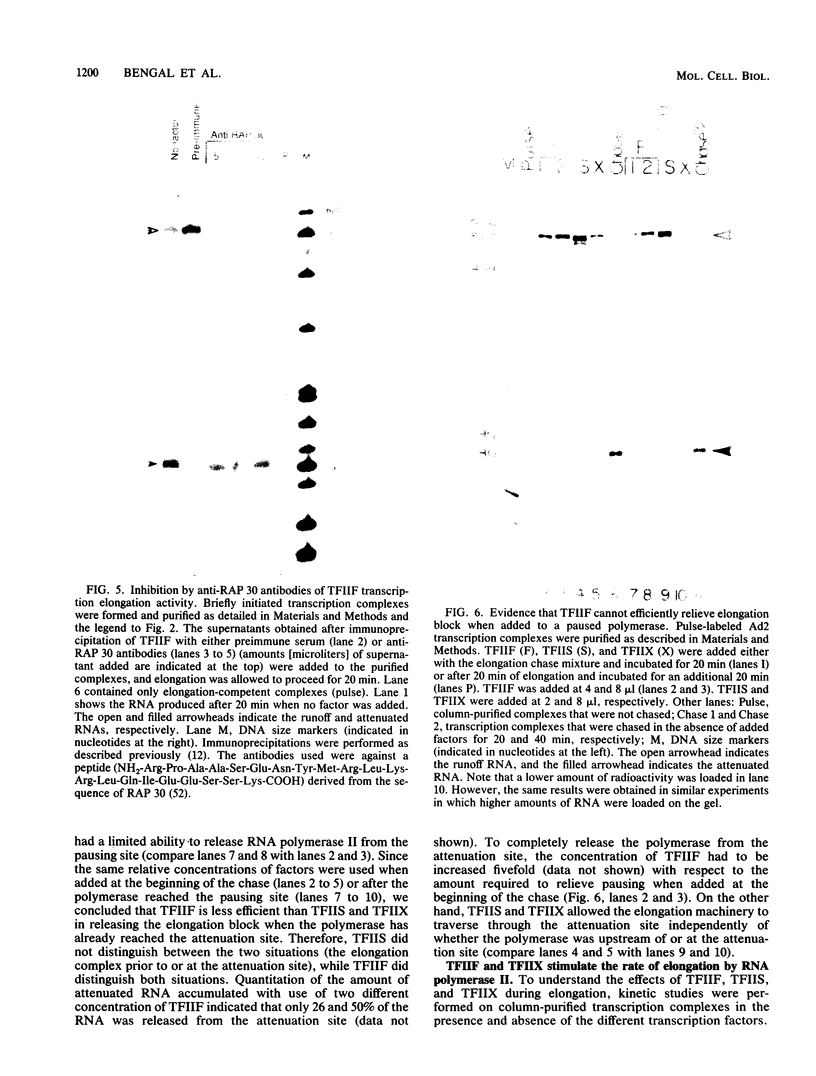
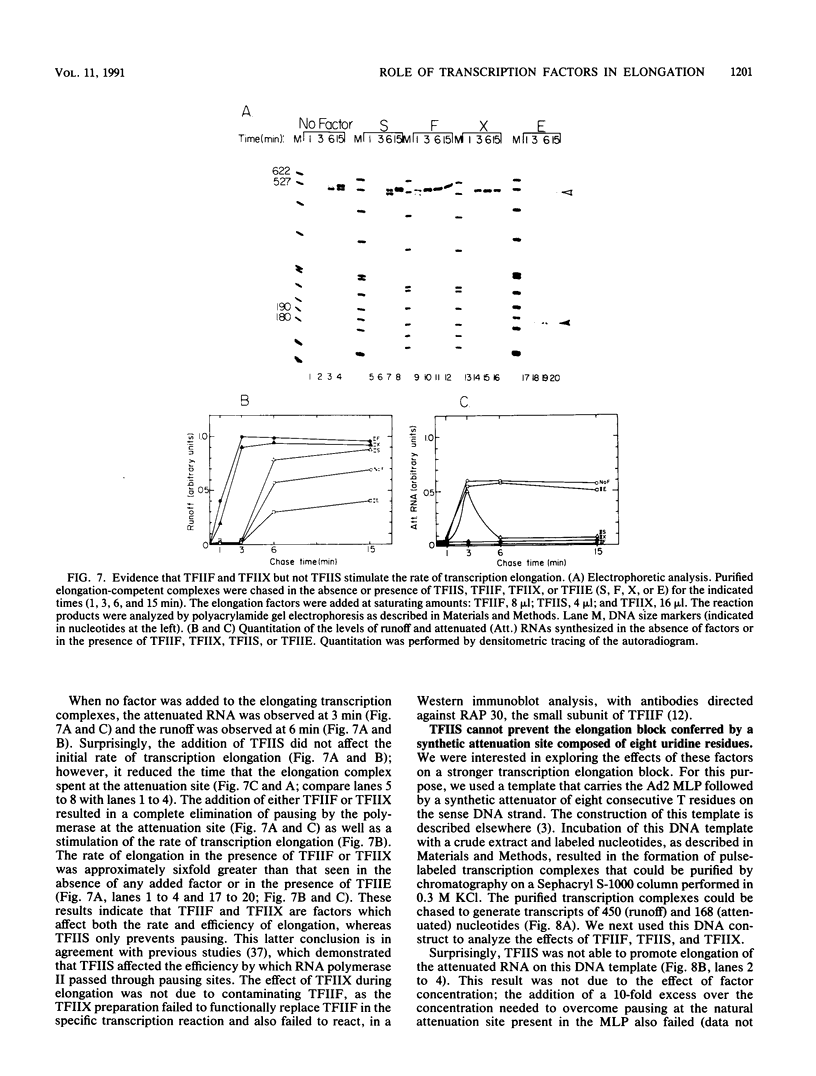
We have used a recently developed system that allows the isolation of complexes competent for RNA polymerase II elongation (E. Bengal, A. Goldring, and Y. Aloni, J. Biol. Chem. 264:18926-18932, 1989). Pulse-labeled transcription complexes were formed at the adenovirus major late promoter with use of HeLa cell extracts. Elongation-competent complexes were purified from most of the proteins present in the extract, as well as from loosely bound elongation factors, by high-salt gel filtration chromatography. We found that under these conditions the nascent RNA was displaced from the DNA during elongation. These column-purified complexes were used to analyze the activities of different transcription factors during elongation by RNA polymerase II. We found that transcription factor IIS (TFIIS), TFIIF, and TFIIX affected the efficiency of elongation through the adenovirus major late promoter attenuation site and a synthetic attenuation site composed of eight T residues. These factors have distinct activities that depend on whether they are added before RNA polymerase has reached the attenuation site or at the time when the polymerase is pausing at the attenuation site. TFIIS was found to have antiattenuation activity, while TFIIF and TFIIX stimulated the rate of elongation. In comparison with TFIIF, TFIIS is loosely bound to the elongation complex. We also found that the activities of the factors are dependent on the nature of the attenuator. These results indicate that at least three factors play a major role during elongation by RNA polymerase II.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aloni Y., Hay N. Attenuation may regulate gene expression in animal viruses and cells. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1985;18(4):327–383. doi: 10.3109/10409238509086785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Asher E., Aloni Y. Transcription of minute virus of mice, an autonomous parvovirus, may be regulated by attenuation. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):266–276. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.266-276.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengal E., Goldring A., Aloni Y. Transcription complexes synthesizing attenuated RNA can serve as a model system for analyzing elongation factors. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):18926–18932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley D. L., Groudine M. Sequence requirements for premature termination of transcription in the human c-myc gene. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):245–256. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90386-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton Z. F., Killeen M., Sopta M., Ortolan L. G., Greenblatt J. RAP30/74: a general initiation factor that binds to RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1602–1613. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton Z. F., Ortolan L. G., Greenblatt J. Proteins that bind to RNA polymerase II are required for accurate initiation of transcription at the adenovirus 2 major late promoter. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2923–2930. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04588.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carcamo J., Lobos S., Merino A., Buckbinder L., Weinmann R., Natarajan V., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Role of factors IID and MLTF in transcription from the adenovirus major late and IVa2 promoters. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7704–7714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dedrick R. L., Chamberlin M. J. Studies on transcription of 3'-extended templates by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Parameters that affect the initiation and elongation reactions. Biochemistry. 1985 Apr 23;24(9):2245–2253. doi: 10.1021/bi00330a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores O., Ha I., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Purification and subunit composition of transcription factor IIF. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5629–5634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores O., Maldonado E., Burton Z., Greenblatt J., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. RNA polymerase II-associating protein 30 is an essential component of transcription factor IIF. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10812–10816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores O., Maldonado E., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Factors IIE and IIF independently interact with RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8913–8921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay N., Aloni Y. Attenuation in SV40 as a mechanism of transcription-termination by RNA polymerase B. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 10;12(3):1401–1414. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.3.1401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay N., Skolnik-David H., Aloni Y. Attenuation in the control of SV40 gene expression. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):183–193. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90102-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez N., Lucito R. Elements required for transcription initiation of the human U2 snRNA gene coincide with elements required for snRNA 3' end formation. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3125–3134. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03179.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi M., Sekimizu K., Natori S. Analysis of the stimulatory factor of RNA polymerase II in the initiation and elongation complex. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):608–611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. C., Rigby P. W., Ziff E. B. Trans-acting protein factors and the regulation of eukaryotic transcription: lessons from studies on DNA tumor viruses. Genes Dev. 1988 Mar;2(3):267–281. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.3.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadesch T. R., Chamberlin M. J. Studies of in vitro transcription by calf thymus RNA polymerase II using a novel duplex DNA template. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5286–5295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane C. M., Chamberlin M. J. Studies on transcription of 3'-extended DNA templates by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Partial purification and characterization of a factor from HeLa cells that facilitates renaturation of the DNA template. Biochemistry. 1985 Apr 23;24(9):2254–2262. doi: 10.1021/bi00330a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao S. Y., Calman A. F., Luciw P. A., Peterlin B. M. Anti-termination of transcription within the long terminal repeat of HIV-1 by tat gene product. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):489–493. doi: 10.1038/330489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerppola T. K., Kane C. M. Intrinsic sites of transcription termination and pausing in the c-myc gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4389–4394. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler M., Ben-Asher E., Aloni Y. Elements modulating the block of transcription elongation at the adenovirus 2 attenuation site. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):9785–9790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maderious A., Chen-Kiang S. Pausing and premature termination of human RNA polymerase II during transcription of adenovirus in vivo and in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):5931–5935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.5931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S., Tjian R. Transcriptional selectivity of viral genes in mammalian cells. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):795–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermelstein F. H., Flores O., Reinberg D. Initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Sep 21;1009(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(89)90071-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller H., Asselin C., Dufort D., Yang J. Q., Gupta K., Marcu K. B., Nepveu A. A cis-acting element in the promoter region of the murine c-myc gene is necessary for transcriptional block. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5340–5349. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. H., Sluder A. E., Greenleaf A. L. Dynamic interaction between a Drosophila transcription factor and RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1465–1475. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. H., Sluder A. E., Greenleaf A. L. Fractionation of transcription factors for RNA polymerase II from Drosophila Kc cell nuclear extracts. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3244–3255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J. How RNA polymerase II terminates transcription in higher eukaryotes. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Mar;14(3):105–110. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90132-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappaport J., Reinberg D., Zandomeni R., Weinmann R. Purification and functional characterization of transcription factor SII from calf thymus. Role in RNA polymerase II elongation. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5227–5232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinberg D., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription in mammalian RNA polymerase II. Functional analysis of initiation factors IIA and IID and identification of a new factor operating at sequences downstream of the initiation site. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3322–3330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinberg D., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Purification and functional analysis of initiation factors IIB and IIE. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3310–3321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinberg D., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Transcription factor IIS stimulates elongation of RNA chains. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3331–3337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reines D., Chamberlin M. J., Kane C. M. Transcription elongation factor SII (TFIIS) enables RNA polymerase II to elongate through a block to transcription in a human gene in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10799–10809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reines D., Wells D., Chamberlin M. J., Kane C. M. Identification of intrinsic termination sites in vitro for RNA polymerase II within eukaryotic gene sequences. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 20;196(2):299–312. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90691-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnekov O., Aloni Y. RNA polymerase II is capable of pausing and prematurely terminating transcription at a precise location in vivo and in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):12–16. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnekov O., Ben-Asher E., Bengal E., Choder M., Hay N., Kessler M., Ragimov N., Seiberg M., Skolnik-David H., Aloni Y. Transcription termination in animal viruses and cells. Gene. 1988 Dec 10;72(1-2):91–104. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90130-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revie D., Dahmus M. E. Purification and partial characterization of a stimulatory factor for lamb thymus RNA polymerase II. Biochemistry. 1979 May 1;18(9):1813–1820. doi: 10.1021/bi00576a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rougvie A. E., Lis J. T. The RNA polymerase II molecule at the 5' end of the uninduced hsp70 gene of D. melanogaster is transcriptionally engaged. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):795–804. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91087-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltzman A. G., Weinmann R. Promoter specificity and modulation of RNA polymerase II transcription. FASEB J. 1989 Apr;3(6):1723–1733. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.6.2649403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiberg M., Kessler M., Levine A. J., Aloni Y. Human RNA polymerase II can prematurely terminate transcription of the adenovirus type 2 late transcription unit at a precise site that resembles a prokaryotic termination signal. Virus Genes. 1987 Nov;1(1):97–116. doi: 10.1007/BF00125689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekimizu K., Kobayashi N., Mizuno D., Natori S. Purification of a factor from Ehrlich ascites tumor cells specifically stimulating RNA polymerase II. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 16;15(23):5064–5070. doi: 10.1021/bi00668a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skarnes W. C., Tessier D. C., Acheson N. H. RNA polymerases stall and/or prematurely terminate nearby both early and late promoters on polyomavirus DNA. J Mol Biol. 1988 Sep 5;203(1):153–171. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90099-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik-David H., Aloni Y. Pausing of RNA polymerase molecules during in vivo transcription of the SV40 leader region. EMBO J. 1983;2(2):179–184. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01402.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik-David H., Hay N., Aloni Y. Site of premature termination of late transcription of simian virus 40 DNA: enhancement by 5,6-dichloro-1-beta-D-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2743–2747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sluder A. E., Greenleaf A. L., Price D. H. Properties of a Drosophila RNA polymerase II elongation factor. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8963–8969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sluder A. E., Price D. H., Greenleaf A. L. Elongation by Drosophila RNA polymerase II. Transcription of 3'-extended DNA templates. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9917–9925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sopta M., Burton Z. F., Greenblatt J. Structure and associated DNA-helicase activity of a general transcription initiation factor that binds to RNA polymerase II. Nature. 1989 Oct 5;341(6241):410–414. doi: 10.1038/341410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sopta M., Carthew R. W., Greenblatt J. Isolation of three proteins that bind to mammalian RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10353–10360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toohey M. G., Jones K. A. In vitro formation of short RNA polymerase II transcripts that terminate within the HIV-1 and HIV-2 promoter-proximal downstream regions. Genes Dev. 1989 Mar;3(3):265–282. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.3.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ucker D. S., Yamamoto K. R. Early events in the stimulation of mammary tumor virus RNA synthesis by glucocorticoids. Novel assays of transcription rates. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7416–7420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vegvar H. E., Lund E., Dahlberg J. E. 3' end formation of U1 snRNA precursors is coupled to transcription from snRNA promoters. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):259–266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90448-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]