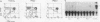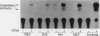Abstract
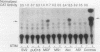
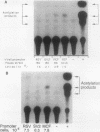
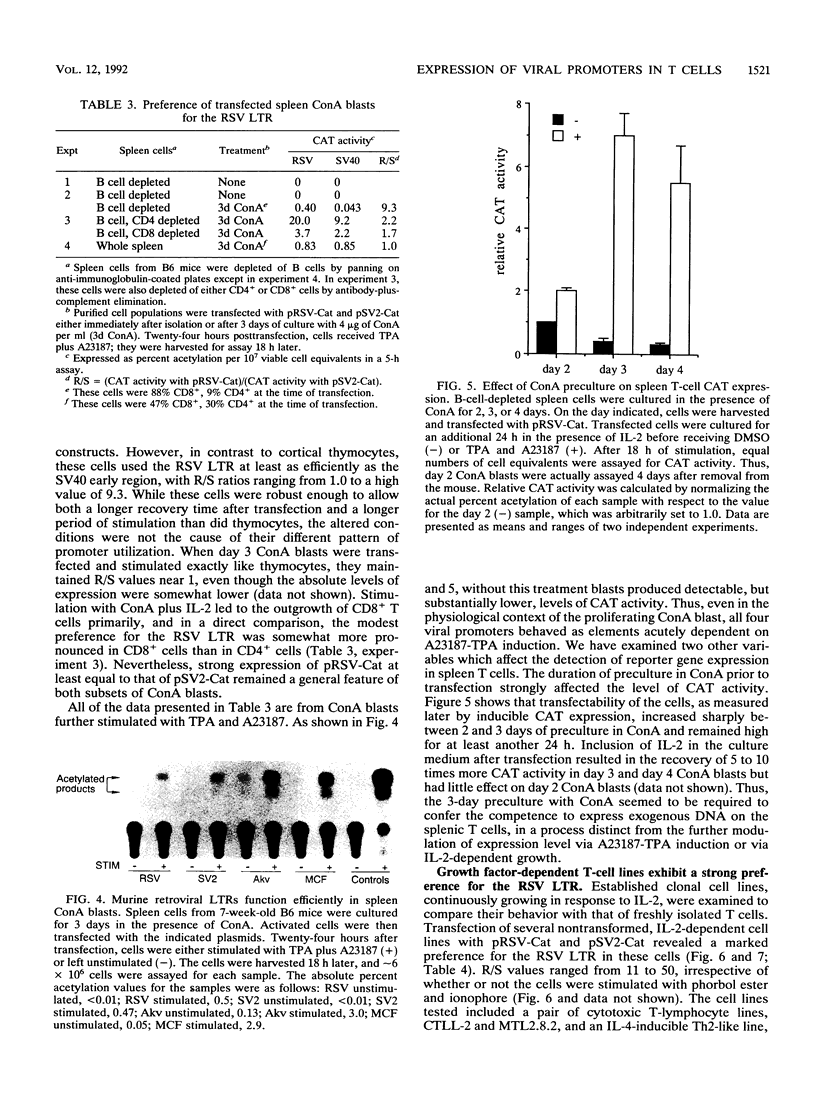
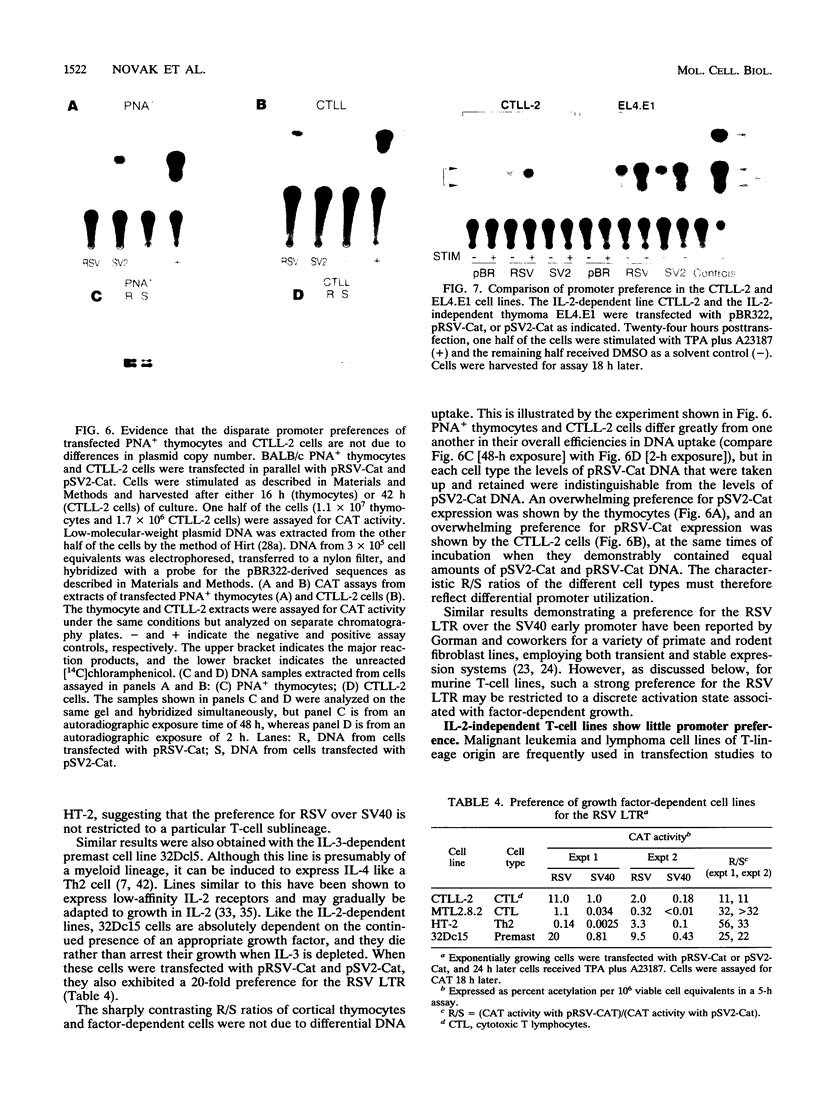
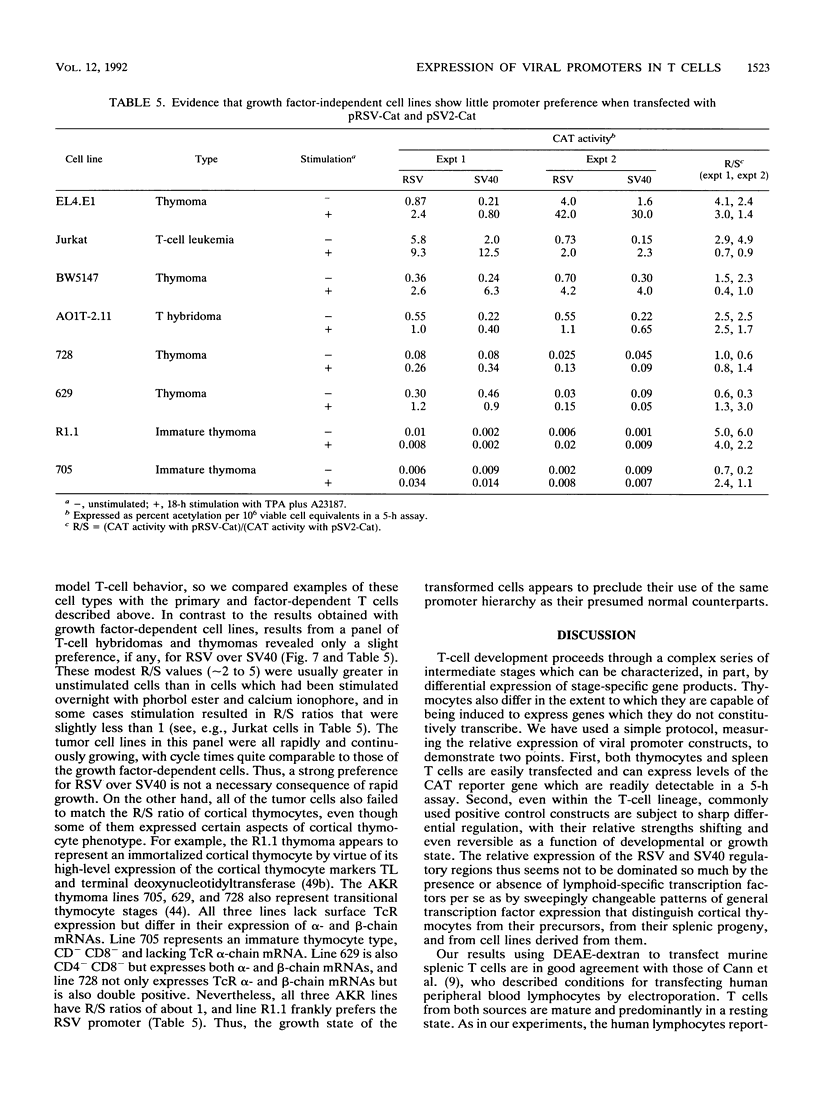
We describe conditions under which exogenous DNA templates can be introduced for transient expression into primary murine T lymphocytes. T cells at various stages of development, including concanavalin A-activated splenic T cells, immature pre-T cells, and even small cortical thymocytes, could be successfully transfected. A variety of model DNA constructs were compared in which different viral promoter regions were used to drive expression of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) reporter gene. All showed enhanced expression in cells that had been acutely stimulated with the Ca2+ ionophore A23187 and phorbol ester as chemical proxies for T-cell receptor-mediated signals. In addition, splenocytes but not thymocytes required prior treatment with a mitogen and interleukin-2 in order to express these constructs, implying that even postmitotic thymocytes may be held in a quasiactivated state. A most striking result was the finding that the viral regulatory sequences in the Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat and the simian virus 40 early region were subject to sharply differential regulation, with a rank order that changed depending on the developmental stage of the T cells. The most immature thymic blasts and several lymphoma cell lines expressed the pRSV-Cat and pSV2-Cat constructs similarly, but cortical thymocytes exhibited a strong preference for pSV2-Cat. Splenic concanavalin A-stimulated blasts, on the other hand, slightly preferred pRSV-Cat, a tendency which became exaggerated in factor-dependent T-cell lines. The ratio of pRSV-Cat to pSV2-Cat expression varied according to cell type by as much as 500-fold. These results argue against a trivial linkage of promoter preference to cell cycle status but instead provide evidence that activation of T cells at distinct stages of differentiation results in the expression of different ensembles of nuclear regulatory proteins. In contrast to the simian virus 40 and Rous sarcoma virus promoter regions, the long terminal repeats of the retroviruses mink cell focus-forming virus and Akv were expressed well in all primary T-lineage cells. Thus, they represent excellent model promoters for engineering developmental stage-independent expression of exogenous genes in murine T cells.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adkins B., Mueller C., Okada C. Y., Reichert R. A., Weissman I. L., Spangrude G. J. Early events in T-cell maturation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:325–365. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.001545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg P. E., Popovic Z., Anderson W. F. Promoter dependence of enhancer activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1664–1668. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg P. E., Yu J. K., Popovic Z., Schumperli D., Johansen H., Rosenberg M., Anderson W. F. Differential activation of the mouse beta-globin promoter by enhancers. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;3(7):1246–1254. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.7.1246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosma M. J., Carroll A. M. The SCID mouse mutant: definition, characterization, and potential uses. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:323–350. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.001543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer P. D., Diamond R. A., Rothenberg E. V. Changes in inducibility of IL-2 receptor alpha-chain and T cell-receptor expression during thymocyte differentiation in the mouse. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 15;142(12):4121–4130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer P. D., Rothenberg E. V. IL-2 receptor inducibility is blocked in cortical-type thymocytes. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):2886–2892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. A., Pierce J. H., Watson C. J., Falco J., Ihle J. N., Paul W. E. B cell stimulatory factor-1/interleukin-4 mRNA is expressed by normal and transformed mast cells. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):809–818. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90339-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant B. J. Renewal and fate in the mammalian thymus: mechanisms and inferences of thymocytokinetics. Eur J Immunol. 1972 Feb;2(1):38–45. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830020109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caplan B., Rothenberg E. High-level secretion of interleukin 2 by a subset of proliferating thymic lymphoblasts. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):1983–1991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Cloyd M. W., Linemeyer D. L., Lander M. R., Rands E., Lowy D. R. Cellular origin and role of mink cell focus-forming viruses in murine thymic lymphomas. Nature. 1982 Jan 7;295(5844):25–31. doi: 10.1038/295025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloyd M. W. Characterization of target cells for MCF viruses in AKR mice. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):217–225. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90512-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloyd M. W., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Lymphomagenicity of recombinant mink cell focus-inducing murine leukemia viruses. J Exp Med. 1980 Mar 1;151(3):542–552. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.3.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A., Barankiewicz J., Lederman H. M., Gelfand E. W. Purine and pyrimidine metabolism in human T lymphocytes. Regulation of deoxyribonucleotide metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12334–12340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. J., Duke R. C. Glucocorticoid activation of a calcium-dependent endonuclease in thymocyte nuclei leads to cell death. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):38–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corcoran L. M., Adams J. M., Dunn A. R., Cory S. Murine T lymphomas in which the cellular myc oncogene has been activated by retroviral insertion. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90306-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cormack B. P., Strubin M., Ponticelli A. S., Struhl K. Functional differences between yeast and human TFIID are localized to the highly conserved region. Cell. 1991 Apr 19;65(2):341–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90167-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuypers H. T., Selten G., Quint W., Zijlstra M., Maandag E. R., Boelens W., van Wezenbeek P., Melief C., Berns A. Murine leukemia virus-induced T-cell lymphomagenesis: integration of proviruses in a distinct chromosomal region. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):141–150. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90309-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkel T. H., Kubo R. T., Cambier J. C. T-cell development and transmembrane signaling: changing biological responses through an unchanging receptor. Immunol Today. 1991 Feb;12(2):79–85. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90162-M. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowlkes B. J., Pardoll D. M. Molecular and cellular events of T cell development. Adv Immunol. 1989;44:207–264. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60643-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Kadonaga J. T., Barrera-Saldaña H., Takahashi K., Chambon P., Tjian R. Bidirectional SV40 transcription mediated by tandem Sp1 binding interactions. Science. 1985 Nov 1;230(4725):511–517. doi: 10.1126/science.2996137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G., Tjian R. A highly conserved domain of TFIID displays species specificity in vivo. Cell. 1991 Apr 19;65(2):333–340. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90166-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C., Padmanabhan R., Howard B. H. High efficiency DNA-mediated transformation of primate cells. Science. 1983 Aug 5;221(4610):551–553. doi: 10.1126/science.6306768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidos C. J., Weissman I. L., Adkins B. Intrathymic maturation of murine T lymphocytes from CD8+ precursors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7542–7546. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullberg M., Smith K. A. Regulation of T cell autocrine growth. T4+ cells become refractory to interleukin 2. J Exp Med. 1986 Feb 1;163(2):270–284. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.2.270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckford S. E., Gelmann E. P., Agnor C. L., Jacobson S., Zinn S., Matis L. A. Distinct signals are required for proliferation and lymphokine gene expression in murine T cell clones. J Immunol. 1986 Dec 1;137(11):3652–3663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollon T., Yoshimura F. K. Mapping of functional regions of murine retrovirus long terminal repeat enhancers: enhancer domains interact and are not independent in their contributions to enhancer activity. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3353–3361. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3353-3361.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kefford R. F., Fox R. M. Purine deoxynucleoside toxicity in nondividing human lymphoid cells. Cancer Res. 1982 Jan;42(1):324–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinnon C., Diamond R. A., Rothenberg E. V. Activation of T cell antigen receptor alpha- and beta-chain genes in the thymus: implications for the lineages of developing cortical thymocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Dec 15;137(12):4010–4015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyasu S., Yodoi J., Nikaido T., Tagaya Y., Taniguchi Y., Honjo T., Yahara I. Expression of interleukin 2 receptors on interleukin 3-dependent cell lines. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 1;136(3):984–987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Khoury G., Gorman C., Howard B., Gruss P. Host-specific activation of transcription by tandem repeats from simian virus 40 and Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6453–6457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Gros G. S., Gillis S., Watson J. D. Induction of IL 2 responsiveness in a murine IL 3-dependent cell line. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):4009–4014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugo J. P., Krishnan S. N., Sailor R. D., Koen P., Malek T., Rothenberg E. Proliferation of thymic stem cells with and without receptors for interleukin 2. Implications for intrathymic antigen recognition. J Exp Med. 1985 May 1;161(5):1048–1062. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.5.1048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugo J. P., Krishnan S. N., Sailor R. D., Rothenberg E. V. Early precursor thymocytes can produce interleukin 2 upon stimulation with calcium ionophore and phorbol ester. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1862–1866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald H. R., Budd R. C., Howe R. C. A CD3- subset of CD4-8+ thymocytes: a rapidly cycling intermediate in the generation of CD4+8+ cells. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Apr;18(4):519–523. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D., Wiadrowski M. Autoradiographic analysis of lymphocyte proliferation in the thymus and in thymic lymphoma tissue. Cancer Res. 1966 Mar;26(3):483–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novak T. J., Rothenberg E. V. Differential transient and long-term expression of DNA sequences introduced into T-lymphocyte lines. DNA. 1986 Dec;5(6):439–451. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1986.5.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novak T. J., White P. M., Rothenberg E. V. Regulatory anatomy of the murine interleukin-2 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 11;18(15):4523–4533. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.15.4523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell P. V., Woller R., Chu A. Stages in development of mink cell focus-inducing (MCF) virus-accelerated leukemia in AKR mice. J Exp Med. 1984 Sep 1;160(3):914–934. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.3.914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richie E. R., McEntire B., Crispe N., Kimura J., Lanier L. L., Allison J. P. Alpha/beta T-cell antigen receptor gene and protein expression occurs at early stages of thymocyte differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1174–1178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riegel J. S., Richie E. R., Allison J. P. Nuclear events after activation of CD4+8+ thymocytes. J Immunol. 1990 May 1;144(9):3611–3618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothenberg E. V., Diamond R. A., Pepper K. A., Yang J. A. IL-2 gene inducibility in T cells before T cell receptor expression. Changes in signaling pathways and gene expression requirements during intrathymic maturation. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 1;144(5):1614–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothenberg E. V., McGuire K. L., Boyer P. D. Molecular indices of functional competence in developing T cells. Immunol Rev. 1988 Aug;104:29–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1988.tb00758.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothenberg E. A specific biosynthetic marker for immature thymic lymphoblasts. Active synthesis of thymus-leukemia antigen restricted to proliferating cells. J Exp Med. 1982 Jan 1;155(1):140–154. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.1.140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothenberg E., Triglia D. Clonal proliferation unlinked to terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase synthesis in thymocytes of young mice. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1627–1633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffer J. D., Jackson S. P., Annarella M. B. Developmental expression of Sp1 in the mouse. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2189–2199. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shastri N., Malissen B., Hood L. Ia-transfected L-cell fibroblasts present a lysozyme peptide but not the native protein to lysozyme-specific T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5885–5889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheiness D., Gardinier M. Expression of a proto-oncogene (proto-myb) in hemopoietic tissues of mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;4(7):1206–1212. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.7.1206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spangrude G. J., Scollay R. Differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells in irradiated mouse thymic lobes. Kinetics and phenotype of progeny. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 1;145(11):3661–3668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck N. A., Renjifo B., Hopkins N. Point mutations in the Moloney murine leukemia virus enhancer identify a lymphoid-specific viral core motif and 1,3-phorbol myristate acetate-inducible element. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):543–550. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.543-550.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. B., Challoner P. B., Neiman P. E., Groudine M. Expression of the c-myb proto-oncogene during cellular proliferation. 1986 Jan 30-Feb 5Nature. 319(6052):374–380. doi: 10.1038/319374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. B., Challoner P. B., Neiman P. E., Groudine M. Levels of c-myc oncogene mRNA are invariant throughout the cell cycle. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):363–366. doi: 10.1038/314363a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullman K. S., Northrop J. P., Verweij C. L., Crabtree G. R. Transmission of signals from the T lymphocyte antigen receptor to the genes responsible for cell proliferation and immune function: the missing link. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:421–452. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.002225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura F. K., Davison B., Chaffin K. Murine leukemia virus long terminal repeat sequences can enhance gene activity in a cell-type-specific manner. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2832–2835. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura F. K. Identification of a DNA fragment from a molecularly cloned mink cell focus-inducing murine leukemia virus specific for xenotropic virus-related sequences. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):348–351. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.348-351.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Boehmer H. Developmental biology of T cells in T cell-receptor transgenic mice. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:531–556. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.002531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]