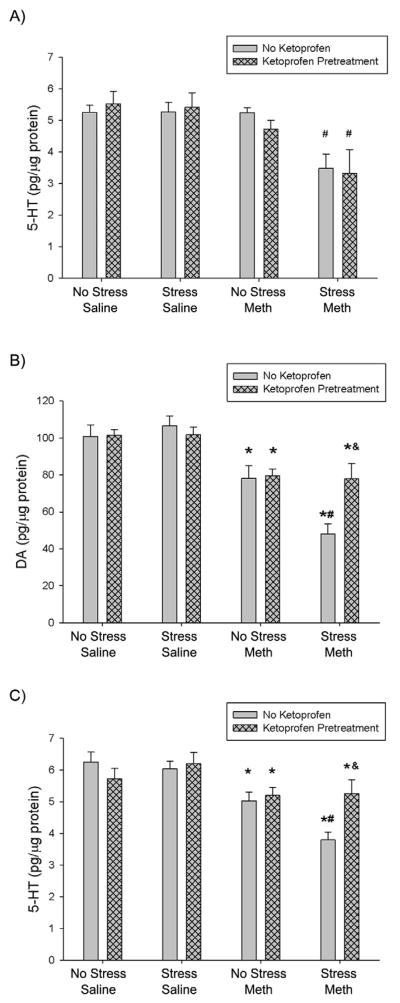
Figure 5.
Effects of ketoprofen pretreatment during drug treatment on stress and Meth-induced hippocampal and striatal monoamine depletions, 7 days after treatment. Meth (7.5 mg/kg q 2hrs, ×4 ip) or saline (1 mL/kg q 2hrs, ×4 ip) was administered to previously stressed or control rats. Some rats received ketoprofen (5 mg/kg, sc) 1 hr before each Meth or saline injection. A) Hippocampal 5-HT: Stress+Meth produced a significant hippocampal 5-HT depletion (#, p<0.005, Tukey’s post hoc test) compared to No Stress+Meth treatments. Ketoprofen pretreatment did not significantly attenuate Stress+Meth-induced hippocampal 5-HT depletions. Striatal B) DA and C) 5-HT: Three-way ANOVA revealed a significant effect of Meth on DA and 5-HT content compared to No Stress+Saline groups (*, p<0.001). Stress+Meth produced a significant DA and 5-HT depletion (#, DA: p<0.01; 5-HT: p<0.05, two-way ANOVA and Tukey post hoc test) compared to No Stress+Meth. Ketoprofen pretreatment attenuated the Stress+Meth-induced DA and 5-HT depletions (&, DA: p<0.005; 5-HT: p<0.005, Tukey’s post hoc test). (n=6–10 for each group)