Abstract
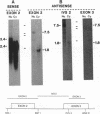
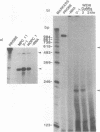
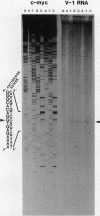
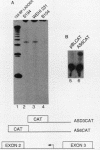
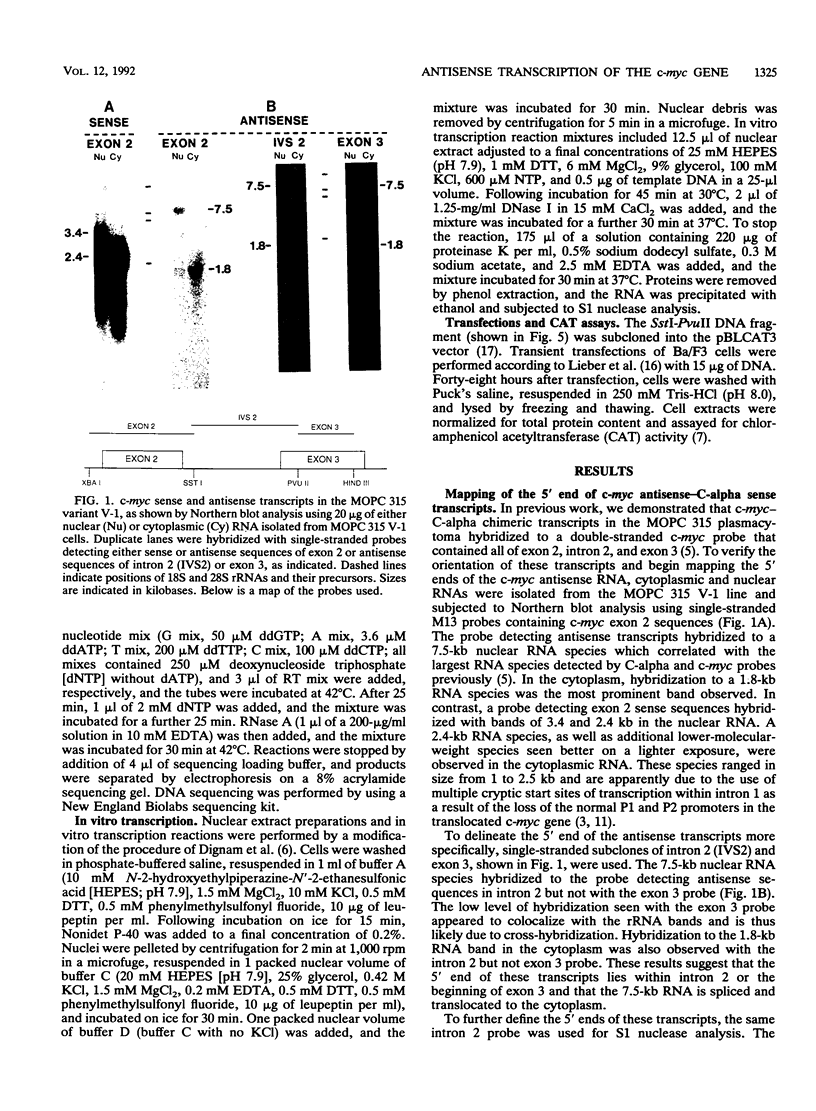
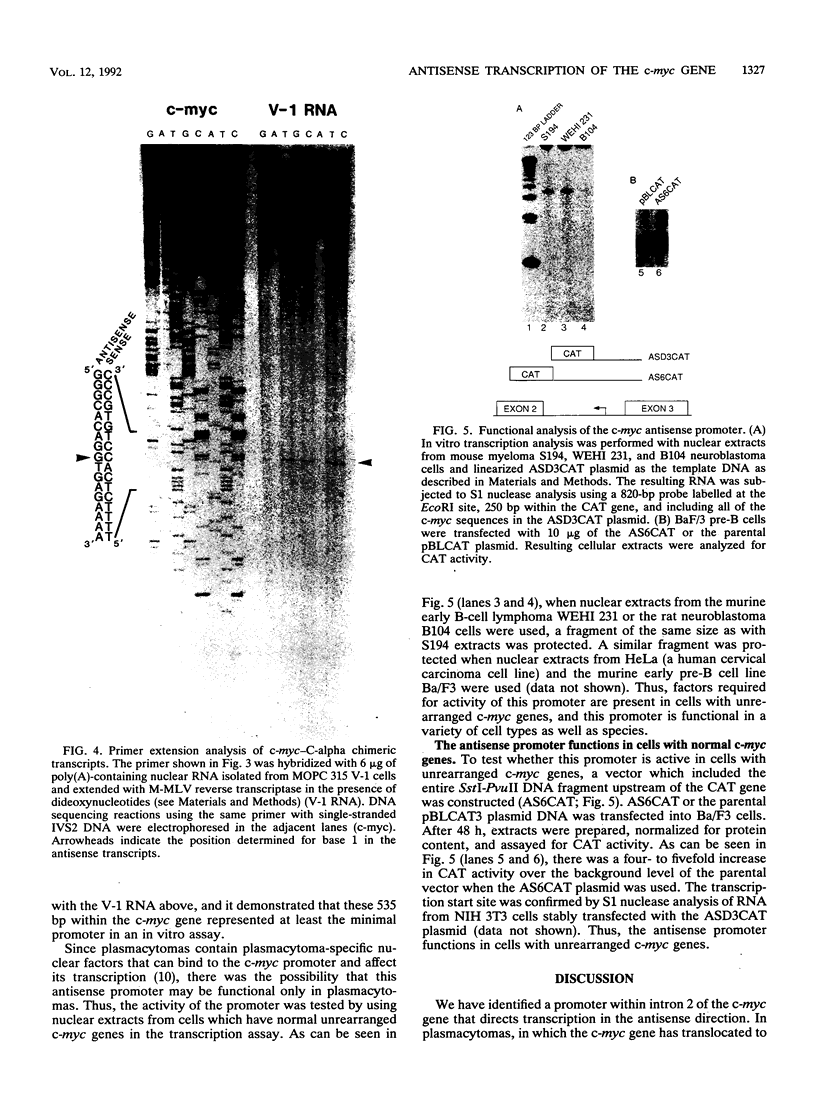
Previously we have demonstrated the existence of stable transcripts from the noncoding strand of a rearranged c-myc gene in murine plasmacytomas in which the oncogene has translocated to an immunoglobulin constant-region gene element (M. Dean, R. B. Kent, and G. E. Sonenshein, Nature [London] 305:443-446, 1983). The resulting RNAs are chimeric, containing c-myc antisense and immunoglobulin sense sequences. A normal unrearranged murine c-myc gene is transcribed in the antisense orientation throughout much of the gene; however, stable transcripts have not been detected. In this study, using Northern (RNA) blot, S1 nuclease, and primer extension analyses, we have mapped the 5' end of the stable chimeric transcripts to a site 175 bp from the start of exon 3, within intron 2 of the c-myc gene. In vitro transcription assays with constructs containing this site and 400 bp upstream, in the antisense orientation, and nuclear extracts from plasmacytoma cells, as well as a number of cell lines with normal unrearranged c-myc genes, indicated that this promoter was functional. This finding was confirmed in transient transfection assays using the antisense promoter linked to the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase reporter gene. These results suggest that a normal promoter of antisense transcription is used following c-myc gene translocation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bender T. P., Thompson C. B., Kuehl W. M. Differential expression of c-myb mRNA in murine B lymphomas by a block to transcription elongation. Science. 1987 Sep 18;237(4821):1473–1476. doi: 10.1126/science.3498214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley D. L., Groudine M. A block to elongation is largely responsible for decreased transcription of c-myc in differentiated HL60 cells. Nature. 1986 Jun 12;321(6071):702–706. doi: 10.1038/321702a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calabi F., Neuberger M. S. Chromosome translocation activates heterogeneously initiated, bipolar transcription of a mouse c-myc gene. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):667–674. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03681.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y., Spicer D. B., Sonenshein G. E. Effects of IL-3 on promoter usage, attenuation and antisense transcription of the c-myc oncogene in the IL-3-dependent Ba/F3 early pre-B cell line. Oncogene. 1991 Nov;6(11):1979–1982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean M., Kent R. B., Sonenshein G. E. Transcriptional activation of immunoglobulin alpha heavy-chain genes by translocation of the c-myc oncogene. 1983 Sep 29-Oct 5Nature. 305(5933):443–446. doi: 10.1038/305443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donoghue M., Ernst H., Wentworth B., Nadal-Ginard B., Rosenthal N. A muscle-specific enhancer is located at the 3' end of the myosin light-chain 1/3 gene locus. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1779–1790. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu N., Messing J. The making of strand-specific M13 probes. Gene. 1982 Mar;17(3):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90143-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakkis E., Calame K. A plasmacytoma-specific factor binds the c-myc promoter region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7031–7035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keath E. J., Kelekar A., Cole M. D. Transcriptional activation of the translocated c-myc oncogene in mouse plasmacytomas: similar RNA levels in tumor and proliferating normal cells. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):521–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90382-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindy M. S., McCormack J. E., Buckler A. J., Levine R. A., Sonenshein G. E. Independent regulation of transcription of the two strands of the c-myc gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2857–2862. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krystal G. W., Armstrong B. C., Battey J. F. N-myc mRNA forms an RNA-RNA duplex with endogenous antisense transcripts. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4180–4191. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krystal G., Birrer M., Way J., Nau M., Sausville E., Thompson C., Minna J., Battey J. Multiple mechanisms for transcriptional regulation of the myc gene family in small-cell lung cancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3373–3381. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine R. A., McCormack J. E., Buckler A., Sonenshein G. E. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional control of c-myc gene expression in WEHI 231 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4112–4116. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieber M. R., Hesse J. E., Mizuuchi K., Gellert M. Developmental stage specificity of the lymphoid V(D)J recombination activity. Genes Dev. 1987 Oct;1(8):751–761. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.8.751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack J. E., Pepe V. H., Kent R. B., Dean M., Marshak-Rothstein A., Sonenshein G. E. Specific regulation of c-myc oncogene expression in a murine B-cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5546–5550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nepveu A., Marcu K. B. Intragenic pausing and anti-sense transcription within the murine c-myc locus. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2859–2865. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04580.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponte P. A., Siekevitz M., Schwartz R. C., Gefter M. L., Sonenshein G. E. Transcription of immunoglobulin heavy-chain sequences from the excluded allele. Nature. 1981 Jun 18;291(5816):594–596. doi: 10.1038/291594a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Baltimore D. The "initiator" as a transcription control element. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama K. M., Inouye M. Antisense RNA. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1990;25(3):155–184. doi: 10.3109/10409239009090608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. Q., Bauer S. R., Mushinski J. F., Marcu K. B. Chromosome translocations clustered 5' of the murine c-myc gene qualitatively affect promoter usage: implications for the site of normal c-myc regulation. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1441–1447. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03800.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]