Abstract
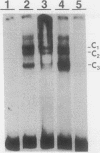
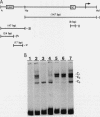
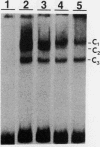
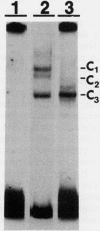
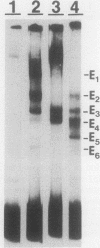
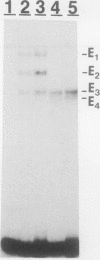
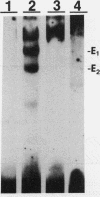
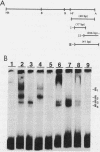
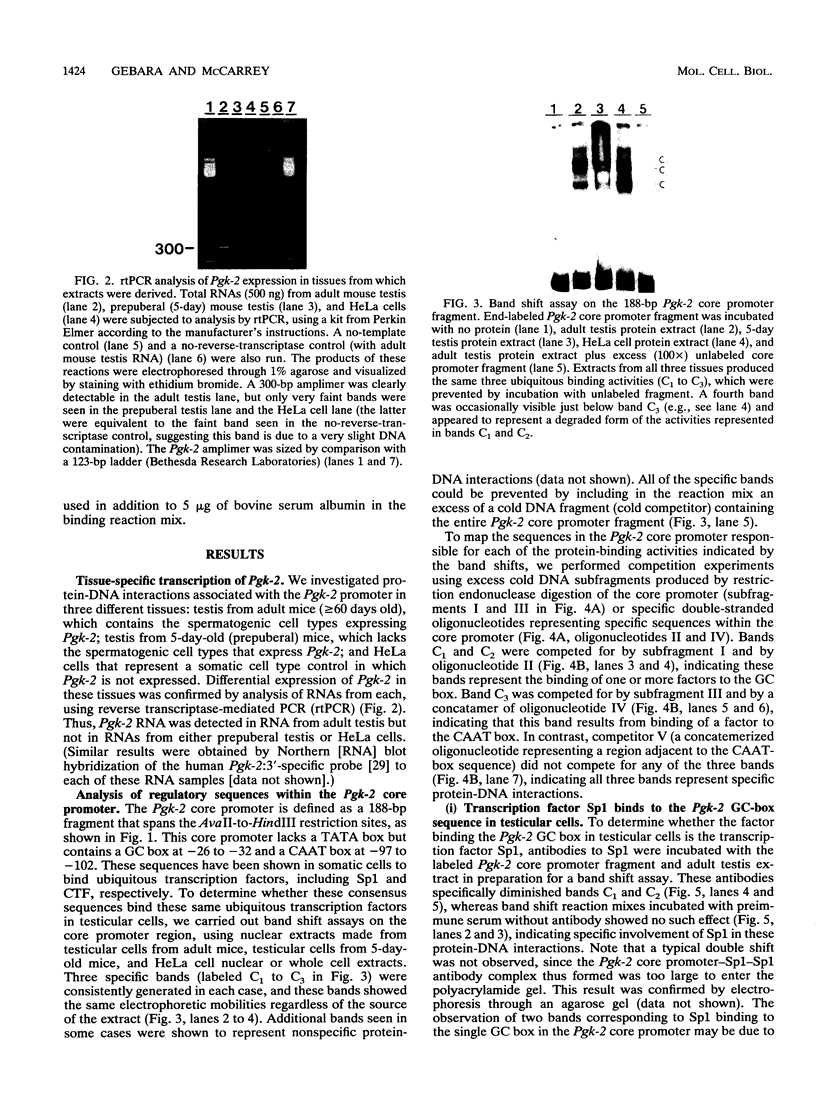
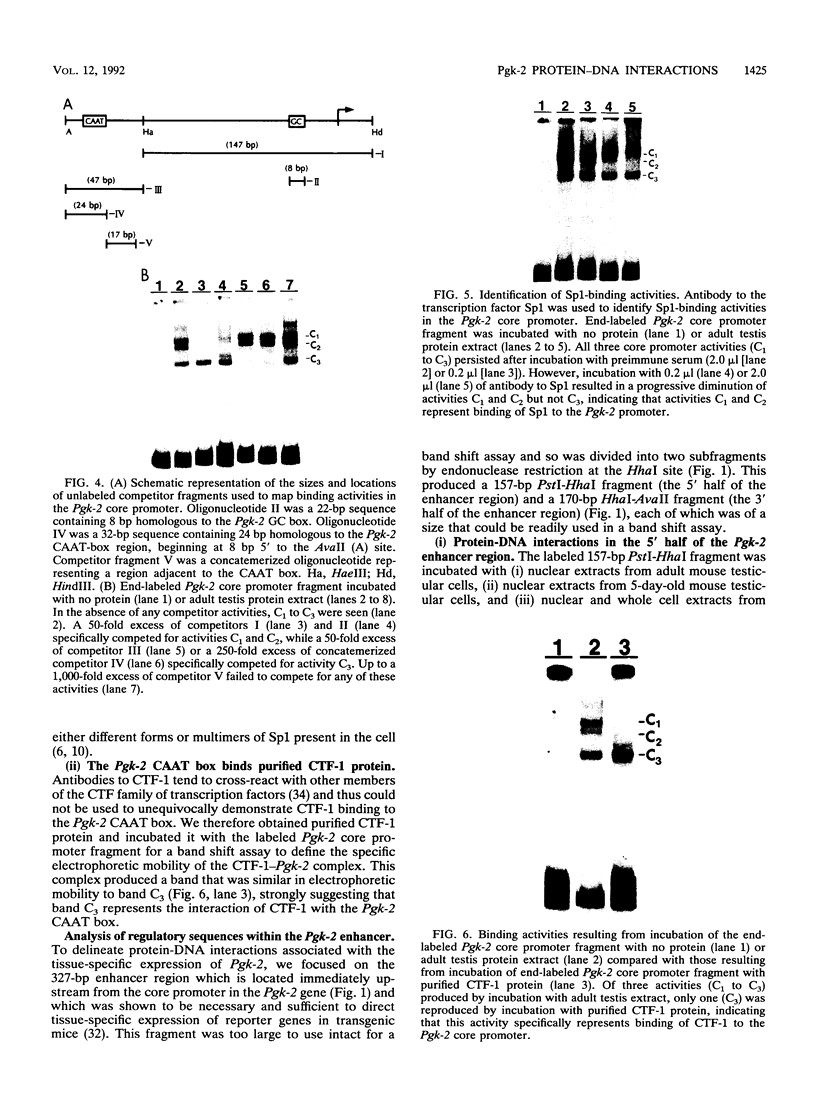
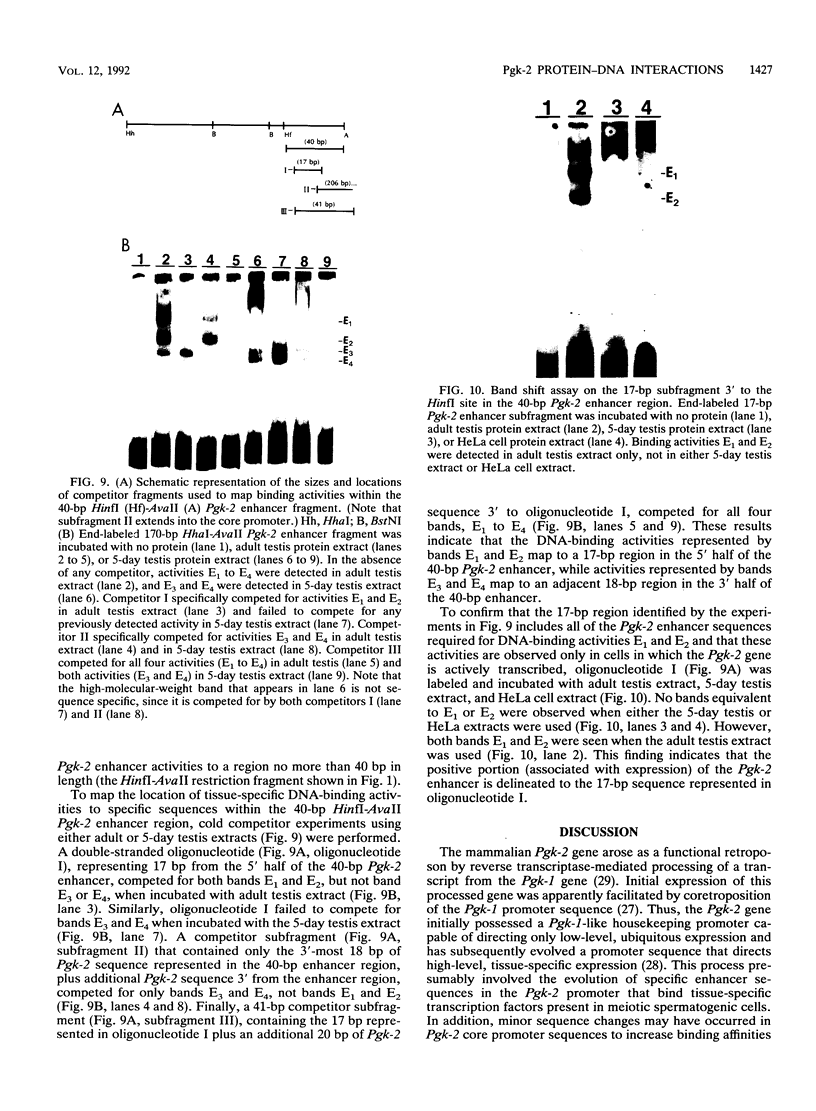
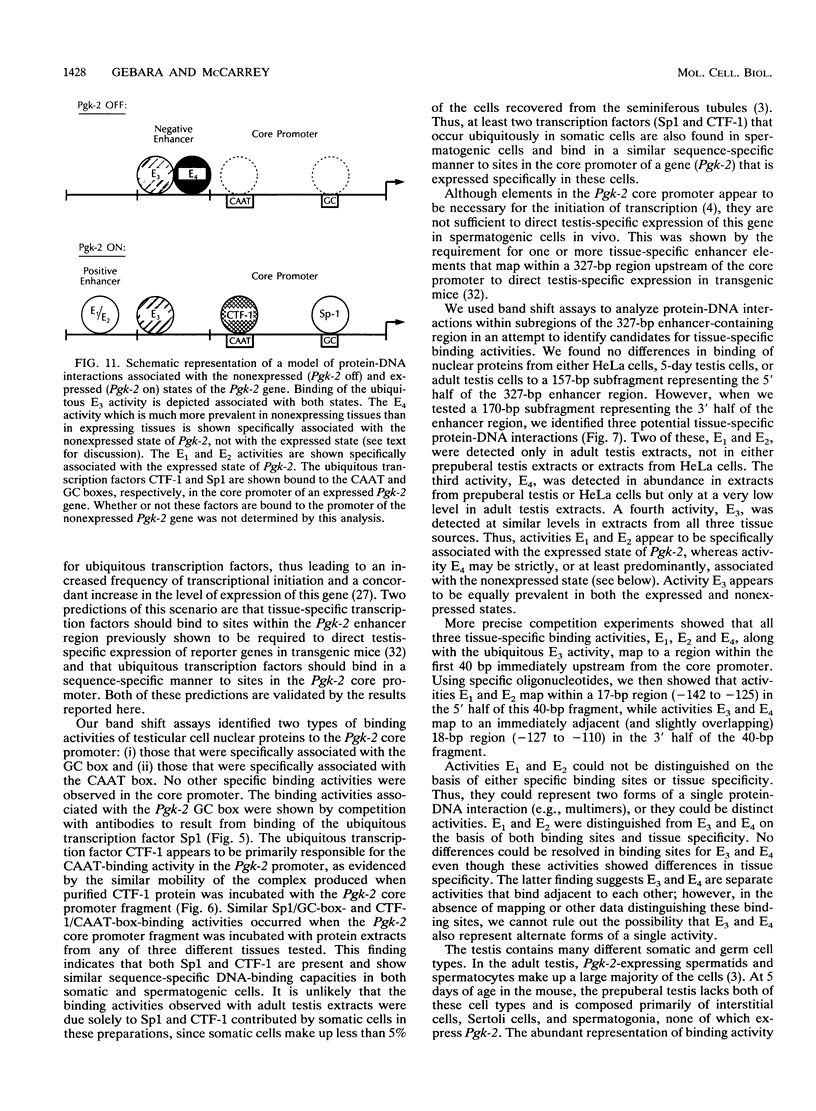
We have identified difference in protein-DNA interactions associated with the promoter of the mammalian spermatogenesis-specific Pgk-2 gene in expressing and nonexpressing cells, using a band shift assay. We compared DNA-binding activities in nuclear protein extracts from expressing adult testis cells versus nonexpressing prepuberal testis cells and nonexpressing somatic cells. One or two DNA-binding activities were found to be uniquely associated with the expressed state of Pgk-2, while a third appears to be associated with the nonexpressed state. All three of these activities map to a region within the first 40 bp upstream from the core promoter of this gene. The Pgk-2 core promoter lacks a TATA box but contain a GC box and a CAAT box. We show that the GC box binds the ubiquitous transcription factor Sp1 and that the CAAT box binds CTF-1, both of which are present in extracts from all three tissue types tested. These results suggest that tissue-specific transcription of the Pgk-2 gene is associated with changes in protein-DNA interactions occurring within a 40-bp enhancer region and that different arrays of protein-DNA interactions in this region are associated with the actively expressed state of the Pgk-2 gene in spermatocytes and spermatids and with the terminally repressed state of Pgk-2 in somatic cells.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barberis A., Superti-Furga G., Busslinger M. Mutually exclusive interaction of the CCAAT-binding factor and of a displacement protein with overlapping sequences of a histone gene promoter. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):347–359. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90489-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellvé A. R., Cavicchia J. C., Millette C. F., O'Brien D. A., Bhatnagar Y. M., Dym M. Spermatogenic cells of the prepuberal mouse. Isolation and morphological characterization. J Cell Biol. 1977 Jul;74(1):68–85. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.1.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boer P. H., Adra C. N., Lau Y. F., McBurney M. W. The testis-specific phosphoglycerate kinase gene pgk-2 is a recruited retroposon. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3107–3112. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. R., Kadonaga J. T., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Purification and biochemical characterization of the promoter-specific transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):47–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3529394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunick D., Johnson P. A., Johnson T. R., Hecht N. B. Transcription of the testis-specific mouse protamine 2 gene in a homologous in vitro transcription system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):891–895. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn A., Bollekens J., Staub A., Benoist C., Mathis D. A multiplicity of CCAAT box-binding proteins. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):863–872. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90513-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Isolation of transcription factors that discriminate between different promoters recognized by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):669–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Multiple specific contacts between a mammalian transcription factor and its cognate promoters. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):409–413. doi: 10.1038/312409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Kadonaga J. T., Barrera-Saldaña H., Takahashi K., Chambon P., Tjian R. Bidirectional SV40 transcription mediated by tandem Sp1 binding interactions. Science. 1985 Nov 1;230(4725):511–517. doi: 10.1126/science.2996137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves B. J., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Homologous recognition of a promoter domain common to the MSV LTR and the HSV tk gene. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):565–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90266-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatamochi A., Paterson B., de Crombrugghe B. Differential binding of a CCAAT DNA binding factor to the promoters of the mouse alpha 2(I) and alpha 1(III) collagen genes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11310–11314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. A., Peschon J. J., Yelick P. C., Palmiter R. D., Hecht N. B. Sequence homologies in the mouse protamine 1 and 2 genes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 May 6;950(1):45–53. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90071-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:799–839. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. A cellular DNA-binding protein that activates eukaryotic transcription and DNA replication. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90358-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Yamamoto K. R., Tjian R. Two distinct transcription factors bind to the HSV thymidine kinase promoter in vitro. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalb V. F., Jr, Bernlohr R. W. A new spectrophotometric assay for protein in cell extracts. Anal Biochem. 1977 Oct;82(2):362–371. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90173-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick D. L., Zinn S. A., Fitzgerald M., Higuchi H., Sabol S. L., Meyerhardt J. Transcription of the rat and mouse proenkephalin genes is initiated at distinct sites in spermatogenic and somatic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3717–3726. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer J. M., Erickson R. P. Developmental program of PGK-1 and PGK-2 isozymes in spermatogenic cells of the mouse: specific activities and rates of synthesis. Dev Biol. 1981 Oct 15;87(1):37–45. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90058-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leegwater P. A., van Driel W., van der Vliet P. C. Recognition site of nuclear factor I, a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein from HeLa cells that stimulates adenovirus DNA replication. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1515–1521. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03811.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li R., Knight J. D., Jackson S. P., Tjian R., Botchan M. R. Direct interaction between Sp1 and the BPV enhancer E2 protein mediates synergistic activation of transcription. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):493–505. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90467-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarrey J. R. Molecular evolution of the human Pgk-2 retroposon. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):949–955. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarrey J. R. Nucleotide sequence of the promoter region of a tissue-specific human retroposon: comparison with its housekeeping progenitor. Gene. 1987;61(3):291–298. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90192-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarrey J. R., Thomas K. Human testis-specific PGK gene lacks introns and possesses characteristics of a processed gene. Nature. 1987 Apr 2;326(6112):501–505. doi: 10.1038/326501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelson A. M., Bruns G. A., Morton C. C., Orkin S. H. The human phosphoglycerate kinase multigene family. HLA-associated sequences and an X-linked locus containing a processed pseudogene and its functional counterpart. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):6982–6992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Mechanism of transcriptional activation by Sp1: evidence for coactivators. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1187–1197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90683-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson M. O., McCarrey J. R., Simon M. I. Transcriptional regulatory regions of testis-specific PGK2 defined in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8437–8441. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffer J. D., Jackson S. P., Annarella M. B. Developmental expression of Sp1 in the mouse. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2189–2199. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro C., Mermod N., Andrews P. C., Tjian R. A family of human CCAAT-box-binding proteins active in transcription and DNA replication: cloning and expression of multiple cDNAs. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):218–224. doi: 10.1038/334218a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Baltimore D. The "initiator" as a transcription control element. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. H., Wilkie T. M., Tomashefsky P., Bellvé A. R., Simon M. I. Differential gene expression during mouse spermatogenesis. Biol Reprod. 1989 Oct;41(4):729–739. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod41.4.729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VandeBerg J. L., Cooper D. W., Close P. J. Testis specific phosphoglycerate kinase B in mouse. J Exp Zool. 1976 Nov;198(2):231–240. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401980213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VandeBerg J. L. The phosphoglycerate kinase isozyme system in mammals: biochemical, genetic, developmental, and evolutionary aspects. Isozymes Curr Top Biol Med Res. 1985;12:133–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]