Abstract
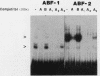
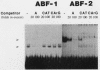
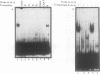
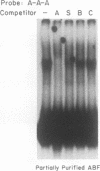
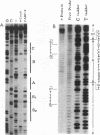
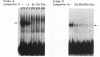
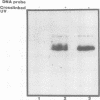
The cardiac myosin light chain-2 (MLC-2) gene promoter contains several positive and negative cis-acting sequences that are involved in the regulation of its expression. We describe here the properties of two activator sequences, elements A and P, and their DNA-binding factors (ABFs). Element A (CCAAAAGTGG), located at -61, has homology with the evolutionarily conserved sequence CC(A/T)6GG, present in the genes of many contractile proteins. Element P (TAACCTTGAAAGC), located 114 bp upstream of element A, is conserved in both chicken and rat cardiac MLC-2 gene promoters. Deletion mutagenesis demonstrated that these two elements are involved in the positive regulation of MLC-2 gene transcription. At least two sequence-specific element A-binding proteins, ABF-1 and ABF-2, were identified by gel shift analysis of the fractionated cardiac nuclear proteins. ABF-1 binds to element A with strict dependence on the internal element A sequence AAAAGT. In contrast, ABF-2 exhibits a relaxed sequence requirement, as it recognizes the consensus CArG and CCAAT box sequences as well. ABF-2 also recognizes the distal element P despite the fact that the sequences of elements A and P are divergent. DNase I footprinting, methylation interference, and gel shift analyses demonstrated unequivocally that the element A-DNA affinity-purified protein ABF-2 binds to element P with sequence specificity. Since both elements A and P play a positive regulatory role in MLC-2 gene transcription and bind to a single protein (ABF-2), it would appear that ABF-2 is a key transcription factor with the ability to recognize divergent sequence elements involved in a common regulatory pathway during myogenesis.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barberis A., Superti-Furga G., Busslinger M. Mutually exclusive interaction of the CCAAT-binding factor and of a displacement protein with overlapping sequences of a histone gene promoter. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):347–359. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90489-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Buschhausen-Denker G., Bober E., Tannich E., Arnold H. H. A novel human muscle factor related to but distinct from MyoD1 induces myogenic conversion in 10T1/2 fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):701–709. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03429.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Tannich E., Buschhausen-Denker G., Arnold H. H. Promoter upstream elements of the chicken cardiac myosin light-chain 2-A gene interact with trans-acting regulatory factors for muscle-specific transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2513–2525. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M., Lin Y. S., Green M. R., Ptashne M. A mechanism for synergistic activation of a mammalian gene by GAL4 derivatives. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):361–364. doi: 10.1038/345361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M. Mechanistic advances in eukaryotic gene activation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;3(3):452–460. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler V. L., Maler B. A., Yamamoto K. R. DNA sequences bound specifically by glucocorticoid receptor in vitro render a heterologous promoter hormone responsive in vivo. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):489–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90430-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Grayson D. R., Xanthopoulos K. G., Darnell J. E., Jr A liver-specific DNA-binding protein recognizes multiple nucleotide sites in regulatory regions of transthyretin, alpha 1-antitrypsin, albumin, and simian virus 40 genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3840–3844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Cheng P. F., Lassar A. B., Weintraub H. The MyoD DNA binding domain contains a recognition code for muscle-specific gene activation. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):733–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90088-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desplan C., Theis J., O'Farrell P. H. The sequence specificity of homeodomain-DNA interaction. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1081–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90123-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn A., Bollekens J., Staub A., Benoist C., Mathis D. A multiplicity of CCAAT box-binding proteins. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):863–872. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90513-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson D. G., Olson E. N. A gene with homology to the myc similarity region of MyoD1 is expressed during myogenesis and is sufficient to activate the muscle differentiation program. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):628–640. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstratiadis A., Posakony J. W., Maniatis T., Lawn R. M., O'Connell C., Spritz R. A., DeRiel J. K., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M., Slightom J. L. The structure and evolution of the human beta-globin gene family. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):653–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90429-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson C. P., Jr, Bernstein S. I. Molecular genetics of myosin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:695–726. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C. K., Holloway J. M., Devary O. V., Rosenfeld M. G. The thyroid hormone receptor binds with opposite transcriptional effects to a common sequence motif in thyroid hormone and estrogen response elements. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):313–323. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90194-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossett L. A., Kelvin D. J., Sternberg E. A., Olson E. N. A new myocyte-specific enhancer-binding factor that recognizes a conserved element associated with multiple muscle-specific genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5022–5033. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson T. A., Kedes L. Identification of multiple proteins that interact with functional regions of the human cardiac alpha-actin promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3269–3283. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson S. A., Spencer M., Sen A., Kumar C., Siddiqui M. A., Chien K. R. Structure, organization, and expression of the rat cardiac myosin light chain-2 gene. Identification of a 250-base pair fragment which confers cardiac-specific expression. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):18142–18148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Tjian R. Affinity purification of sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5889–5893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kageyama R., Pastan I. Molecular cloning and characterization of a human DNA binding factor that represses transcription. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):815–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90605-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimes B. W., Brandt B. L. Properties of a clonal muscle cell line from rat heart. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Mar 15;98(2):367–381. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90447-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landolfi N. F., Capra J. D., Tucker P. W. Protein-nucleotide contacts in the immunoglobulin heavy-chain promoter region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3851–3855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Carey M., Ptashne M., Green M. R. How different eukaryotic transcriptional activators can cooperate promiscuously. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):359–361. doi: 10.1038/345359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mar J. H., Ordahl C. P. M-CAT binding factor, a novel trans-acting factor governing muscle-specific transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4271–4283. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S., Tjian R. Transcriptional selectivity of viral genes in mammalian cells. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):795–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A., Kedes L. Upstream regions of the human cardiac actin gene that modulate its transcription in muscle cells: presence of an evolutionarily conserved repeated motif. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2125–2136. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwa T., Kedes L. Duplicated CArG box domains have positive and mutually dependent regulatory roles in expression of the human alpha-cardiac actin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2803–2813. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohun T. J., Taylor M. V., Garrett N., Gurdon J. B. The CArG promoter sequence is necessary for muscle-specific transcription of the cardiac actin gene in Xenopus embryos. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1153–1161. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03486.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ordahl C. P., Cooper T. A. Strong homology in promoter and 3'-untranslated regions of chick and rat alpha-actin genes. Nature. 1983 May 26;303(5915):348–349. doi: 10.1038/303348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer K., Prezant T., Guarente L. Yeast HAP1 activator binds to two upstream activation sites of different sequence. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90751-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez J. F., Rodriguez D., Rodriguez J. R., McGowan E. B., Esteban M. Expression of the firefly luciferase gene in vaccinia virus: a highly sensitive gene marker to follow virus dissemination in tissues of infected animals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1667–1671. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal N. Muscle cell differentiation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;1(6):1094–1101. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(89)80056-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro C., Mermod N., Andrews P. C., Tjian R. A family of human CCAAT-box-binding proteins active in transcription and DNA replication: cloning and expression of multiple cDNAs. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):218–224. doi: 10.1038/334218a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassoon D., Lyons G., Wright W. E., Lin V., Lassar A., Weintraub H., Buckingham M. Expression of two myogenic regulatory factors myogenin and MyoD1 during mouse embryogenesis. Nature. 1989 Sep 28;341(6240):303–307. doi: 10.1038/341303a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen R. A., Goswami S. K., Mascareno E., Kumar A., Siddiqui M. A. Tissue-specific transcription of the cardiac myosin light-chain 2 gene is regulated by an upstream repressor element. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1676–1685. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. W., Sawadogo M. DNA-binding and transcriptional properties of human transcription factor TFIID after mild proteolysis. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3415–3420. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh K., Schimmel P. Two nuclear factors compete for the skeletal muscle actin promoter. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9429–9432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R. Steroid receptor regulated transcription of specific genes and gene networks. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:209–252. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.001233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarraga A. M., Danishefsky K., Deshpande A., Nicholson D., Mendola C., Siddiqui M. A. Characterization of 5'-flanking region of heart myosin light chain 2A gene. Structural and functional evidence for promoter activity. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 15;261(29):13852–13860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]