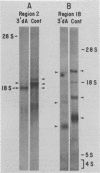
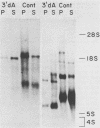
Abstract
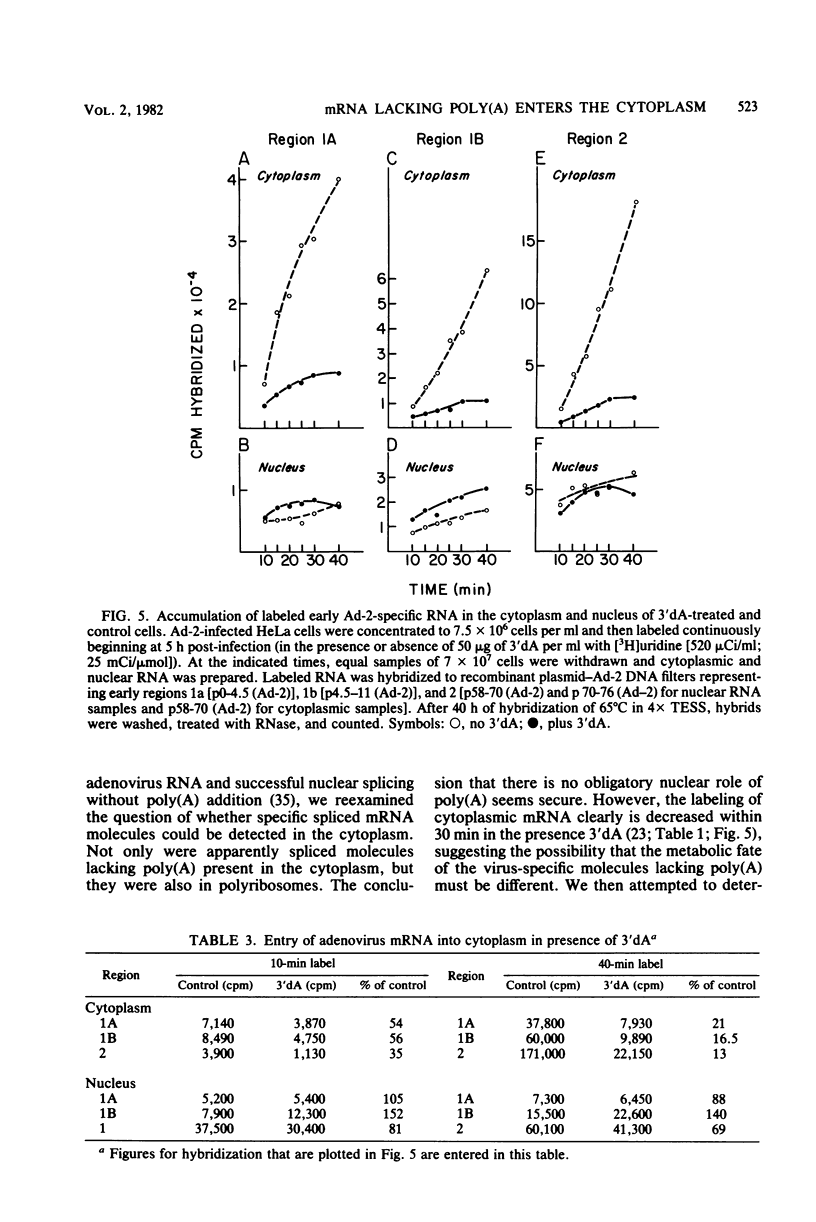
Labeled adenovirus type 2 nuclear RNA molecules from cells treated with 3'-deoxyadenosine (3'dA) were earlier reported to lack polyadenylic acid [poly(A)], but to be correctly spliced in the nucleus (M. Zeevi et al., Cell 26:39-46, 1981). We have now found that the shortened mRNA molecules, lacking poly(A), can also be found in the cytoplasm of 3'dA-treated cells in association with the polyribosomes. In addition, the accumulation of labeled, nuclear adenovirus-specific RNA complementary to early regions 1a, 1b, and 2 of the adenovirus genome was approximately equal in 3'dA-treated and control cells. At the initial appearance of newly labeled adenovirus type 2 RNA (10 min) in the cytoplasm, there was one-half as much labeled RNA in 3'dA-treated cells as in the control. However, control cells accumulated additional mRNA in the cytoplasm very rapidly in the first 40 min of labeling, whereas the 3'dA-treated cells did not. Therefore, it appears that the correctly spliced, poly(A)- mRNA molecules that are labeled in the presence of 3'dA can be transported from the nucleus with nearly the same frequency and the same exit time as in control cells and can be translated in the cytoplasm but have a much shorter half-life than the poly(A)+ mRNA molecules from control infected cells. From these results it is suggested that the role of poly(A) may be entirely to increase the longevity of cytoplasmic mRNA.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adesnik M., Darnell J. E. Biogenesis and characterization of histone messenger RNA in HeLa cells. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 28;67(3):397–406. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90458-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adesnik M., Salditt M., Thomas W., Darnell J. E. Evidence that all messenger RNA molecules (except histone messenger RNA) contain Poly (A) sequences and that the Poly(A) has a nuclear function. J Mol Biol. 1972 Oct 28;71(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90397-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aleström P., Akusjärvi G., Perricaudet M., Mathews M. B., Klessig D. F., Pettersson U. The gene for polypeptide IX of adenovirus type 2 and its unspliced messenger RNA. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):671–681. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80044-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Structure of the adenovirus 2 early mRNAs. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):695–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90252-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Ultraviolet mapping of the adenovirus 2 early promoters. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):45–55. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90184-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G. Characteristics and significance of the polyadenylate sequence in mammalian messenger RNA. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1976;17:117–148. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60068-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G. The Role of the poly(A) sequence in mammalian messenger RNA. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1981;10(1):1–38. doi: 10.3109/10409238109114634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Broker T. R., Lewis J. B. Complex splicing patterns of RNAs from the early regions of adenovirus-2. J Mol Biol. 1979 Oct 25;134(2):265–303. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Philipson L., Wall R., Adesnik M. Polyadenylic acid sequences: role in conversion of nuclear RNA into messenger RNA. Science. 1971 Oct 29;174(4008):507–510. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4008.507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M., Fraser N., Ziff E., Weber J., Wilson M., Darnell J. E. The initiation sites for RNA transcription in Ad2 DNA. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):733–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90273-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan H., Penman S. Regulation of protein synthesis in mammalian cells. II. Inhibition of protein synthesis at the level of initiation during mitosis. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jun 28;50(3):655–670. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90091-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint J. The topography and transcription of the adenovirus genome. Cell. 1977 Feb;10(2):153–166. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. I., Burns A. T., Christmann J. L., Deeley R. G. Cloning of a double-stranded cDNA that codes for a portion of chicken preproalbumin. A general method for isolating a specific DNA sequence from partially purified mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 10;253(23):8629–8639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpold M. M., Wilson M. C., Darnell J. E., Jr Chinese hamster polyadenylated messenger ribonucleic acid: relationship to non-polyadenylated sequences and relative conservation during messenger ribonucleic acid processing. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;1(2):188–198. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.2.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huez G., Bruck C., Cleuter Y. Translational stability of native and deadenylylated rabbit globin mRNA injected into HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):908–911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitchingman G. R., Westphal H. The structure of adenovirus 2 early nuclear and cytoplasmic RNAs. J Mol Biol. 1980 Feb 15;137(1):23–48. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90155-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrogan M., Spector D. J., Goldenberg C. J., Halbert D., Raskas H. J. Purification of specific adenovirus 2 RNAs by preparative hybridization and selective thermal elution. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Feb;6(2):593–607. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.2.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Definition and mapping of adenovirus 2 nuclear transcription. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):768–785. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65072-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nudel U., Soreq H., Littauer U. Z. Globin mRNA species containing poly(A) segments of different lengths. Their functional stability in Xenopus oocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Apr 15;64(1):115–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10279.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penman S., Rosbash M., Penman M. Messenger and heterogeneous nuclear RNA in HeLa cells: differential inhibition by cordycepin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Dec;67(4):1878–1885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.4.1878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson U., Mathews M. B. The gene and messenger RNA for adenovirus polypeptide IX. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):741–750. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90274-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipson L., Wall R., Glickman G., Darnell J. E. Addition of polyadenylate sequences to virus-specific RNA during adenovirus replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2806–2809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salditt-Georgieff M., Harpold M. M., Wilson M. C., Darnell J. E., Jr Large heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleic acid has three times as many 5' caps as polyadenylic acid segments, and most caps do not enter polyribosomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;1(2):179–187. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.2.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawicki S. G., Jelinek W., Darnell J. E. 3'-Terminal addition to HeLa cell nuclear and cytoplasmic poly (A). J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):219–235. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90051-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal P. B., Fraser N. W., Darnell J. E., Jr Early Ad-2 transcription units: only promoter-proximal RNA continues to be made in the presence of DRB. Virology. 1979 Apr 15;94(1):185–191. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90448-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheiness D., Puckett L., Darnell J. E. Possible relationship of poly(A) shortening to mRNA turnover. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1077–1081. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siev M., Weinberg R., Penman S. The selective interruption of nucleolar RNA synthesis in HeLa cells by cordycepin. J Cell Biol. 1969 May;41(2):510–520. doi: 10.1083/jcb.41.2.510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer R. H., Penman S. Stability of HeLa cell mRNA in actinomycin. Nature. 1972 Nov 10;240(5376):100–102. doi: 10.1038/240100a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. J., McGrogan M., Raskas H. J. Regulation of the appearance of cytoplasmic RNAs from region 1 of the adenovirus 2 genome. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 15;126(3):395–414. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90048-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P. K., Dawid I. B. Secondary structure maps of RNA: processing of HeLa ribosomal RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2827–2831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. C., Fraser N. W., Darnell J. E., Jr Mapping of RNA initiation sites by high doses of uv irradiation: evidence for three independent promoters within the left 11% of the Ad-2 genome. Virology. 1979 Apr 15;94(1):175–184. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90447-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. C., Sawicki S. G., Salditt-Georgieff M., Darnell J. E. Adenovirus type 2 mRNA in transformed cells: map positions and difference in transport time. J Virol. 1978 Jan;25(1):97–103. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.1.97-103.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. C., Sawicki S. G., White P. A., Darnell J. E., Jr A correlation between the rate of poly(A) shortening and half-life of messenger RNA in adenovirus transformed cells. J Mol Biol. 1978 Nov 25;126(1):23–36. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90277-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeevi M., Nevins J. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Nuclear RNA is spliced in the absence of poly(A) addition. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(1 Pt 1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziff E. B. Transcription and RNA processing by the DNA tumour viruses. Nature. 1980 Oct 9;287(5782):491–499. doi: 10.1038/287491a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]