Abstract
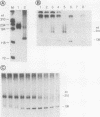
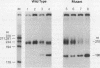
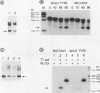
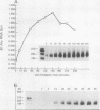
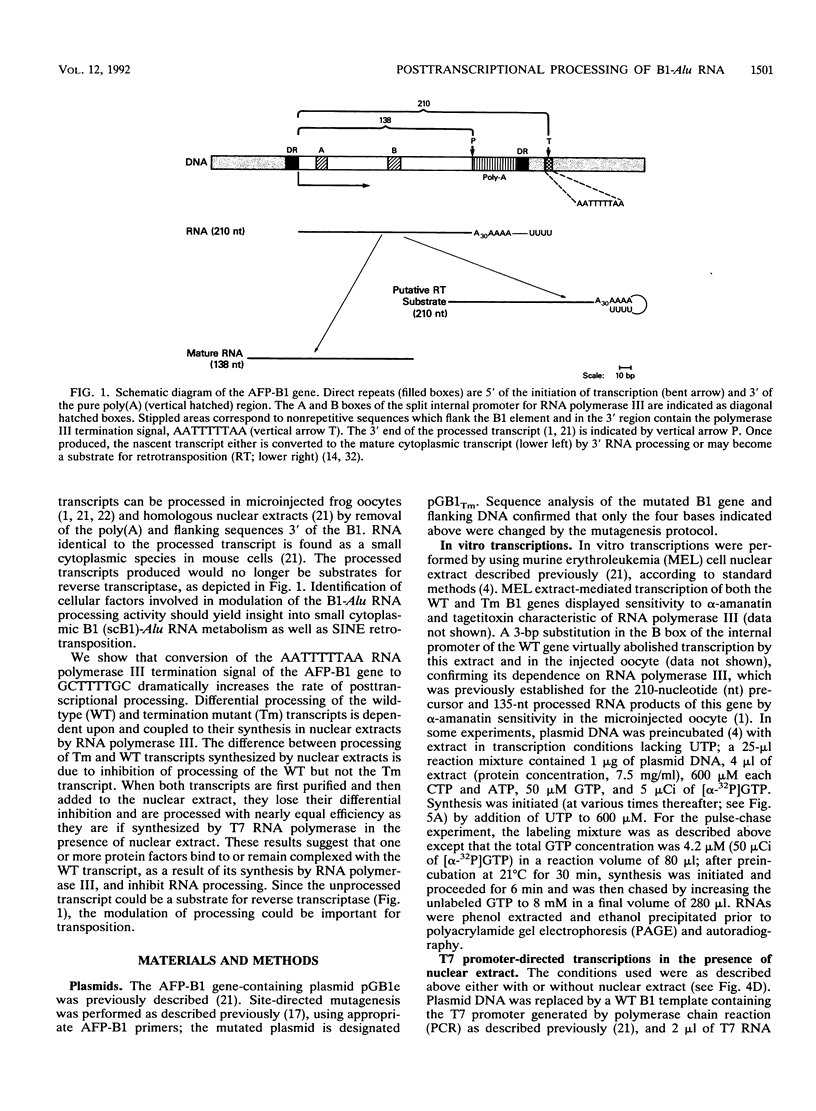
The dispersion of short interspersed elements (SINEs) probably occurred through an RNA intermediate. B1 is a murine homolog of the human SINE Alu; these elements are composed of 5' G + C-rich regions juxtaposed to A-rich tracts and are flanked by direct repeats. Internal promoters direct RNA polymerase III to transcribe B1 and Alu elements and proceed into the 3' flanking DNA until it reaches a (dT)4 termination signal. The resulting transcripts contain 3'-terminal oligo(U) tracts which can presumably base pair with the A-rich tract to form self-primed templates for reverse transcriptase and retrotransposition. Nuclear extracts from mouse tissue culture cells contain an RNA processing activity that removes the A-rich and 3'-terminal regions from purified B1 RNAs (R. Maraia, Nucleic Acids Res. 19:5695-5702, 1991). In this study, we examined transcription and RNA processing in these nuclear extracts. In contrast to results with use of purified RNA, nascent transcripts synthesized in nuclear extract by RNA polymerase III are not processed, suggesting that the transposition-intermediate-like RNA is shielded from processing by a protein(s). Alteration of an AATTTT TAA termination signal to a GCTTTTGC signal activated processing by greater than 100-fold in coupled transcription/processing reactions. A similar difference was found when expression was compared in frog oocytes. No difference in processing was found if the transcripts were made by T7 RNA polymerase in the presence of the nuclear extract, indicating that the different processing effects of the two terminators were dependent on synthesis by polymerase III. The modulation of processing of B1-Alu transcripts and the potential for retrotransposition of B1 and Alu DNA sequences are discussed.
Full text
PDF


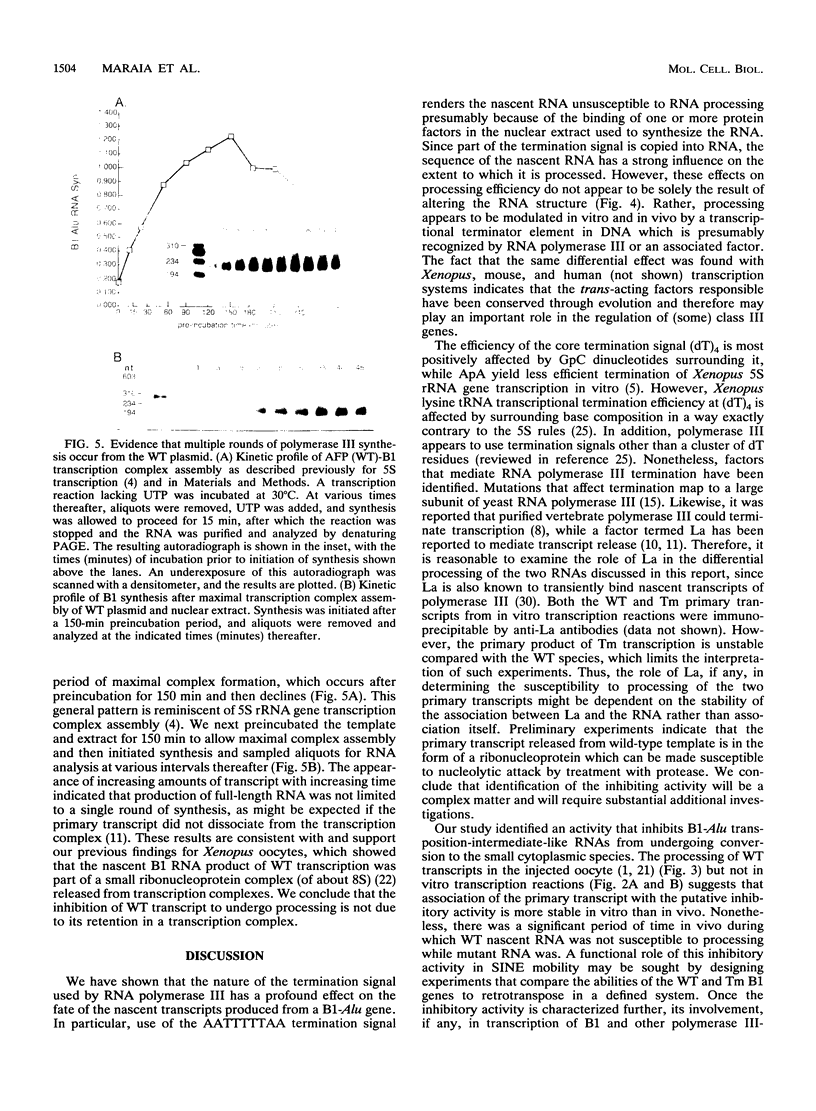


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adeniyi-Jones S., Zasloff M. Transcription, processing and nuclear transport of a B1 Alu RNA species complementary to an intron of the murine alpha-fetoprotein gene. Nature. 1985 Sep 5;317(6032):81–84. doi: 10.1038/317081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batzer M. A., Gudi V. A., Mena J. C., Foltz D. W., Herrera R. J., Deininger P. L. Amplification dynamics of human-specific (HS) Alu family members. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 11;19(13):3619–3623. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.13.3619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batzer M. A., Kilroy G. E., Richard P. E., Shaikh T. H., Desselle T. D., Hoppens C. L., Deininger P. L. Structure and variability of recently inserted Alu family members. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6793–6798. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieker J. J., Martin P. L., Roeder R. G. Formation of a rate-limiting intermediate in 5S RNA gene transcription. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):119–127. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90315-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. Nucleotide sequences in Xenopus 5S DNA required for transcription termination. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90522-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britten R. J., Baron W. F., Stout D. B., Davidson E. H. Sources and evolution of human Alu repeated sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4770–4774. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M. F., Singh K., Botchan M., Cozzarelli N. R. Induction of specific transcription by RNA polymerase III in transformed cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3068–3076. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cozzarelli N. R., Gerrard S. P., Schlissel M., Brown D. D., Bogenhagen D. F. Purified RNA polymerase III accurately and efficiently terminates transcription of 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):829–835. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90540-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godbout R., Ingram R., Tilghman S. M. Multiple regulatory elements in the intergenic region between the alpha-fetoprotein and albumin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):477–487. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb E., Steitz J. A. Function of the mammalian La protein: evidence for its action in transcription termination by RNA polymerase III. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):851–861. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03446.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb E., Steitz J. A. The RNA binding protein La influences both the accuracy and the efficiency of RNA polymerase III transcription in vitro. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):841–850. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03445.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess J., Perez-Stable C., Wu G. J., Weir B., Tinoco I., Jr, Shen C. K. End-to-end transcription of an Alu family repeat. A new type of polymerase-III-dependent terminator and its evolutionary implication. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jul 5;184(1):7–21. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90039-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard B. H., Sakamoto K. Alu interspersed repeats: selfish DNA or a functional gene family? New Biol. 1990 Sep;2(9):759–770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagadeeswaran P., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M. Short interspersed repetitive DNA elements in eucaryotes: transposable DNA elements generated by reverse transcription of RNA pol III transcripts? Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):141–142. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90296-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James P., Whelen S., Hall B. D. The RET1 gene of yeast encodes the second-largest subunit of RNA polymerase III. Structural analysis of the wild-type and ret1-1 mutant alleles. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5616–5624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W. R., Schmid C. W. Repetitive sequences in eukaryotic DNA and their expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:813–844. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.004121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. H., Howard B. H. A rapid method for site-specific mutagenesis and directional subcloning by using the polymerase chain reaction to generate recombinant circles. Biotechniques. 1990 Feb;8(2):178–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurka J., Smith T. A fundamental division in the Alu family of repeated sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4775–4778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen N., Zwieb C. SRP-RNA sequence alignment and secondary structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 25;19(2):209–215. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.2.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maraia R. J. The subset of mouse B1 (Alu-equivalent) sequences expressed as small processed cytoplasmic transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5695–5702. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maraia R., Zasloff M., Plotz P., Adeniyi-Jones S. Pathway of B1-Alu expression in microinjected oocytes: Xenopus laevis proteins associated with nuclear precursor and processed cytoplasmic RNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4433–4440. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matera A. G., Hellmann U., Hintz M. F., Schmid C. W. Recently transposed Alu repeats result from multiple source genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):6019–6023. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.6019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matera A. G., Hellmann U., Schmid C. W. A transpositionally and transcriptionally competent Alu subfamily. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5424–5432. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazabraud A., Scherly D., Müller F., Rungger D., Clarkson S. G. Structure and transcription termination of a lysine tRNA gene from Xenopus laevis. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 20;195(4):835–845. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90488-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quentin Y. Successive waves of fixation of B1 variants in rodent lineage history. J Mol Evol. 1989 Apr;28(4):299–305. doi: 10.1007/BF02103425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quentin Y. The Alu family developed through successive waves of fixation closely connected with primate lineage history. J Mol Evol. 1988;27(3):194–202. doi: 10.1007/BF02100074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefano J. E. Purified lupus antigen La recognizes an oligouridylate stretch common to the 3' termini of RNA polymerase III transcripts. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90083-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strub K., Moss J., Walter P. Binding sites of the 9- and 14-kilodalton heterodimeric protein subunit of the signal recognition particle (SRP) are contained exclusively in the Alu domain of SRP RNA and contain a sequence motif that is conserved in evolution. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):3949–3959. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.3949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Arsdell S. W., Denison R. A., Bernstein L. B., Weiner A. M., Manser T., Gesteland R. F. Direct repeats flank three small nuclear RNA pseudogenes in the human genome. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(1 Pt 1):11–17. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace M. R., Andersen L. B., Saulino A. M., Gregory P. E., Glover T. W., Collins F. S. A de novo Alu insertion results in neurofibromatosis type 1. Nature. 1991 Oct 31;353(6347):864–866. doi: 10.1038/353864a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. J., Stott D., Rigby P. W. Regulation of RNA polymerase III transcription in response to F9 embryonal carcinoma stem cell differentiation. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1081–1092. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90764-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. J., Stott D., Rigby P. W. Regulation of RNA polymerase III transcription in response to Simian virus 40 transformation. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3713–3721. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07584.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willard C., Nguyen H. T., Schmid C. W. Existence of at least three distinct Alu subfamilies. J Mol Evol. 1987;26(3):180–186. doi: 10.1007/BF02099850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young P. R., Scott R. W., Hamer D. H., Tilghman S. M. Construction and expression in vivo of an internally deleted mouse alpha-fetoprotein gene: presence of a transcribed Alu-like repeat within the first intervening sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 25;10(10):3099–3116. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.10.3099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]