Abstract
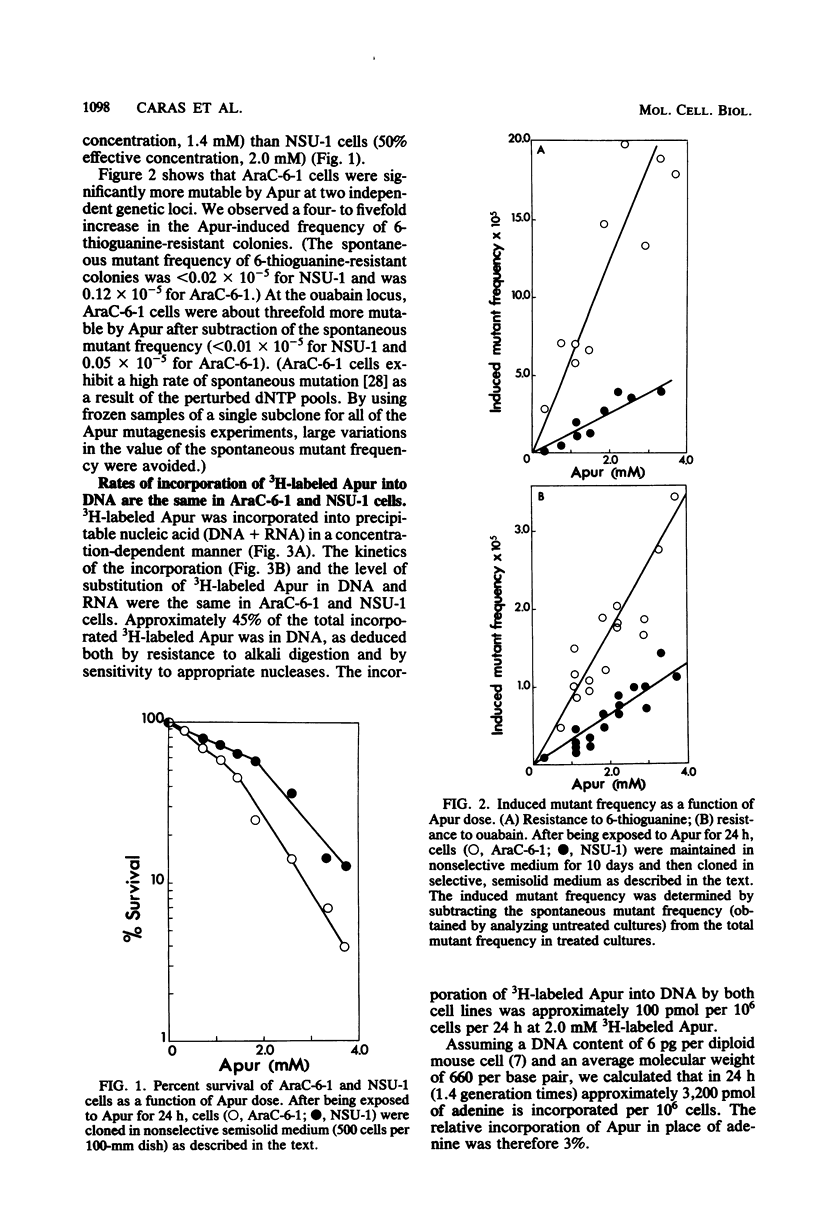
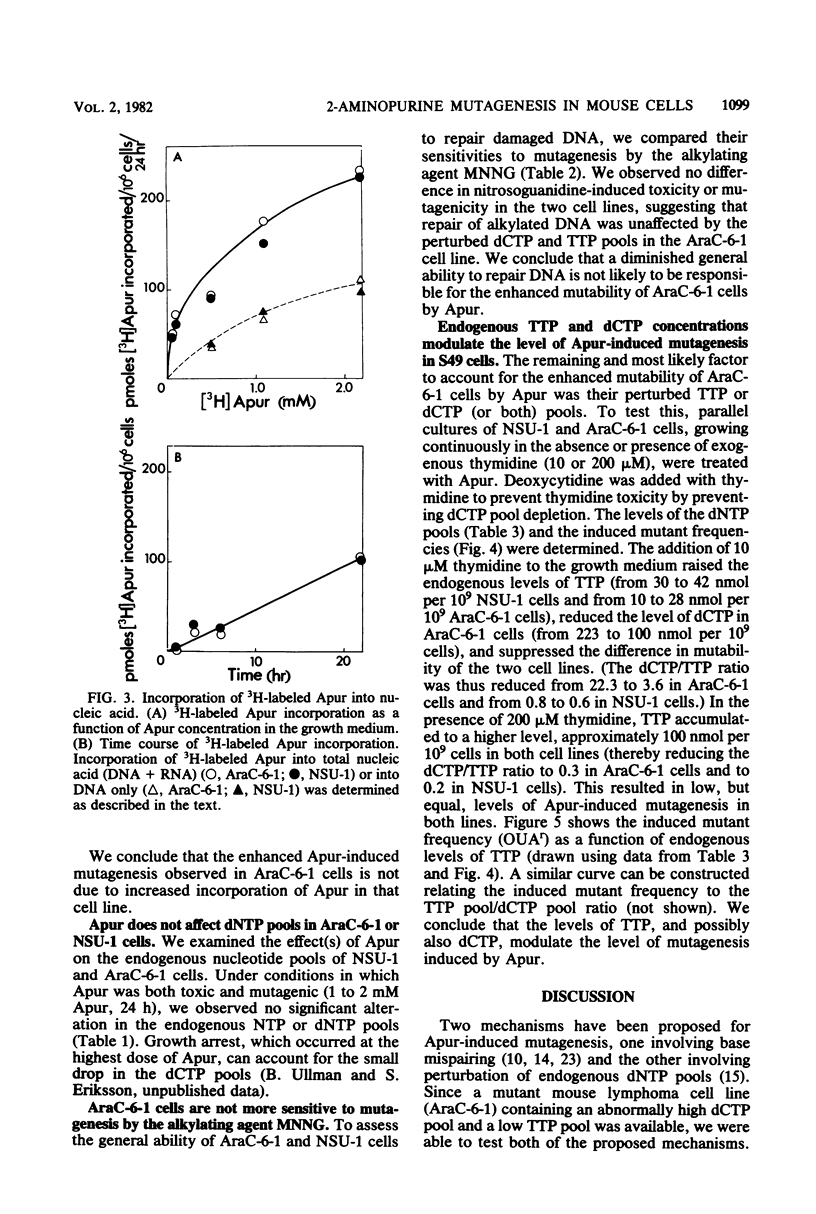
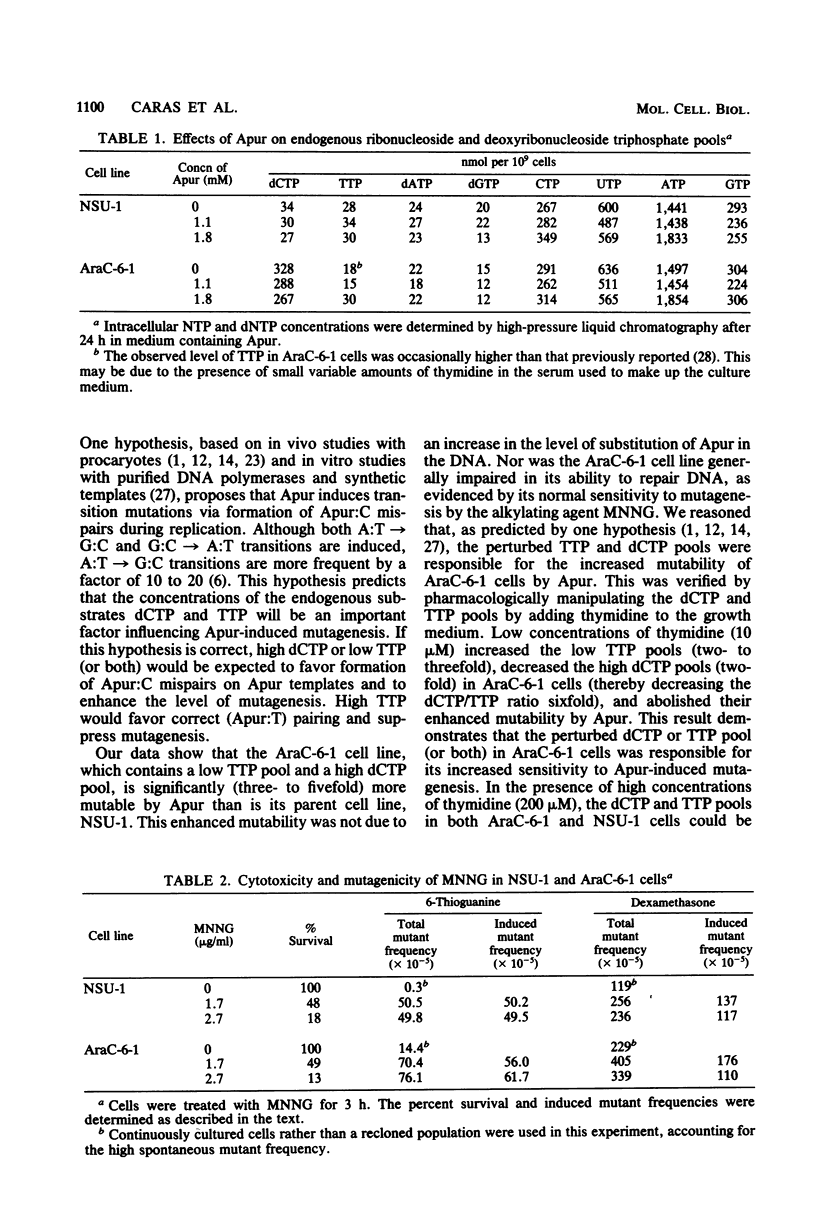
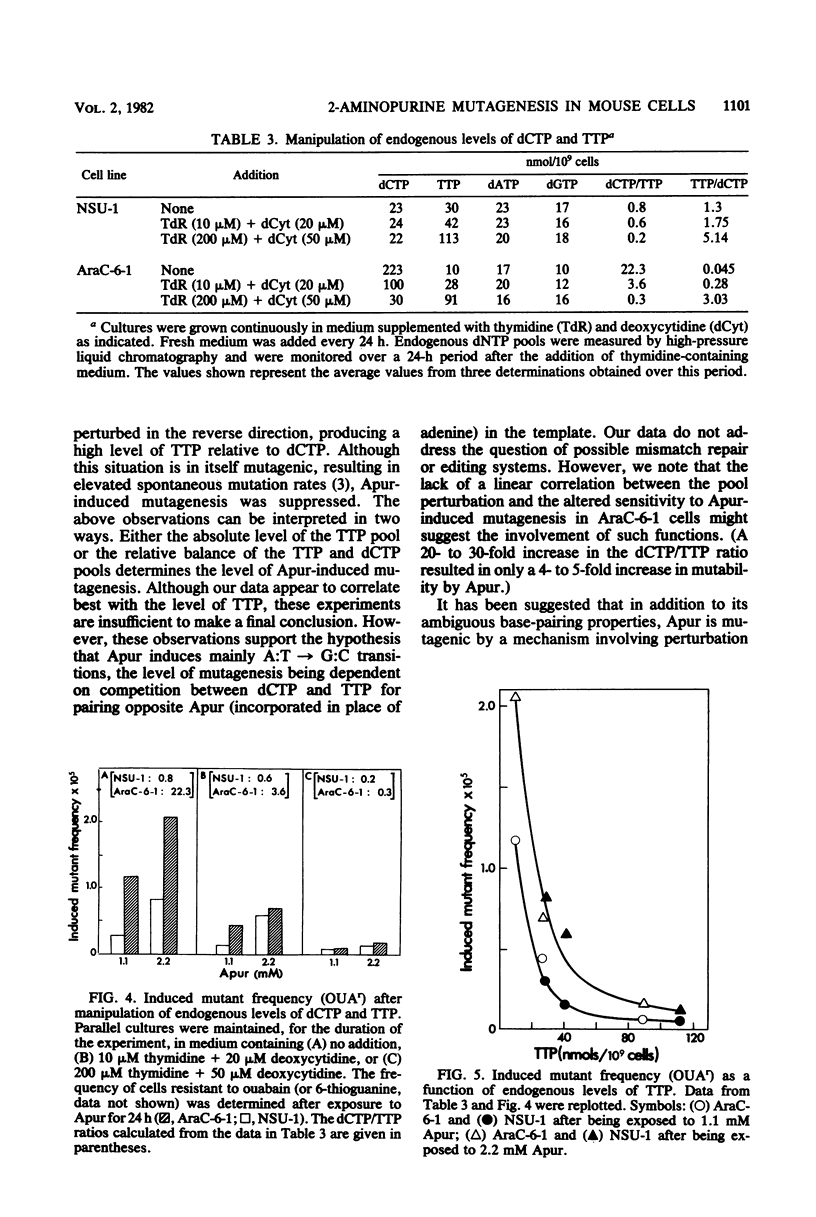
We investigated the mechanism of action of 2-aminopurine (Apur) in eucaryotic cells. By analogy with studies in procaryotic systems, the base analog is presumed to incorporate into DNA predominantly opposite T where, upon subsequent DNA replication, it can mispair with C, inducing an A:T leads to G:C transition. This model predicts that Apur-induced mutagenesis will be enhanced by factors that favor formation of Apur-C mispairs, e.g., high levels of dCTP or low levels of TTP. We describe the use of a mutant T-lymphosarcoma cell line, AraC-6-1, which has an abnormally high dCTP pool and a low TTP pool, to test this prediction. AraC-6-1 cells were three- to fivefold more mutable by Apur than their parental cell line, NSU-1. This enhanced mutability by Apur could not be explained by altered incorporation of 3H-labeled Apur, by generally impaired ability to repair DNA damage, or by a direct effect of Apur on the endogenous deoxynucleotide pools. The addition of 10 microM thymidine to the growth medium of AraC-6-1 cells lowered their high dCTP pool (two- to threefold), raised the TTP pool (two- to threefold), and abolished their enhanced mutability by Apur. Further manipulation to produce an abnormally high TTP/dCTP ratio suppressed Apur-induced mutagenesis (8- to 10-fold) in both AraC-6-1 and NSU-1 cells. These observations support the hypothesis that Apur induces A:T leads to G:C transitions in mammalian cells by a mispairing mechanism.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett J. C. Induction of gene mutation in and cell transformation of mammalian cells by modified purines: 2-aminopurine and 6-N-hydroxylaminopurine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5685–5689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley M. O., Sharkey N. A. Mutagenicity of thymidine to cultured Chinese hamster cells. Nature. 1978 Aug 10;274(5671):607–608. doi: 10.1038/274607a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan T. S. Deoxyguanosine toxicity on lymphoid cells as a cause for immunosuppression in purine nucleoside phosphorylase deficiency. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):523–530. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90238-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clive D., Johnson K. O., Spector J. F., Batson A. G., Brown M. M. Validation and characterization of the L5178Y/TK+/- mouse lymphoma mutagen assay system. Mutat Res. 1979 Jan;59(1):61–108. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(79)90195-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fersht A. R. Fidelity of replication of phage phi X174 DNA by DNA polymerase III holoenzyme: spontaneous mutation by misincorporation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4946–4950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederiksen S. Effect of 2-aminopurine and 2-aminopurine 2'-deoxyriboside on nucleic acid synthesis in Ehrlich ascites cells in vitro. Biochem Pharmacol. 1965 May;14(5):651–660. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(65)90083-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich U., Coffino P. Mutagenesis in S49 mouse lymphoma cells: induction of resistance to ouabain, 6-thioguanine, and dibutyryl cyclic AMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):679–683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman M. F., Hopkins R., Gore W. C. 2-Aminopurine-induced mutagenesis in T4 bacteriophage: a model relating mutation frequency to 2-aminopurine incorporation in DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4806–4810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibner U., Alberts B. M. Fidelity of DNA replication catalysed in vitro on a natural DNA template by the T4 bacteriophage multi-enzyme complex. Nature. 1980 May 29;285(5763):300–305. doi: 10.1038/285300a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins R. L., Goodman M. F. Deoxyribonucleotide pools, base pairing, and sequence configuration affecting bromodeoxyuridine- and 2-aminopurine-induced mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1801–1805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins R., Goodman M. F. Asymmetry in forming 2-aminopurine . hydroxymethylcytosine heteroduplexes; A model giving misincorporation frequencies and rounds of DNA replication from base-pair populations in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1979 Nov 25;135(1):1–22. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90337-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horibata K., Harris A. W. Mouse myelomas and lymphomas in culture. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Apr;60(1):61–77. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90489-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Loeb L. A. On the fidelity of DNA replication. Effect of divalent metal ion activators and deoxyrionucleoside triphosphate pools on in vitro mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):5718–5725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Loeb L. A. On the fidelity of DNA replication. The accuracy of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I in copying natural DNA in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9961–9966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuth M., Green H. Induction of a deoxycytidineless state in cultured mammalian cells by bromodeoxyuridine. Cell. 1974 Jun;2(2):109–112. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90099-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuth M., L'Heureux-Huard N., Trudel M. Characterization of a mutator gene in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6505–6509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuth M. Role of deoxynucleoside triphosphate pools in the cytotoxic and mutagenic effects of DNA alkylating agents. Somatic Cell Genet. 1981 Jan;7(1):89–102. doi: 10.1007/BF01544750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore E. C., Hurlbert R. B. Regulation of mammalian deoxyribonucleotide biosynthesis by nucleotides as activators and inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1966 Oct 25;241(20):4802–4809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley C. H., Tomkins G. M. Isolation of lymphoma cell variants resistant to killing by glucocorticoids. Cell. 1974 Aug;2(4):213–220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90013-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullman B., Gudas L. J., Clift S. M., Martin D. W., Jr Isolation and characterization of purine-nucleoside phosphorylase-deficient T-lymphoma cells and secondary mutants with altered ribonucleotide reductase: genetic model for immunodeficiency disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullman B., Gudas L. J., Cohen A., Martin D. W., Jr Deoxyadenosine metabolism and cytotoxicity in cultured mouse T lymphoma cells: a model for immunodeficiency disease. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):365–375. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90122-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe S. M., Goodman M. F. On the molecular basis of transition mutations: frequencies of forming 2-aminopurine.cytosine and adenine.cytosine base mispairs in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2864–2868. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg G., Ullman B., Martin D. W., Jr Mutator phenotypes in mammalian cell mutants with distinct biochemical defects and abnormal deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate pools. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2447–2451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weymouth L. A., Loeb L. A. Mutagenesis during in vitro DNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1924–1928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



