Abstract
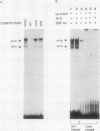
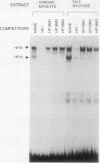
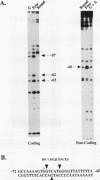
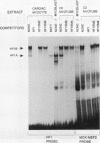
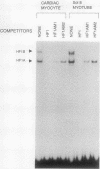
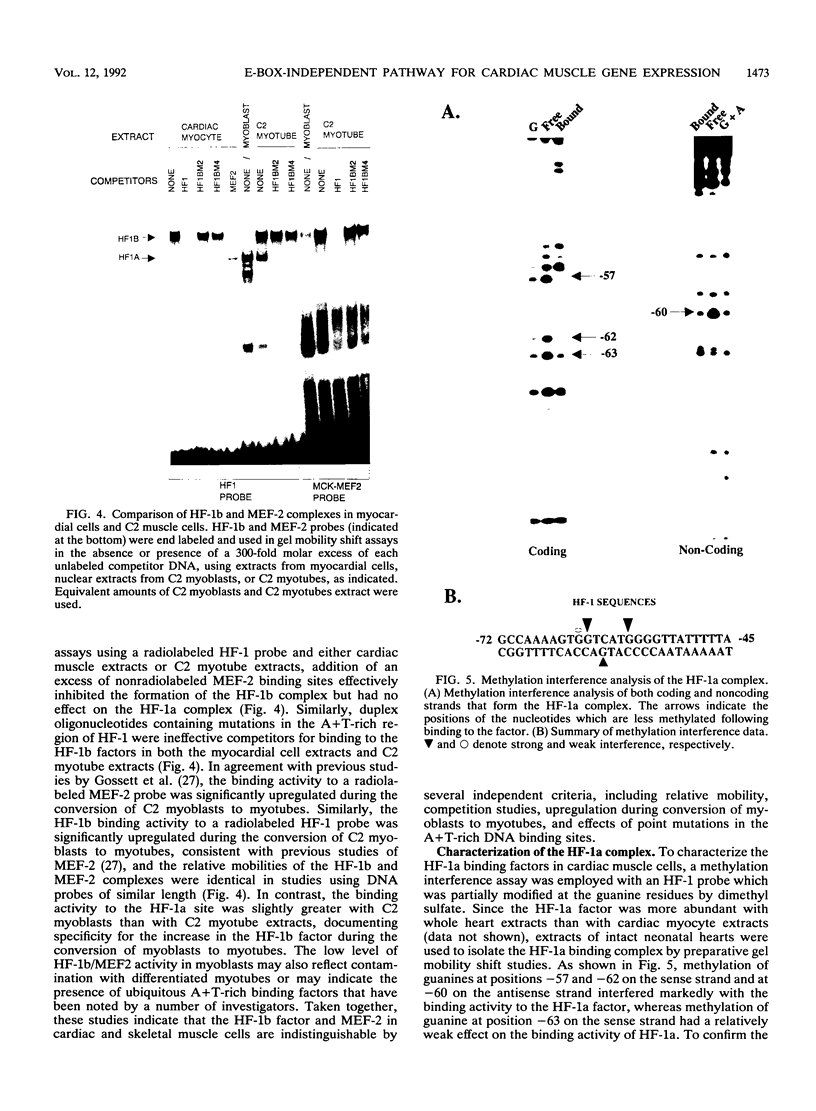
Recent studies have identified a conserved 28-bp element (HF-1) within the rat cardiac MLC-2 gene which confers cardiac muscle-specific and inducible expression during myocardial cell hypertrophy. Utilizing a combination of independent experimental approaches, this study characterizes two cardiac nuclear factors which bind to HF-1, a ubiquitous factor (HF-1a), and an A + T-rich binding factor (HF-1b) which is preferentially expressed in differentiated cardiac and skeletal muscle cells. The HF-1a binding site is located in a core region of the 28-bp conserved element, immediately upstream from the A + T-rich HF-1b site, which is homologous to the MEF-2 site found in a number of muscle genes. By a number of separate criteria (gel mobility shift, competition, and mutagenesis studies), HF-1b and MEF-2 appear to be indistinguishable and thus are either identical or closely related muscle factors. Transient assays of luciferase reporter genes containing point mutations throughout the 28-bp HF-1 regulatory element document the importance of both the HF-1a and HF-1b sites in transient assays in ventricular muscle cells. In the native 250-bp MLC-2 promoter fragment, mutations in the single E box had little effect on cardiac muscle specificity, while point mutations in either the HF-1a or HF-1b binding site significantly reduced promoter activity, underscoring the importance of both the HF-1a and HF-1b sites in the transcriptional activation of this cardiac muscle gene. Thus, this study provides evidence that a novel, ubiquitous factor (HF-1a) and a muscle factor (HF-1b/MEF-2) can form a novel, E-box-independent pathway for muscle-specific expression in ventricular cardiac muscle cells.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behringer R. R., Peschon J. J., Messing A., Gartside C. L., Hauschka S. D., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Heart and bone tumors in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2648–2652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benezra R., Davis R. L., Lockshon D., Turner D. L., Weintraub H. The protein Id: a negative regulator of helix-loop-helix DNA binding proteins. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):49–59. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90214-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergsma D. J., Grichnik J. M., Gossett L. M., Schwartz R. J. Delimitation and characterization of cis-acting DNA sequences required for the regulated expression and transcriptional control of the chicken skeletal alpha-actin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2462–2475. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Weintraub H. Differences and similarities in DNA-binding preferences of MyoD and E2A protein complexes revealed by binding site selection. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1104–1110. doi: 10.1126/science.2174572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvagnet P. F., Strehler E. E., White G. E., Strehler-Page M. A., Nadal-Ginard B., Mahdavi V. Multiple positive and negative 5' regulatory elements control the cell-type-specific expression of the embryonic skeletal myosin heavy-chain gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4377–4389. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Bober E., Winter B., Rosenthal N., Arnold H. H. Myf-6, a new member of the human gene family of myogenic determination factors: evidence for a gene cluster on chromosome 12. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):821–831. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08179.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Buschhausen-Denker G., Bober E., Tannich E., Arnold H. H. A novel human muscle factor related to but distinct from MyoD1 induces myogenic conversion in 10T1/2 fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):701–709. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03429.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buskin J. N., Hauschka S. D. Identification of a myocyte nuclear factor that binds to the muscle-specific enhancer of the mouse muscle creatine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2627–2640. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr C. S., Sharp P. A. A helix-loop-helix protein related to the immunoglobulin E box-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4384–4388. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherrington J. M., Mocarski E. S. Human cytomegalovirus ie1 transactivates the alpha promoter-enhancer via an 18-base-pair repeat element. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1435–1440. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1435-1440.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien K. R., Knowlton K. U., Zhu H., Chien S. Regulation of cardiac gene expression during myocardial growth and hypertrophy: molecular studies of an adaptive physiologic response. FASEB J. 1991 Dec;5(15):3037–3046. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.15.1835945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisaka O., Capecchi M. R. Regionally restricted developmental defects resulting from targeted disruption of the mouse homeobox gene hox-1.5. Nature. 1991 Apr 11;350(6318):473–479. doi: 10.1038/350473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cserjesi P., Olson E. N. Myogenin induces the myocyte-specific enhancer binding factor MEF-2 independently of other muscle-specific gene products. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4854–4862. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Weintraub H., Lassar A. B. Expression of a single transfected cDNA converts fibroblasts to myoblasts. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):987–1000. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90585-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donoghue M., Ernst H., Wentworth B., Nadal-Ginard B., Rosenthal N. A muscle-specific enhancer is located at the 3' end of the myosin light-chain 1/3 gene locus. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1779–1790. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field L. J. Atrial natriuretic factor-SV40 T antigen transgenes produce tumors and cardiac arrhythmias in mice. Science. 1988 Feb 26;239(4843):1029–1033. doi: 10.1126/science.2964082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C. K., Devary O. V., Rosenfeld M. G. Multiple cell type-specific proteins differentially regulate target sequence recognition by the alpha retinoic acid receptor. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):729–738. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90139-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossett L. A., Kelvin D. J., Sternberg E. A., Olson E. N. A new myocyte-specific enhancer-binding factor that recognizes a conserved element associated with multiple muscle-specific genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5022–5033. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson T. A., Kedes L. Identification of multiple proteins that interact with functional regions of the human cardiac alpha-actin promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3269–3283. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson S. A., Spencer M., Sen A., Kumar C., Siddiqui M. A., Chien K. R. Structure, organization, and expression of the rat cardiac myosin light chain-2 gene. Identification of a 250-base pair fragment which confers cardiac-specific expression. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):18142–18148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson S. A., Xu Y. C., Chien K. R. Nucleotide sequence of full length cDNAs encoding rat cardiac myosin light chain-2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 25;16(10):4722–4722. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.10.4722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iannello R. C., Mar J. H., Ordahl C. P. Characterization of a promoter element required for transcription in myocardial cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):3309–3316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa M., Chiu R., Karin M. Transcription factor AP-2 mediates induction by two different signal-transduction pathways: protein kinase C and cAMP. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90152-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwaki K., Sukhatme V. P., Shubeita H. E., Chien K. R. Alpha- and beta-adrenergic stimulation induces distinct patterns of immediate early gene expression in neonatal rat myocardial cells. fos/jun expression is associated with sarcomere assembly; Egr-1 induction is primarily an alpha 1-mediated response. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13809–13817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson T., Allard M. F., Sreenan C. M., Doss L. K., Bishop S. P., Swain J. L. The c-myc proto-oncogene regulates cardiac development in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3709–3716. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Buskin J. N., Lockshon D., Davis R. L., Apone S., Hauschka S. D., Weintraub H. MyoD is a sequence-specific DNA binding protein requiring a region of myc homology to bind to the muscle creatine kinase enhancer. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):823–831. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90935-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Davis R. L., Wright W. E., Kadesch T., Murre C., Voronova A., Baltimore D., Weintraub H. Functional activity of myogenic HLH proteins requires hetero-oligomerization with E12/E47-like proteins in vivo. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):305–315. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90620-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. R., Henderson S. A., Reynolds R., Dunnmon P., Yuan D., Chien K. R. Alpha 1-adrenergic stimulation of cardiac gene transcription in neonatal rat myocardial cells. Effects on myosin light chain-2 gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 25;263(15):7352–7358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Z. Y., Dechesne C. A., Eldridge J., Paterson B. M. An avian muscle factor related to MyoD1 activates muscle-specific promoters in nonmuscle cells of different germ-layer origin and in BrdU-treated myoblasts. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):986–996. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mar J. H., Antin P. B., Cooper T. A., Ordahl C. P. Analysis of the upstream regions governing expression of the chicken cardiac troponin T gene in embryonic cardiac and skeletal muscle cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;107(2):573–585. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.2.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mar J. H., Ordahl C. P. A conserved CATTCCT motif is required for skeletal muscle-specific activity of the cardiac troponin T gene promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6404–6408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mar J. H., Ordahl C. P. M-CAT binding factor, a novel trans-acting factor governing muscle-specific transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4271–4283. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miner J. H., Wold B. Herculin, a fourth member of the MyoD family of myogenic regulatory genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1089–1093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A., Kedes L. Upstream regions of the human cardiac actin gene that modulate its transcription in muscle cells: presence of an evolutionarily conserved repeated motif. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2125–2136. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Timmons P. M., Hébert J. M., Rigby P. W., Tjian R. Transcription factor AP-2 is expressed in neural crest cell lineages during mouse embryogenesis. Genes Dev. 1991 Jan;5(1):105–119. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.1.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Vaessin H., Caudy M., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N., Cabrera C. V., Buskin J. N., Hauschka S. D., Lassar A. B. Interactions between heterologous helix-loop-helix proteins generate complexes that bind specifically to a common DNA sequence. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):537–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90434-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson C., Shen L. P., Meister A., Fodor E., Rutter W. J. Pan: a transcriptional regulator that binds chymotrypsin, insulin, and AP-4 enhancer motifs. Genes Dev. 1990 Jun;4(6):1035–1043. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.6.1035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen D. B., Eckstein F. High-efficiency oligonucleotide-directed plasmid mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1451–1455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N. MyoD family: a paradigm for development? Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1454–1461. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes S. J., Konieczny S. F. Identification of MRF4: a new member of the muscle regulatory factor gene family. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2050–2061. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal N. Identification of regulatory elements of cloned genes with functional assays. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:704–720. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sartorelli V., Webster K. A., Kedes L. Muscle-specific expression of the cardiac alpha-actin gene requires MyoD1, CArG-box binding factor, and Sp1. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1811–1822. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassoon D., Lyons G., Wright W. E., Lin V., Lassar A., Weintraub H., Buckingham M. Expression of two myogenic regulatory factors myogenin and MyoD1 during mouse embryogenesis. Nature. 1989 Sep 28;341(6240):303–307. doi: 10.1038/341303a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scales J. B., Olson E. N., Perry M. Two distinct Xenopus genes with homology to MyoD1 are expressed before somite formation in early embryogenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1516–1524. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen A., Dunnmon P., Henderson S. A., Gerard R. D., Chien K. R. Terminally differentiated neonatal rat myocardial cells proliferate and maintain specific differentiated functions following expression of SV40 large T antigen. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):19132–19136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm R., Baumruker T., Franza B. R., Jr, Herr W. A 100-kD HeLa cell octamer binding protein (OBP100) interacts differently with two separate octamer-related sequences within the SV40 enhancer. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1147–1160. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Identification of a protein-binding site that mediates transcriptional response of the c-fos gene to serum factors. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):567–574. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90882-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voss J. W., Wilson L., Rosenfeld M. G. POU-domain proteins Pit-1 and Oct-1 interact to form a heteromeric complex and can cooperate to induce expression of the prolactin promoter. Genes Dev. 1991 Jul;5(7):1309–1320. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.7.1309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Davis R., Tapscott S., Thayer M., Krause M., Benezra R., Blackwell T. K., Turner D., Rupp R., Hollenberg S. The myoD gene family: nodal point during specification of the muscle cell lineage. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):761–766. doi: 10.1126/science.1846704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright W. E., Sassoon D. A., Lin V. K. Myogenin, a factor regulating myogenesis, has a domain homologous to MyoD. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):607–617. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90583-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee S. P., Mock D., Maltby V., Silver M., Rossant J., Bernstein A., Pawson T. Cardiac and neurological abnormalities in v-fps transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5873–5877. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou D. X., Yen T. S. The ubiquitous transcription factor Oct-1 and the liver-specific factor HNF-1 are both required to activate transcription of a hepatitis B virus promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1353–1359. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu H., Garcia A. V., Ross R. S., Evans S. M., Chien K. R. A conserved 28-base-pair element (HF-1) in the rat cardiac myosin light-chain-2 gene confers cardiac-specific and alpha-adrenergic-inducible expression in cultured neonatal rat myocardial cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2273–2281. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]