Abstract
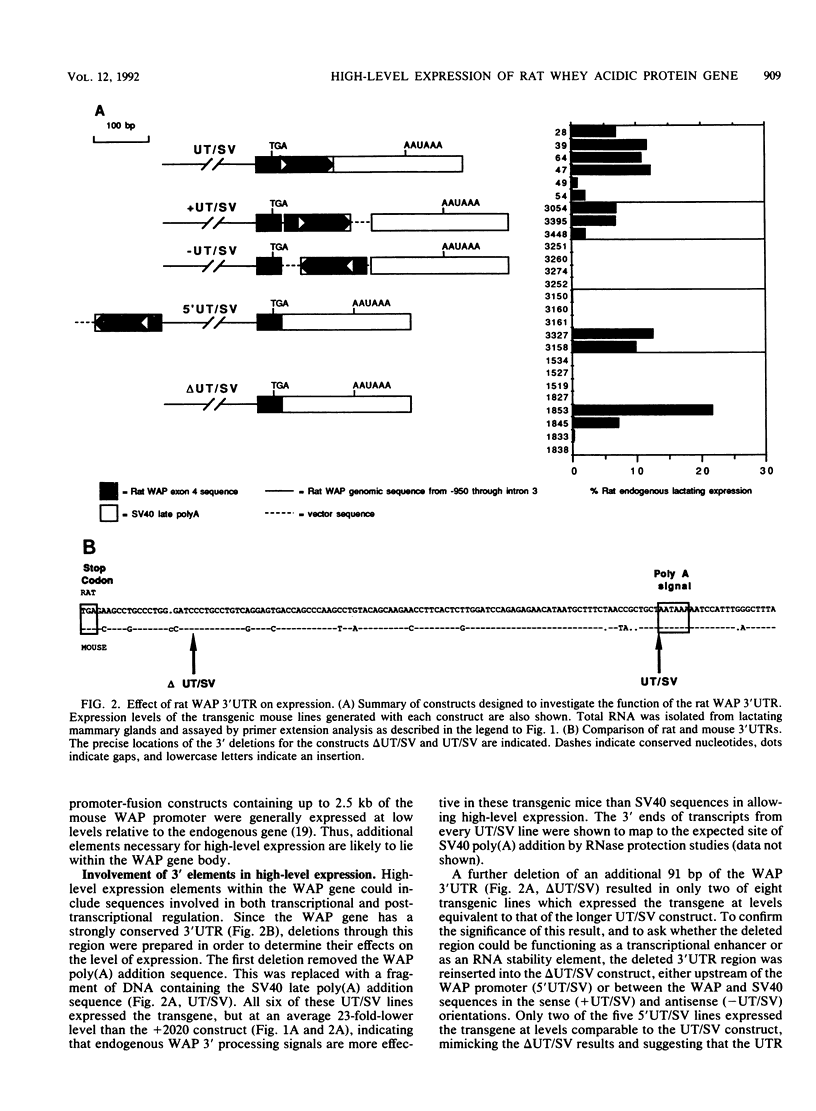
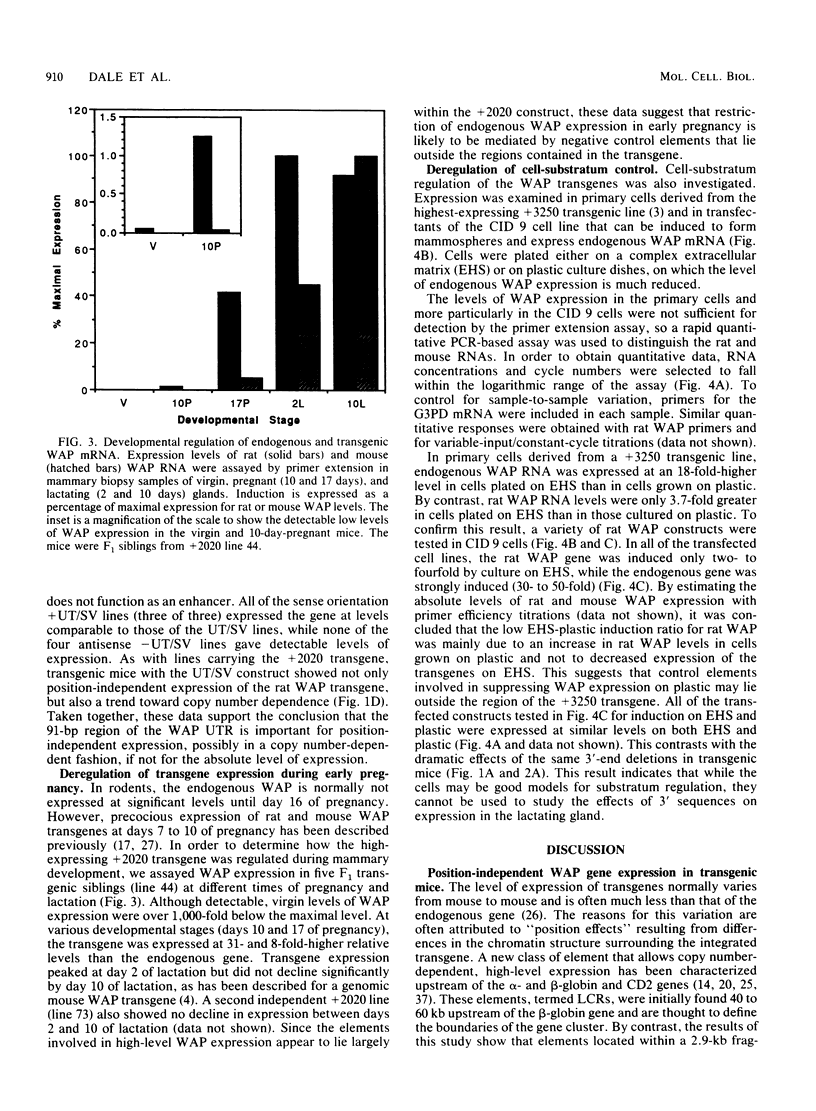
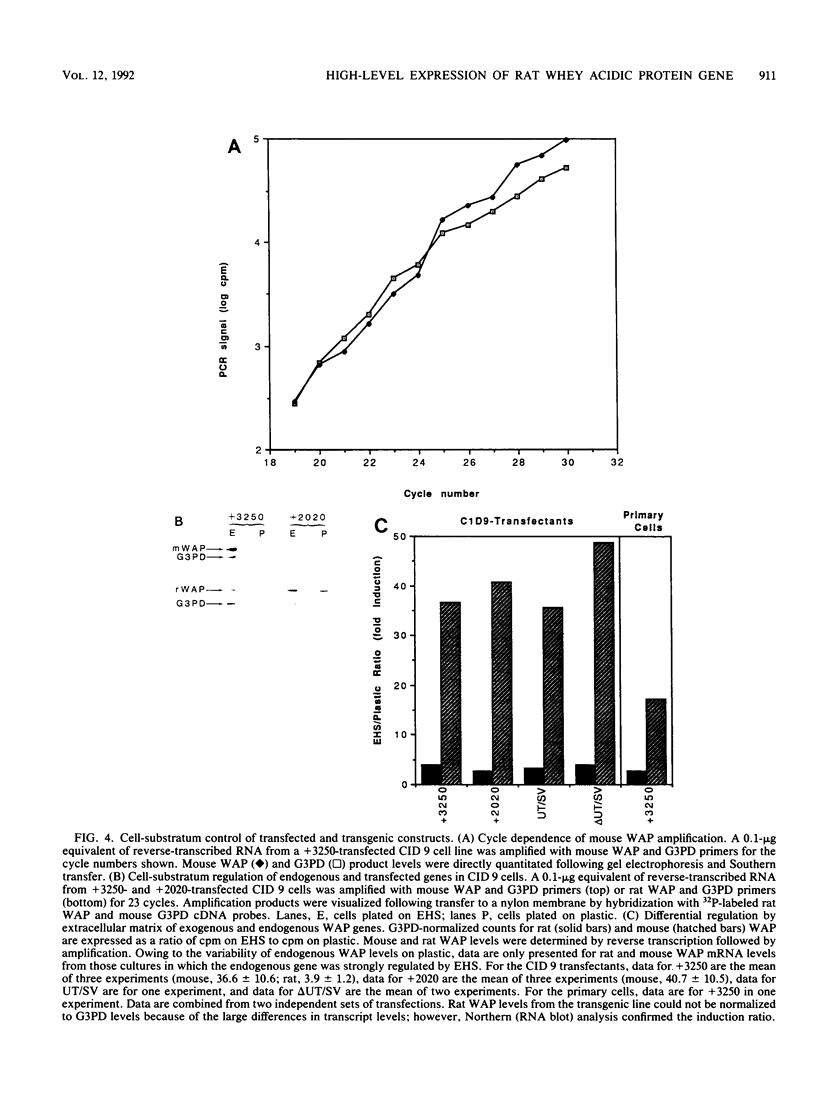
The high-level expression of the rat whey acidic protein (WAP) gene in transgenic mice depends on the interaction of 5'-flanking promoter sequences and intragenic sequences. Constructs containing 949 bp of promoter sequences and only 70 bp of 3'-flanking DNA were expressed at uniformly high levels, comparable to or higher than that of the endogenous gene. Although this WAP transgene was developmentally regulated, it was expressed earlier during pregnancy than was the endogenous WAP gene. Replacement of 3' sequences, including the WAP poly(A) addition site, with simian virus 40 late poly(A) sequences resulted in an approximately 20-fold reduction in the expression of WAP mRNA in the mammary gland during lactation. Nevertheless, position-independent expression of the transgene was still observed. Further deletion of 91 bp of conserved WAP 3' untranslated region (UTR) led to integration site-dependent expression. Position independence was restored following reinsertion of the WAP 3' UTR into the deleted construct at the same location, but only when the insertion was in the sense orientation. The marked differences observed between the expression levels of the 3'-end deletion constructs in transgenic mice were not seen in transfected CID 9 mammary epithelial cells. In these cells, expression of the endogenous WAP gene was dependent on the interaction of these cells with a complex extracellular matrix. In contrast, the transfected WAP constructs were not dependent on extracellular matrix for expression. Thus, both the abnormal expression of WAP in cells cultured on plastic and the precocious developmental expression of WAP in transgenic mice may reflect the absence of a negative control element(s) within these recombinant constructs.
Full text
PDF


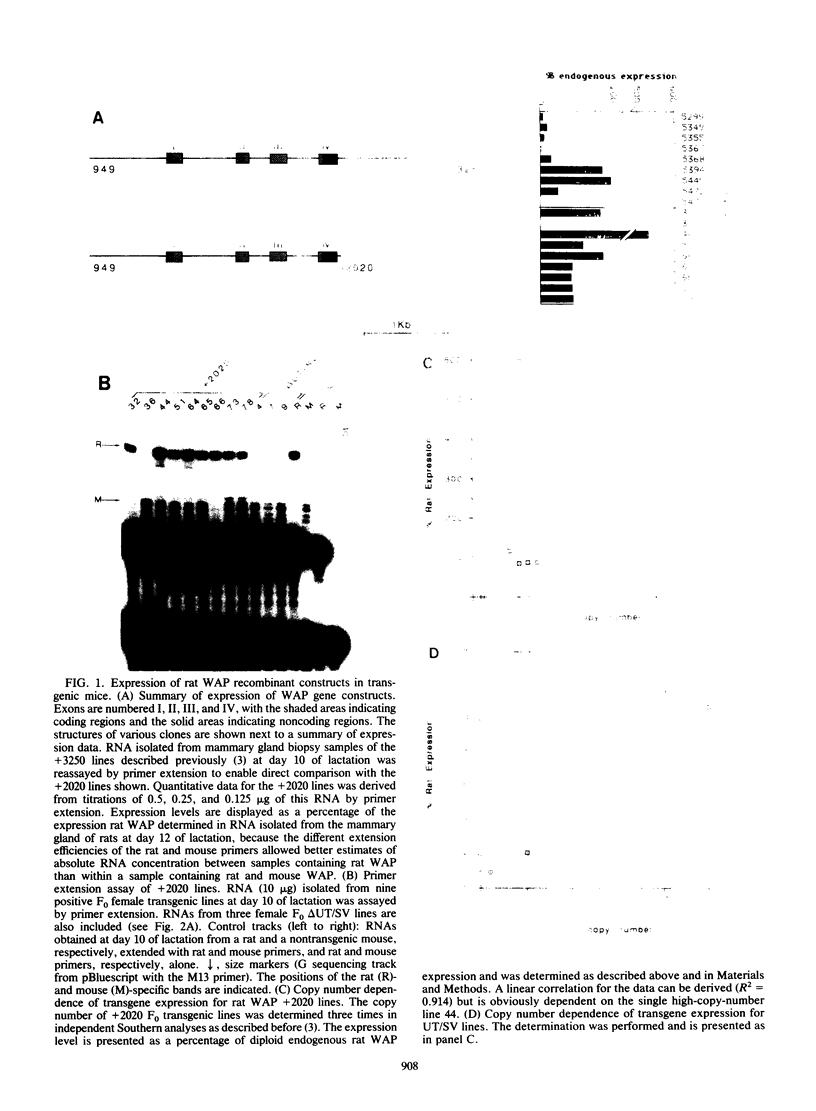



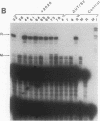
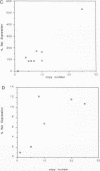
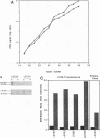
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer T. K., Cordingley M. G., Wolford R. G., Hager G. L. Transcription factor access is mediated by accurately positioned nucleosomes on the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):688–698. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barcellos-Hoff M. H., Aggeler J., Ram T. G., Bissell M. J. Functional differentiation and alveolar morphogenesis of primary mammary cultures on reconstituted basement membrane. Development. 1989 Feb;105(2):223–235. doi: 10.1242/dev.105.2.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayna E. M., Rosen J. M. Tissue-specific, high level expression of the rat whey acidic protein gene in transgenic mice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):2977–2985. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.2977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burdon T., Sankaran L., Wall R. J., Spencer M., Hennighausen L. Expression of a whey acidic protein transgene during mammary development. Evidence for different mechanisms of regulation during pregnancy and lactation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 15;266(11):6909–6914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell S. M., Rosen J. M., Hennighausen L. G., Strech-Jurk U., Sippel A. E. Comparison of the whey acidic protein genes of the rat and mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8685–8697. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. H., Bissell M. J. A novel regulatory mechanism for whey acidic protein gene expression. Cell Regul. 1989 Nov;1(1):45–54. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Yen T. J. Multiple determinants of eukaryotic mRNA stability. New Biol. 1989 Nov;1(2):121–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. The HIV-1 Tat protein: an RNA sequence-specific processivity factor? Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):655–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90129-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielson K. G., Oborn C. J., Durban E. M., Butel J. S., Medina D. Epithelial mouse mammary cell line exhibiting normal morphogenesis in vivo and functional differentiation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3756–3760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves D. R., Wilson F. D., Lang G., Kioussis D. Human CD2 3'-flanking sequences confer high-level, T cell-specific, position-independent gene expression in transgenic mice. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):979–986. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90631-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg N. M., Anderson J. W., Hsueh A. J., Nishimori K., Reeves J. J., deAvila D. M., Ward D. N., Rosen J. M. Expression of biologically active heterodimeric bovine follicle-stimulating hormone in milk of transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8327–8331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F., van Assendelft G. B., Greaves D. R., Kollias G. Position-independent, high-level expression of the human beta-globin gene in transgenic mice. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90584-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Günzburg W. H., Salmons B., Zimmermann B., Müller M., Erfle V., Brem G. A mammary-specific promoter directs expression of growth hormone not only to the mammary gland, but also to Bergman glia cells in transgenic mice. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Jan;5(1):123–133. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-1-123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Position-effect variegation after 60 years. Trends Genet. 1990 Dec;6(12):422–426. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90304-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs D. R., Wood W. G., Jarman A. P., Sharpe J., Lida J., Pretorius I. M., Ayyub H. A major positive regulatory region located far upstream of the human alpha-globin gene locus. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1588–1601. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs A. A., Richards D. A., Kessler D. J., Rosen J. M. Complex hormonal regulation of rat casein gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3598–3605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman H. K., McGarvey M. L., Hassell J. R., Star V. L., Cannon F. B., Laurie G. W., Martin G. R. Basement membrane complexes with biological activity. Biochemistry. 1986 Jan 28;25(2):312–318. doi: 10.1021/bi00350a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E. Y., Lee W. H., Kaetzel C. S., Parry G., Bissell M. J. Interaction of mouse mammary epithelial cells with collagen substrata: regulation of casein gene expression and secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1419–1423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. F., DeMayo F. J., Atiee S. H., Rosen J. M. Tissue-specific expression of the rat beta-casein gene in transgenic mice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1027–1041. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H. Globin gene regulation and switching: circa 1990. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):665–672. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90133-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Germ-line transformation of mice. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:465–499. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.002341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittius C. W., Sankaran L., Topper Y. J., Hennighausen L. Comparison of the regulation of the whey acidic protein gene with that of a hybrid gene containing the whey acidic protein gene promoter in transgenic mice. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Nov;2(11):1027–1032. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-11-1027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitman M., Lee E., Westphal H., Felsenfeld G. Site-independent expression of the chicken beta A-globin gene in transgenic mice. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):749–752. doi: 10.1038/348749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen J. M., Bayna E., Lee K. F. Analysis of milk protein gene expression in transgenic mice. Mol Biol Med. 1989 Dec;6(6):501–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen J. M., Rodgers J. R., Couch C. H., Bisbee C. A., David-Inouye Y., Campbell S. M., Yu-Lee L. Y. Multihormonal regulation of milk protein gene expression. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;478:63–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb15521.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidhauser C., Bissell M. J., Myers C. A., Casperson G. F. Extracellular matrix and hormones transcriptionally regulate bovine beta-casein 5' sequences in stably transfected mouse mammary cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9118–9122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons J. P., McClenaghan M., Clark A. J. Alteration of the quality of milk by expression of sheep beta-lactoglobulin in transgenic mice. Nature. 1987 Aug 6;328(6130):530–532. doi: 10.1038/328530a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweetser D. A., Birkenmeier E. H., Hoppe P. C., McKeel D. W., Gordon J. I. Mechanisms underlying generation of gradients in gene expression within the intestine: an analysis using transgenic mice containing fatty acid binding protein-human growth hormone fusion genes. Genes Dev. 1988 Oct;2(10):1318–1332. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.10.1318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thepot D., Devinoy E., Fontaine M. L., Hubert C., Houdebine L. M. Complete sequence of the rabbit whey acidic protein gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 25;18(12):3641–3641. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.12.3641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townes T. M., Behringer R. R. Human globin locus activation region (LAR): role in temporal control. Trends Genet. 1990 Jul;6(7):219–223. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90182-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilotte J. L., Soulier S., Stinnakre M. G., Massoud M., Mercier J. C. Efficient tissue-specific expression of bovine alpha-lactalbumin in transgenic mice. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Dec 8;186(1-2):43–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]