Abstract
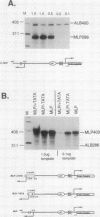
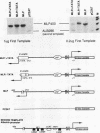
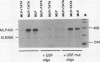
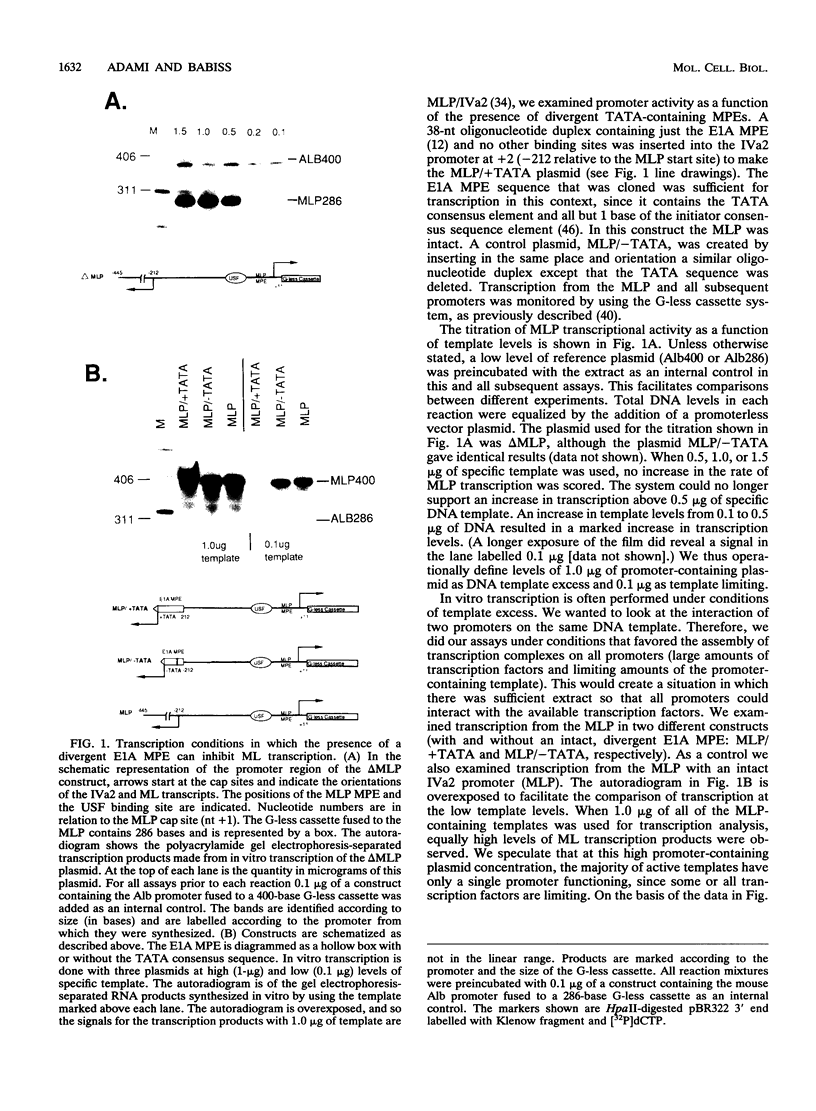
By in vitro analysis, the major late promoter (MLP) of adenovirus has been shown to be a simple promoter requiring two elements for efficient transcription: a minimal promoter element (MPE), where the general transcription factor-polymerase II complex binds, and a single functional upstream promoter element (UPE) which interacts with USF. Two hundred bases upstream of the MLP cap site and divergently oriented is the IVa2 promoter. This promoter has its own MPE but shares the MLP UPE, suggesting the possibility that these promoters are coordinately regulated. To determine mechanistically how this might function, we replaced the weak IVa2 minimal promoter with a strong MPE (from the viral E1A gene) and observed mutual inhibition of both promoters and unstable transcription factor binding. Only by duplication of the UPE could this inhibition be relieved. When tested independently, both promoters were shown to require the USF site for maximal activity. These results are compatible with a model in which USF can stably interact with only one transcription complex at a time. When two divergently oriented general transcription complexes compete efficiently for binding of USF, transcription is reduced to the same levels as if the USF site were absent.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brady J., Radonovich M., Vodkin M., Natarajan V., Thoren M., Das G., Janik J., Salzman N. P. Site-specific base substitution and deletion mutations that enhance or suppress transcription of the SV40 major late RNA. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):625–633. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90318-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandl C. J., Struhl K. Yeast GCN4 transcriptional activator protein interacts with RNA polymerase II in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2652–2656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S., Hahn S., Guarente L., Sharp P. A. Five intermediate complexes in transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):549–561. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90578-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burbelo P. D., Martin G. R., Yamada Y. Alpha 1(IV) and alpha 2(IV) collagen genes are regulated by a bidirectional promoter and a shared enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9679–9682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill K. B., Carmichael G. G. Deletion analysis of the polyomavirus late promoter: evidence for both positive and negative elements in the absence of early proteins. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3634–3642. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3634-3642.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carcamo J., Maldonado E., Cortes P., Ahn M. H., Ha I., Kasai Y., Flint J., Reinberg D. A TATA-like sequence located downstream of the transcription initiation site is required for expression of an RNA polymerase II transcribed gene. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1611–1622. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M., Lin Y. S., Green M. R., Ptashne M. A mechanism for synergistic activation of a mammalian gene by GAL4 derivatives. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):361–364. doi: 10.1038/345361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carthew R. W., Chodosh L. A., Sharp P. A. An RNA polymerase II transcription factor binds to an upstream element in the adenovirus major late promoter. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comb M., Mermod N., Hyman S. E., Pearlberg J., Ross M. E., Goodman H. M. Proteins bound at adjacent DNA elements act synergistically to regulate human proenkephalin cAMP inducible transcription. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3793–3805. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03264.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison B. L., Egly J. M., Mulvihill E. R., Chambon P. Formation of stable preinitiation complexes between eukaryotic class B transcription factors and promoter sequences. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):680–686. doi: 10.1038/301680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyen N., Dreyfus M., Rougeon F. Regulatory elements involved in the bidirectional activity of an immunoglobulin promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):1977–1987. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fire A., Baker C. C., Manley J. L., Ziff E. B., Sharp P. A. In vitro transcription of adenovirus. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):703–719. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.703-719.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J., Wu F., Gaynor R. Upstream regulatory regions required to stabilize binding to the TATA sequence in an adenovirus early promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8367–8385. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski K., Carneiro M., Schibler U. Tissue-specific in vitro transcription from the mouse albumin promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):767–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregor P. D., Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. The adenovirus major late transcription factor USF is a member of the helix-loop-helix group of regulatory proteins and binds to DNA as a dimer. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1730–1740. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grichnik J. M., French B. A., Schwartz R. J. The chicken skeletal alpha-actin gene promoter region exhibits partial dyad symmetry and a capacity to drive bidirectional transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4587–4597. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hen R., Sassone-Corsi P., Corden J., Gaub M. P., Chambon P. Sequences upstream from the T-A-T-A box are required in vivo and in vitro for efficient transcription from the adenovirus serotype 2 major late promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7132–7136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbomel P. Synergistic activation of eukaryotic transcription: the multiacceptor target hypothesis. New Biol. 1990 Dec;2(12):1063–1070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbst R. S., Boczko E. M., Darnell J. E., Jr, Babiss L. E. The mouse albumin enhancer contains a negative regulatory element that interacts with a novel DNA-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):3896–3905. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.3896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuchel R., Matthias P., Schaffner W. Two closely spaced promoters are equally activated by a remote enhancer: evidence against a scanning model for enhancer action. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):8931–8947. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.22.8931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann A., Garfinkel M. D., Meyerowitz E. M. cis-acting sequences required for expression of the divergently transcribed Drosophila melanogaster Sgs-7 and Sgs-8 glue protein genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):2971–2979. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.2971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi M., Hai T., Lin Y. S., Green M. R., Roeder R. G. Transcription factor ATF interacts with the TATA factor to facilitate establishment of a preinitiation complex. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1033–1042. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90118-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang D. H., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Activation of the adenovirus EIIa late promoter by a single-point mutation which enhances binding of transcription factor IID. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12596–12601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennard A. C., Egly J. M. The bidirectional upstream element of the adenovirus-2 major late promoter binds a single monomeric molecule of the upstream factor. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3027–3034. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02608.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong K., Lee W., Berk A. J. High-level transcription from the adenovirus major late promoter requires downstream binding sites for late-phase-specific factors. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):51–60. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.51-60.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maire P., Wuarin J., Schibler U. The role of cis-acting promoter elements in tissue-specific albumin gene expression. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):343–346. doi: 10.1126/science.2711183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncollin V., Kempf A., Egly J. M. The mammalian upstream element factor recognizes two sites in the adenovirus type 2 IVa2-major late promoter intergenic region and stimulates both promoters. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3199–3206. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3199-3206.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondésert G., Kédinger C. Cooperation between upstream and downstream elements of the adenovirus major late promoter for maximal late phase-specific transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 25;19(12):3221–3228. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.12.3221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima N., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II: purification, genetic specificity, and TATA box-promoter interactions of TFIID. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4028–4040. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natarajan V., Madden M. J., Salzman N. P. Positive and negative control sequences within the distal domain of the adenovirus IVa2 promoter overlap with the major late promoter. J Virol. 1985 Jul;55(1):10–15. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.1.10-15.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natarajan V., Madden M. J., Salzman N. P. Proximal and distal domains that control in vitro transcription of the adenovirus IVa2 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6290–6294. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reach M., Babiss L. E., Young C. S. The upstream factor-binding site is not essential for activation of transcription from the adenovirus major late promoter. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5851–5860. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5851-5860.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinberg D., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription in mammalian RNA polymerase II. Functional analysis of initiation factors IIA and IID and identification of a new factor operating at sequences downstream of the initiation site. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3322–3330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinberg D., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Purification and functional analysis of initiation factors IIB and IIE. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3310–3321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltzman A. G., Weinmann R. Promoter specificity and modulation of RNA polymerase II transcription. FASEB J. 1989 Apr;3(6):1723–1733. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.6.2649403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by human RNA polymerase II: analysis by a rapid and quantitative in vitro assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4394–4398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a gene-specific transcription factor with the adenovirus major late promoter upstream of the TATA box region. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Sentenac A. RNA polymerase B (II) and general transcription factors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:711–754. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.003431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatt M. D., Rusconi S., Schaffner W. A single DNA-binding transcription factor is sufficient for activation from a distant enhancer and/or from a promoter position. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):481–487. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08134.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schilling L. J., Farnham P. J. Identification of a new promoter upstream of the murine dihydrofolate reductase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4568–4570. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Muller M., Kaltschmidt C., Renkawitz R. Many transcription factors interact synergistically with steroid receptors. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1418–1420. doi: 10.1126/science.3201230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Baltimore D. The "initiator" as a transcription control element. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyndall C., La Mantia G., Thacker C. M., Favaloro J., Kamen R. A region of the polyoma virus genome between the replication origin and late protein coding sequences is required in cis for both early gene expression and viral DNA replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6231–6250. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. W., Roeder R. G., Sawadogo M. Physical analysis of transcription preinitiation complex assembly on a class II gene promoter. Science. 1988 Sep 9;241(4871):1335–1338. doi: 10.1126/science.3413495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. W., Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Stability of transcription complexes on class II genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):342–344. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West R. W., Jr, Yocum R. R., Ptashne M. Saccharomyces cerevisiae GAL1-GAL10 divergent promoter region: location and function of the upstream activating sequence UASG. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2467–2478. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T. J., Fried M. The MES-1 murine enhancer element is closely associated with the heterogeneous 5' ends of two divergent transcription units. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4558–4569. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman J. L., Roeder R. G. Binding of transcription factor TFIID to the major late promoter during in vitro nucleosome assembly potentiates subsequent initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1987 Nov 20;51(4):613–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90130-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman J. L., Roeder R. G., Kingston R. E. An upstream transcription factor, USF (MLTF), facilitates the formation of preinitiation complexes during in vitro chromatin assembly. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1299–1308. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08239.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]