Abstract
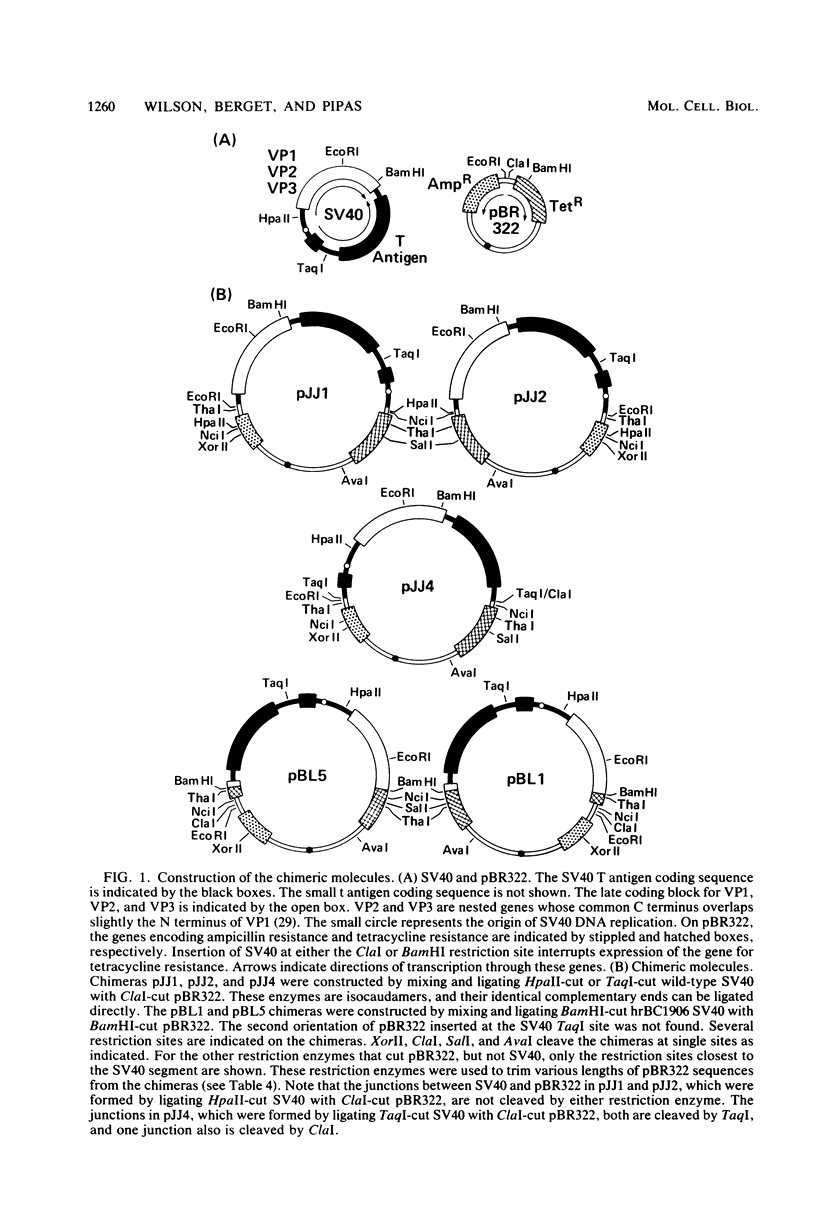
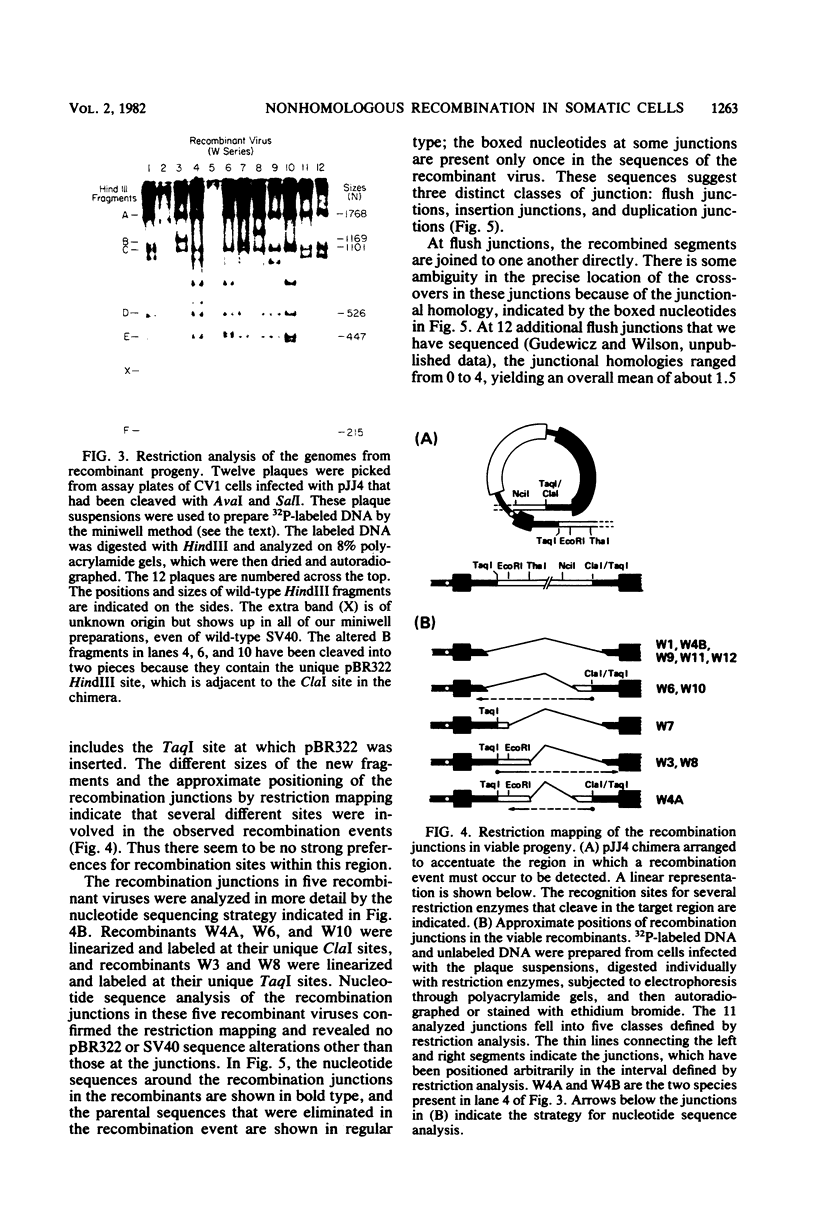
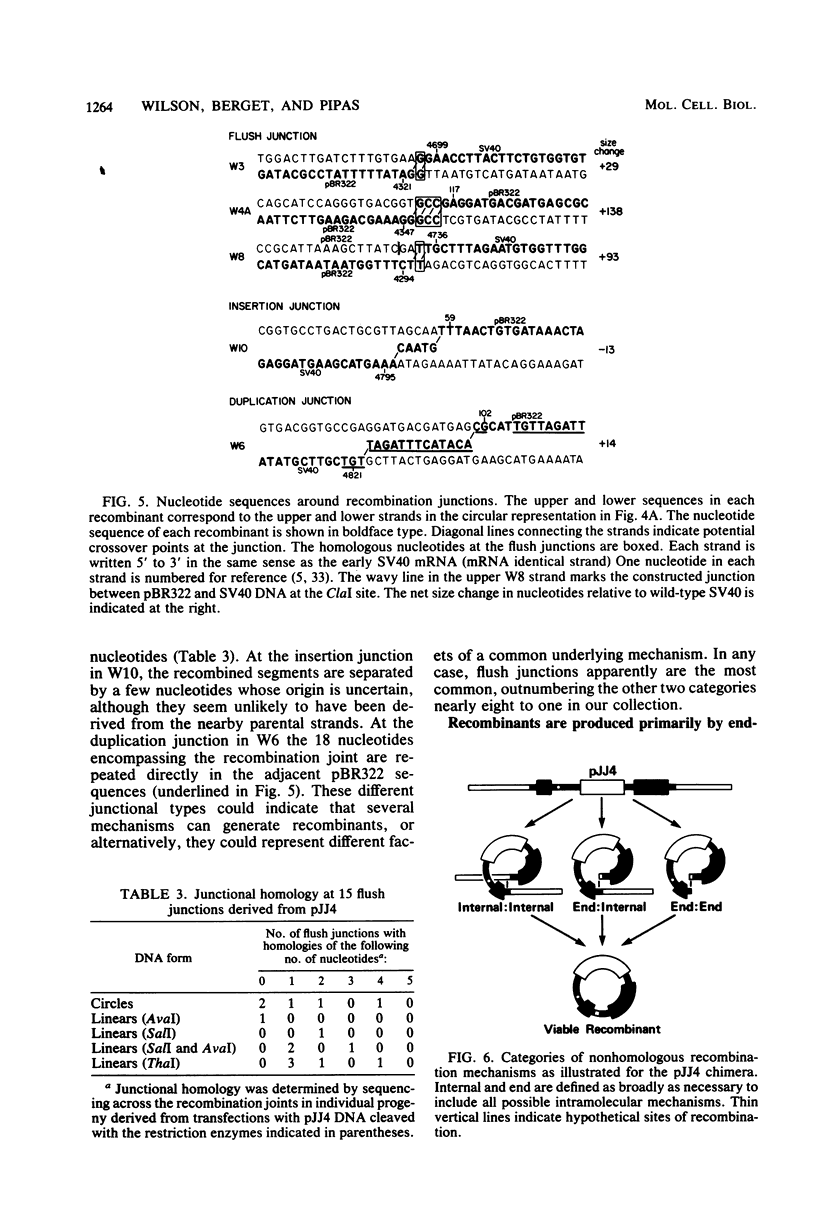
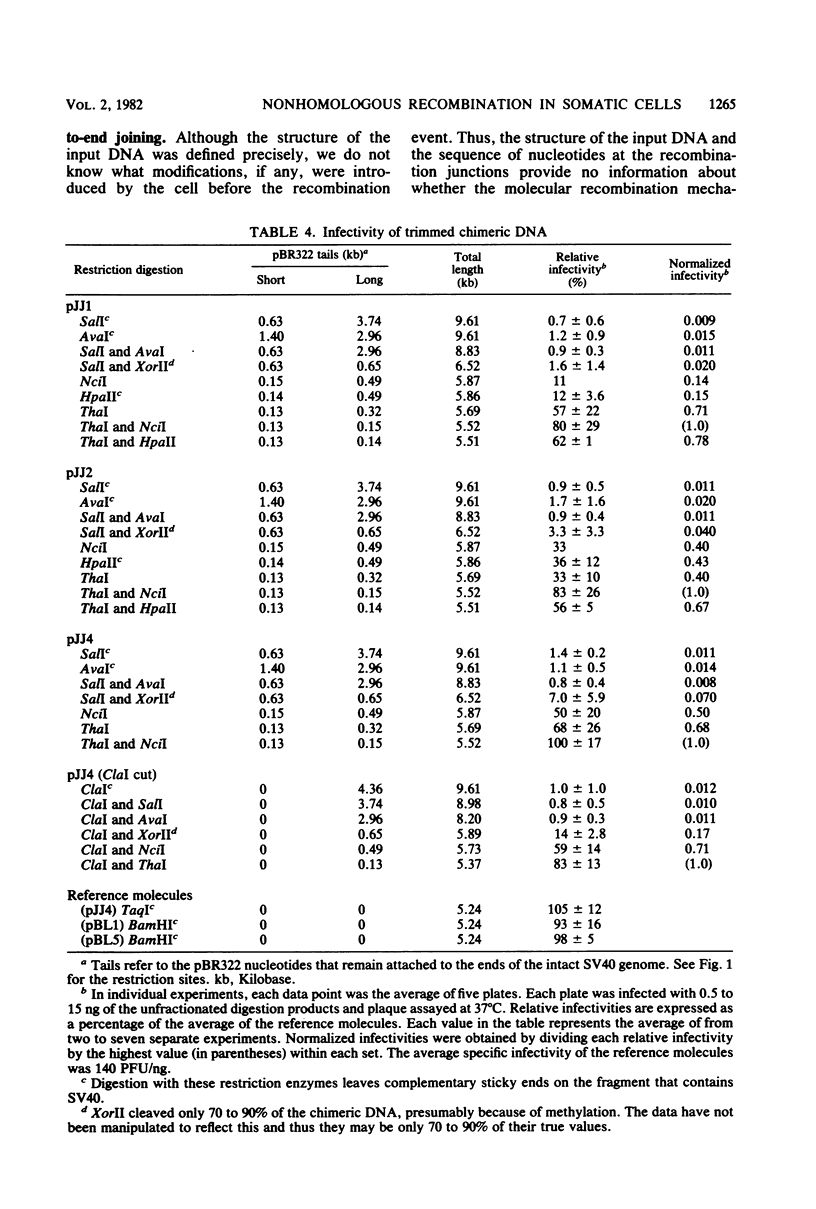
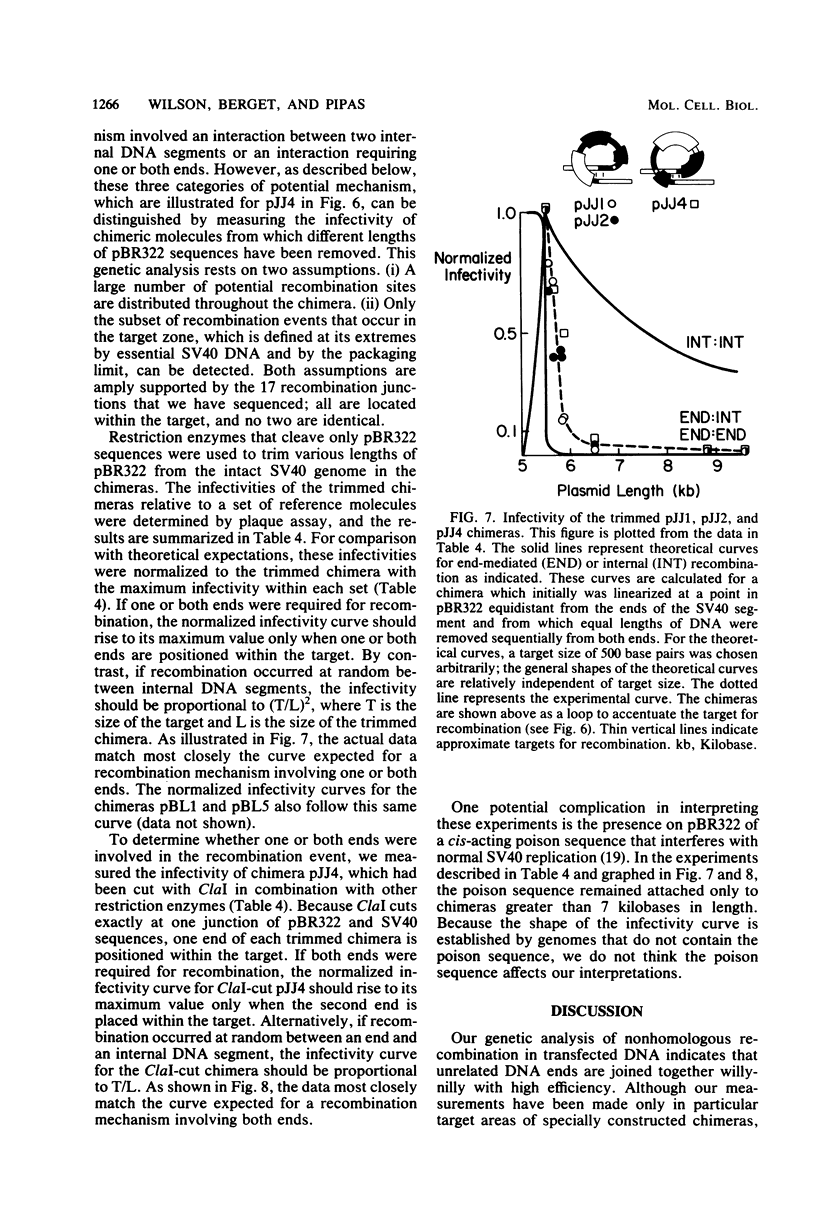
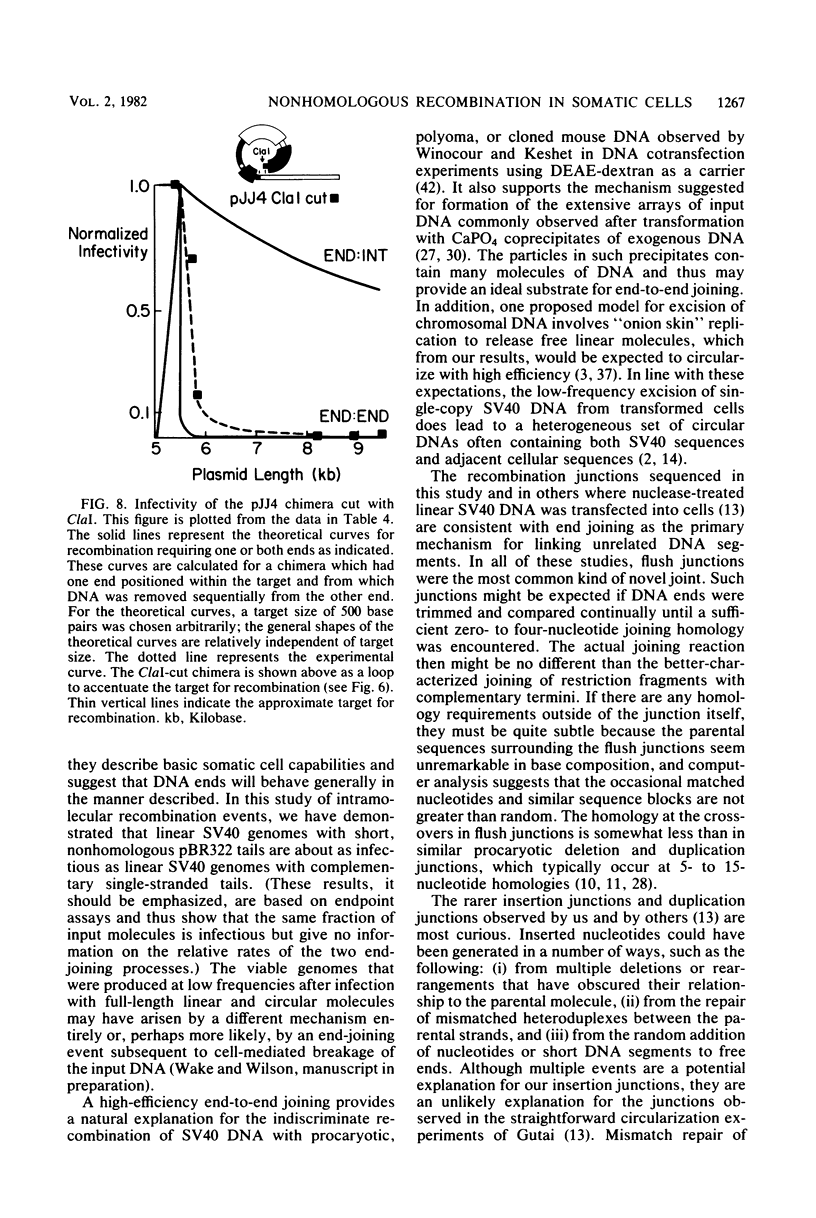
Molecular substrates for probing nonhomologous recombination in somatic cells were constructed by inserting pBR322 sequences at selected sites on the simian virus 40 (SV40) genome. The chimeric products are too large to be packaged into an SV40 capsid. Therefore, production of viable progeny requires that most of the pBR322 sequences be deleted without altering any SV40 sequences that are essential for lytic infection. As judged by plaque assay, these recombination events occur at readily detectable frequencies after transfection into CV1 monkey kidney cells. Depending on the site of pBR322 insertion, the infectivities of the full-length circular or linear chimeras ranged from 0.02 to 2% of the infectivity of linear wild-type SV40 DNA. Nucleotide sequence analysis of several recombinant progeny revealed three distinct classes of recombination junction and indicated that the causative recombination events were minimally dependent on sequence homology. Potential mechanisms involving recombination at internal sites or at ends were distinguished by measuring the infectivity of chimeric molecules from which various lengths of pBR322 had been removed. These data support end-to-end joining as the primary mechanism by which DNA segments recombine nonhomologously in somatic cells. This end joining appears to be very efficient, since SV40 genomes with complementary single-stranded tails or with short non-complementary pBR322 tails were comparably infectious. Overall, this study indicates that mammalian somatic cells are quite efficient at the willy-nilly end-to-end joining of unrelated DNA segments.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolivar F., Backman K. Plasmids of Escherichia coli as cloning vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:245–267. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botchan M., Stringer J., Mitchison T., Sambrook J. Integration and excision of SV40 DNA from the chromosome of a transformed cell. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):143–152. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90242-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botchan M., Topp W., Sambrook J. Studies on simian virus 40 excision from cellular chromosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):709–719. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brack C., Hirama M., Lenhard-Schuller R., Tonegawa S. A complete immunoglobulin gene is created by somatic recombination. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90078-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calos M. P., Miller J. H. Transposable elements. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):579–595. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90305-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chia W., Rigby P. W. Fate of viral DNA in nonpermissive cells infected with simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6638–6642. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. M., Kim S. K., Hood L. E. DNA sequences mediating class switching in alpha-immunoglobulins. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1360–1365. doi: 10.1126/science.6774415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubbs D. R., Rachmeler M., Kit S. Recombination between temperature-sensitive mutants of simian virus 40. Virology. 1974 Jan;57(1):161–174. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90117-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlund T., Normark S. Recombination between short DNA homologies causes tandem duplication. Nature. 1981 Jul 16;292(5820):269–271. doi: 10.1038/292269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farabaugh P. J., Schmeissner U., Hofer M., Miller J. H. Genetic studies of the lac repressor. VII. On the molecular nature of spontaneous hotspots in the lacI gene of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 25;126(4):847–857. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90023-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S. P., Berg P. Structure and formation of circular dimers of simian virus 40 DNA. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):295–302. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.295-302.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D., Lane D., Lipsich L., Wigler M., Botchan M. Characteristics of an SV40-plasmid recombinant and its movement into and out of the genome of a murine cell. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):127–139. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90120-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel M. A., Byrne J. C., Martin M. A. Biologic activity of oligomeric forms of SV40 DNA. Virology. 1978 Jun 15;87(2):239–246. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90129-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. D., Selsing E., Wells R. D. A rapid microscale technique for isolation of recombinant plasmid DNA suitable for restriction enzyme analysis. Plasmid. 1980 Jan;3(1):88–91. doi: 10.1016/s0147-619x(80)90037-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurosawa Y., Tonegawa S. Organization, structure, and assembly of immunoglobulin heavy chain diversity DNA segments. J Exp Med. 1982 Jan 1;155(1):201–218. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.1.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. Inhibition of SV40 replication in simian cells by specific pBR322 DNA sequences. Nature. 1981 Sep 3;293(5827):79–81. doi: 10.1038/293079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maki R., Traunecker A., Sakano H., Roeder W., Tonegawa S. Exon shuffling generates an immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2138–2142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan J. H., Pagano J. S. Enchancement of the infectivity of simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid with diethylaminoethyl-dextran. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 Aug;41(2):351–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertz J. E., Berg P. Viable deletion mutants of simian virus 40: selective isolation by means of a restriction endonuclease from Hemophilus parainfluenzae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4879–4883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertz J. E., Carbon J., Herzberg M., Davis R. W., Berg P. Isolation and characterization of individual clones of simian virus 40 mutants containing deletions duplications and insertions in their DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):69–84. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A. Integration and excision of bacteriophage lambda: the mechanism of conservation site specific recombination. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:143–167. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.001043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perucho M., Hanahan D., Wigler M. Genetic and physical linkage of exogenous sequences in transformed cells. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):309–317. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90178-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pribnow D., Sigurdson D. C., Gold L., Singer B. S., Napoli C., Brosius J., Dull T. J., Noller H. F. rII cistrons of bacteriophage T4. DNA sequence around the intercistronic divide and positions of genetic landmarks. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 5;149(3):337–376. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90477-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy V. B., Thimmappaya B., Dhar R., Subramanian K. N., Zain B. S., Pan J., Ghosh P. K., Celma M. L., Weissman S. M. The genome of simian virus 40. Science. 1978 May 5;200(4341):494–502. doi: 10.1126/science.205947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins D. M., Ripley S., Henderson A. S., Axel R. Transforming DNA integrates into the host chromosome. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):29–39. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90267-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Sugden B., Sambrook J. Detection of two restriction endonuclease activities in Haemophilus parainfluenzae using analytical agarose--ethidium bromide electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 31;12(16):3055–3063. doi: 10.1021/bi00740a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenk T. E., Carbon J., Berg P. Construction and analysis of viable deletion mutants of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):664–671. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.664-671.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):77–90. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thimmappaya B., Shenk T. Nucleotide sequence analysis of viable deletion mutants lacking segments of the simian virus 40 genome coding for small t antigen. J Virol. 1979 Jun;30(3):668–673. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.3.668-673.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upcroft P., Carter B., Kidson C. Analysis of recombination in mammalian cells using SV40 genome segments having homologous overlapping termini. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jun 25;8(12):2725–2736. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.12.2725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upcroft P., Carter B., Kidson C. Mammalian cell function mediating recombination of genetic elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 11;8(23):5835–5844. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.23.5835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. On the possibility of metabolic control of replicon "misfiring": relationship to emergence of malignant phenotypes in mammalian cell lineages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3673–3677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volckaert G., Feunteun J., Crawford L. V., Berg P., Fiers W. Nucleotide sequence deletions within the coding region for small-t antigen of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1979 Jun;30(3):674–682. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.3.674-682.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wake C. T., Wilson J. H. Defined oligomeric SV40 DNA: a sensitive probe of general recombination in somatic cells. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):141–148. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90121-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wake C. T., Wilson J. H. Simian virus 40 recombinants are produced at high frequency during infection with genetically mixed oligomeric DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2876–2880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. H., DePamphilis M., Berg P. Simian virus 40-permissive cell interactions: selection and characterization of spontaneously arising monkey cells that are resistant to simian virus 40 infection. J Virol. 1976 Nov;20(2):391–399. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.2.391-399.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winocour E., Keshet I. Indiscriminate recombination in simian virus 40-infected monkey cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4861–4865. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolgemuth D. J., Hsu M. T. Visualization of genetic recombination intermediates of human adenovirus type 2 DNA from infected HeLa cells. Nature. 1980 Sep 11;287(5778):168–171. doi: 10.1038/287168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodworth-Gutai M. Recombination in SV40-infected cells: viral DNA sequences at sites of circularization of transfecting linear DNA. Virology. 1981 Mar;109(2):353–365. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90506-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young C. S., Silverstein S. J. The kinetics of adenovirus recombination in homotypic and heterotypic genetic crosses. Virology. 1980 Mar;101(2):503–515. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90464-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]