Abstract
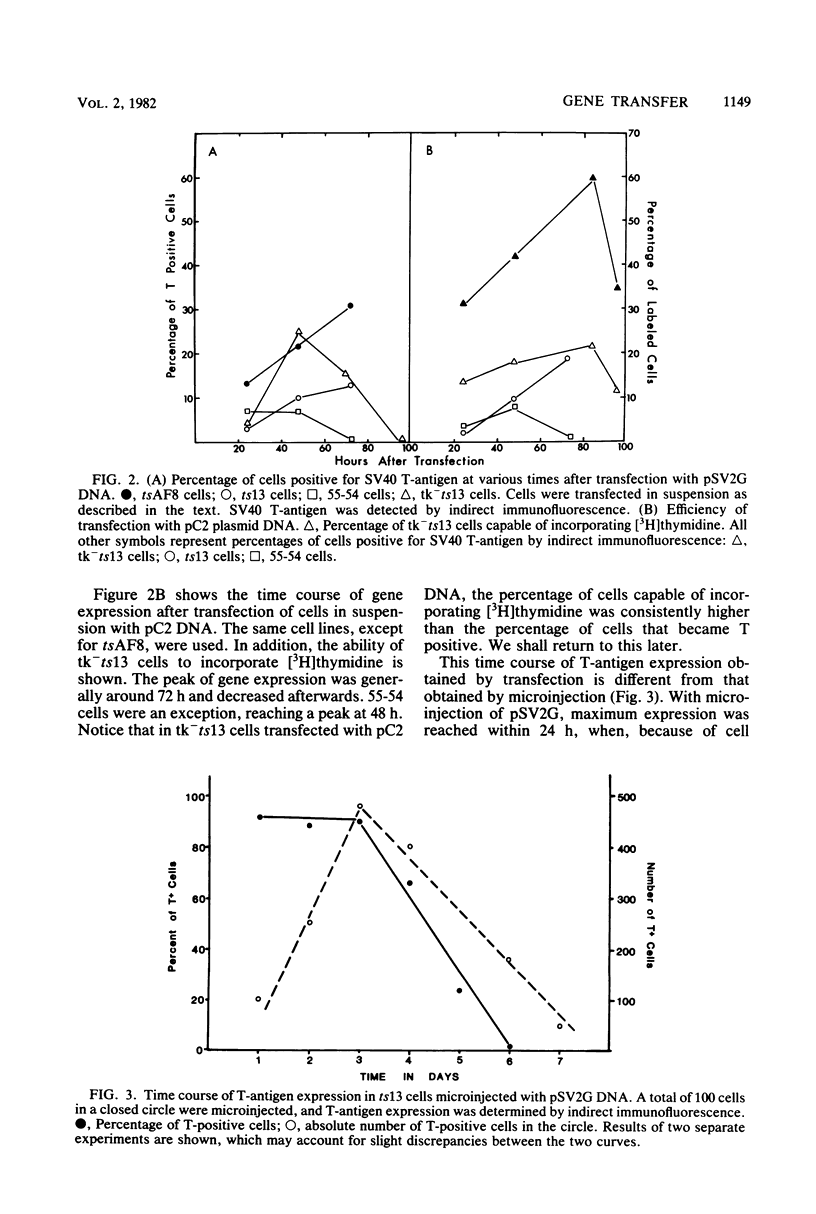
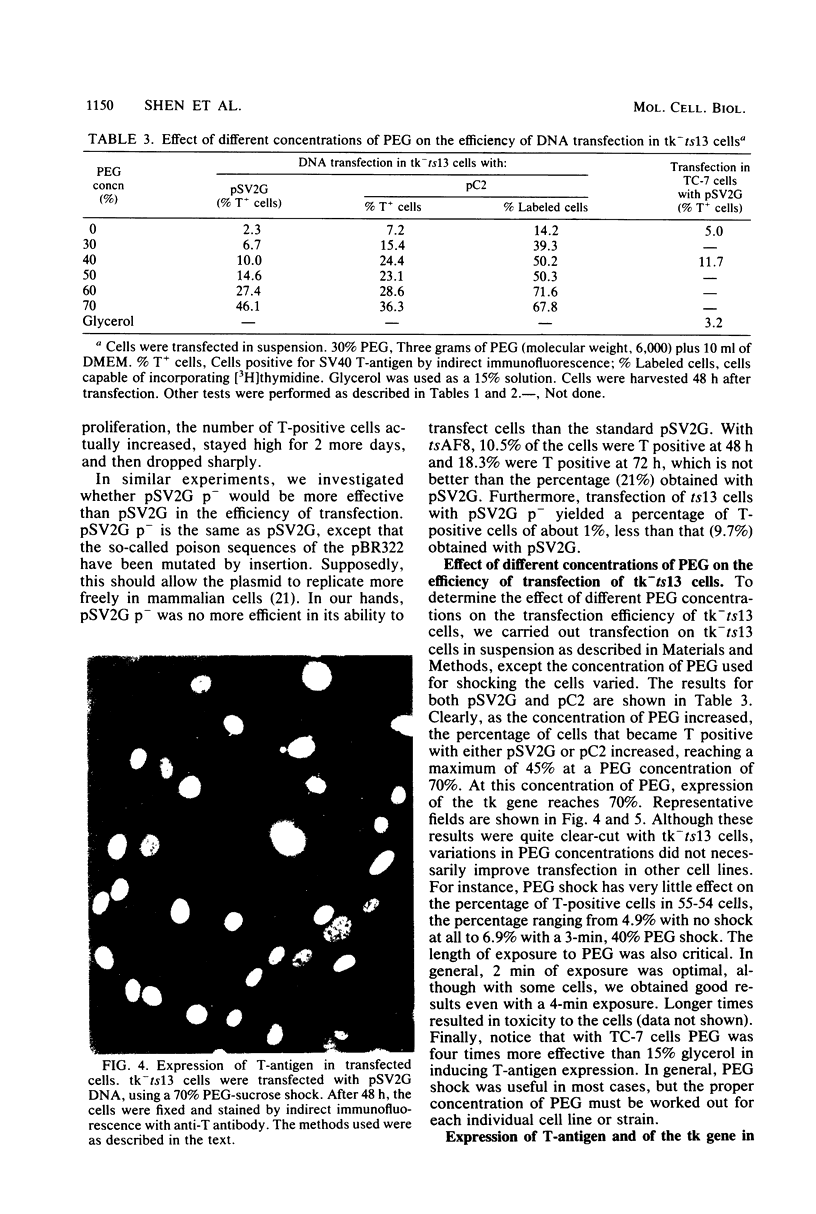
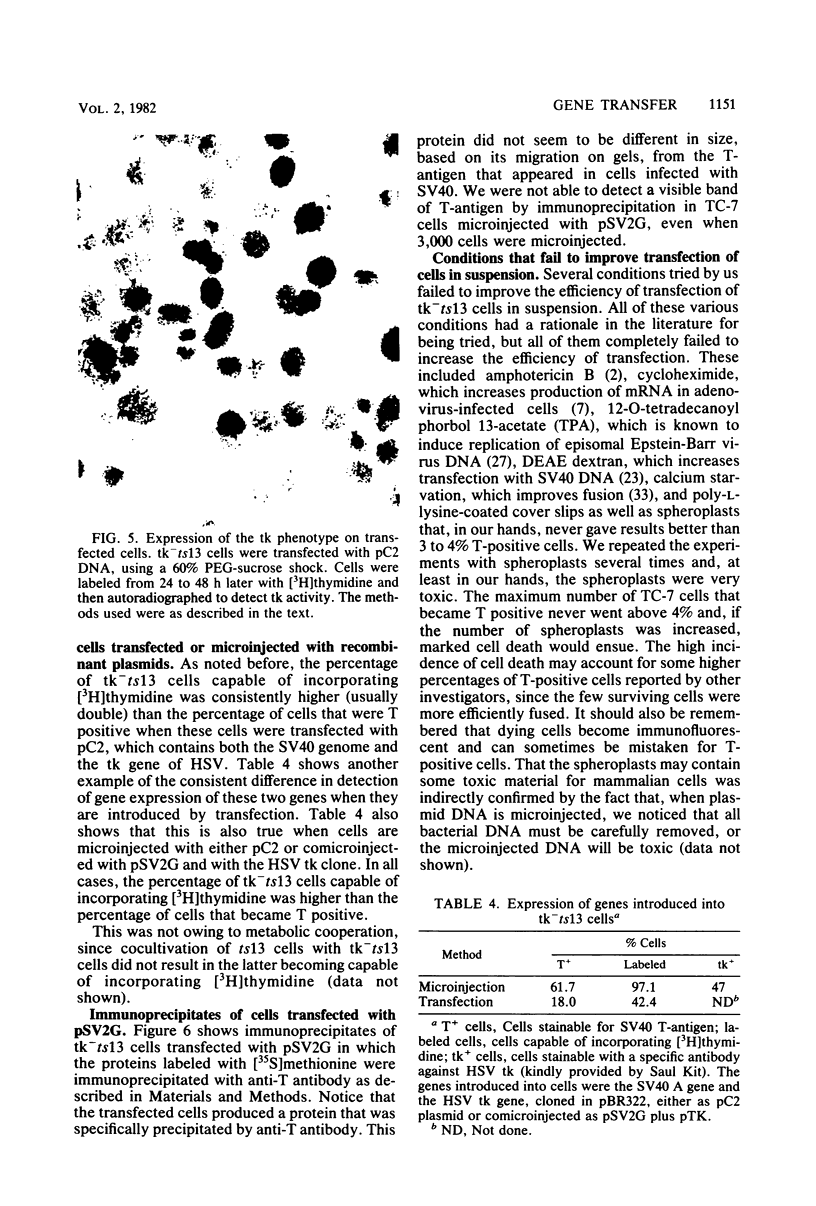
We have developed a procedure that gives a very high efficiency of transfection in mammalian cells with low-molecular-weight DNA (approximately 10(4) base pairs). The procedure uses cells in suspension that are shocked with polyethylene glycol 4 h after replating. We compared this transfection technique to the standard technique involving manual microinjection of DNA into the nuclei of mammalian cells, using recombinant plasmids containing the simian virus 40 A gene or the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene or both. The efficiency of transfection depends on a number of variables, the most important of which is the difference in transfectability of different cell lines. In our laboratory, the cell line that had the highest efficiency of transfection was tk-ts13, which is derived from baby hamster kidney cells that are deficient in thymidine kinase and temperature sensitive for growth. Under the appropriate conditions, as many as 70% of these cells can be transfected so that transient gene expression can be detected. With the manual microinjection technique, gene expression is independent of the cell line used and occurs faster than after transfection. The results suggest that the critical stage in transfection is the delivery of DNA molecules to the nucleus. Our experiments also indicate that an enzymatic function, in our case, thymidine kinase activity, gives a higher percentage of positive transfectants than when proteins are visualized only by indirect immunofluorescence. The transfection procedure described in this paper is simple and reproducible and, although less efficient than microinjection, ought to be useful in phenotypic and genotypic studies in which transfer of genes to a large number of cells is desirable.
Full text
PDF

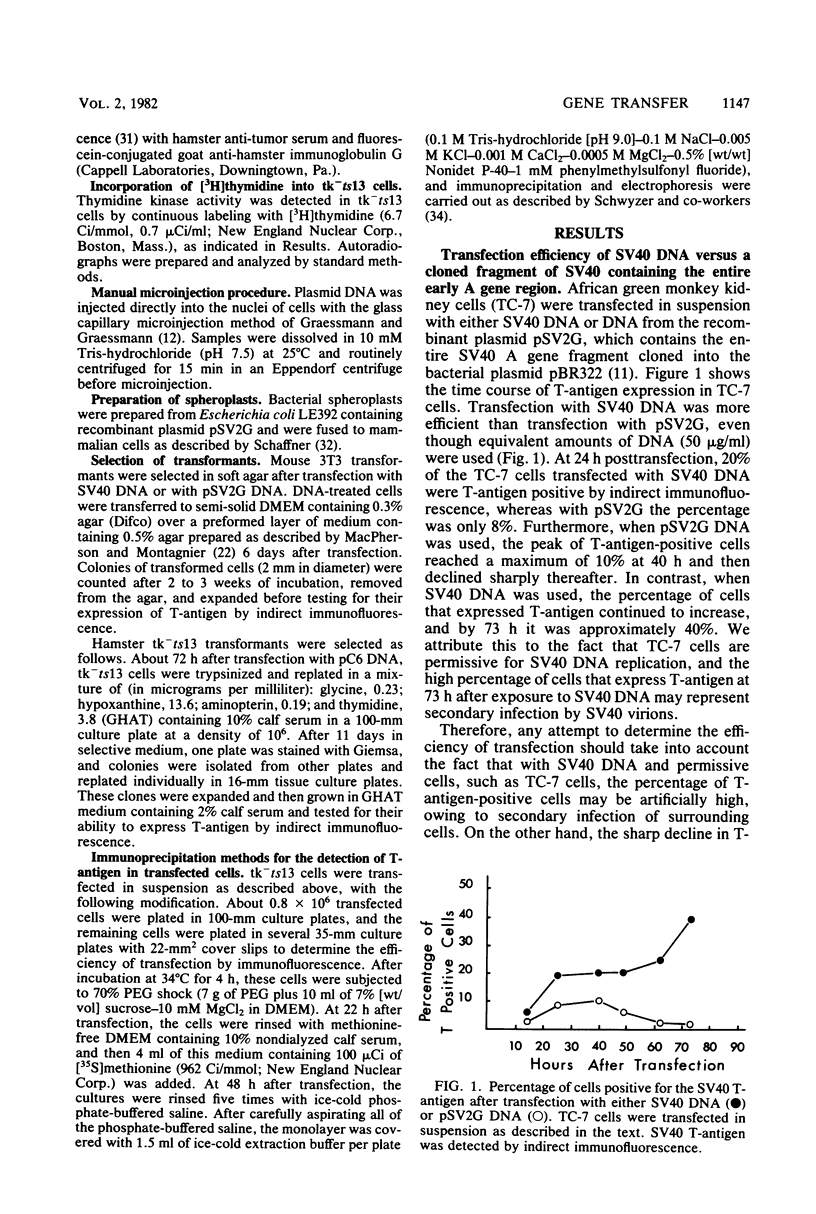
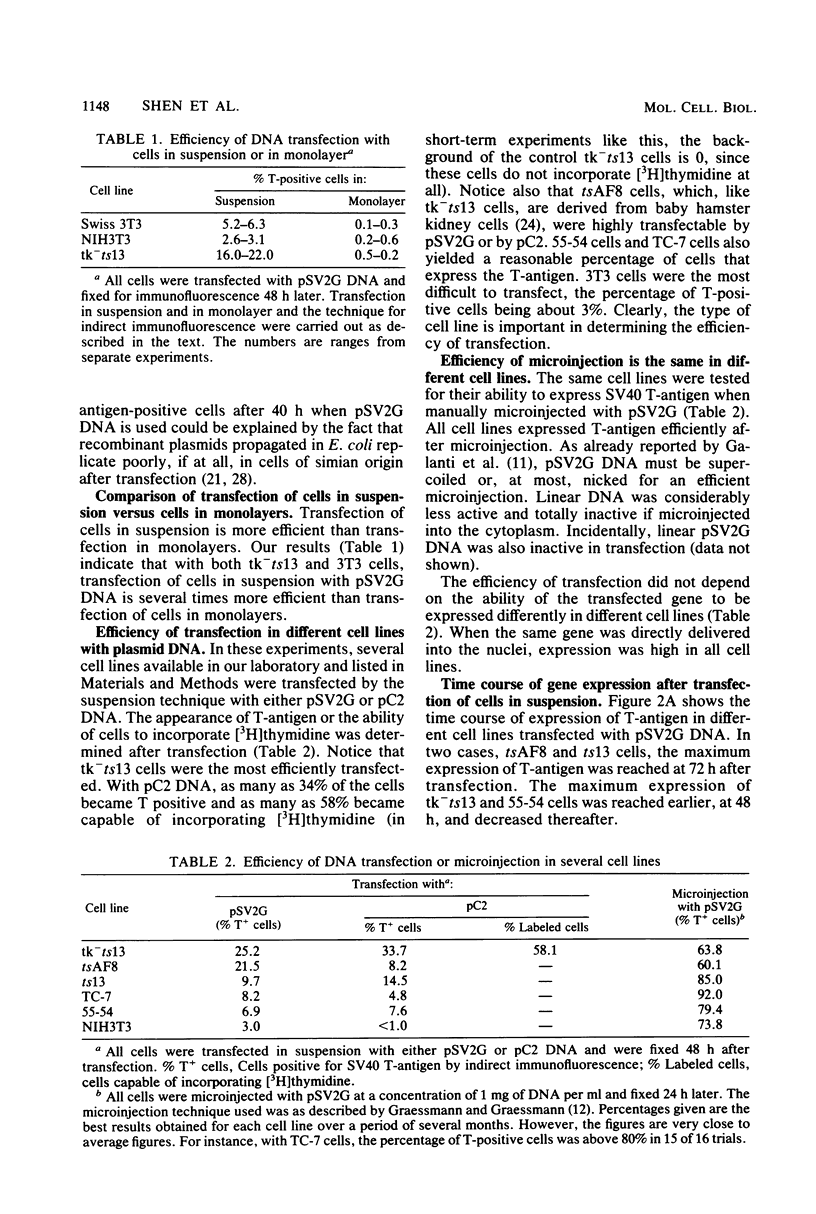



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashihara T., Chang S. D., Baserga R. Constancy of the shift-up point in two temperature-sensitive mammalian cell lines that arrest in G1. J Cell Physiol. 1978 Jul;96(1):15–22. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040960103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Zeev A., Becker Y. Requirement of host cell RNA polymerase II in the replication of herpes simplex virus in alpha-amanitin-sensitive and -resistant cell lines. Virology. 1977 Jan;76(1):246–253. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90300-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstin S. J., Meiss H. K., Basilico C. A temperature-sensitive cell cycle mutant of the BHK cell line. J Cell Physiol. 1974 Dec;84(3):397–408. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040840308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capecchi M. R. High efficiency transformation by direct microinjection of DNA into cultured mammalian cells. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):479–488. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90358-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Sharp P. A. SV40 DNA transfection of cells in suspension: analysis of efficiency of transcription and translation of T-antigen. Gene. 1981 Mar;13(2):197–202. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corsaro C. M., Pearson M. L. Enhancing the efficiency of DNA-mediated gene transfer in mammalian cells. Somatic Cell Genet. 1981 Sep;7(5):603–616. doi: 10.1007/BF01549662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A. Analysis of early adenovirus 2 RNA using Eco R-R1 viral DNA fragments. J Virol. 1975 May;15(5):1202–1213. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.5.1202-1213.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M. Loss of mouse chromosomes in somatic cell hybrids between HT-1080 human fibrosarcoma cells and mouse peritioneal macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3248–3252. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floros J., Jonak G., Galanti N., Baserga R. Induction of cell DNA replication in G1-specific ts mutants by microinjection of SV40 DNA. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Mar;132(1):215–223. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90097-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanti N., Jonak G. J., Soprano K. J., Floros J., Kaczmarek L., Weissman S., Reddy V. B., Tilghman S. M., Baserga R. Characterization and biological activity of cloned simian virus 40 DNA fragments. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 25;256(12):6469–6474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graessmann M., Graessman A. "Early" simian-virus-40-specific RNA contains information for tumor antigen formation and chromatin replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):366–370. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttner K. M., Barbosa J. A., Scangos G. A., Pratcheva D. D., Ruddle F. H. DNA-mediated gene transfer without carrier DNA. J Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;91(1):153–156. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.1.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttner K. M., Scangos G. A., Ruddle F. H. DNA-mediated gene transfer of a circular plasmid into murine cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5820–5824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki S., Diamond L., Baserga R. Induction of cellular deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in butyrate-treated cells by simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;1(11):1038–1047. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.11.1038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kit S., Otsuka H., Qavi H., Trkula D., Dubbs D. R., Hazen M. Biochemical transformation of thymidine kinase (TK)-deficient mouse cells by herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA fragments purified from hybrid plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Nov 25;8(22):5233–5253. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.22.5233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linnenbach A., Huebner K., Croce C. M. DNA-transformed murine teratocarcinoma cells: regulation of expression of simian virus 40 tumor antigen in stem versus differentiated cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4875–4879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loyter A., Scangos G. A., Ruddle F. H. Mechanisms of DNA uptake by mammalian cells: fate of exogenously added DNA monitored by the use of fluorescent dyes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):422–426. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. Inhibition of SV40 replication in simian cells by specific pBR322 DNA sequences. Nature. 1981 Sep 3;293(5827):79–81. doi: 10.1038/293079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACPHERSON I., MONTAGNIER L. AGAR SUSPENSION CULTURE FOR THE SELECTIVE ASSAY OF CELLS TRANSFORMED BY POLYOMA VIRUS. Virology. 1964 Jun;23:291–294. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90301-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan J. H., Pagano J. S. Enchancement of the infectivity of simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid with diethylaminoethyl-dextran. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 Aug;41(2):351–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meiss H. K., Basilico C. Temperature sensitive mutants of BHK 21 cells. Nat New Biol. 1972 Sep 20;239(90):66–68. doi: 10.1038/newbio239066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Wertheim P., Wilson G., Robinson J., Geelen J. L., van der Noordaa J., van der Eb A. J. Transfection of human lymphoblastoid cells with herpes simplex viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):949–953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller C., Graessmann A., Graessmann M. Mapping of early SV40-specific functions by microinjection of different early viral DNA fragments. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):579–585. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90026-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerow G. R., Cooper N. R. Isolation of Epstein Barr-virus and studies of its neutralization by human IgG and complement. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):272–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POPE J. H., ROWE W. P. DETECTION OF SPECIFIC ANTIGEN IN SV40-TRANSFORMED CELLS BY IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE. J Exp Med. 1964 Aug 1;120:121–128. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.2.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peden K. W., Pipas J. M., Pearson-White S., Nathans D. Isolation of mutants of an animal virus in bacteria. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1392–1396. doi: 10.1126/science.6251547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellicer A., Robins D., Wold B., Sweet R., Jackson J., Lowy I., Roberts J. M., Sim G. K., Silverstein S., Axel R. Altering genotype and phenotype by DNA-mediated gene transfer. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1414–1422. doi: 10.1126/science.7414320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellicer A., Wigler M., Axel R., Silverstein S. The transfer and stable integration of the HSV thymidine kinase gene into mouse cells. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):133–141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90308-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W. Direct transfer of cloned genes from bacteria to mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2163–2167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneiderman S., Farber J. L., Baserga R. A simple method for decreasing the toxicity of polyethylene glycol in mammalian cell hybridization. Somatic Cell Genet. 1979 Mar;5(2):263–269. doi: 10.1007/BF01539165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwyzer M., Weil R., Frank G., Zuber H. Amino acid sequence analysis of fragments generated by partial proteolysis from large simian virus 40 tumor antigen. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5627–5634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih C., Shilo B. Z., Goldfarb M. P., Dannenberg A., Weinberg R. A. Passage of phenotypes of chemically transformed cells via transfection of DNA and chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5714–5718. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soprano K. J., Dev V. G., Croce C. M., Baserga R. Reactivation of silent rRNA genes by simian virus 40 in human-mouse hybrid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3885–3889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talavera A., Basilico C. Temperature sensitive mutants of BHK cells affected in cell cycle progression. J Cell Physiol. 1977 Sep;92(3):425–436. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040920310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R., Urlaub G., Chasin L. DNA-mediated transfer of the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1373–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold B., Wigler M., Lacy E., Maniatis T., Silverstein S., Axel R. Introduction and expression of a rabbit beta-globin gene in mouse fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5684–5688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]