Abstract
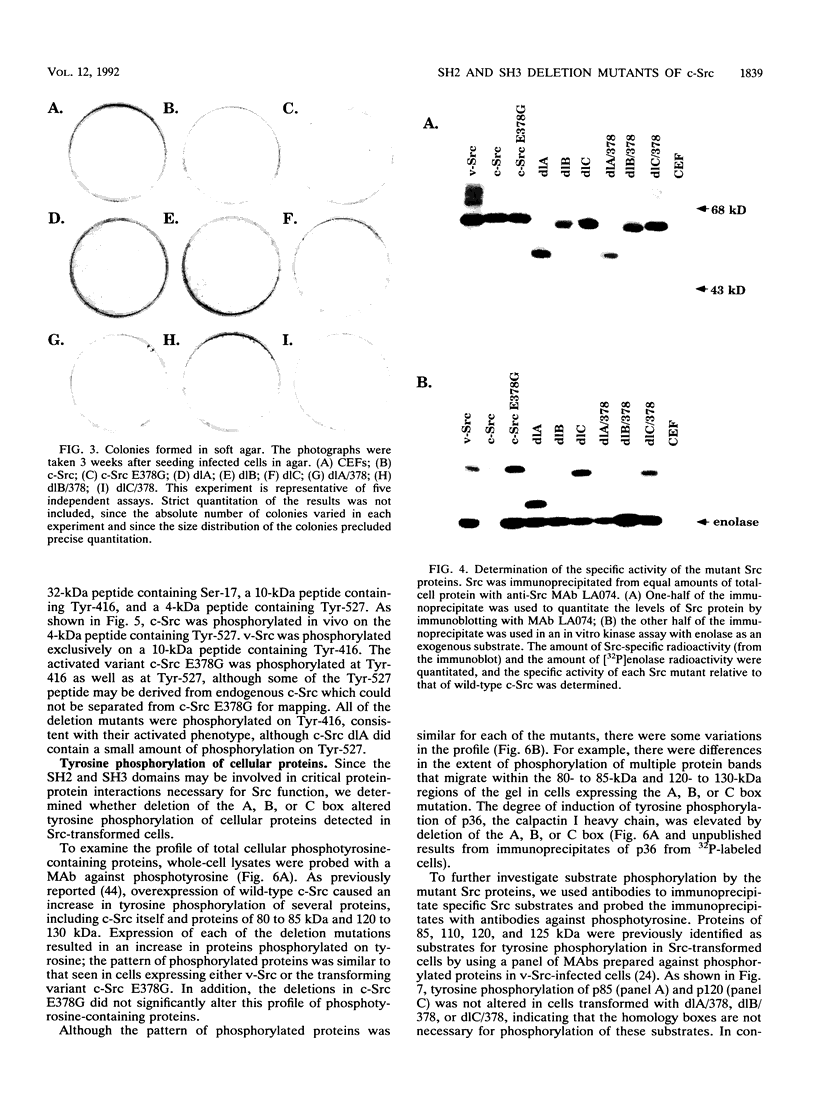
The amino-termina, noncatalytic half of Src contains two domains, designated the Src homology 2 (SH2) and Src homology 3 (SH3) domains, that are highly conserved among members of the Src family of tyrosine kinases. The SH2 domain (which can be further divided into the B and C homology boxes) and the SH3 domain (also referred to as the A box) are also found in several proteins otherwise unrelated to protein tyrosine kinases. It is believed that these domains are important for directing specific protein-protein interactions necessary for the proper functioning of Src. To determine the importance of the SH2 and SH3 domains in regulating the functions of c-Src, we evaluated mutants of c-Src lacking the A box (residues 88 to 137), the B box (residues 148 to 187) or the C box (residues 220 to 231). Each of these deletions caused a 14- to 30-fold increase in the in vitro level of kinase activity of c-Src. Chicken embryo fibroblasts expressing the deletion mutants displayed a transformed cell morphology, formed colonies in soft agar, and contained elevated levels of cellular phosphotyrosine-containing proteins. Src substrates p36, p85, p120, p125, the GTPase-activating protein (GAP), and several GAP-associated proteins were phosphorylated on tyrosine in cells expressing the A, B, or C box deletion mutant. p110 was highly phosphorylated in cells expressing the C box mutant, was weakly phosphorylated in cells expressing the B box mutant, and was not phosphorylated in cells expressing the A box mutant. Expression of the mutant proteins caused a reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton similar to that seen in v-Src-transformed cells. In addition, deletion of the A, B, or C box did not diminish the transforming or enzymatic activity of an activated variant of c-Src, E378G. These data indicate that deletion of the A, B, or C homology box causes an activation of the catalytic and transforming potential of c-Src and that while these mutations caused subtle differences in substrate phosphorylation, the homology boxes are not required for many of the phenotypic changes associated with transformation by Src.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D., Koch C. A., Grey L., Ellis C., Moran M. F., Pawson T. Binding of SH2 domains of phospholipase C gamma 1, GAP, and Src to activated growth factor receptors. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):979–982. doi: 10.1126/science.2173144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouton A. H., Kanner S. B., Vines R. R., Wang H. C., Gibbs J. B., Parsons J. T. Transformation by pp60src or stimulation of cells with epidermal growth factor induces the stable association of tyrosine-phosphorylated cellular proteins with GTPase-activating protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):945–953. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brott B. K., Decker S., O'Brien M. C., Jove R. Molecular features of the viral and cellular Src kinases involved in interactions with the GTPase-activating protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5059–5067. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brott B. K., Decker S., Shafer J., Gibbs J. B., Jove R. GTPase-activating protein interactions with the viral and cellular Src kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):755–759. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Darrow D. Analysis of the catalytic domain of phosphotransferase activity of two avian sarcoma virus-transforming proteins. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4550–4557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright C. A., Eckhart W., Simon S., Kaplan P. L. Cell transformation by pp60c-src mutated in the carboxy-terminal regulatory domain. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):83–91. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90758-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R., Garber E. A., Hanafusa H. N-terminal deletions in Rous sarcoma virus p60src: effects on tyrosine kinase and biological activities and on recombination in tissue culture with the cellular src gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2789–2795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R., Garber E. A., Pellman D., Hanafusa H. A short sequence in the p60src N terminus is required for p60src myristylation and membrane association and for cell transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1834–1842. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David-Pfeuty T., Singer S. J. Altered distributions of the cytoskeletal proteins vinculin and alpha-actinin in cultured fibroblasts transformed by Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6687–6691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeClue J. E., Martin G. S. Linker insertion-deletion mutagenesis of the v-src gene: isolation of host- and temperature-dependent mutants. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):542–554. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.542-554.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drubin D. G., Mulholland J., Zhu Z. M., Botstein D. Homology of a yeast actin-binding protein to signal transduction proteins and myosin-I. Nature. 1990 Jan 18;343(6255):288–290. doi: 10.1038/343288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis C., Moran M., McCormick F., Pawson T. Phosphorylation of GAP and GAP-associated proteins by transforming and mitogenic tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):377–381. doi: 10.1038/343377a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui Y., Hanafusa H. Requirement of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase modification for its association with p60src. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1972–1979. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui Y., Kornbluth S., Jong S. M., Wang L. H., Hanafusa H. Phosphatidylinositol kinase type I activity associates with various oncogene products. Oncogene Res. 1989;4(4):283–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui Y., O'Brien M. C., Hanafusa H. Deletions in the SH2 domain of p60v-src prevent association with the detergent-insoluble cellular matrix. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1207–1213. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandori C. Regulation of kinase activity. Nature. 1989 Apr 6;338(6215):467–467. doi: 10.1038/338467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai H., Varmus H. E. Mutations in src homology regions 2 and 3 of activated chicken c-src that result in preferential transformation of mouse or chicken cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8592–8596. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai H., Varmus H. E. Site-directed mutagenesis of the SH2- and SH3-coding domains of c-src produces varied phenotypes, including oncogenic activation of p60c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1307–1318. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iba H., Cross F. R., Garber E. A., Hanafusa H. Low level of cellular protein phosphorylation by nontransforming overproduced p60c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):1058–1066. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.1058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iba H., Takeya T., Cross F. R., Hanafusa T., Hanafusa H. Rous sarcoma virus variants that carry the cellular src gene instead of the viral src gene cannot transform chicken embryo fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4424–4428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. J., Coussens P. M., Danko A. V., Shalloway D. Overexpressed pp60c-src can induce focus formation without complete transformation of NIH 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):1073–1083. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.1073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jove R., Mayer B. J., Iba H., Laugier D., Poirier F., Calothy G., Hanafusa T., Hanafusa H. Genetic analysis of p60v-src domains involved in the induction of different cell transformation parameters. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):840–848. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.840-848.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanner S. B., Reynolds A. B., Vines R. R., Parsons J. T. Monoclonal antibodies to individual tyrosine-phosphorylated protein substrates of oncogene-encoded tyrosine kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3328–3332. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanner S. B., Reynolds A. B., Wang H. C., Vines R. R., Parsons J. T. The SH2 and SH3 domains of pp60src direct stable association with tyrosine phosphorylated proteins p130 and p110. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1689–1698. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07693.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J. M., Mardon G., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. The first seven amino acids encoded by the v-src oncogene act as a myristylation signal: lysine 7 is a critical determinant. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2435–2441. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato J. Y., Takeya T., Grandori C., Iba H., Levy J. B., Hanafusa H. Amino acid substitutions sufficient to convert the nontransforming p60c-src protein to a transforming protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4155–4160. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiecik T. E., Shalloway D. Activation and suppression of pp60c-src transforming ability by mutation of its primary sites of tyrosine phosphorylation. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90756-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Anderson D., Moran M. F., Ellis C., Pawson T. SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):668–674. doi: 10.1126/science.1708916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozma L. M., Weber M. J. Constitutive phosphorylation of the receptor for insulinlike growth factor I in cells transformed by the src oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3626–3634. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kypta R. M., Goldberg Y., Ulug E. T., Courtneidge S. A. Association between the PDGF receptor and members of the src family of tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):481–492. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A. D., Courtneidge S. A., Bishop J. M. Structural and functional domains of the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein (pp60src). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1624–1628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. B., Brugge J. S. Biological and biochemical properties of the c-src+ gene product overexpressed in chicken embryo fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3332–3341. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. B., Dorai T., Wang L. H., Brugge J. S. The structurally distinct form of pp60c-src detected in neuronal cells is encoded by a unique c-src mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):4142–4145. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.4142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. B., Iba H., Hanafusa H. Activation of the transforming potential of p60c-src by a single amino acid change. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4228–4232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez R., Mathey-Prevot B., Bernards A., Baltimore D. Neuronal pp60c-src contains a six-amino acid insertion relative to its non-neuronal counterpart. Science. 1987 Jul 24;237(4813):411–415. doi: 10.1126/science.2440106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda M., Mayer B. J., Fukui Y., Hanafusa H. Binding of transforming protein, P47gag-crk, to a broad range of phosphotyrosine-containing proteins. Science. 1990 Jun 22;248(4962):1537–1539. doi: 10.1126/science.1694307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Hanafusa H. Association of the v-crk oncogene product with phosphotyrosine-containing proteins and protein kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2638–2642. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Jackson P. K., Baltimore D. The noncatalytic src homology region 2 segment of abl tyrosine kinase binds to tyrosine-phosphorylated cellular proteins with high affinity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):627–631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarley D. J., Parsons J. T., Benjamin D. C., Parsons S. J. Inhibition of the tyrosine kinase activity of v-src, v-fgr, and v-yes gene products by a monoclonal antibody which binds both amino and carboxy peptide fragments of pp60v-src. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):1927–1937. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.1927-1937.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran M. F., Koch C. A., Anderson D., Ellis C., England L., Martin G. S., Pawson T. Src homology region 2 domains direct protein-protein interactions in signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8622–8626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran M. F., Polakis P., McCormick F., Pawson T., Ellis C. Protein-tyrosine kinases regulate the phosphorylation, protein interactions, subcellular distribution, and activity of p21ras GTPase-activating protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1804–1812. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemeth S. P., Fox L. G., DeMarco M., Brugge J. S. Deletions within the amino-terminal half of the c-src gene product that alter the functional activity of the protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1109–1119. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigg E. A., Sefton B. M., Hunter T., Walter G., Singer S. J. Immunofluorescent localization of the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus with antibodies against a synthetic src peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5322–5326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien M. C., Fukui Y., Hanafusa H. Activation of the proto-oncogene p60c-src by point mutations in the SH2 domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2855–2862. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R. C., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Expression of v-src and chicken c-src in rat cells demonstrates qualitative differences between pp60v-src and pp60c-src. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90308-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons J. T., Weber M. J. Genetics of src: structure and functional organization of a protein tyrosine kinase. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;147:79–127. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74697-0_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piwnica-Worms H., Saunders K. B., Roberts T. M., Smith A. E., Cheng S. H. Tyrosine phosphorylation regulates the biochemical and biological properties of pp60c-src. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90757-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potts W. M., Reynolds A. B., Lansing T. J., Parsons J. T. Activation of pp60c-src transforming potential by mutations altering the structure of an amino terminal domain containing residues 90-95. Oncogene Res. 1988;3(4):343–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyper J. M., Bolen J. B. Identification of a novel neuronal C-SRC exon expressed in human brain. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2035–2040. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond V. W., Parsons J. T. Identification of an amino terminal domain required for the transforming activity of the Rous sarcoma virus src protein. Virology. 1987 Oct;160(2):400–410. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resh M. D., Ling H. P. Identification of a 32K plasma membrane protein that binds to the myristylated amino-terminal sequence of p60v-src. Nature. 1990 Jul 5;346(6279):84–86. doi: 10.1038/346084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resh M. D. Specific and saturable binding of pp60v-src to plasma membranes: evidence for a myristyl-src receptor. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):281–286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90842-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds A. B., Kanner S. B., Wang H. C., Parsons J. T. Stable association of activated pp60src with two tyrosine-phosphorylated cellular proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3951–3958. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds A. B., Vila J., Lansing T. J., Potts W. M., Weber M. J., Parsons J. T. Activation of the oncogenic potential of the avian cellular src protein by specific structural alteration of the carboxy terminus. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2359–2364. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02512.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodaway A. R., Sternberg M. J., Bentley D. L. Similarity in membrane proteins. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):624–624. doi: 10.1038/342624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrschneider L. R. Adhesion plaques of Rous sarcoma virus-transformed cells contain the src gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3514–3518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussel R. R., Brodeur S. R., Shalloway D., Laudano A. P. Selective binding of activated pp60c-src by an immobilized synthetic phosphopeptide modeled on the carboxyl terminus of pp60c-src. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10696–10700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Miki S., Tachibana H., Hayashi F., Akiyama T., Fukami Y. A synthetic peptide corresponding to residues 137 to 157 of p60v-src inhibits tyrosine-specific protein kinases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Sep 28;171(3):1152–1159. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90805-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuh S. M., Brugge J. S. Investigation of factors that influence phosphorylation of pp60c-src on tyrosine 527. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2465–2471. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw A. S., Amrein K. E., Hammond C., Stern D. F., Sefton B. M., Rose J. K. The lck tyrosine protein kinase interacts with the cytoplasmic tail of the CD4 glycoprotein through its unique amino-terminal domain. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):627–636. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl M. L., Ferenz C. R., Kelleher K. L., Kriz R. W., Knopf J. L. Sequence similarity of phospholipase C with the non-catalytic region of src. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):269–272. doi: 10.1038/332269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarone G., Cirillo D., Giancotti F. G., Comoglio P. M., Marchisio P. C. Rous sarcoma virus-transformed fibroblasts adhere primarily at discrete protrusions of the ventral membrane called podosomes. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Jul;159(1):141–157. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(85)80044-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner J. M., Brodsky M. H., Irving B. A., Levin S. D., Perlmutter R. M., Littman D. R. Interaction of the unique N-terminal region of tyrosine kinase p56lck with cytoplasmic domains of CD4 and CD8 is mediated by cysteine motifs. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):755–765. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90090-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verderame M. F., Kaplan J. M., Varmus H. E. A mutation in v-src that removes a single conserved residue in the SH-2 domain of pp60v-src restricts transformation in a host-dependent manner. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):338–348. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.338-348.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. C., Parsons J. T. Deletions and insertions within an amino-terminal domain of pp60v-src inactivate transformation and modulate membrane stability. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):291–302. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.291-302.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasilenko W. J., Payne D. M., Fitzgerald D. L., Weber M. J. Phosphorylation and activation of epidermal growth factor receptors in cells transformed by the src oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):309–321. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]