Abstract
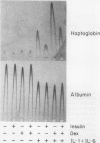
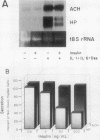
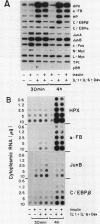
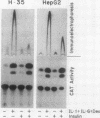
Several endocrine hormones which influence liver metabolism are known to increase in activity during the acute phase of injury or inflammation. We determined whether these hormones have the potential to influence acute-phase protein production in human and rat hepatoma cells. Catecholamines, glucagon, growth hormone, triiodothyronine, and cyclic nucleotides individually or in combination did not modulate the basal or the interleukin-1 (IL-1)-, IL-6-, and dexamethasone-stimulated levels of acute-phase plasma proteins. Insulin, however, was found to be a rapid, nonspecific, and dose-dependent inhibitor of the cytokine and glucocorticoid stimulation of acute-phase protein gene expression and to exert its effect at the transcriptional level. The insulin inhibition applied to all cytokines tested but to various degrees, depending upon the particular acute-phase gene. Insulin resulted in an early and prominent increase in the transcription of genes encoding the AP-1 components of JunA, JunB, and c-Fos, as has been observed for other growth factors. However, the effect of insulin on C/EBP beta was unexpected and paradoxical: while insulin completely inhibited the transcriptional activation of the C/EBP beta gene in cytokine- and dexamethasone-treated cells, the level of cytoplasmic C/EBP beta RNA was elevated. Quantitation of C/EBP beta mRNA by Northern (RNA) blot analysis and of C/EBP beta DNA binding activity by Southwestern (DNA-protein) blot analysis showed that insulin, when combined with cytokines and dexamethasone, stimulated both the mRNA and DNA binding activity by a factor of 1.6 compared with that of cells treated with cytokines and dexamethasone alone. Transient transfection of H-35 and HepG2 cells with a chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) gene expression vector containing the C/EBP beta response element also resulted in a 1.5-fold increase of C/EBP beta-mediated transcription in insulin-treated cells. Transfection of CAT gene constructs containing increasing lengths of heptaglobin gene 5' flanking sequences indicated that insulin inhibition of IL-6 stimulation required the presence of the region from -4100 to -1030. These results suggest that insulin has the potential to control the transcription of acute-phase genes by at least two separate mechanisms.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almendral J. M., Sommer D., Macdonald-Bravo H., Burckhardt J., Perera J., Bravo R. Complexity of the early genetic response to growth factors in mouse fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2140–2148. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagdade J. D., Root R. K., Bulger R. J. Impaired leukocyte function in patients with poorly controlled diabetes. Diabetes. 1974 Jan;23(1):9–15. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagdade J. D., Stewart M., Walters E. Impaired granulocyte adherence. A reversible defect in host defense in patients with poorly controlled diabetes. Diabetes. 1978 Jun;27(6):677–681. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.6.677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H. Hepatic acute phase reaction in vivo and in vitro. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1989 Feb;25(2):115–126. doi: 10.1007/BF02626167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Hill R. E., Sauder D. N., Jahreis G. P. Regulation of major acute-phase plasma proteins by hepatocyte-stimulating factors of human squamous carcinoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;102(2):370–383. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.2.370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Jahreis G. P., Morella K. K. Interaction of cytokine- and glucocorticoid-response elements of acute-phase plasma protein genes. Importance of glucocorticoid receptor level and cell type for regulation of the elements from rat alpha 1-acid glycoprotein and beta-fibrinogen genes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22275–22281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Morella K. K., Jahreis G. P., Marinković S. Distinct regulation of the interleukin-1 and interleukin-6 response elements of the rat haptoglobin gene in rat and human hepatoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5967–5976. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Prowse K. R., Marinković S., Won K. A., Jahreis G. P. Stimulation of hepatic acute phase response by cytokines and glucocorticoids. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;557:280-95, discussion 295-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb24021.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Richards C., Gauldie J. Interaction among hepatocyte-stimulating factors, interleukin 1, and glucocorticoids for regulation of acute phase plasma proteins in human hepatoma (HepG2) cells. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 15;139(12):4122–4128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensi G., Raugei G., Klefenz H., Cortese R. Structure and expression of the human haptoglobin locus. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):119–126. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02325.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder C., Lauritzen T., Faber O., Pramming S. Insulin pharmacokinetics. Diabetes Care. 1984 Mar-Apr;7(2):188–199. doi: 10.2337/diacare.7.2.188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black P. R., Brooks D. C., Bessey P. Q., Wolfe R. R., Wilmore D. W. Mechanisms of insulin resistance following injury. Ann Surg. 1982 Oct;196(4):420–435. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198210000-00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao Z., Umek R. M., McKnight S. L. Regulated expression of three C/EBP isoforms during adipose conversion of 3T3-L1 cells. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1538–1552. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlier M. F. Actin: protein structure and filament dynamics. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clowes G. H., Jr, O'Donnell T. F., Blackburn G. L., Maki T. N. Energy metabolism and proteolysis in traumatized and septic man. Surg Clin North Am. 1976 Oct;56(5):1169–1184. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)41036-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dominioni L., Dionigi R., Zanello M., Monico R., Cremaschi R., Dionigi R., Ballabio A., Massa M., Comelli M., Dal Ri P. Sepsis score and acute-phase protein response as predictors of outcome in septic surgical patients. Arch Surg. 1987 Feb;122(2):141–146. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1987.01400140023001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filkins J. P. Phases of glucose dyshomeostasis in endotoxicosis. Circ Shock. 1978;5(4):347–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frayn K. N. Insulin secretion after injuries of differing severity in the rat. Br J Exp Pathol. 1976 Jun;57(3):316–320. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauldie J., Richards C., Harnish D., Lansdorp P., Baumann H. Interferon beta 2/B-cell stimulatory factor type 2 shares identity with monocyte-derived hepatocyte-stimulating factor and regulates the major acute phase protein response in liver cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7251–7255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granner D. K., Sasaki K., Chu D. Multihormonal regulation of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene transcription. The dominant role of insulin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;478:175–190. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb15530.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hack C. E., De Groot E. R., Felt-Bersma R. J., Nuijens J. H., Strack Van Schijndel R. J., Eerenberg-Belmer A. J., Thijs L. G., Aarden L. A. Increased plasma levels of interleukin-6 in sepsis. Blood. 1989 Oct;74(5):1704–1710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. E., Shaw P. H., Boyd P. A., Baumann H., Hastie N. D. Plasma protease inhibitors in mouse and man: divergence within the reactive centre regions. Nature. 1984 Sep 13;311(5982):175–177. doi: 10.1038/311175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshi H., Kan M., McKeehan W. L. Direct analysis of growth factor requirements for isolated human fetal hepatocytes. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1987 Oct;23(10):723–732. doi: 10.1007/BF02620987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles B. B., Howe C. C., Aden D. P. Human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines secrete the major plasma proteins and hepatitis B surface antigen. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):497–499. doi: 10.1126/science.6248960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohase M., May L. T., Tamm I., Vilcek J., Sehgal P. B. A cytokine network in human diploid fibroblasts: interactions of beta-interferons, tumor necrosis factor, platelet-derived growth factor, and interleukin-1. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):273–280. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner I. The phenomenon of the acute phase response. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;389:39–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb22124.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamers W. H., Hanson R. W., Meisner H. M. cAMP stimulates transcription of the gene for cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase in rat liver nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5137–5141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le P. T., Mortensen R. F. In vitro induction of hepatocyte synthesis of the acute phase reactant mouse serum amyloid P-component by macrophages and IL 1. J Leukoc Biol. 1984 Jun;35(6):587–603. doi: 10.1002/jlb.35.6.587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopata M. A., Cleveland D. W., Sollner-Webb B. High level transient expression of a chloramphenicol acetyl transferase gene by DEAE-dextran mediated DNA transfection coupled with a dimethyl sulfoxide or glycerol shock treatment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5707–5717. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacCuish A. C., Urbaniak S. J., Campbell C. J., Duncan L. J., Irvine W. J. Phytohemagglutinin transformation and circulating lymphocyte subpopulations in insulin-dependent diabetic patients. Diabetes. 1974 Aug;23(8):708–712. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.8.708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinković S., Baumann H. Structure, hormonal regulation, and identification of the interleukin-6- and dexamethasone-responsive element of the rat haptoglobin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1573–1583. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May L. T., Ghrayeb J., Santhanam U., Tatter S. B., Sthoeger Z., Helfgott D. C., Chiorazzi N., Grieninger G., Sehgal P. B. Synthesis and secretion of multiple forms of beta 2-interferon/B-cell differentiation factor 2/hepatocyte-stimulating factor by human fibroblasts and monocytes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7760–7766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messina J. L. Insulin's regulation of c-fos gene transcription in hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11700–11705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliviero S., Cortese R. The human haptoglobin gene promoter: interleukin-6-responsive elements interact with a DNA-binding protein induced by interleukin-6. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1145–1151. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03485.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilkis S. J., Fox E., Wolfe L., Rothbarth L., Colosia A., Stewart H. B., el-Maghrabi M. R. Hormonal modulation of key hepatic regulatory enzymes in the gluconeogenic/glycolytic pathway. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;478:1–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb15517.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prowse K. R., Baumann H. Hepatocyte-stimulating factor, beta 2 interferon, and interleukin-1 enhance expression of the rat alpha 1-acid glycoprotein gene via a distal upstream regulatory region. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):42–51. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REUBER M. D. A transplantable bile-secreting hepatocellular carcinoma in the rat. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1961 Apr;26:891–899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shangraw R. E., Jahoor F., Miyoshi H., Neff W. A., Stuart C. A., Herndon D. N., Wolfe R. R. Differentiation between septic and postburn insulin resistance. Metabolism. 1989 Oct;38(10):983–989. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(89)90010-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeke B. Crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:47–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb03778.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilmore D. W. Hormonal responses and their effect on metabolism. Surg Clin North Am. 1976 Oct;56(5):999–1018. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)41029-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe R. R., Durkot M. J., Allsop J. R., Burke J. F. Glucose metabolism in severely burned patients. Metabolism. 1979 Oct;28(10):1031–1039. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(79)90007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Won K. A., Baumann H. NF-AB, a liver-specific and cytokine-inducible nuclear factor that interacts with the interleukin-1 response element of the rat alpha 1-acid glycoprotein gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3001–3008. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Won K. A., Baumann H. The cytokine response element of the rat alpha 1-acid glycoprotein gene is a complex of several interacting regulatory sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):3965–3978. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.3965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynshaw-Boris A., Short J. M., Loose D. S., Hanson R. W. Characterization of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) promoter-regulatory region. I. Multiple hormone regulatory elements and the effects of enhancers. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9714–9720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vasconcelos P. R., Kettlewell M. G., Williamson D. H. Time course of changes in hepatic metabolism in response to sepsis in the rat: impairment of gluconeogenesis and ketogenesis in vitro. Clin Sci (Lond) 1987 Jun;72(6):683–691. doi: 10.1042/cs0720683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Deventer S. J., Büller H. R., ten Cate J. W., Aarden L. A., Hack C. E., Sturk A. Experimental endotoxemia in humans: analysis of cytokine release and coagulation, fibrinolytic, and complement pathways. Blood. 1990 Dec 15;76(12):2520–2526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]