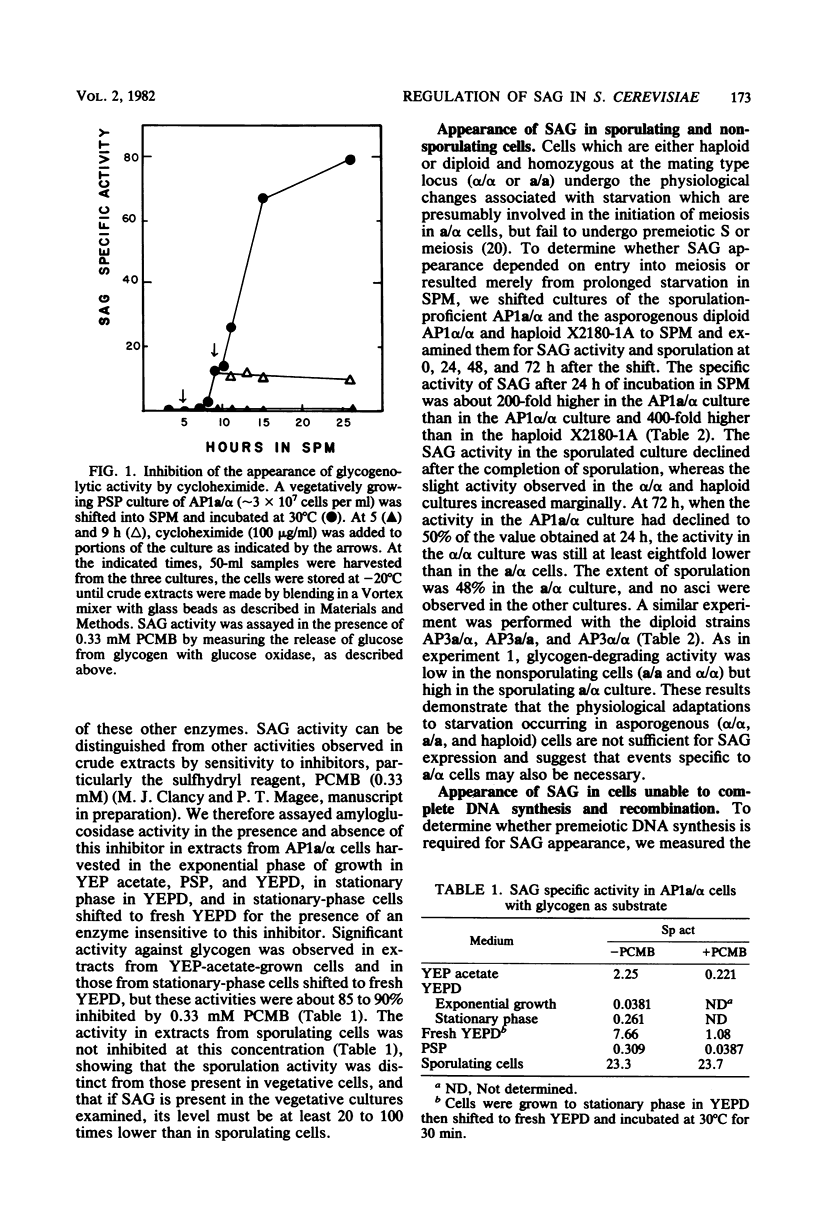
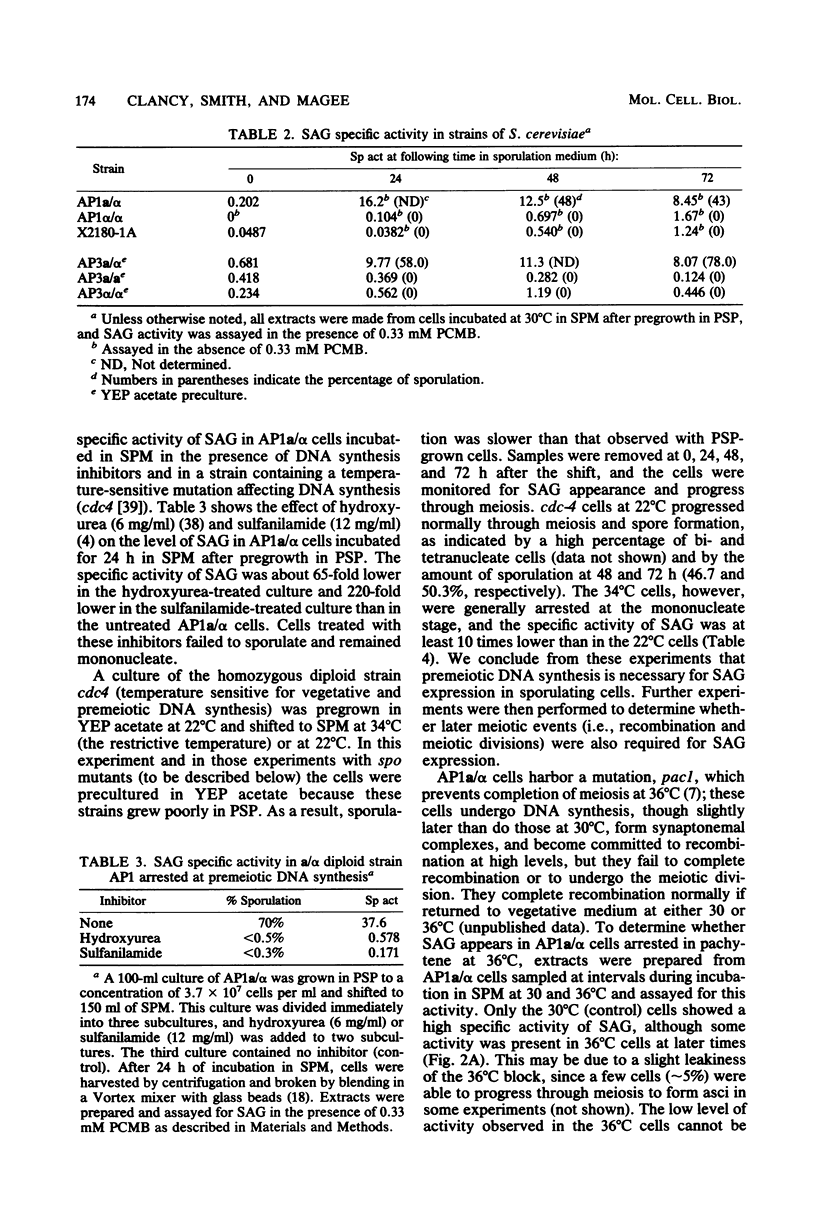
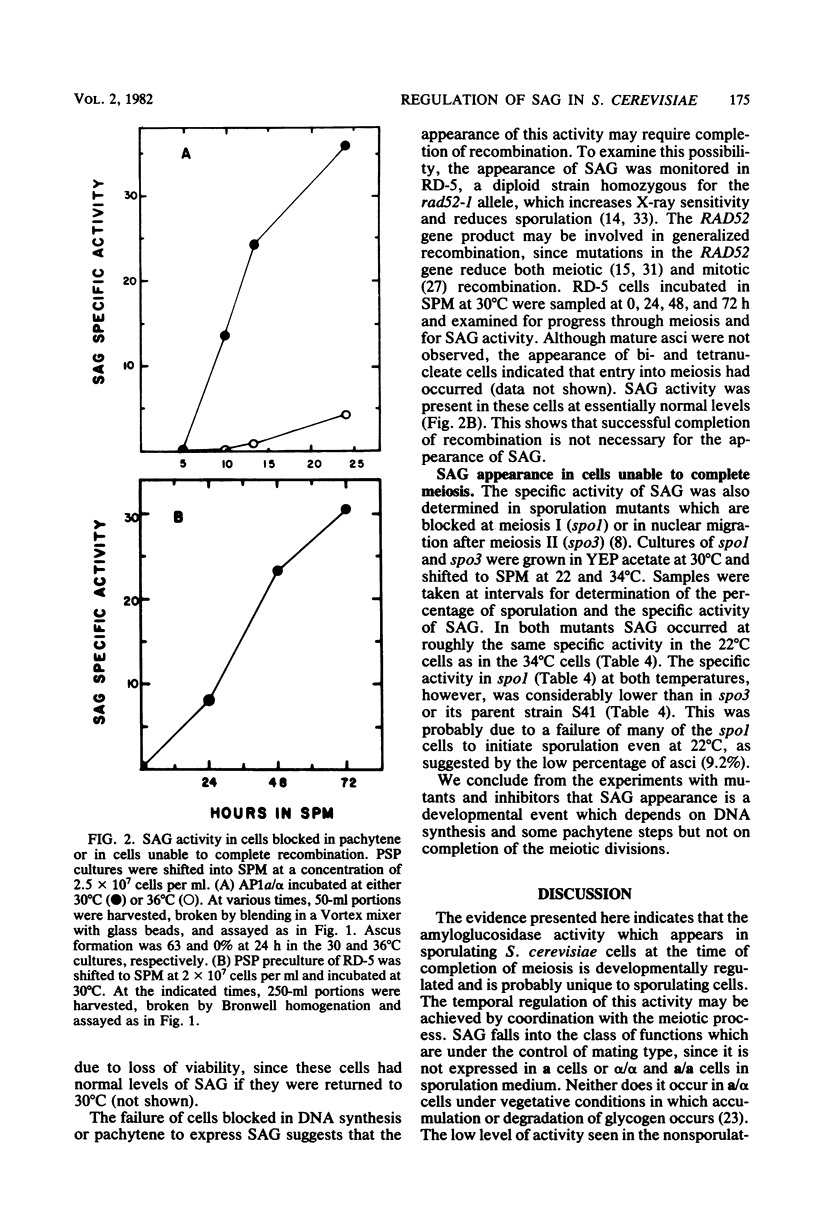
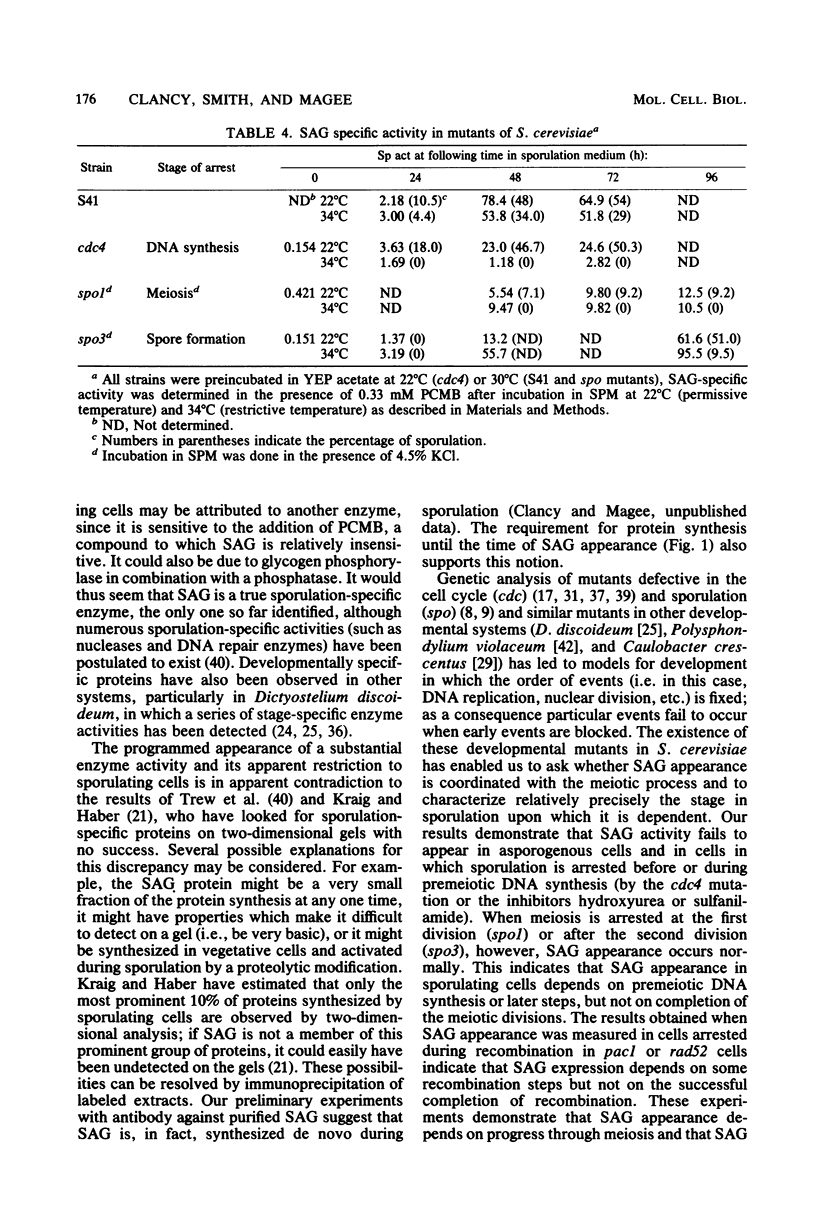
Abstract
An alpha-glucosidase activity (SAG) occurs in a/alpha Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells beginning at about 8 to 10 h after the initiation of sporulation. This enzyme is responsible for the rapid degradation of intracellular glycogen which follows the completion of meiosis in these cells. SAG differs from similar activities present in vegetative cells and appears to be a sporulation-specific enzyme. Cells arrested at various stages in sporulation (DNA replication, recombination, meiosis I, and meiosis II) were examined for SAG activity; the results show that SAG appearance depends on DNA synthesis and some recombination events but not on the meiotic divisions.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alton T. H., Lodish H. F. Developmental changes in messenger RNAs and protein synthesis in Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Biol. 1977 Oct 1;60(1):180–206. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett T., Pachl C., Gergen J. P., Wensink P. C. The isolation and characterization of Drosophila yolk protein genes. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):729–738. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90436-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung K. K., Newton A. Patterns of protein synthesis during development in Caulobacter crescentus. Dev Biol. 1977 Apr;56(2):417–425. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90281-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonna W. J., Gentile J. M., Magee P. T. Inhibiton by sulfanilamide of sporulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Jun;23(6):659–671. doi: 10.1139/m77-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonna W. J., Magee P. T. Glycogenolytic enzymes in sporulating yeast. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):844–853. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.844-853.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidow L. S., Goetsch L., Byers B. Preferential Occurrence of Nonsister Spores in Two-Spored Asci of SACCHAROMYCES CEREVISIAE: Evidence for Regulation of Spore-Wall Formation by the Spindle Pole Body. Genetics. 1980 Mar;94(3):581–595. doi: 10.1093/genetics/94.3.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esposito M. S., Esposito R. E., Arnaud M., Halvorson H. O. Acetate utilization and macromolecular synthesis during sporulation of yeast. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):180–186. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.180-186.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esposito M. S., Esposito R. E. Genes controlling meiosis and spore formation in yeast. Genetics. 1974 Sep;78(1):215–225. doi: 10.1093/genetics/78.1.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esposito R. E., Frink N., Bernstein P., Esposito M. S. The genetic control of sporulation in Saccharomyces. II. Dominance and complementation of mutants of meiosis and spore formation. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;114(3):241–248. doi: 10.1007/BF01788893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fosset M., Muir L. W., Nielsen L. D., Fischer E. H. Purification and properties of yeast glycogen phosphorylase a and b. Biochemistry. 1971 Oct 26;10(22):4105–4113. doi: 10.1021/bi00798a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz H., Hartwich G., Werle E. Uber Proteaseinhibitoren. I. Isolierung und Charakterisierung des Trypsininhibitors aus Pankreasgewebe und Pankreassekret vom Hund. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1966;345(2):150–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Game J. C., Mortimer R. K. A genetic study of x-ray sensitive mutants in yeast. Mutat Res. 1974 Sep;24(3):281–292. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(74)90176-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Game J. C., Zamb T. J., Braun R. J., Resnick M., Roth R. M. The Role of Radiation (rad) Genes in Meiotic Recombination in Yeast. Genetics. 1980 Jan;94(1):51–68. doi: 10.1093/genetics/94.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOPKINS R. H., KULKA D. The glucamylase and debrancher of S. diastaticus. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1957 Jul;69:45–55. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(57)90471-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H. Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell cycle. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Jun;38(2):164–198. doi: 10.1128/br.38.2.164-198.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hereford L. M., Hartwell L. H. Sequential gene function in the initiation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae DNA synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1974 Apr 15;84(3):445–461. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90451-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper A. K., Magee P. T., Welch S. K., Friedman M., Hall B. D. Macromolecule synthesis and breakdown in relation to sporulation and meiosis in yeast. J Bacteriol. 1974 Aug;119(2):619–628. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.2.619-628.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraig E., Haber J. E. Messenger ribonucleic acid and protein metabolism during sporulation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1980 Dec;144(3):1098–1112. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.3.1098-1112.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai H. Y., Axelrod B. The specificity of the synthetic reaction of two yeast alpha-glucosidases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 May 23;391(1):121–128. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90158-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie S. H., Pringle J. R. Reserve carbohydrate metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: responses to nutrient limitation. J Bacteriol. 1980 Sep;143(3):1384–1394. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.3.1384-1394.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loomis W. F., Jr Developmental regulation of alkaline phosphatase in Dictyostelium discoideum. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):417–422. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.417-422.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loomis W. F., White S., Dimond R. L. A sequence of dependent stages in the development of Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Biol. 1976 Oct 15;53(2):171–177. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(76)90221-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malone R. E., Esposito R. E. The RAD52 gene is required for homothallic interconversion of mating types and spontaneous mitotic recombination in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):503–507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman R. B., Federoff H. J., Eccleshall T. R., Buchferer B., Marmur J. Purification and characterization of an alpha-glucosidase from Saccharomyces carlsbergensis. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 31;17(22):4657–4661. doi: 10.1021/bi00615a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osley M. A., Newton A. Temporal control of the cell cycle in Caulobacter crescentus: roles of DNA chain elongation and completion. J Mol Biol. 1980 Mar 25;138(1):109–128. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(80)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piñon R., Salts Y., Simchen G. Nuclear and mitochondrial DNA synthesis during yeast sporulation. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Feb;83(2):231–238. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90334-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prakash S., Prakash L., Burke W., Montelone B. A. Effects of the RAD52 Gene on Recombination in SACCHAROMYCES CEREVISIAE. Genetics. 1980 Jan;94(1):31–50. doi: 10.1093/genetics/94.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle J. R. Methods for avoiding proteolytic artefacts in studies of enzymes and other proteins from yeasts. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;12:149–184. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60956-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick M. A. Genetic control of radiation sensitivity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1969 Jul;62(3):519–531. doi: 10.1093/genetics/62.3.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R., Halvorson H. O. Sporulation of yeast harvested during logarithmic growth. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):831–832. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.831-832.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R., Lusnak K. DNA synthesis during yeast sporulation: genetic control of an early developmental event. Science. 1970 Apr 24;168(3930):493–494. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3930.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R., Sussman M. Trehalose 6-phosphate synthetase (uridine diphosphate glucose: d-glucose 6-phosphate 1-glucosyltransferase) and its regulation during slime mold development. J Biol Chem. 1968 Oct 10;243(19):5081–5087. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schild D., Byers B. Meiotic effects of DNA-defective cell division cycle mutations of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Chromosoma. 1978 Dec 21;70(1):109–130. doi: 10.1007/BF00292220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva-Lopez E., Zamb T. J., Roth R. Role of premeiotic replication in gene conversion. Nature. 1975 Jan 17;253(5488):212–214. doi: 10.1038/253212a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simchen G., Hirschberg J. Effects of the mitotic cell-cycle mutation cdc4 on yeast meiosis. Genetics. 1977 May;86(1):57–72. doi: 10.1093/genetics/86.1.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trew B. J., Friesen J. D., Moens P. B. Two-dimensional protein patterns during growth and sporulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1979 Apr;138(1):60–69. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.1.60-69.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren A. J., Warren W. D., Cox E. C. Genetic and morphological study of aggregation in the cellular slime mold Polysphondylium violaceum. Genetics. 1976 May;83(1):25–47. doi: 10.1093/genetics/83.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



