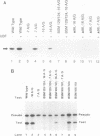
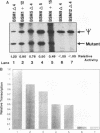
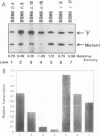
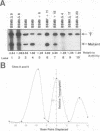
Abstract
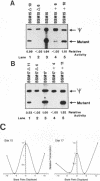
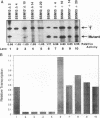
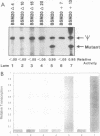
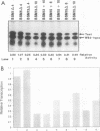
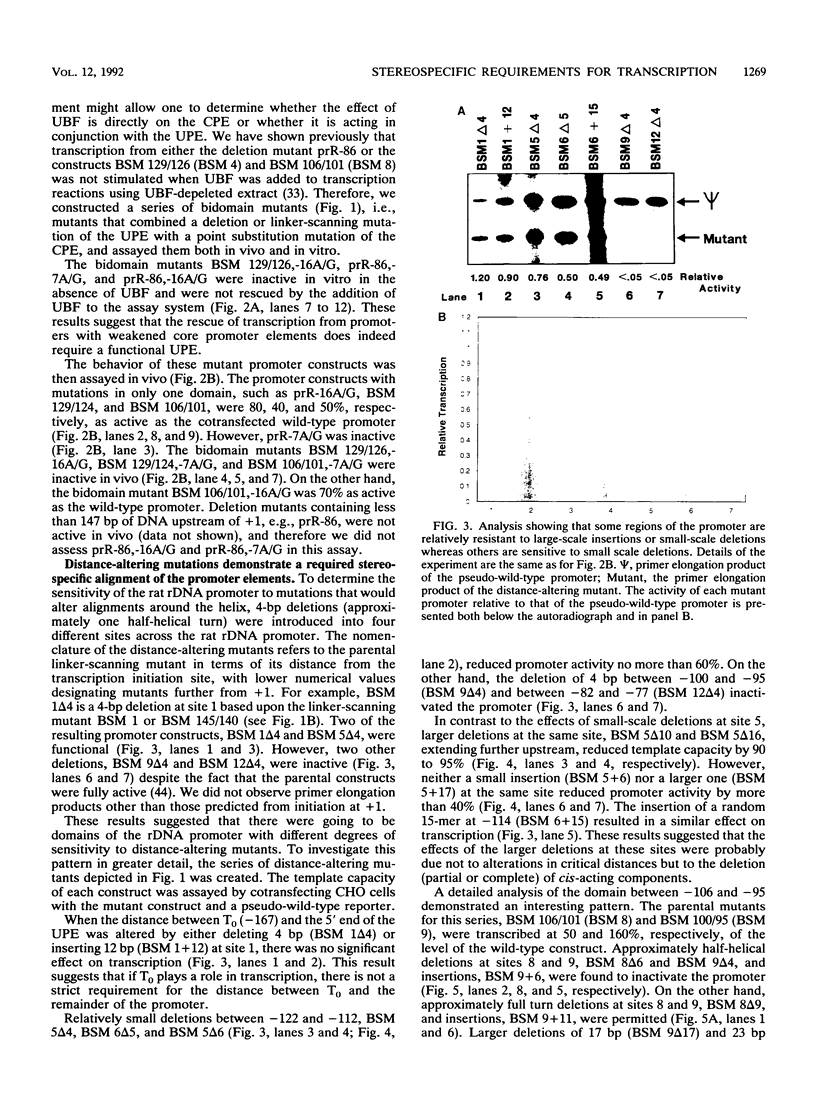
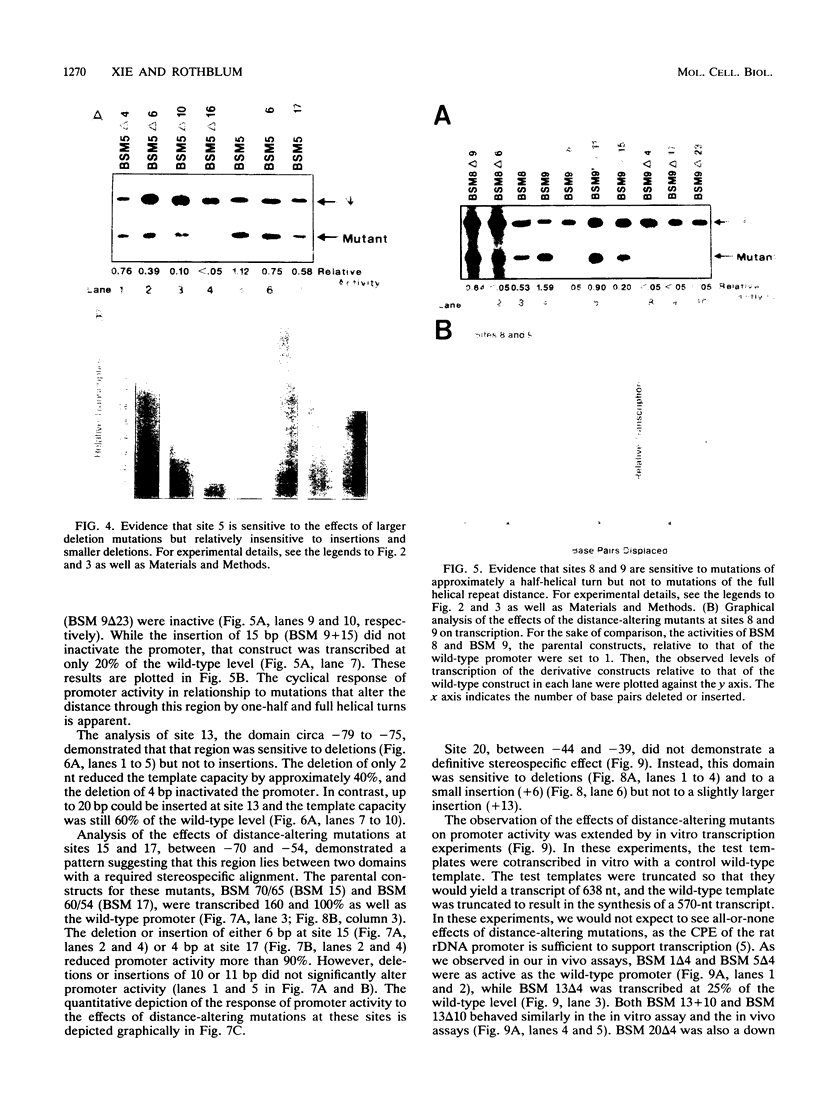
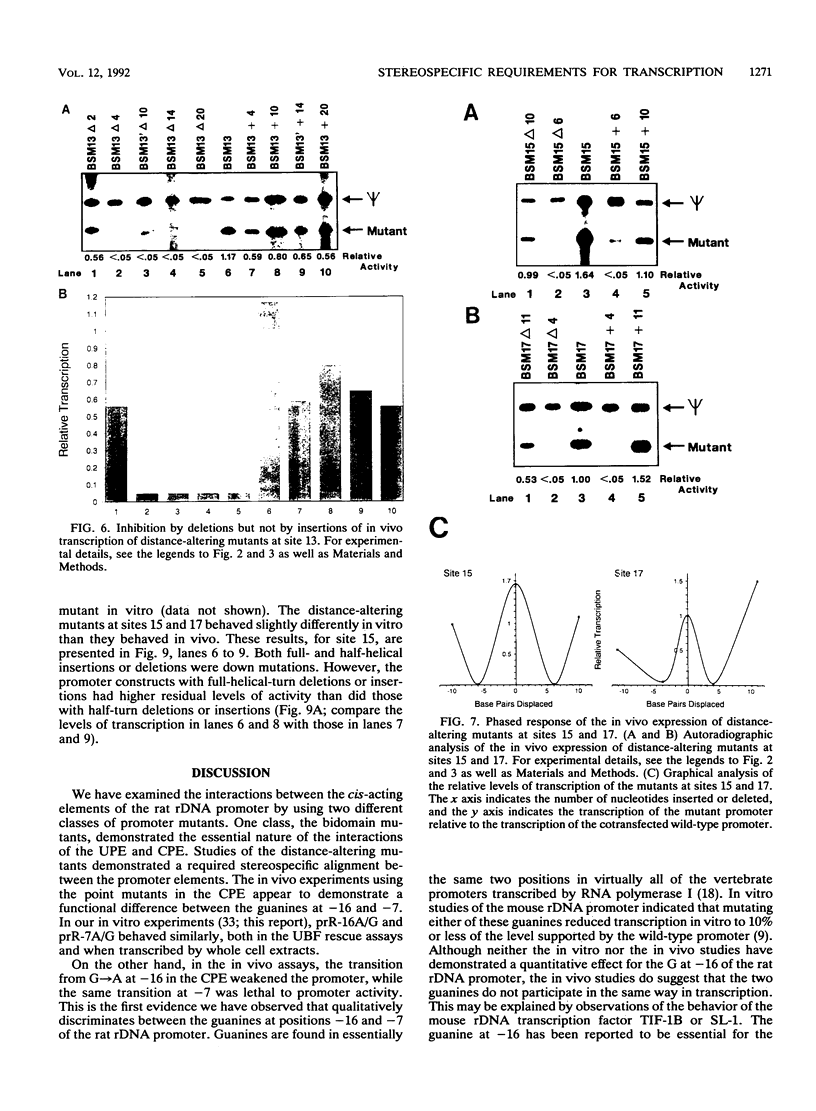
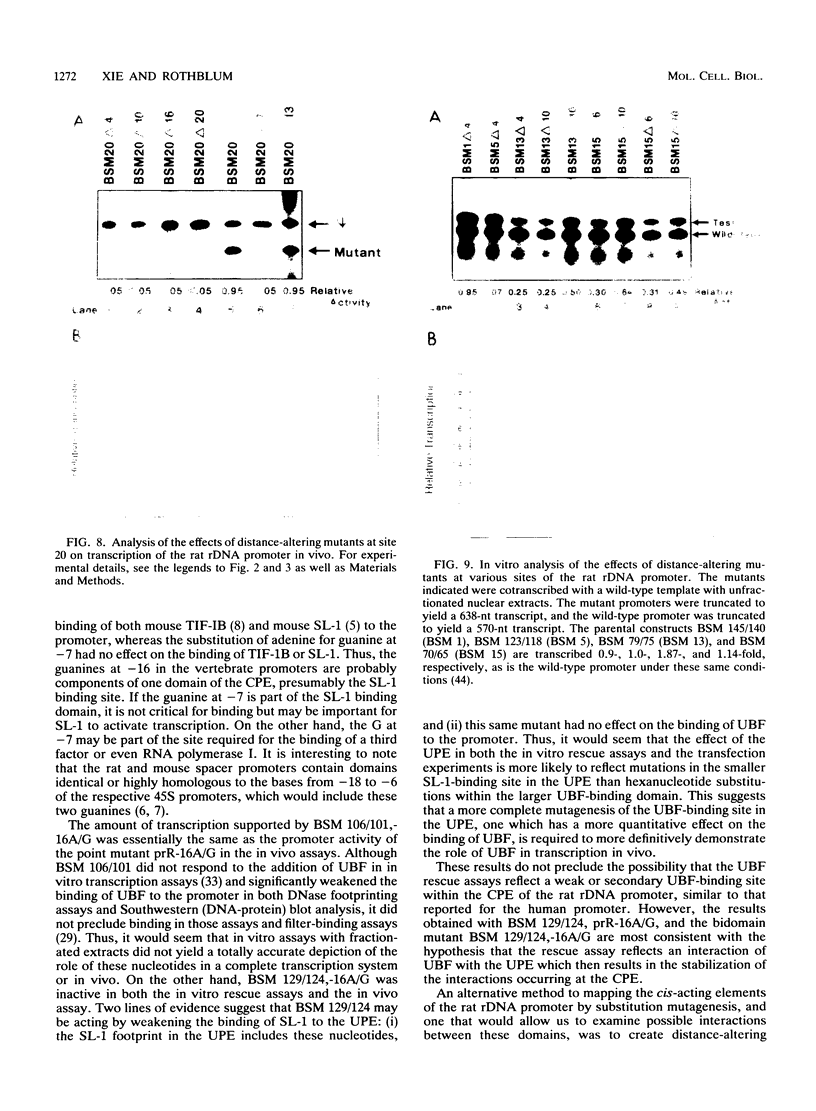
Efficient transcription from the rat rDNA promoter results from an undefined interaction between the core (CPE) and upstream (UPE) promoter elements or the protein complexes which form on them. These interactions were demonstrated by the behavior of promoters that contained either linker-scanning or deletion mutations of the UPE in combination with point mutations of the CPE (bidomain mutants). In vivo transcription experiments using point mutations within the CPE (G----A mutation at either -16 or -7) demonstrated that the CPE may in fact consist of two domains. Whereas both of these mutants were rescued by the addition of UBF to in vitro transcription reactions, the CPE mutant -7A/G was inactive in vivo. Experiments with these bidomain mutants demonstrated that the UPE was required for the rescue of the CPE mutants. We also examined the hypothesis that this interaction might require a stereospecific alignment of the promoter elements. Our results indicate that the promoter consists of several domains with differing responses to mutations that alter the distance between, or within, the promoter elements. For example, the insertion or deletion of half-multiples of the helical repeat distance between -167 and -147 had no significant effect on transcription. On the other hand, some sites were sensitive to deletions of any size but not to insertions of up to 20 bp. The analyses of two sites yielded results suggesting that they lay between domains of the promoter that must be on the same side of the DNA helix for promoter activity. The first of these sites mapped between -106 and -95.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bateman E., Paule M. R. Promoter occlusion during ribosomal RNA transcription. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):985–992. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90113-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell S. P., Jantzen H. M., Tjian R. Assembly of alternative multiprotein complexes directs rRNA promoter selectivity. Genes Dev. 1990 Jun;4(6):943–954. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.6.943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell S. P., Learned R. M., Jantzen H. M., Tjian R. Functional cooperativity between transcription factors UBF1 and SL1 mediates human ribosomal RNA synthesis. Science. 1988 Sep 2;241(4870):1192–1197. doi: 10.1126/science.3413483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy B. G., Yang-Yen H. F., Rothblum L. I. Additional RNA polymerase I initiation site within the nontranscribed spacer region of the rat rRNA gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2388–2396. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy B., Haglund R., Rothblum L. I. Regions upstream from the core promoter of the rat ribosomal gene are required for the formation of a stable transcription initiation complex by RNA polymerase I in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jul 14;909(2):133–144. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(87)90035-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow K. L., Hogan M. E., Schwartz R. J. Phased cis-acting promoter elements interact at short distances to direct avian skeletal alpha-actin gene transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1301–1305. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dandanell G., Hammer K. Two operator sites separated by 599 base pairs are required for deoR repression of the deo operon of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3333–3338. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04085.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn T. M., Hahn S., Ogden S., Schleif R. F. An operator at -280 base pairs that is required for repression of araBAD operon promoter: addition of DNA helical turns between the operator and promoter cyclically hinders repression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5017–5020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaston K., Bell A., Kolb A., Buc H., Busby S. Stringent spacing requirements for transcription activation by CRP. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):733–743. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiduschek E. P., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Transcription by RNA polymerase III. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:873–914. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Kuhn A., Bartsch I., Rosenbauer H. A transcription terminator located upstream of the mouse rDNA initiation site affects rRNA synthesis. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):901–911. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90805-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haglund R. E., Rothblum L. I. Isolation, fractionation and reconstitution of a nuclear extract capable of transcribing ribosomal DNA. Mol Cell Biochem. 1987 Jan;73(1):11–20. doi: 10.1007/BF00229371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haltiner M. M., Smale S. T., Tjian R. Two distinct promoter elements in the human rRNA gene identified by linker scanning mutagenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):227–235. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson S. L., Ryan K., Sollner-Webb B. The promoter-proximal rDNA terminator augments initiation by preventing disruption of the stable transcription complex caused by polymerase read-in. Genes Dev. 1989 Feb;3(2):212–223. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.2.212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson S. L., Sollner-Webb B. The mouse ribosomal DNA promoter has more stringent requirements in vivo than in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4970–4973. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson S., Sollner-Webb B. A transcriptional terminator is a novel element of the promoter of the mouse ribosomal RNA gene. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):891–900. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90804-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochschild A., Ptashne M. Cooperative binding of lambda repressors to sites separated by integral turns of the DNA helix. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):681–687. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90833-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M. H., Learned R. M., Tjian R. Analysis of clustered point mutations in the human ribosomal RNA gene promoter by transient expression in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):669–673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kownin P., Bateman E., Paule M. R. Eukaryotic RNA polymerase I promoter binding is directed by protein contacts with transcription initiation factor and is DNA sequence-independent. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):693–699. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90327-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Learned R. M., Cordes S., Tjian R. Purification and characterization of a transcription factor that confers promoter specificity to human RNA polymerase I. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1358–1369. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Learned R. M., Learned T. K., Haltiner M. M., Tjian R. T. Human rRNA transcription is modulated by the coordinate binding of two factors to an upstream control element. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):847–857. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90559-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majumdar A., Adhya S. Demonstration of two operator elements in gal: in vitro repressor binding studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6100–6104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McStay B., Reeder R. H. A termination site for Xenopus RNA polymerase I also acts as an element of an adjacent promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):913–920. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90806-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McStay B., Reeder R. H. An RNA polymerase I termination site can stimulate the adjacent ribosomal gene promoter by two distinct mechanisms in Xenopus laevis. Genes Dev. 1990 Jul;4(7):1240–1251. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.7.1240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miesfeld R., Arnheim N. Species-specific rDNA transcription is due to promoter-specific binding factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;4(2):221–227. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.2.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishima Y., Financsek I., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Fractionation and reconstitution of factors required for accurate transcription of mammalian ribosomal RNA genes: identification of a species-dependent initiation factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6659–6670. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pape L. K., Windle J. J., Sollner-Webb B. Half helical turn spacing changes convert a frog into a mouse rDNA promoter: a distant upstream domain determines the helix face of the initiation site. Genes Dev. 1990 Jan;4(1):52–62. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.1.52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H., Pennock D., McStay B., Roan J., Tolentino E., Walker P. Linker scanner mutagenesis of the Xenopus laevis ribosomal gene promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 25;15(18):7429–7441. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.18.7429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothblum L. I., Reddy R., Cassidy B. Transcription initiation site of rat ribosomal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7345–7362. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Tjian R. Transcription of herpes simplex virus tk sequences under the control of wild-type and mutant human RNA polymerase I promoters. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):352–362. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. D., Oriahi E., Lowe D., Yang-Yen H. F., O'Mahony D., Rose K., Chen K., Rothblum L. I. Characterization of factors that direct transcription of rat ribosomal DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3105–3116. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. D., Oriahi E., Yang-Yen H. F., Xie W. Q., Chen C., Rothblum L. I. Interaction of RNA polymerase I transcription factors with a promoter in the nontranscribed spacer of rat ribosomal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 11;18(7):1677–1685. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.7.1677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Vigneron M., Matthes H., Wildeman A., Zenke M., Chambon P. Requirement of stereospecific alignments for initiation from the simian virus 40 early promoter. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):121–126. doi: 10.1038/319121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tower J., Culotta V. C., Sollner-Webb B. Factors and nucleotide sequences that direct ribosomal DNA transcription and their relationship to the stable transcription complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3451–3462. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unterberg C., Börchers T., Højrup P., Roepstorff P., Knudsen J., Spener F. Cardiac fatty acid-binding proteins. Isolation and characterization of the mitochondrial fatty acid-binding protein and its structural relationship with the cytosolic isoforms. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16255–16261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windle J. J., Sollner-Webb B. Two distant and precisely positioned domains promote transcription of Xenopus laevis rRNA genes: analysis with linker-scanning mutants. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4585–4593. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L., Berk A. Constraints on spacing between transcription factor binding sites in a simple adenovirus promoter. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):403–411. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie W. Q., O'Mahony D. J., Smith S. D., Rothblum L. Complementary in vivo and in vitro analyses of the interactions between the cis-acting elements of the rat rDNA promoter. 1991 May 29-Jun 12Mol Cell Biochem. 104(1-2):127–135. doi: 10.1007/BF00229812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zehring W. A., Greenleaf A. L. The carboxyl-terminal repeat domain of RNA polymerase II is not required for transcription factor Sp1 to function in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8351–8353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]