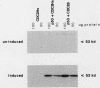
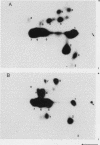
Abstract
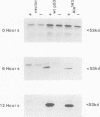
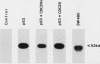
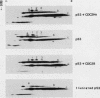
Human wild-type and mutant p53 genes were expressed under the control of a galactose-inducible promoter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The growth rate of the yeast was reduced in cells expressing wild-type p53, whereas cells transformed with mutant p53 genes derived from human tumors were less affected. Coexpression of the normal p53 protein with the human cell cycle-regulated protein kinase CDC2Hs resulted in much more pronounced growth inhibition that for p53 alone. Cells expressing p53 and CDC2Hs were partially arrested in G1, as determined by morphological analysis and flow cytometry. p53 was phosphorylated when expressed in the yeast, but differences in phosphorylation did not explain the growth inhibition attributable to coexpression of p53 and CDC2Hs. These results suggest that wild-type p53 has a growth-inhibitory activity in S. cerevisiae similar to that observed in mammalian cells and suggests that this yeast may provide a useful model for defining the pathways through which p53 acts.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker S. J., Markowitz S., Fearon E. R., Willson J. K., Vogelstein B. Suppression of human colorectal carcinoma cell growth by wild-type p53. Science. 1990 Aug 24;249(4971):912–915. doi: 10.1126/science.2144057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff J. R., Friedman P. N., Marshak D. R., Prives C., Beach D. Human p53 is phosphorylated by p60-cdc2 and cyclin B-cdc2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4766–4770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang F., Herskowitz I. Identification of a gene necessary for cell cycle arrest by a negative growth factor of yeast: FAR1 is an inhibitor of a G1 cyclin, CLN2. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):999–1011. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90503-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diller L., Kassel J., Nelson C. E., Gryka M. A., Litwak G., Gebhardt M., Bressac B., Ozturk M., Baker S. J., Vogelstein B. p53 functions as a cell cycle control protein in osteosarcomas. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5772–5781. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion E. A., Grisafi P. L., Fink G. R. FUS3 encodes a cdc2+/CDC28-related kinase required for the transition from mitosis into conjugation. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):649–664. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90668-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Jang S. K. Presence of a potent transcription activating sequence in the p53 protein. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1046–1049. doi: 10.1126/science.2144363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerring S. L., Spencer F., Hieter P. The CHL 1 (CTF 1) gene product of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is important for chromosome transmission and normal cell cycle progression in G2/M. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4347–4358. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07884.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghiara J. B., Richardson H. E., Sugimoto K., Henze M., Lew D. J., Wittenberg C., Reed S. I. A cyclin B homolog in S. cerevisiae: chronic activation of the Cdc28 protein kinase by cyclin prevents exit from mitosis. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):163–174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90417-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadwiger J. A., Wittenberg C., Richardson H. E., de Barros Lopes M., Reed S. I. A family of cyclin homologs that control the G1 phase in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6255–6259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds P. W., Finlay C. A., Quartin R. S., Baker S. J., Fearon E. R., Vogelstein B., Levine A. J. Mutant p53 DNA clones from human colon carcinomas cooperate with ras in transforming primary rat cells: a comparison of the "hot spot" mutant phenotypes. Cell Growth Differ. 1990 Dec;1(12):571–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollstein M., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Harris C. C. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):49–53. doi: 10.1126/science.1905840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley J. H., Dean A. M., Sohl J. L., Koshland D. E., Jr, Stroud R. M. Regulation of an enzyme by phosphorylation at the active site. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1012–1016. doi: 10.1126/science.2204109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutter K. J., Eipel H. E. Microbial determinations by flow cytometry. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Aug;113(2):369–375. doi: 10.1099/00221287-113-2-369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M., Davis R. W. Sequences that regulate the divergent GAL1-GAL10 promoter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1440–1448. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern S. E., Kinzler K. W., Baker S. J., Nigro J. M., Rotter V., Levine A. J., Friedman P., Prives C., Vogelstein B. Mutant p53 proteins bind DNA abnormally in vitro. Oncogene. 1991 Jan;6(1):131–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern S. E., Kinzler K. W., Bruskin A., Jarosz D., Friedman P., Prives C., Vogelstein B. Identification of p53 as a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1708–1711. doi: 10.1126/science.2047879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. G., Nurse P. Complementation used to clone a human homologue of the fission yeast cell cycle control gene cdc2. Nature. 1987 May 7;327(6117):31–35. doi: 10.1038/327031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luna E. J., Kidd G. H., Branton D. Identification by peptide analysis of the spectrin-binding protein in human erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 10;254(7):2526–2532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez J., Georgoff I., Martinez J., Levine A. J. Cellular localization and cell cycle regulation by a temperature-sensitive p53 protein. Genes Dev. 1991 Feb;5(2):151–159. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.2.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurides P. A., Akkaraju G. R., Jagus R. Evaluation of protein phosphorylation state by a combination of vertical slab gel isoelectric focusing and immunoblotting. Anal Biochem. 1989 Nov 15;183(1):144–151. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90182-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meek D. W., Eckhart W. Phosphorylation of p53 in normal and simian virus 40-transformed NIH 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):461–465. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendenhall M. D., Jones C. A., Reed S. I. Dual regulation of the yeast CDC28-p40 protein kinase complex: cell cycle, pheromone, and nutrient limitation effects. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):927–935. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90519-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendenhall M. D., Richardson H. E., Reed S. I. Dominant negative protein kinase mutations that confer a G1 arrest phenotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4426–4430. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer W. E., Shields M. T., Amin M., Sauve G. J., Appella E., Romano J. W., Ullrich S. J. Negative growth regulation in a glioblastoma tumor cell line that conditionally expresses human wild-type p53. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6166–6170. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalovitz D., Halevy O., Oren M. Conditional inhibition of transformation and of cell proliferation by a temperature-sensitive mutant of p53. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):671–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90113-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner J., Cook A., Mason J. p53 is associated with p34cdc2 in transformed cells. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2885–2889. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07478.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigro J. M., Cho K. R., Fearon E. R., Kern S. E., Ruppert J. M., Oliner J. D., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Scrambled exons. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):607–613. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90244-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers S., Kataoka T., Fasano O., Goldfarb M., Strathern J., Broach J., Wigler M. Genes in S. cerevisiae encoding proteins with domains homologous to the mammalian ras proteins. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):607–612. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90340-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raycroft L., Wu H. Y., Lozano G. Transcriptional activation by wild-type but not transforming mutants of the p53 anti-oncogene. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1049–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.2144364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I., Hadwiger J. A., Lörincz A. T. Protein kinase activity associated with the product of the yeast cell division cycle gene CDC28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4055–4059. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riabowol K., Draetta G., Brizuela L., Vandre D., Beach D. The cdc2 kinase is a nuclear protein that is essential for mitosis in mammalian cells. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):393–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90914-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson H. E., Wittenberg C., Cross F., Reed S. I. An essential G1 function for cyclin-like proteins in yeast. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1127–1133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90768-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stürzbecher H. W., Maimets T., Chumakov P., Brain R., Addison C., Simanis V., Rudge K., Philp R., Grimaldi M., Court W. p53 interacts with p34cdc2 in mammalian cells: implications for cell cycle control and oncogenesis. Oncogene. 1990 Jun;5(6):795–781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Matsumoto K., Toh-E A. IRA1, an inhibitory regulator of the RAS-cyclic AMP pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):757–768. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittenberg C., Reed S. I. Conservation of function and regulation within the Cdc28/cdc2 protein kinase family: characterization of the human Cdc2Hs protein kinase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):4064–4068. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.4064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarger J. G., Armilei G., Gorman M. C. Transcription terminator-like element within a Saccharomyces cerevisiae promoter region. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1095–1101. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]