Abstract
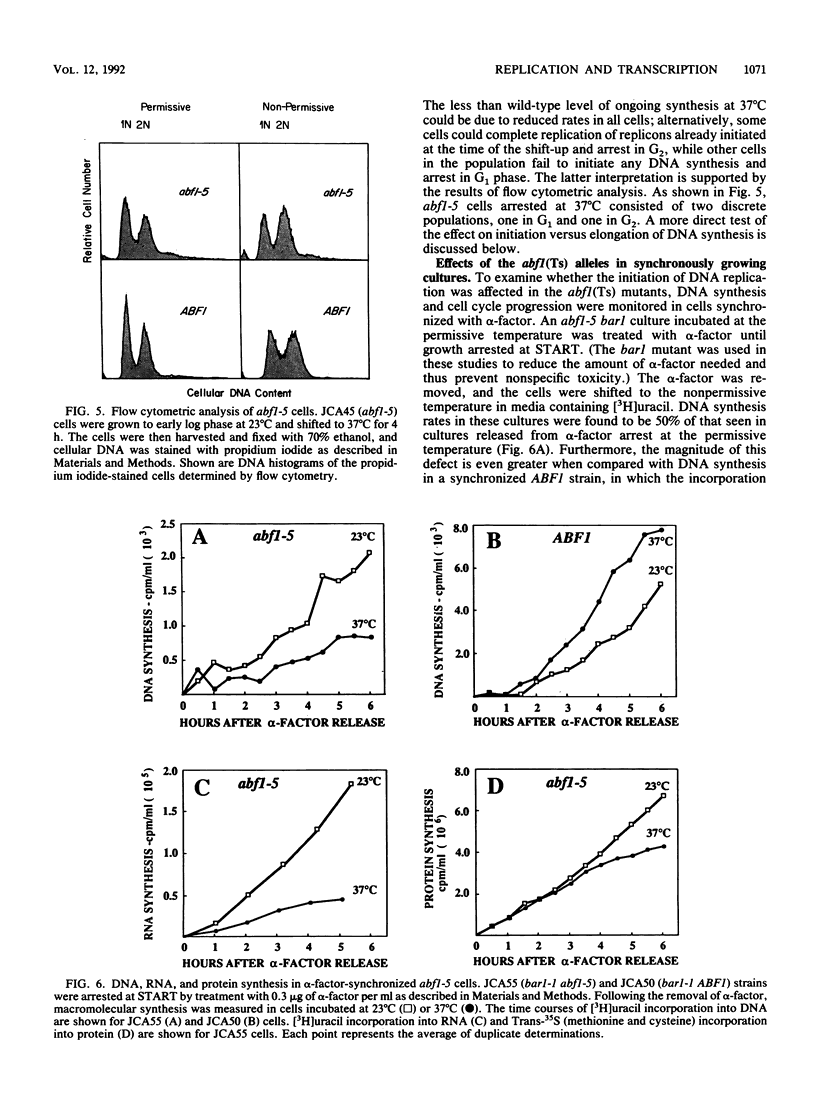
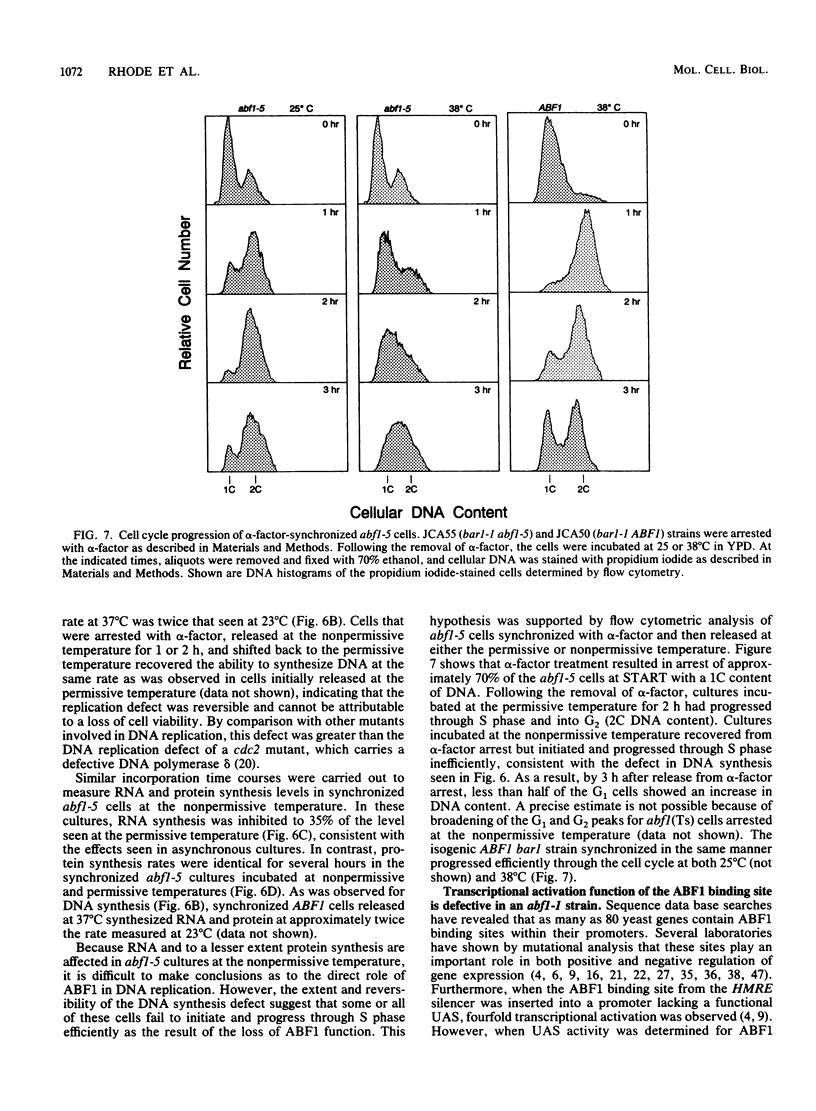
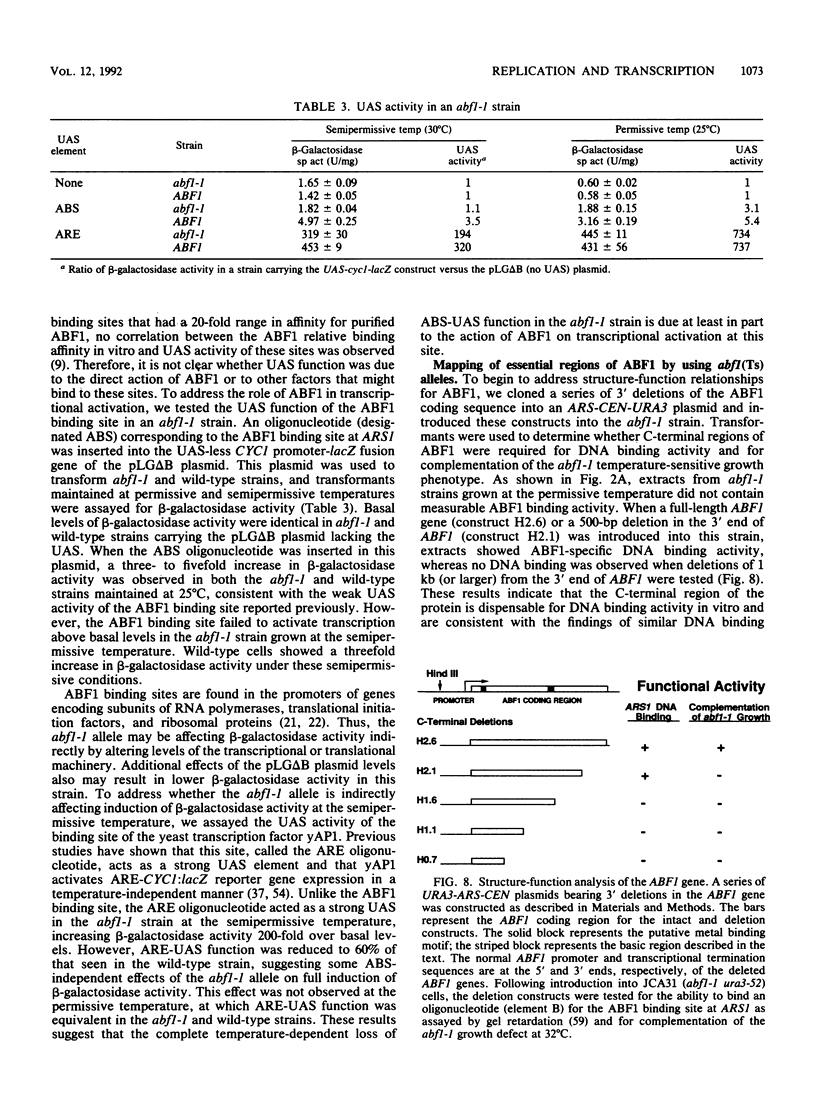
Autonomously replicating sequence (ARS) binding factor 1 (ABF1) is an abundant DNA-binding protein that specifically recognizes the motif RTCRYN5ACG at many sites in the yeast genome, including promoter elements, mating-type silencers, and ARSs. Mutational analysis of these sites suggests that ABF1 is involved in constitutive and carbon source-regulated transcriptional activation, transcriptional silencing, and ARS activity. To better assess the role of ABF1 in DNA replication and transcriptional control, temperature-sensitive lethal mutations in the ABF1 gene were isolated. Several of the abf1(Ts) strains show rapid growth arrest at the nonpermissive temperature. At the semipermissive temperature, these strains show an ARS-specific defect in the mitotic stability of ARS-CEN plasmids, such that the abf1 mutants show defects in ARS function identical to those of mutants bearing the mutations in the cis-acting ABF1 binding sites analyzed previously by numerous investigators. Flow cytometric analysis and in vivo DNA labeling experiments on an alpha-factor synchronized abf1(Ts) strain showed that at the nonpermissive temperature, these cells fail to progress efficiently from G1 through S phase and synthesize DNA at 25% of the level seen in the isogenic ABF1 strain. RNA synthesis is also reduced in the abf1(Ts) strains. In addition, transcriptional activation by an ABF1 binding site upstream activation sequence is completely defective in an abf1(Ts) strain at the semipermissive temperature. These phenotypes provide evidence that the same protein, ABF1, functions in the initiation of DNA replication and transcriptional activation.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bender A., Sprague G. F., Jr MAT alpha 1 protein, a yeast transcription activator, binds synergistically with a second protein to a set of cell-type-specific genes. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):681–691. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90326-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswas E. E., Stefanec M. J., Biswas S. B. Molecular cloning of a gene encoding an ARS binding factor from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6689–6692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouton A. H., Smith M. M. Fine-structure analysis of the DNA sequence requirements for autonomous replication of Saccharomyces cerevisiae plasmids. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2354–2363. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand A. H., Micklem G., Nasmyth K. A yeast silencer contains sequences that can promote autonomous plasmid replication and transcriptional activation. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):709–719. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90094-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer B. J., Fangman W. L. The localization of replication origins on ARS plasmids in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):463–471. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90642-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brindle P. K., Holland J. P., Willett C. E., Innis M. A., Holland M. J. Multiple factors bind the upstream activation sites of the yeast enolase genes ENO1 and ENO2: ABFI protein, like repressor activator protein RAP1, binds cis-acting sequences which modulate repression or activation of transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4872–4885. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broach J. R., Li Y. Y., Feldman J., Jayaram M., Abraham J., Nasmyth K. A., Hicks J. B. Localization and sequence analysis of yeast origins of DNA replication. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):1165–1173. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman A. R., Kimmerly W. J., Rine J., Kornberg R. D. Two DNA-binding factors recognize specific sequences at silencers, upstream activating sequences, autonomously replicating sequences, and telomeres in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):210–225. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budd M. E., Wittrup K. D., Bailey J. E., Campbell J. L. DNA polymerase I is required for premeiotic DNA replication and sporulation but not for X-ray repair in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):365–376. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budd M., Campbell J. L. Temperature-sensitive mutations in the yeast DNA polymerase I gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2838–2842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busby S., Irani M., Crombrugghe B. Isolation of mutant promoters in the Escherichia coli galactose operon using local mutagenesis on cloned DNA fragments. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jan 15;154(2):197–209. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90060-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celniker S. E., Sweder K., Srienc F., Bailey J. E., Campbell J. L. Deletion mutations affecting autonomously replicating sequence ARS1 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2455–2466. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers A., Stanway C., Tsang J. S., Henry Y., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M. ARS binding factor 1 binds adjacent to RAP1 at the UASs of the yeast glycolytic genes PGK and PYK1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 25;18(18):5393–5399. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.18.5393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasman D. I., Lue N. F., Buchman A. R., LaPointe J. W., Lorch Y., Kornberg R. D. A yeast protein that influences the chromatin structure of UASG and functions as a powerful auxiliary gene activator. Genes Dev. 1990 Apr;4(4):503–514. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.4.503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng L., Kelly T. J. Transcriptional activator nuclear factor I stimulates the replication of SV40 minichromosomes in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):541–551. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90037-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christ C., Tye B. K. Functional domains of the yeast transcription/replication factor MCM1. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):751–763. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad M. N., Newlon C. S. Saccharomyces cerevisiae cdc2 mutants fail to replicate approximately one-third of their nuclear genome. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):1000–1012. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.1000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L. Transcriptional elements as components of eukaryotic origins of DNA replication. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):635–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90398-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Della Seta F., Ciafré S. A., Marck C., Santoro B., Presutti C., Sentenac A., Bozzoni I. The ABF1 factor is the transcriptional activator of the L2 ribosomal protein genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2437–2441. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Della Seta F., Treich I., Buhler J. M., Sentenac A. ABF1 binding sites in yeast RNA polymerase genes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):15168–15175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diffley J. F., Stillman B. Purification of a yeast protein that binds to origins of DNA replication and a transcriptional silencer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2120–2124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diffley J. F., Stillman B. Similarity between the transcriptional silencer binding proteins ABF1 and RAP1. Science. 1989 Nov 24;246(4933):1034–1038. doi: 10.1126/science.2511628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolan J. W., Fields S. Overproduction of the yeast STE12 protein leads to constitutive transcriptional induction. Genes Dev. 1990 Apr;4(4):492–502. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.4.492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsman J. C., Gozdzicka-Jozefiak A., van Heeswijk W. C., Grivell L. A. Multi-functional DNA proteins in yeast: the factors GFI and GFII are identical to the ARS-binding factor ABFI and the centromere-binding factor CPF1 respectively. Yeast. 1991 May-Jun;7(4):401–412. doi: 10.1002/yea.320070410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsman J. C., van Heeswijk W. C., Grivell L. A. Identification of two factors which bind to the upstream sequences of a number of nuclear genes coding for mitochondrial proteins and to genetic elements important for cell division in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7287–7301. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Civalier C., Tye B. K. Specific interaction between a Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein and a DNA element associated with certain autonomously replicating sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):743–746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francesconi S. C., Eisenberg S. Purification and characterization of OBF1: a Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein that binds to autonomously replicating sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2906–2913. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francesconi S. C., Eisenberg S. The multifunctional protein OBF1 is phosphorylated at serine and threonine residues in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4089–4093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez C., Guo Z. S., Roberts J., DePamphilis M. L. Simian virus 40 origin auxiliary sequences weakly facilitate T-antigen binding but strongly facilitate DNA unwinding. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1719–1728. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halfter H., Kavety B., Vandekerckhove J., Kiefer F., Gallwitz D. Sequence, expression and mutational analysis of BAF1, a transcriptional activator and ARS1-binding protein of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4265–4272. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08612.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halfter H., Müller U., Winnacker E. L., Gallwitz D. Isolation and DNA-binding characteristics of a protein involved in transcription activation of two divergently transcribed, essential yeast genes. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):3029–3037. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08453.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamil K. G., Nam H. G., Fried H. M. Constitutive transcription of yeast ribosomal protein gene TCM1 is promoted by uncommon cis- and trans-acting elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4328–4341. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harshman K. D., Moye-Rowley W. S., Parker C. S. Transcriptional activation by the SV40 AP-1 recognition element in yeast is mediated by a factor similar to AP-1 that is distinct from GCN4. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):321–330. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90393-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herruer M. H., Mager W. H., Doorenbosch T. M., Wessels P. L., Wassenaar T. M., Planta R. J. The extended promoter of the gene encoding ribosomal protein S33 in yeast consists of multiple protein binding elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7427–7439. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann J. F., Gasser S. M. Identification and purification of a protein that binds the yeast ARS consensus sequence. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):951–960. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90319-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman J. A., Spotila L. D., Nawotka K. A., el-Assouli S. M., Davis L. R. The in vivo replication origin of the yeast 2 microns plasmid. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):473–481. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90643-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman J. A., Zhu J. G., Davis L. R., Newlon C. S. Close association of a DNA replication origin and an ARS element on chromosome III of the yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14A):6373–6384. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.6373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. M., Snyder M., Chang L. M., Davis R. W., Campbell J. L. Isolation of the gene encoding yeast DNA polymerase I. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):369–377. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90042-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. A cellular DNA-binding protein that activates eukaryotic transcription and DNA replication. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90358-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearsey S. Structural requirements for the function of a yeast chromosomal replicator. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):299–307. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90326-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keleher C. A., Passmore S., Johnson A. D. Yeast repressor alpha 2 binds to its operator cooperatively with yeast protein Mcm1. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5228–5230. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmerly W., Buchman A., Kornberg R., Rine J. Roles of two DNA-binding factors in replication, segregation and transcriptional repression mediated by a yeast silencer. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2241–2253. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03064.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kipling D., Tambini C., Kearsey S. E. rar mutations which increase artificial chromosome stability in Saccharomyces cerevisiae identify transcription and recombination proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 11;19(7):1385–1391. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.7.1385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lustig A. J., Kurtz S., Shore D. Involvement of the silencer and UAS binding protein RAP1 in regulation of telomere length. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):549–553. doi: 10.1126/science.2237406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maine G. T., Sinha P., Tye B. K. Mutants of S. cerevisiae defective in the maintenance of minichromosomes. Genetics. 1984 Mar;106(3):365–385. doi: 10.1093/genetics/106.3.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohr I. J., Clark R., Sun S., Androphy E. J., MacPherson P., Botchan M. R. Targeting the E1 replication protein to the papillomavirus origin of replication by complex formation with the E2 transactivator. Science. 1990 Dec 21;250(4988):1694–1699. doi: 10.1126/science.2176744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow B. E., Johnson S. P., Warner J. R. Proteins that bind to the yeast rDNA enhancer. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):9061–9068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieto-Sotelo J., Wiederrecht G., Okuda A., Parker C. S. The yeast heat shock transcription factor contains a transcriptional activation domain whose activity is repressed under nonshock conditions. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):807–817. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90124-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill E. A., Fletcher C., Burrow C. R., Heintz N., Roeder R. G., Kelly T. J. Transcription factor OTF-1 is functionally identical to the DNA replication factor NF-III. Science. 1988 Sep 2;241(4870):1210–1213. doi: 10.1126/science.3413485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palzkill T. G., Newlon C. S. A yeast replication origin consists of multiple copies of a small conserved sequence. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):441–450. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90164-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passmore S., Maine G. T., Elble R., Christ C., Tye B. K. Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein involved in plasmid maintenance is necessary for mating of MAT alpha cells. J Mol Biol. 1988 Dec 5;204(3):593–606. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90358-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhode P. R., Sweder K. S., Oegema K. F., Campbell J. L. The gene encoding ARS-binding factor I is essential for the viability of yeast. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12A):1926–1939. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12a.1926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt A. M., Herterich S. U., Krauss G. A single-stranded DNA binding protein from S. cerevisiae specifically recognizes the T-rich strand of the core sequence of ARS elements and discriminates against mutant sequences. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):981–985. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08032.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore D., Nasmyth K. Purification and cloning of a DNA binding protein from yeast that binds to both silencer and activator elements. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90095-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore D., Stillman D. J., Brand A. H., Nasmyth K. A. Identification of silencer binding proteins from yeast: possible roles in SIR control and DNA replication. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):461–467. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04776.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T. Nucleosome positioning can affect the function of a cis-acting DNA element in vivo. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):387–389. doi: 10.1038/343387a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M., Buchman A. R., Davis R. W. Bent DNA at a yeast autonomously replicating sequence. Nature. 1986 Nov 6;324(6092):87–89. doi: 10.1038/324087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srienc F., Bailey J. E., Campbell J. L. Effect of ARS1 mutations on chromosome stability in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1676–1684. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strich R., Woontner M., Scott J. F. Mutations in ARS1 increase the rate of simple loss of plasmids in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast. 1986 Sep;2(3):169–178. doi: 10.1002/yea.320020305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweder K. S., Rhode P. R., Campbell J. L. Purification and characterization of proteins that bind to yeast ARSs. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17270–17277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoma F., Bergman L. W., Simpson R. T. Nuclease digestion of circular TRP1ARS1 chromatin reveals positioned nucleosomes separated by nuclease-sensitive regions. J Mol Biol. 1984 Aug 25;177(4):715–733. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umek R. M., Kowalski D. Yeast regulatory sequences preferentially adopt a non-B conformation in supercoiled DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 11;15(11):4467–4480. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.11.4467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker S. S., Francesconi S. C., Eisenberg S. A DNA replication enhancer in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4665–4669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker S. S., Francesconi S. C., Tye B. K., Eisenberg S. The OBF1 protein and its DNA-binding site are important for the function of an autonomously replicating sequence in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2914–2921. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. S., Eckdahl T. T., Anderson J. N. Bent DNA functions as a replication enhancer in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2763–2769. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]