Abstract
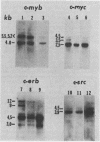
The oncogenes (v-onc genes) of rapidly transforming retroviruses have homologs (c-onc genes) in the genomes of normal cells. In this study, we characterized and quantitated transcription from four c-onc genes, c-myb, c-myc, c-erb, and c-src, in a variety of chicken cells and tissues. Electrophoretic analysis of polyadenylated RNA, followed by transfer to nitrocellulose and hybridization to cloned onc probes showed that c-myb, c-myc, and c-src each give rise to a single mature transcript, whereas c-erb gives rise to multiple transcripts (B. Vennstrom and J. M. Bishop, Cell, in press) which vary in abundance among different cells and tissues. Transcription from c-myb, c-myc, c-erb, and c-src was quantitated by a “dot-blot” hybridization assay. We found that c-myc, c-erb, and c-src transcription could be detected in nearly all cells and tissues examined, whereas c-myb transcription was detected only in some hemopoietic cells; these cells, however, belong to several different lineages. Thus, in no case was expression of a c-onc gene restricted to a single cell lineage. There appeared to be a correlation between levels of c-myb expression and hemopoietic activity of the tissues and cells examined, which suggests that c-myb may be expressed primarily in immature hemopoietic cells. An examination of c-onc RNA levels in target cells and tissues for viruses carrying the corresponding v-onc genes revealed no obvious correlation, direct or inverse, between susceptibility to transformation by a given v-onc gene and expression of the homologous c-onc gene.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BALUDA M. A., GOETZ I. E. Morphological conversion of cell cultures by avian myeloblastosis virus. Virology. 1961 Oct;15:185–199. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90234-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. H. Expression of endogenous avian myeloblastosis virus information in different chicken cells. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):162–170. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.162-170.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffin J. M., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., Essex M., Hardy W. D., Jr, Martin G. S., Rosenberg N. E., Scolnick E. M., Weinberg R. A., Vogt P. K. Proposal for naming host cell-derived inserts in retrovirus genomes. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):953–957. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.953-957.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper M. D., Purchase H. G., Bockman D. E., Gathings W. E. Studies on the nature of the abnormality of B cell differentiation in avian lymphoid leukosis: production of heterogeneous IgM by tumor cells. J Immunol. 1974 Oct;113(4):1210–1222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLorbe W. J., Luciw P. A., Goodman H. M., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Molecular cloning and characterization of avian sarcoma virus circular DNA molecules. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):50–61. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.50-61.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodge W. H., Moscovici C. Colony formation by chicken hematopoietic cells and virus-induced myeloblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1973 Jun;81(3):371–386. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040810310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodge W. H., Silva R. F., Moscovici C. The origin of chicken hematopoietic colonies as assayed in semisolid agar. J Cell Physiol. 1975 Feb;85(1):25–29. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040850104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durban E. M., Boettiger D. Differential effects of transforming avian RNA tumor viruses on avian macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3600–3604. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durban E. M., Boettiger D. Replicating, differentiated macrophages can serve as in vitro targets for transformation by avian myeloblastosis virus. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):488–492. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.488-492.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazzolo L., Samarut J., Bouabdelli M., Blanchet J. P. Early precursors in the erythroid lineage are the specific target cells of avian erythroblastosis virus in vitro. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):683–691. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90544-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda T. J., Sheiness D. K., Fanshier L., Bishop J. M., Moscovici C., Moscovici M. G. The genome and the intracellular RNAs of avian myeloblastosis virus. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):279–290. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90292-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf T., Beug H. Avian leukemia viruses: interaction with their target cells in vivo and in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 17;516(3):269–299. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(78)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf T., Beug H., Hayman M. J. Target cell specificity of defective avian leukemia viruses: hematopoietic target cells for a given virus type can be infected but not transformed by strains of a different type. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):389–393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf T., von Kirchbach A., Beug H. Characterization of the hematopoietic target cells of AEV, MC29 and AMV avian leukemia viruses. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Feb;131(2):331–343. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90236-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward W. S., Neel B. G., Astrin S. M. Activation of a cellular onc gene by promoter insertion in ALV-induced lymphoid leukosis. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):475–480. doi: 10.1038/290475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscovici C., Vogt P. K. Effects of genetic cellular resistance on cell transformation and virus replication in chicken hematopoietic cell cultures infected with avian myeloblastosis virus (BAI-A). Virology. 1968 Aug;35(4):487–497. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90278-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson D. L., Varmus H. E. Structural analysis of the intracellular RNAs of murine mammary tumor virus. J Virol. 1979 May;30(2):576–589. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.2.576-589.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussel M., Saule S., Lagrou C., Rommens C., Beug H., Graf T., Stehelin D. Three new types of viral oncogene of cellular origin specific for haematopoietic cell transformation. Nature. 1979 Oct 11;281(5731):452–455. doi: 10.1038/281452a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saule S., Roussel M., Lagrou C., Stehelin D. Characterization of the oncogene (erb) of avian erythroblastosis virus and its cellular progenitor. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):409–419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.409-419.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scolnick E. M., Weeks M. O., Shih T. Y., Ruscetti S. K., Dexter T. M. Markedly elevated levels of an endogenous sarc protein in a hemopoietic precursor cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Jan;1(1):66–74. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.1.66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheiness D., Bishop J. M. DNA and RNA from uninfected vertebrate cells contain nucleotide sequences related to the putative transforming gene of avian myelocytomatosis virus. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):514–521. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.514-521.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheiness D., Bister K., Moscovici C., Fanshier L., Gonda T., Bishop J. M. Avian retroviruses that cause carcinoma and leukemia: identification of nucleotide sequences associated with pathogenicity. J Virol. 1980 Mar;33(3):962–968. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.3.962-968.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. H., Baker B., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Characteristics of cellular RNA related to the transforming gene of avian sarcoma viruses. Cell. 1978 Feb;13(2):381–386. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90206-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. H., Smith K., Padgett T., McCombe P., Roulland-Dussoix D., Moscovici C., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Uninfected avian cells contain RNA related to the transforming gene of avian sarcoma viruses. Cell. 1978 Feb;13(2):371–379. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90205-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vennström B., Fanshier L., Moscovici C., Bishop J. M. Molecular cloning of the avian erythroblastosis virus genome and recovery of oncogenic virus by transfection of chicken cells. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):575–585. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.575-585.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]