Abstract
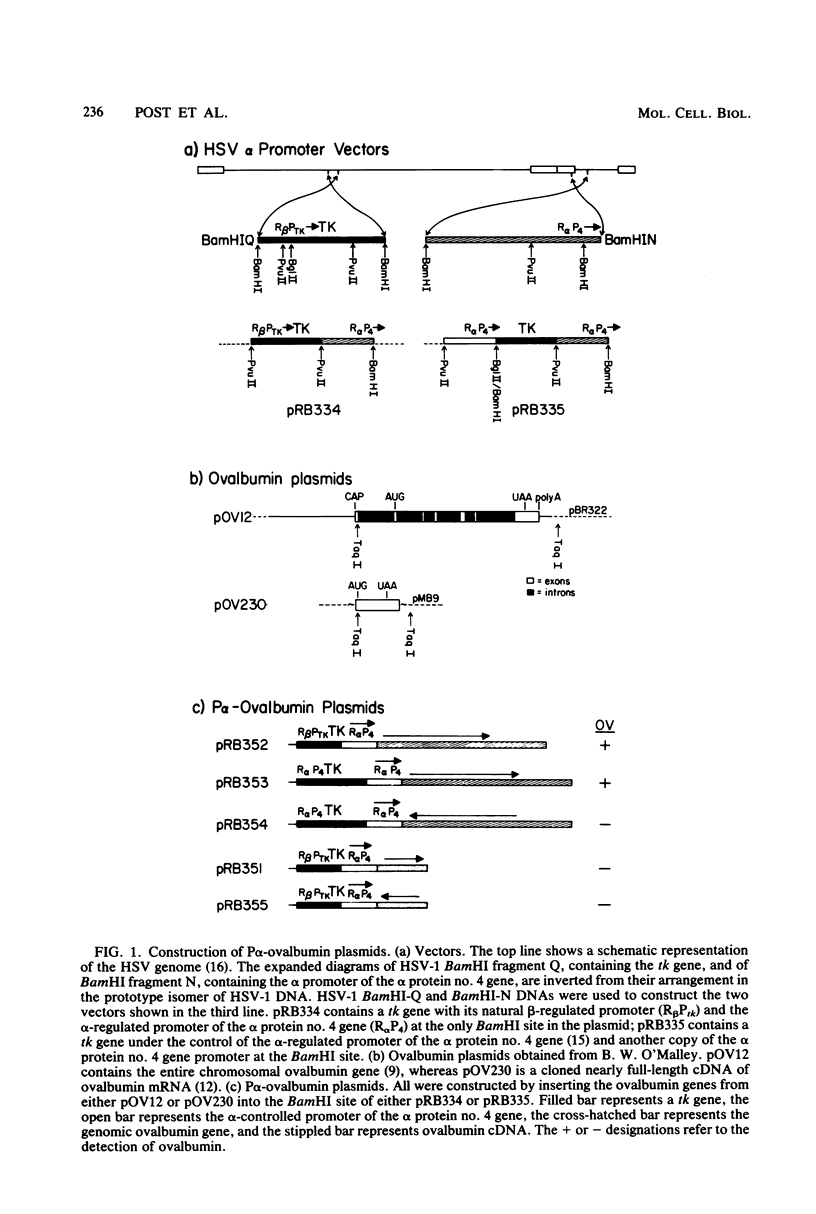
We are describing a system for the introduction, selection, and expression of eucaryotic genes in higher eucaryotic cells. The carrier consisted of the herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) tk gene covalently linked to an HSV-1 alpha promoter directed away from the tk gene. In this study we fused to the alpha promoter the 5' transcribed noncoding sequences and the coding sequences of the chicken oviduct ovalbumin gene. Cells converted to the TK+ phenotype with this chimeric fragment produced an ovalbumin precursor which was processed and secreted into the extracellular fluid. The ovalbumin gene utilized the HSV-1 alpha promoter and was regulated as a viral gene inasmuch as inversion of the genomic DNA relative to the alpha promoter resulted in no ovalbumin synthesis, and production of ovalbumin was enhanced after superinfection with HSV-1. Synthesis of ovalbumin was not detected when cDNA was linked to the HSV-1 alpha promoter. The carrier system described in this study is suitable for introduction, selection, and expression of eucaryotic genes whose natural promoter is either weak or requires the presence of regulatory elements which may be absent from undifferentiated cells in culture.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Breathnach R., Mantei N., Chambon P. Corrected splicing of a chicken ovalbumin gene transcript in mouse L cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):740–744. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser T. H., Bruce B. J. Chicken ovalbumin is synthesized and secreted by Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5936–5940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamer D. H., Leder P. Splicing and the formation of stable RNA. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1299–1302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90240-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. XI. Identification and relative molar rates of synthesis of structural and nonstructural herpes virus polypeptides in the infected cell. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1347–1365. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1347-1365.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. I. Cascade regulation of the synthesis of three groups of viral proteins. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):8–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.8-19.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis: sequential transition of polypeptide synthesis requires functional viral polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1276–1280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIT S., DUBBS D. R., PIEKARSKI L. J., HSU T. C. DELETION OF THYMIDINE KINASE ACTIVITY FROM L CELLS RESISTANT TO BROMODEOXYURIDINE. Exp Cell Res. 1963 Aug;31:297–312. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(63)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kit S., Dubbs D. R., Schaffer P. A. Thymidine kinase activity of biochemically transformed mouse cells after superinfection by thymidine kinase-negative, temperature-sensitive, herpes simplex virus mutants. Virology. 1978 Apr;85(2):456–463. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90452-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E. C., Woo S. L., Bordelon-Riser M. E., Fraser T. H., O'Malley B. W. Ovalbumin is synthesized in mouse cells transformed with the natural chicken ovalbumin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):244–248. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiden J. M., Buttyan R., Spear P. G. Herpes simplex virus gene expression in transformed cells. I. Regulation of the viral thymidine kinase gene in transformed L cells by products of superinfecting virus. J Virol. 1976 Nov;20(2):413–424. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.2.413-424.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackem S., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis: transcription-initiation sites and domains of alpha genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7122–7126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse L. S., Pereira L., Roizman B., Schaffer P. A. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus (HSV) DNA. X. Mapping of viral genes by analysis of polypeptides and functions specified by HSV-1 X HSV-2 recombinants. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):389–410. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.389-410.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Conley A. J., Mocarski E. S., Roizman B. Cloning of reiterated and nonreiterated herpes simplex virus 1 sequences as BamHI fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4201–4205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Mackem S., Roizman B. Regulation of alpha genes of herpes simplex virus: expression of chimeric genes produced by fusion of thymidine kinase with alpha gene promoters. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):555–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90346-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roizman B. The organization of the herpes simplex virus genomes. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:25–57. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.000325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roop D. R., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Definition of the 5' and 3' ends of transcripts of the ovalbumin gene. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):63–68. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90388-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramani S., Mulligan R., Berg P. Expression of the mouse dihydrofolate reductase complementary deoxyribonucleic acid in simian virus 40 vectors. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;1(9):854–864. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.9.854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickens M. P., Woo S., O'Malley B. W., Gurdon J. B. Expression of a chicken chromosomal ovalbumin gene injected into frog oocyte nuclei. Nature. 1980 Jun 26;285(5767):628–634. doi: 10.1038/285628a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Silverstein S., Lee L. S., Pellicer A., Cheng Y. c., Axel R. Transfer of purified herpes virus thymidine kinase gene to cultured mouse cells. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90333-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Sweet R., Sim G. K., Wold B., Pellicer A., Lacy E., Maniatis T., Silverstein S., Axel R. Transformation of mammalian cells with genes from procaryotes and eucaryotes. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]