Abstract
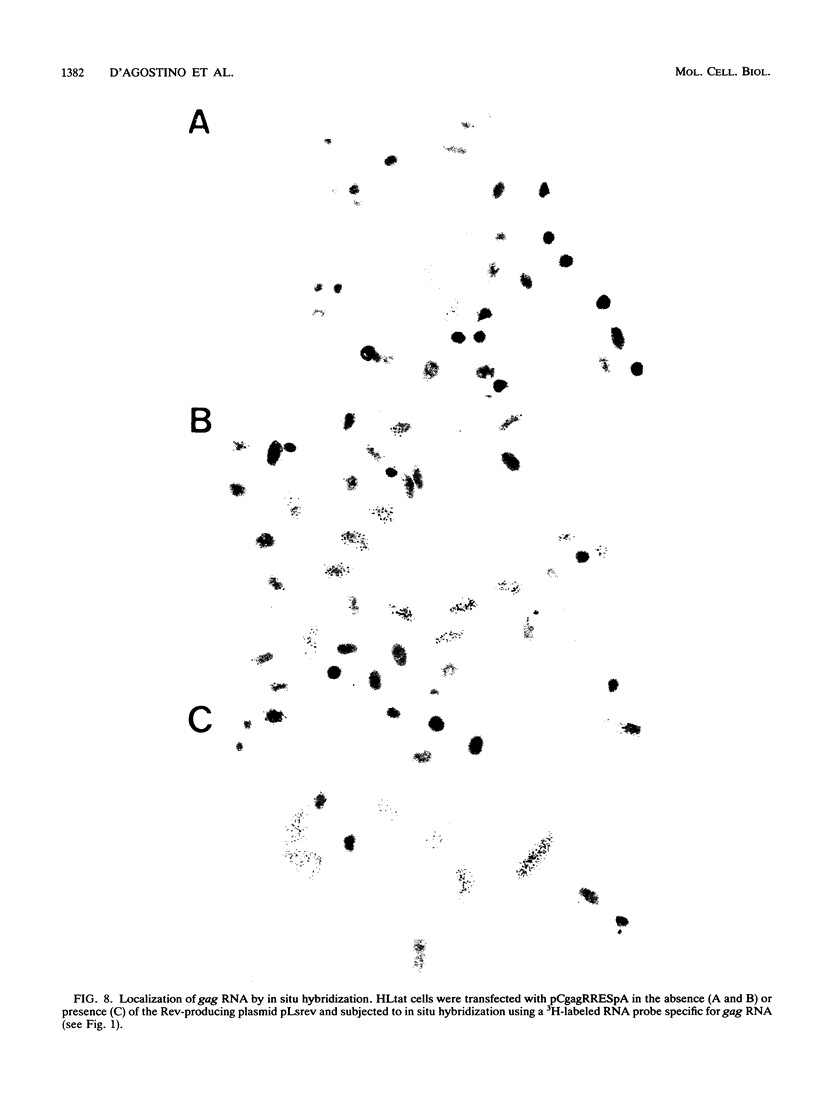
Biochemical examination of the Rev-dependent expression of gag mRNAs produced from gag-Rev-responsive element (RRE) expression plasmids showed a large discrepancy between the level of cytoplasmic gag mRNA and the produced Gag protein. Significant levels of the mRNA produced in the absence of Rev were localized in the cytoplasm, while very low levels of Gag protein were produced. In the presence of Rev, the levels of mRNA increased by 4- to 16-fold, while the Gag protein production increased by 800-fold. These findings indicated that in addition to promoting nucleus-to-cytoplasm transport, Rev increased the utilization of cytoplasmic viral mRNA. Poly(A) selection and in vitro translation of cytoplasmic gag mRNA verified that the mRNA produced in the absence of Rev was functional. To analyze the translational defect in the absence of Rev, we examined the association of the cytoplasmic gag mRNA with ribosomes. gag mRNA produced in the absence of Rev was excluded from polysomes, while gag mRNA produced in the presence of Rev was associated with polysomes and produced Gag protein. These observations showed that the presence of Rev was required for efficient loading of gag mRNA onto polysomes. This effect required the presence of the RRE on the mRNA. Analysis of mRNAs produced from a rev-minus proviral clone confirmed that the presence of Rev promoted polysomal loading of both gag/pol and vpu/env mRNAs. The localization of gag mRNA was also examined by in situ hybridization. This analysis showed that in the presence of Rev, most of the gag mRNA was found in the cytoplasm, while in the absence of Rev, most of the gag mRNA was found in the nucleus and in the region surrounding the nucleus. These results suggest that a substantial fraction of the gag mRNA is retained in distinct cytoplasmic compartments in the absence and presence of Rev. These findings indicate that the presence of Rev is required along the entire mRNA transport and utilization pathway for the stabilization, correct localization, and efficient translation of RRE-containing mRNAs.
Full text
PDF





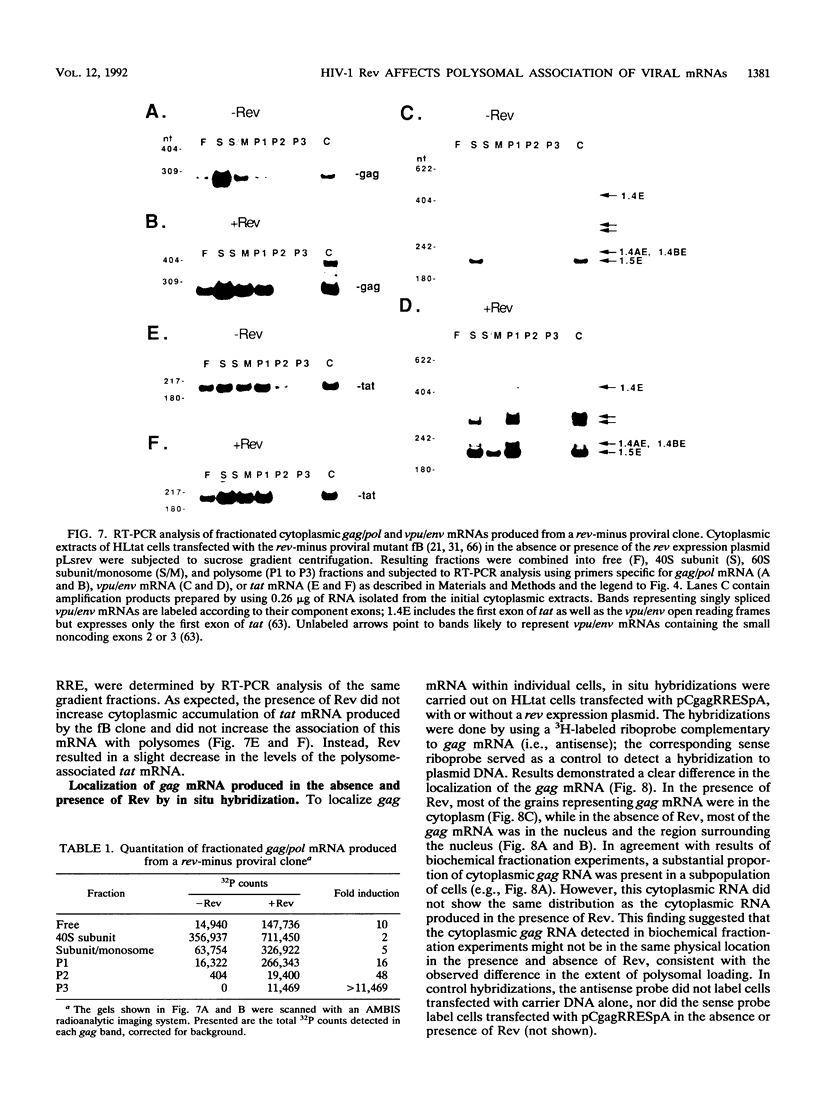





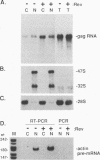
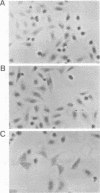
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed Y. F., Hanly S. M., Malim M. H., Cullen B. R., Greene W. C. Structure-function analyses of the HTLV-I Rex and HIV-1 Rev RNA response elements: insights into the mechanism of Rex and Rev action. Genes Dev. 1990 Jun;4(6):1014–1022. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.6.1014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrigo S. J., Chen I. S. Rev is necessary for translation but not cytoplasmic accumulation of HIV-1 vif, vpr, and env/vpu 2 RNAs. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):808–819. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrigo S. J., Weitsman S., Rosenblatt J. D., Chen I. S. Analysis of rev gene function on human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication in lymphoid cells by using a quantitative polymerase chain reaction method. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4875–4881. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4875-4881.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aziz N., Munro H. N. Both subunits of rat liver ferritin are regulated at a translational level by iron induction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 24;14(2):915–927. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.2.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benko D. M., Robinson R., Solomin L., Mellini M., Felber B. K., Pavlakis G. N. Binding of trans-dominant mutant Rev protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 to the cis-acting Rev-responsive element does not affect the fate of viral mRNA. New Biol. 1990 Dec;2(12):1111–1122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasier A. R., Tate J. E., Habener J. F. Optimized use of the firefly luciferase assay as a reporter gene in mammalian cell lines. Biotechniques. 1989 Nov-Dec;7(10):1116–1122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey J. L., Koeller D. M., Ramin V. C., Klausner R. D., Harford J. B. Iron regulation of transferrin receptor mRNA levels requires iron-responsive elements and a rapid turnover determinant in the 3' untranslated region of the mRNA. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3693–3699. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08544.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. P. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):132–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90716-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. D., Sharp P. A. Regulation by HIV Rev depends upon recognition of splice sites. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):789–795. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90602-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Lopata M. A., MacDonald R. J., Cowan N. J., Rutter W. J., Kirschner M. W. Number and evolutionary conservation of alpha- and beta-tubulin and cytoplasmic beta- and gamma-actin genes using specific cloned cDNA probes. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90238-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane A. W., Chen C. H., Rosen C. A. Specific interaction of the human immunodeficiency virus Rev protein with a structured region in the env mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1198–1202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Hauber J., Campbell K., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A., Rosen C. A. Subcellular localization of the human immunodeficiency virus trans-acting art gene product. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2498–2501. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2498-2501.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daefler S., Klotman M. E., Wong-Staal F. Trans-activating rev protein of the human immunodeficiency virus 1 interacts directly and specifically with its target RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4571–4575. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly T. J., Cook K. S., Gray G. S., Maione T. E., Rusche J. R. Specific binding of HIV-1 recombinant Rev protein to the Rev-responsive element in vitro. Nature. 1989 Dec 14;342(6251):816–819. doi: 10.1038/342816a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayton A. I., Terwilliger E. F., Potz J., Kowalski M., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. Cis-acting sequences responsive to the rev gene product of the human immunodeficiency virus. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1988;1(5):441–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayton E. T., Powell D. M., Dayton A. I. Functional analysis of CAR, the target sequence for the Rev protein of HIV-1. Science. 1989 Dec 22;246(4937):1625–1629. doi: 10.1126/science.2688093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dokhelar M. C., Pickford H., Sodroski J., Haseltine W. A. HTLV-I p27rex regulates gag and env protein expression. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1989;2(5):431–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerman M., Vazeux R., Peden K. The rev gene product of the human immunodeficiency virus affects envelope-specific RNA localization. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1155–1165. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90053-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg M. B., Jarrett R. F., Aldovini A., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. HTLV-III expression and production involve complex regulation at the levels of splicing and translation of viral RNA. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):807–817. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90062-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felber B. K., Derse D., Athanassopoulos A., Campbell M., Pavlakis G. N. Cross-activation of the Rex proteins of HTLV-I and BLV and of the Rev protein of HIV-1 and nonreciprocal interactions with their RNA responsive elements. New Biol. 1989 Dec;1(3):318–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felber B. K., Drysdale C. M., Pavlakis G. N. Feedback regulation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 expression by the Rev protein. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3734–3741. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3734-3741.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felber B. K., Hadzopoulou-Cladaras M., Cladaras C., Copeland T., Pavlakis G. N. rev protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 affects the stability and transport of the viral mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1495–1499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher A. G., Collalti E., Ratner L., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. A molecular clone of HTLV-III with biological activity. Nature. 1985 Jul 18;316(6025):262–265. doi: 10.1038/316262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett E. D., Tiley L. S., Cullen B. R. Rev activates expression of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 vif and vpr gene products. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1653–1657. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1653-1657.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez I. L., Gorski J. L., Campen T. J., Dorney D. J., Erickson J. M., Sylvester J. E., Schmickel R. D. Variation among human 28S ribosomal RNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7666–7670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene W. C. Regulation of HIV-1 gene expression. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:453–475. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadzopoulou-Cladaras M., Felber B. K., Cladaras C., Athanassopoulos A., Tse A., Pavlakis G. N. The rev (trs/art) protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 affects viral mRNA and protein expression via a cis-acting sequence in the env region. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1265–1274. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1265-1274.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarskjöld M. L., Heimer J., Hammarskjöld B., Sangwan I., Albert L., Rekosh D. Regulation of human immunodeficiency virus env expression by the rev gene product. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):1959–1966. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.1959-1966.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanly S. M., Rimsky L. T., Malim M. H., Kim J. H., Hauber J., Duc Dodon M., Le S. Y., Maizel J. V., Cullen B. R., Greene W. C. Comparative analysis of the HTLV-I Rex and HIV-1 Rev trans-regulatory proteins and their RNA response elements. Genes Dev. 1989 Oct;3(10):1534–1544. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.10.1534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heaphy S., Dingwall C., Ernberg I., Gait M. J., Green S. M., Karn J., Lowe A. D., Singh M., Skinner M. A. HIV-1 regulator of virion expression (Rev) protein binds to an RNA stem-loop structure located within the Rev response element region. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):685–693. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90671-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland S. M., Ahmad N., Maitra R. K., Wingfield P., Venkatesan S. Human immunodeficiency virus rev protein recognizes a target sequence in rev-responsive element RNA within the context of RNA secondary structure. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5966–5975. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5966-5975.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue J., Seiki M., Yoshida M. The second pX product p27 chi-III of HTLV-1 is required for gag gene expression. FEBS Lett. 1986 Dec 15;209(2):187–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81108-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue J., Yoshida M., Seiki M. Transcriptional (p40x) and post-transcriptional (p27x-III) regulators are required for the expression and replication of human T-cell leukemia virus type I genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3653–3657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kass S., Craig N., Sollner-Webb B. Primary processing of mammalian rRNA involves two adjacent cleavages and is not species specific. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2891–2898. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyokawa T., Seiki M., Iwashita S., Imagawa K., Shimizu F., Yoshida M. p27x-III and p21x-III, proteins encoded by the pX sequence of human T-cell leukemia virus type I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8359–8363. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Harford J. B. cis-trans models for post-transcriptional gene regulation. Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):870–872. doi: 10.1126/science.2683086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawczyk Z., Wu C. Isolation of RNA for dot hybridization by heparin-DNase I treatment of whole cell lysate. Anal Biochem. 1987 Aug 15;165(1):20–27. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90195-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Böhnlein S., Hauber J., Cullen B. R. Functional dissection of the HIV-1 Rev trans-activator--derivation of a trans-dominant repressor of Rev function. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90416-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Hauber J., Le S. Y., Maizel J. V., Cullen B. R. The HIV-1 rev trans-activator acts through a structured target sequence to activate nuclear export of unspliced viral mRNA. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):254–257. doi: 10.1038/338254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Tiley L. S., McCarn D. F., Rusche J. R., Hauber J., Cullen B. R. HIV-1 structural gene expression requires binding of the Rev trans-activator to its RNA target sequence. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):675–683. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90670-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermer B., Felber B. K., Campbell M., Pavlakis G. N. Identification of trans-dominant HIV-1 rev protein mutants by direct transfer of bacterially produced proteins into human cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 25;18(8):2037–2044. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.8.2037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng S. Y., Gunning P., Eddy R., Ponte P., Leavitt J., Shows T., Kedes L. Evolution of the functional human beta-actin gene and its multi-pseudogene family: conservation of noncoding regions and chromosomal dispersion of pseudogenes. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2720–2732. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen H. S., Cochrane A. W., Dillon P. J., Nalin C. M., Rosen C. A. Interaction of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Rev protein with a structured region in env mRNA is dependent on multimer formation mediated through a basic stretch of amino acids. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1357–1364. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen H. S., Nelbock P., Cochrane A. W., Rosen C. A. Secondary structure is the major determinant for interaction of HIV rev protein with RNA. Science. 1990 Feb 16;247(4944):845–848. doi: 10.1126/science.2406903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlakis G. N., Felber B. K. Regulation of expression of human immunodeficiency virus. New Biol. 1990 Jan;2(1):20–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner L., Fisher A., Jagodzinski L. L., Mitsuya H., Liou R. S., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. Complete nucleotide sequences of functional clones of the AIDS virus. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1987 Spring;3(1):57–69. doi: 10.1089/aid.1987.3.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner L., Haseltine W., Patarca R., Livak K. J., Starcich B., Josephs S. F., Doran E. R., Rafalski J. A., Whitehorn E. A., Baumeister K. Complete nucleotide sequence of the AIDS virus, HTLV-III. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):277–284. doi: 10.1038/313277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimsky L., Hauber J., Dukovich M., Malim M. H., Langlois A., Cullen B. R., Greene W. C. Functional replacement of the HIV-1 rev protein by the HTLV-1 rex protein. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):738–740. doi: 10.1038/335738a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen C. A., Pavlakis G. N. Tat and Rev: positive regulators of HIV gene expression. AIDS. 1990 Jun;4(6):499–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen C. A., Terwilliger E., Dayton A., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. Intragenic cis-acting art gene-responsive sequences of the human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2071–2075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S., Felber B. K., Benko D. M., Fenyö E. M., Pavlakis G. N. Cloning and functional analysis of multiply spliced mRNA species of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2519–2529. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2519-2529.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S., Felber B. K., Fenyö E. M., Pavlakis G. N. Env and Vpu proteins of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 are produced from multiple bicistronic mRNAs. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5448–5456. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5448-5456.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S., Felber B. K., Pavlakis G. N. Distinct RNA sequences in the gag region of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 decrease RNA stability and inhibit expression in the absence of Rev protein. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):150–159. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.150-159.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodroski J., Goh W. C., Rosen C., Dayton A., Terwilliger E., Haseltine W. A second post-transcriptional trans-activator gene required for HTLV-III replication. Nature. 1986 May 22;321(6068):412–417. doi: 10.1038/321412a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomin L., Felber B. K., Pavlakis G. N. Different sites of interaction for Rev, Tev, and Rex proteins within the Rev-responsive element of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6010–6017. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6010-6017.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G., Siegmann M., Bowman P. D., Gordon J. The isolation and analysis of polysomes and ribosomal RNA from cells growing in monolayer culture. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Sep;108(2):253–258. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(77)80032-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unge T., Solomin L., Mellini M., Derse D., Felber B. K., Pavlakis G. N. The Rex regulatory protein of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I binds specifically to its target site within the viral RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7145–7149. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapp M. L., Green M. R. Sequence-specific RNA binding by the HIV-1 Rev protein. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):714–716. doi: 10.1038/342714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]