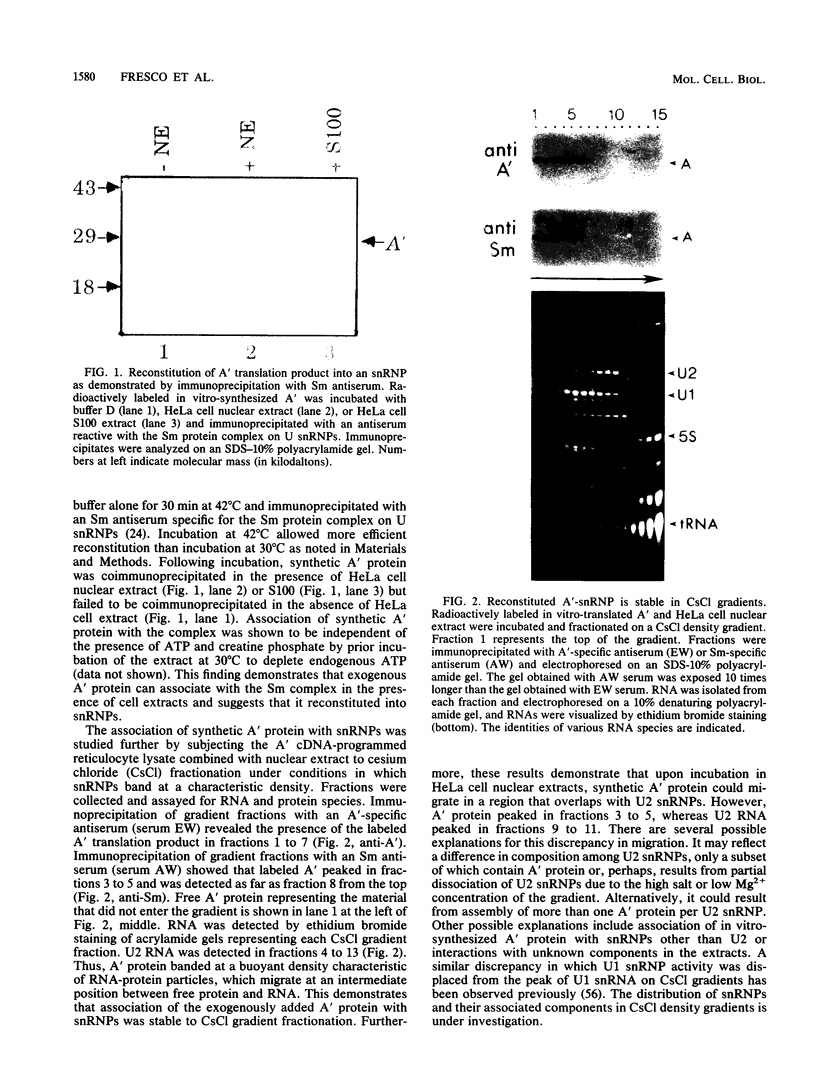
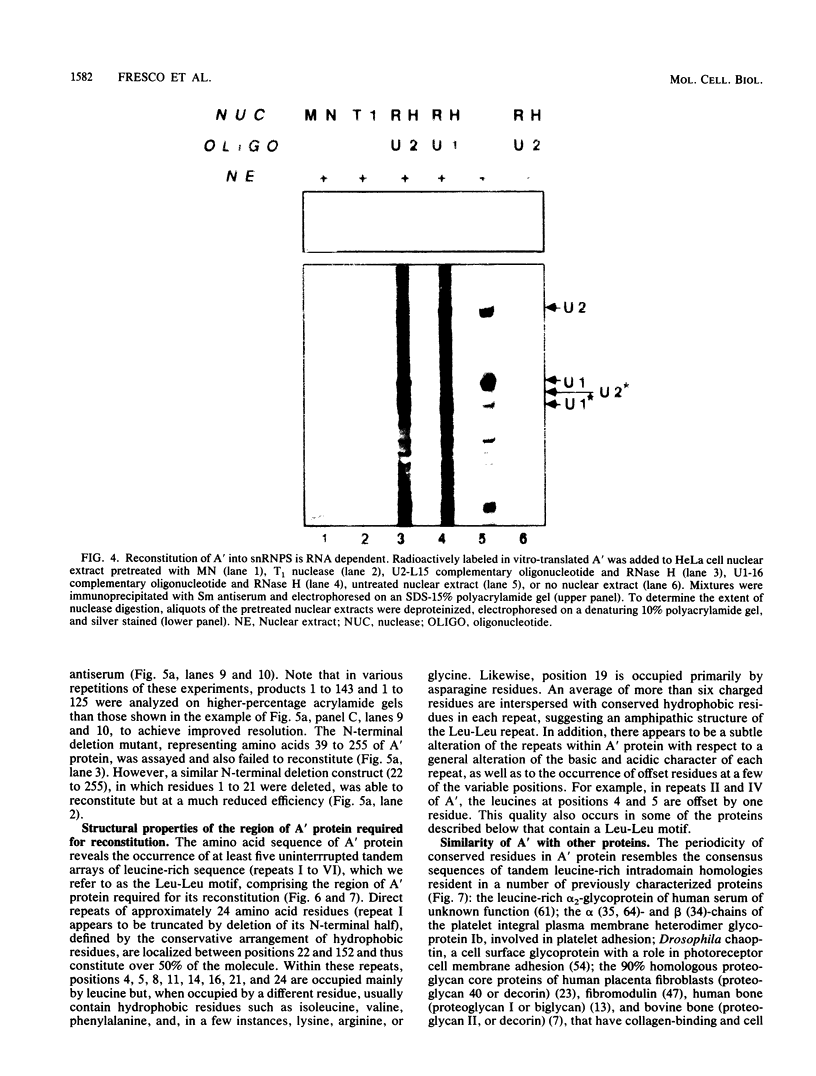
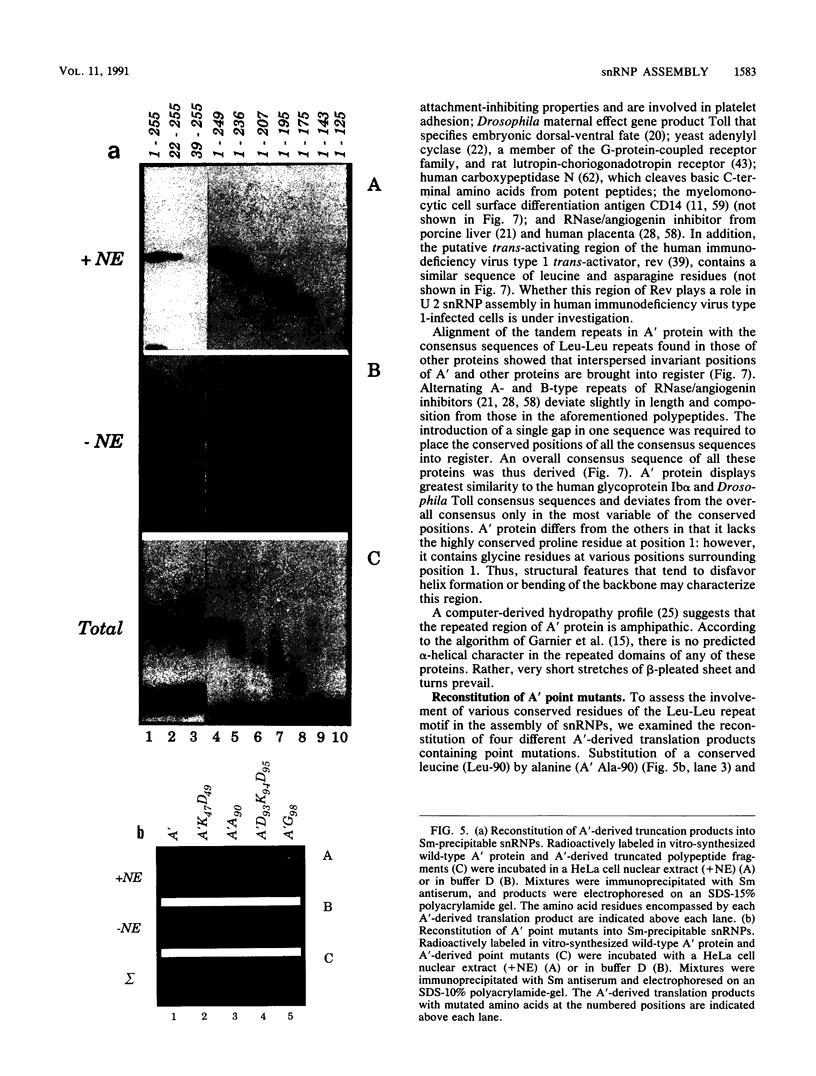
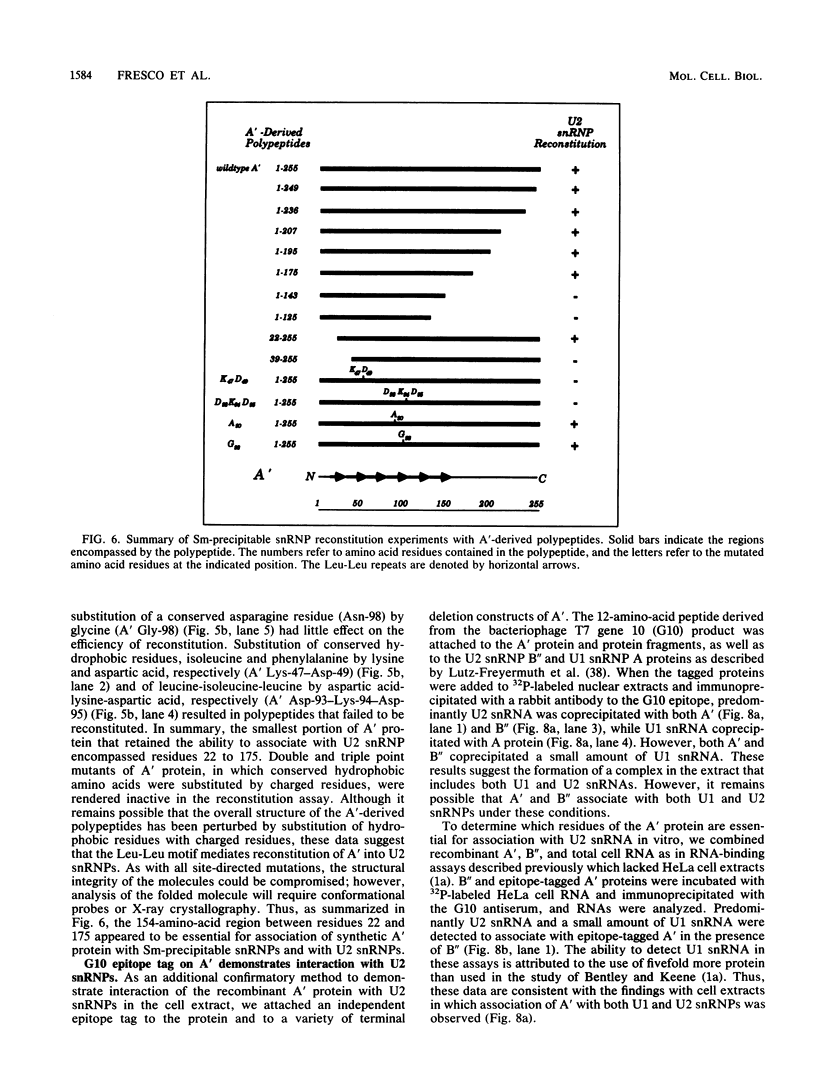
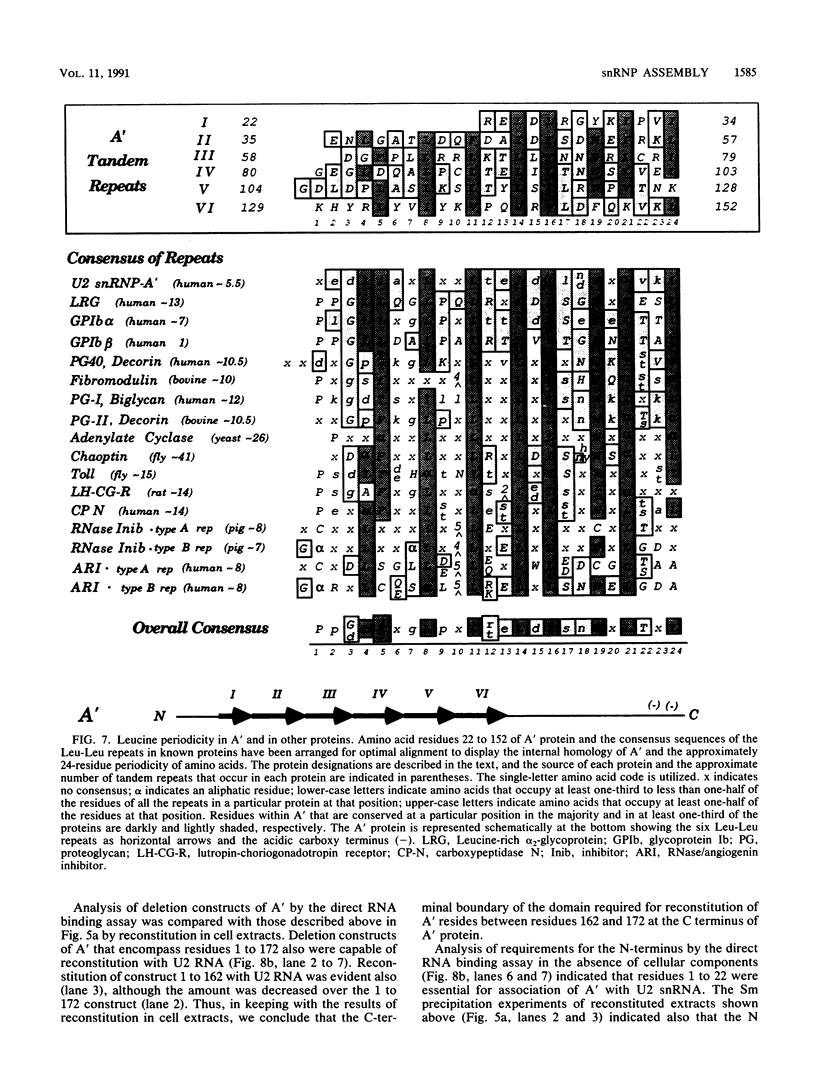
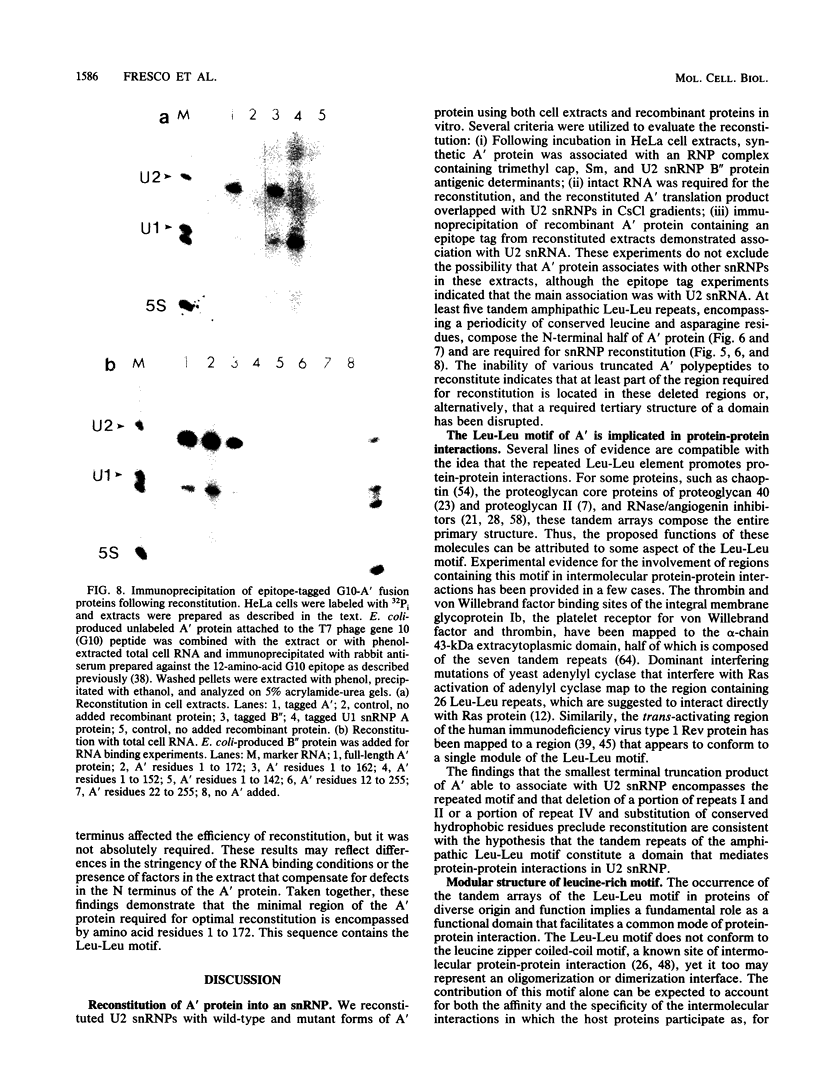
Abstract
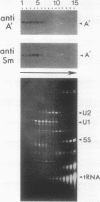
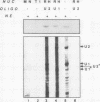
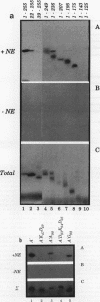
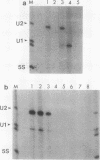
Recombinant A' protein could be reconstituted into U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles (snRNPs) upon addition to HeLa cell extracts as determined by coimmunoprecipitation and particle density; however, direct binding to U2 RNA could not be demonstrated except in the presence of the U2 snRNP B" protein. Mutational analysis indicated that a central core region of A' was required for particle reconstitution. This region consists of five tandem repeats of approximately 24 amino acids each that exhibit a periodicity of leucine and asparagine residues that is distinct from the leucine zipper. Similar leucine-rich (Leu-Leu motif) repeats are characteristic of a diverse array of soluble and membrane-associated proteins from yeasts to humans but have not been reported previously to reside in nuclear proteins. Several of these proteins, including Toll, chaoptin, RNase/angiogenin inhibitors, lutropin-choriogonadotropin receptor, carboxypeptidase N, adenylyl cyclase, CD14, and human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Rev, may be involved in protein-protein interactions. Our findings suggest that in cell extracts the Leu-Leu motif of A' is required for reconstitution with U2 snRNPs and perhaps with other components involved in splicing through protein-protein interactions.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam S. A., Nakagawa T., Swanson M. S., Woodruff T. K., Dreyfuss G. mRNA polyadenylate-binding protein: gene isolation and sequencing and identification of a ribonucleoprotein consensus sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2932–2943. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black D. L., Chabot B., Steitz J. A. U2 as well as U1 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins are involved in premessenger RNA splicing. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):737–750. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90270-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn P., Wilson G., Moore S. Ribonuclease inhibitor from human placenta. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 25;252(16):5904–5910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branlant C., Krol A., Ebel J. P., Lazar E., Haendler B., Jacob M. U2 RNA shares a structural domain with U1, U4, and U5 RNAs. EMBO J. 1982;1(10):1259–1265. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb00022.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T. H., Clark M. W., Lustig A. J., Cusick M. E., Abelson J. RNA11 protein is associated with the yeast spliceosome and is localized in the periphery of the cell nucleus. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2379–2393. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craft J., Mimori T., Olsen T. L., Hardin J. A. The U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle as an autoantigen. Analysis with sera from patients with overlap syndromes. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jun;81(6):1716–1724. doi: 10.1172/JCI113511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day A. A., McQuillan C. I., Termine J. D., Young M. R. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of the cDNA for small proteoglycan II of bovine bone. Biochem J. 1987 Dec 15;248(3):801–805. doi: 10.1042/bj2480801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabrizio P., McPheeters D. S., Abelson J. In vitro assembly of yeast U6 snRNP: a functional assay. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2137–2150. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeney R. J., Zieve G. W. Nuclear exchange of the U1 and U2 snRNP-specific proteins. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):871–881. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrero E., Goyert S. M. Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the monocyte differentiation antigen, CD14. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 11;16(9):4173–4173. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.9.4173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field J., Xu H. P., Michaeli T., Ballester R., Sass P., Wigler M., Colicelli J. Mutations of the adenylyl cyclase gene that block RAS function in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Science. 1990 Jan 26;247(4941):464–467. doi: 10.1126/science.2405488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher L. W., Termine J. D., Young M. F. Deduced protein sequence of bone small proteoglycan I (biglycan) shows homology with proteoglycan II (decorin) and several nonconnective tissue proteins in a variety of species. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4571–4576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fresco L. D., Kurilla M. G., Keene J. D. Rapid inhibition of processing and assembly of small nuclear ribonucleoproteins after infection with vesicular stomatitis virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1148–1155. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerke V., Steitz J. A. A protein associated with small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles recognizes the 3' splice site of premessenger RNA. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):973–984. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90812-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habets W. J., Sillekens P. T., Hoet M. H., Schalken J. A., Roebroek A. J., Leunissen J. A., van de Ven W. J., van Venrooij W. J. Analysis of a cDNA clone expressing a human autoimmune antigen: full-length sequence of the U2 small nuclear RNA-associated B" antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2421–2425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamm J., van Santen V. L., Spritz R. A., Mattaj I. W. Loop I of U1 small nuclear RNA is the only essential RNA sequence for binding of specific U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4787–4791. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto C., Hudson K. L., Anderson K. V. The Toll gene of Drosophila, required for dorsal-ventral embryonic polarity, appears to encode a transmembrane protein. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):269–279. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90516-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofsteenge J., Kieffer B., Matthies R., Hemmings B. A., Stone S. R. Amino acid sequence of the ribonuclease inhibitor from porcine liver reveals the presence of leucine-rich repeats. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 15;27(23):8537–8544. doi: 10.1021/bi00423a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka T., Broek D., Wigler M. DNA sequence and characterization of the S. cerevisiae gene encoding adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):493–505. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90179-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krusius T., Ruoslahti E. Primary structure of an extracellular matrix proteoglycan core protein deduced from cloned cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7683–7687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurilla M. G., Keene J. D. The leader RNA of vesicular stomatitis virus is bound by a cellular protein reactive with anti-La lupus antibodies. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):837–845. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90541-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee F. S., Auld D. S., Vallee B. L. Tryptophan fluorescence as a probe of placental ribonuclease inhibitor binding to angiogenin. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 10;28(1):219–224. doi: 10.1021/bi00427a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee F. S., Fox E. A., Zhou H. M., Strydom D. J., Vallee B. L. Primary structure of human placental ribonuclease inhibitor. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 15;27(23):8545–8553. doi: 10.1021/bi00423a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee F. S., Shapiro R., Vallee B. L. Tight-binding inhibition of angiogenin and ribonuclease A by placental ribonuclease inhibitor. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 10;28(1):225–230. doi: 10.1021/bi00427a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee F. S., Vallee B. L. Modular mutagenesis of human placental ribonuclease inhibitor, a protein with leucine-rich repeats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1879–1883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lelay-Taha M. N., Reveillaud I., Sri-Widada J., Brunel C., Jeanteur P. RNA-protein organization of U1, U5 and U4-U6 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins in HeLa cells. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jun 5;189(3):519–532. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90321-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A. Antibodies to small nuclear RNAs complexed with proteins are produced by patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5495–5499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liautard J. P., Sri-Widada J., Brunel C., Jeanteur P. Structural organization of ribonucleoproteins containing small nuclear RNAs from HeLa cells. Proteins interact closely with a similar structural domain of U1, U2, U4 and U5 small nuclear RNAs. J Mol Biol. 1982 Dec 15;162(3):623–643. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90392-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez J. A., Chung D. W., Fujikawa K., Hagen F. S., Davie E. W., Roth G. J. The alpha and beta chains of human platelet glycoprotein Ib are both transmembrane proteins containing a leucine-rich amino acid sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2135–2139. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez J. A., Chung D. W., Fujikawa K., Hagen F. S., Papayannopoulou T., Roth G. J. Cloning of the alpha chain of human platelet glycoprotein Ib: a transmembrane protein with homology to leucine-rich alpha 2-glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5615–5619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luhrmann R., Appel B., Bringmann P., Rinke J., Reuter R., Rothe S., Bald R. Isolation and characterization of rabbit anti-m3 2,2,7G antibodies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7103–7113. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutz-Freyermuth C., Keene J. D., Lutz-Reyermuth C. The U1 RNA-binding site of the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (snRNP)-associated A protein suggests a similarity with U2 snRNPs. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2975–2982. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutz-Freyermuth C., Query C. C., Keene J. D. Quantitative determination that one of two potential RNA-binding domains of the A protein component of the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein complex binds with high affinity to stem-loop II of U1 RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6393–6397. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Böhnlein S., Hauber J., Cullen B. R. Functional dissection of the HIV-1 Rev trans-activator--derivation of a trans-dominant repressor of Rev function. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90416-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., De Robertis E. M. Nuclear segregation of U2 snRNA requires binding of specific snRNP proteins. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90314-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., Habets W. J., van Venrooij W. J. Monospecific antibodies reveal details of U2 snRNP structure and interaction between U1 and U2 snRNPs. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):997–1002. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04314.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarland K. C., Sprengel R., Phillips H. S., Köhler M., Rosemblit N., Nikolics K., Segaloff D. L., Seeburg P. H. Lutropin-choriogonadotropin receptor: an unusual member of the G protein-coupled receptor family. Science. 1989 Aug 4;245(4917):494–499. doi: 10.1126/science.2502842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPheeters D. S., Fabrizio P., Abelson J. In vitro reconstitution of functional yeast U2 snRNPs. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2124–2136. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermer B., Felber B. K., Campbell M., Pavlakis G. N. Identification of trans-dominant HIV-1 rev protein mutants by direct transfer of bacterially produced proteins into human cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 25;18(8):2037–2044. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.8.2037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson K. K., Green M. R. Mammalian U2 snRNP has a sequence-specific RNA-binding activity. Genes Dev. 1989 Oct;3(10):1562–1571. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.10.1562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea E. K., Rutkowski R., Kim P. S. Evidence that the leucine zipper is a coiled coil. Science. 1989 Jan 27;243(4890):538–542. doi: 10.1126/science.2911757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldberg A., Antonsson P., Lindblom K., Heinegård D. A collagen-binding 59-kd protein (fibromodulin) is structurally related to the small interstitial proteoglycans PG-S1 and PG-S2 (decorin). EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2601–2604. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08399.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton J. R., Patterson R. J., Pederson T. Reconstitution of the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):4030–4037. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.4030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton J. R., Pederson T. The Mr 70,000 protein of the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle binds to the 5' stem-loop of U1 RNA and interacts with Sm domain proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):747–751. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikielny C. W., Bindereif A., Green M. R. In vitro reconstitution of snRNPs: a reconstituted U4/U6 snRNP participates in splicing complex formation. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):479–487. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Query C. C., Bentley R. C., Keene J. D. A common RNA recognition motif identified within a defined U1 RNA binding domain of the 70K U1 snRNP protein. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):89–101. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90175-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Query C. C., Bentley R. C., Keene J. D. A specific 31-nucleotide domain of U1 RNA directly interacts with the 70K small nuclear ribonucleoprotein component. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4872–4881. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinke R., Krantz D. E., Yen D., Zipursky S. L. Chaoptin, a cell surface glycoprotein required for Drosophila photoreceptor cell morphogenesis, contains a repeat motif found in yeast and human. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):291–301. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90518-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusconi S., Yamamoto K. R. Functional dissection of the hormone and DNA binding activities of the glucocorticoid receptor. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1309–1315. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02369.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Zamore P. D., Green M. R. A factor, U2AF, is required for U2 snRNP binding and splicing complex assembly. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):207–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90509-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherly D., Boelens W., Dathan N. A., van Venrooij W. J., Mattaj I. W. Major determinants of the specificity of interaction between small nuclear ribonucleoproteins U1A and U2B'' and their cognate RNAs. Nature. 1990 Jun 7;345(6275):502–506. doi: 10.1038/345502a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R., Schneider-Scherzer E., Thurnher M., Auer B., Schweiger M. The primary structure of human ribonuclease/angiogenin inhibitor (RAI) discloses a novel highly diversified protein superfamily with a common repetitive module. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4151–4156. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03310.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setoguchi M., Nasu N., Yoshida S., Higuchi Y., Akizuki S., Yamamoto S. Mouse and human CD14 (myeloid cell-specific leucine-rich glycoprotein) primary structure deduced from cDNA clones. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jul 7;1008(2):213–222. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(80)90012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillekens P. T., Beijer R. P., Habets W. J., van Verooij W. J. Molecular cloning of the cDNA for the human U2 snRNA-specific A' protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):1893–1906. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.1893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Takahashi Y., Putnam F. W. Periodicity of leucine and tandem repetition of a 24-amino acid segment in the primary structure of leucine-rich alpha 2-glycoprotein of human serum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1906–1910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan F., Weerasinghe D. K., Skidgel R. A., Tamei H., Kaul R. K., Roninson I. B., Schilling J. W., Erdös E. G. The deduced protein sequence of the human carboxypeptidase N high molecular weight subunit reveals the presence of leucine-rich tandem repeats. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):13–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tazi J., Alibert C., Temsamani J., Reveillaud I., Cathala G., Brunel C., Jeanteur P. A protein that specifically recognizes the 3' splice site of mammalian pre-mRNA introns is associated with a small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):755–766. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90518-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titani K., Takio K., Handa M., Ruggeri Z. M. Amino acid sequence of the von Willebrand factor-binding domain of platelet membrane glycoprotein Ib. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5610–5614. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieben E. D., Madore S. J., Pederson T. Protein binding sites are conserved in U1 small nuclear RNA from insects and mammals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1217–1220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieben E. D., Madore S. J., Pederson T. U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein studied by in vitro assembly. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;96(6):1751–1755. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.6.1751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieve G. W., Sauterer R. A. Cell biology of the snRNP particles. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1990;25(1):1–46. doi: 10.3109/10409239009090604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]