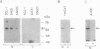Abstract
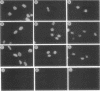
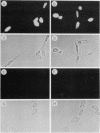
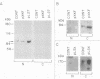
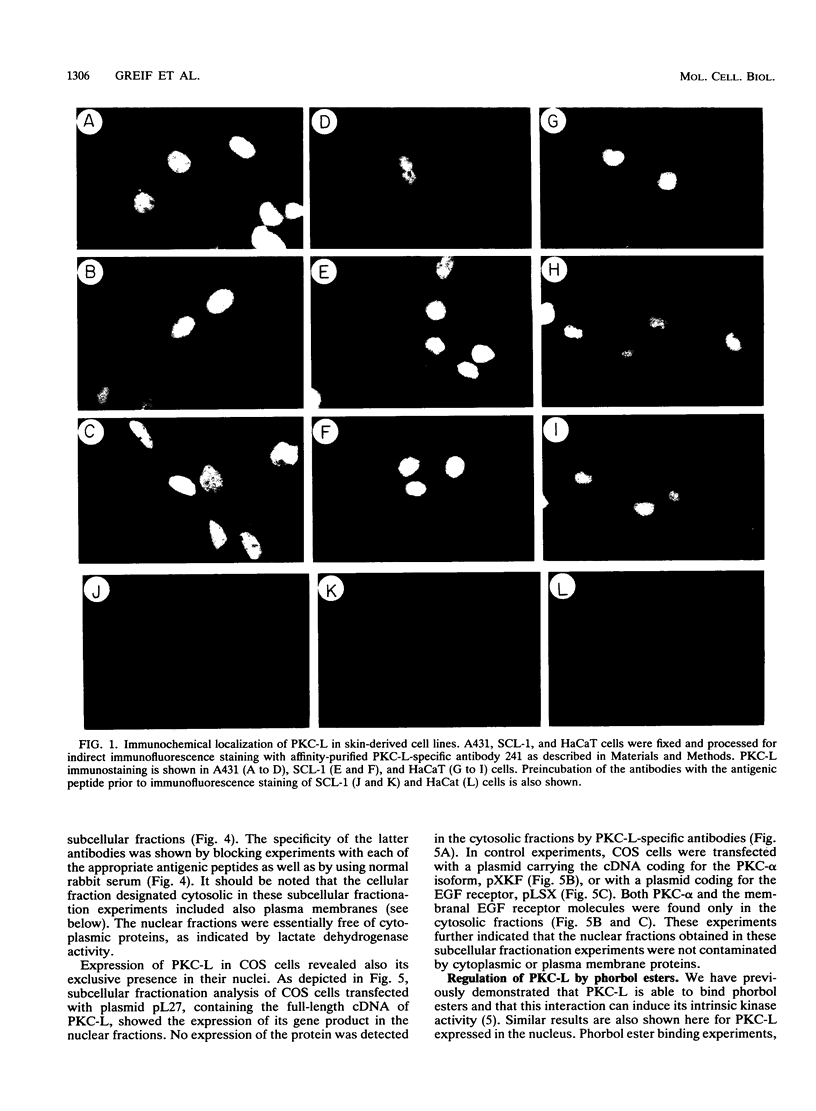
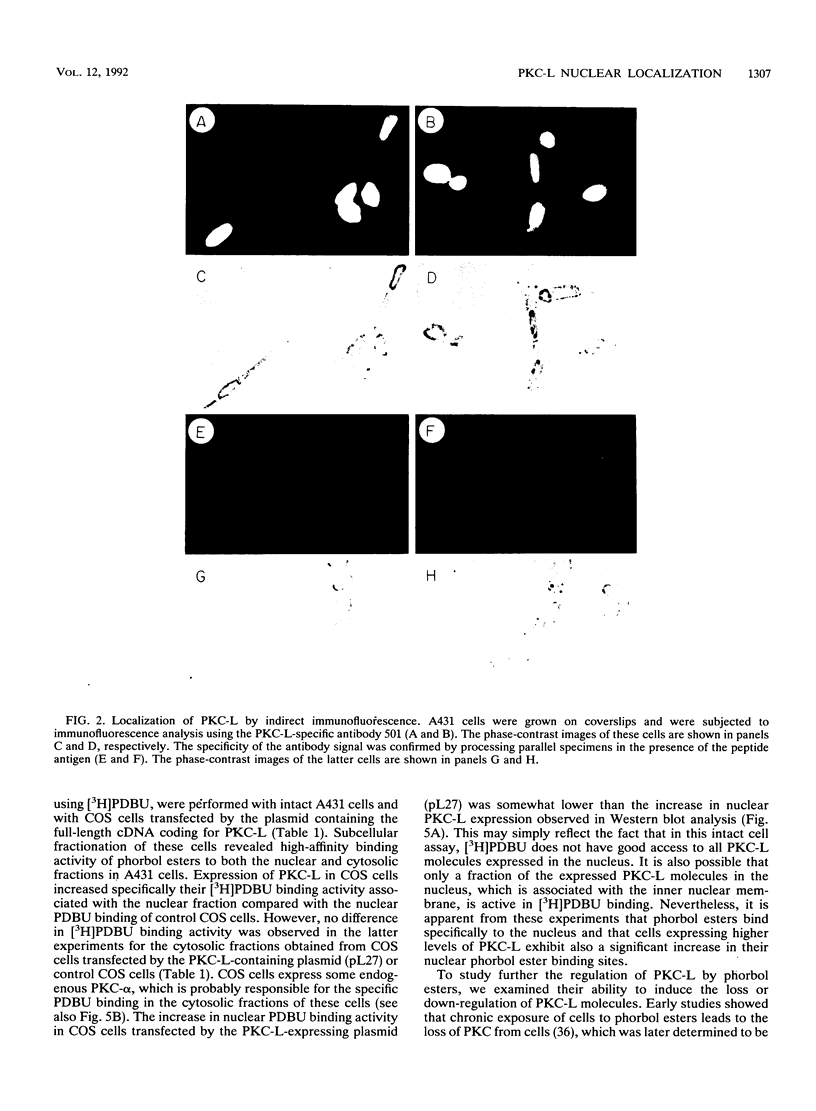
The tumor promoters phorbol esters are thought to induce changes in cell growth and gene expression by direct activation of protein kinase C (PKC). However, the molecular mechanisms by which PKC molecules transduce signals into the cell nucleus are unknown. In this study, we provide evidence for a direct target for phorbol esters in the nucleus. We demonstrate that the new PKC-related family member, PKC-L, recently isolated by us, is expressed specifically in the cell nucleus. Localization of PKC-L in the cell nucleus is shown both by immunofluorescence staining and by subcellular fractionation experiments of several human cell lines, including the human epidermoid carcinoma line A431. Treatment of these cells by phorbol esters does not induce the down-regulation of PKC-L, in contrast to their effect on classical PKC family members. This is the only PKC isoenzyme described so far that resides permanently and specifically in the cell nucleus. PKC-L may function as an important link in tumor promoting, e.g., as a nuclear regulator of gene expression that changes the phosphorylation state of transcriptional components such as the AP-1 complex.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Hattori K., Smeal T., Karin M. The jun proto-oncogene is positively autoregulated by its product, Jun/AP-1. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):875–885. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90143-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ase K., Berry N., Kikkawa U., Kishimoto A., Nishizuka Y. Differential down-regulation of protein kinase C subspecies in KM3 cells. FEBS Lett. 1988 Aug 29;236(2):396–400. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashendel C. L., Staller J. M., Boutwell R. K. Identification of a calcium- and phospholipid- dependent phorbol ester binding activity in the soluble fraction of mouse tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Feb 28;111(1):340–345. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(83)80157-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacher N., Zisman Y., Berent E., Livneh E. Isolation and characterization of PKC-L, a new member of the protein kinase C-related gene family specifically expressed in lung, skin, and heart. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):126–133. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell R. M., Burns D. J. Lipid activation of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):4661–4664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boukamp P., Petrussevska R. T., Breitkreutz D., Hornung J., Markham A., Fusenig N. E. Normal keratinization in a spontaneously immortalized aneuploid human keratinocyte cell line. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):761–771. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., Smeal T., Defize L. H., Angel P., Woodgett J. R., Karin M., Hunter T. Activation of protein kinase C decreases phosphorylation of c-Jun at sites that negatively regulate its DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):573–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90241-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambier J. C., Newell M. K., Justement L. B., McGuire J. C., Leach K. L., Chen Z. Z. Ia binding ligands and cAMP stimulate nuclear translocation of PKC in B lymphocytes. Nature. 1987 Jun 18;327(6123):629–632. doi: 10.1038/327629a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coussens L., Parker P. J., Rhee L., Yang-Feng T. L., Chen E., Waterfield M. D., Francke U., Ullrich A. Multiple, distinct forms of bovine and human protein kinase C suggest diversity in cellular signaling pathways. Science. 1986 Aug 22;233(4766):859–866. doi: 10.1126/science.3755548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldar H., Zisman Y., Ullrich A., Livneh E. Overexpression of protein kinase C alpha-subtype in Swiss/3T3 fibroblasts causes loss of both high and low affinity receptor numbers for epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):13290–13296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields A. P., Pettit G. R., May W. S. Phosphorylation of lamin B at the nuclear membrane by activated protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8253–8260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hocevar B. A., Fields A. P. Selective translocation of beta II-protein kinase C to the nucleus of human promyelocytic (HL60) leukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):28–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Housey G. M., O'Brian C. A., Johnson M. D., Kirschmeier P., Weinstein I. B. Isolation of cDNA clones encoding protein kinase C: evidence for a protein kinase C-related gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1065–1069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiley S., Schaap D., Parker P., Hsieh L. L., Jaken S. Protein kinase C heterogeneity in GH4C1 rat pituitary cells. Characterization of a Ca2(+)-independent phorbol ester receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):15704–15712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiss Z., Deli E., Kuo J. F. Temporal changes in intracellular distribution of protein kinase C during differentiation of human leukemia HL60 cells induced by phorbol ester. FEBS Lett. 1988 Apr 11;231(1):41–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80698-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knopf J. L., Lee M. H., Sultzman L. A., Kriz R. W., Loomis C. R., Hewick R. M., Bell R. M. Cloning and expression of multiple protein kinase C cDNAs. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):491–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90874-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kris R. M., Lax I., Gullick W., Waterfield M. D., Ullrich A., Fridkin M., Schlessinger J. Antibodies against a synthetic peptide as a probe for the kinase activity of the avian EGF receptor and v-erbB protein. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):619–625. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90210-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamph W. W., Wamsley P., Sassone-Corsi P., Verma I. M. Induction of proto-oncogene JUN/AP-1 by serum and TPA. Nature. 1988 Aug 18;334(6183):629–631. doi: 10.1038/334629a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach K. L., James M. L., Blumberg P. M. Characterization of a specific phorbol ester aporeceptor in mouse brain cytosol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4208–4212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach K. L., Powers E. A., Ruff V. A., Jaken S., Kaufmann S. Type 3 protein kinase C localization to the nuclear envelope of phorbol ester-treated NIH 3T3 cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):685–695. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livneh E., Benveniste M., Prywes R., Felder S., Kam Z., Schlessinger J. Large deletions in the cytoplasmic kinase domain of the epidermal growth factor receptor do not affect its laternal mobility. J Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;103(2):327–331. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naito S., Walker S. M., von Eschenbach A. C., Fidler I. J. Evidence for metastatic heterogeneity of human renal cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 1988 Nov-Dec;8(6):1163–1167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedel J. E., Kuhn L. J., Vandenbark G. R. Phorbol diester receptor copurifies with protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):36–40. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):305–312. doi: 10.1126/science.3014651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The molecular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):661–665. doi: 10.1038/334661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S., Akita Y., Konno Y., Imajoh S., Suzuki K. A novel phorbol ester receptor/protein kinase, nPKC, distantly related to the protein kinase C family. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):731–741. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90091-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S., Kawasaki H., Imajoh S., Suzuki K., Inagaki M., Yokokura H., Sakoh T., Hidaka H. Tissue-specific expression of three distinct types of rabbit protein kinase C. Nature. 1987 Jan 8;325(7000):161–166. doi: 10.1038/325161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Fujii T., Ogita K., Kikkawa U., Igarashi K., Nishizuka Y. Protein kinase C zeta subspecies from rat brain: its structure, expression, and properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3099–3103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Fujii T., Ogita K., Kikkawa U., Igarashi K., Nishizuka Y. The structure, expression, and properties of additional members of the protein kinase C family. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6927–6932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Kurokawa T., Fujii T., Kawahara K., Igarashi K., Kikkawa U., Ogita K., Nishizuka Y. Two types of complementary DNAs of rat brain protein kinase C. Heterogeneity determined by alternative splicing. FEBS Lett. 1986 Oct 6;206(2):347–352. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osada S., Mizuno K., Saido T. C., Akita Y., Suzuki K., Kuroki T., Ohno S. A phorbol ester receptor/protein kinase, nPKC eta, a new member of the protein kinase C family predominantly expressed in lung and skin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22434–22440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker P. J., Coussens L., Totty N., Rhee L., Young S., Chen E., Stabel S., Waterfield M. D., Ullrich A. The complete primary structure of protein kinase C--the major phorbol ester receptor. Science. 1986 Aug 22;233(4766):853–859. doi: 10.1126/science.3755547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Pena A., Rozengurt E. Disappearance of Ca2+-sensitive, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase activity in phorbol ester-treated 3T3 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 16;120(3):1053–1059. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogue P., Labourdette G., Masmoudi A., Yoshida Y., Huang F. L., Huang K. P., Zwiller J., Vincendon G., Malviya A. N. Rat liver nuclei protein kinase C is the isozyme type II. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):4161–4165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperling R., Sperling J., Levine A. D., Spann P., Stark G. R., Kornberg R. D. Abundant nuclear ribonucleoprotein form of CAD RNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):569–575. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strulovici B., Daniel-Issakani S., Baxter G., Knopf J., Sultzman L., Cherwinski H., Nestor J., Jr, Webb D. R., Ransom J. Distinct mechanisms of regulation of protein kinase C epsilon by hormones and phorbol diesters. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):168–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. P., Talwar H. S., Anderson W. B. Phorbol ester-mediated association of protein kinase C to the nuclear fraction in NIH 3T3 cells. Cancer Res. 1988 Apr 1;48(7):1910–1919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilgen W., Boukamp P., Breitkreutz D., Dzarlieva R. T., Engstner M., Haag D., Fusenig N. E. Preservation of morphological, functional, and karyotypic traits during long-term culture and in vivo passage of two human skin squamous cell carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1983 Dec;43(12 Pt 1):5995–6011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodgett J. R., Hunter T. Immunological evidence for two physiological forms of protein kinase C. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):85–96. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S., Parker P. J., Ullrich A., Stabel S. Down-regulation of protein kinase C is due to an increased rate of degradation. Biochem J. 1987 Jun 15;244(3):775–779. doi: 10.1042/bj2440775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]