Abstract
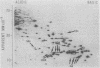
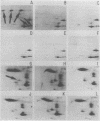
We examined the synthesis and turnover of individual proteins in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell cycle. Proteins were pulse-labeled with radioactive isotope (35S or 14C) in cells at discrete cycle stages and then resolved on two-dimensional gels and analyzed by a semiautomatic procedure for quantitating gel electropherogram-autoradiographs. The cells were obtained by one of three methods: (i) isolation of synchronous subpopulations of growing cells by zonal centrifugation; (ii) fractionation of pulse-labeled steady-state cultures according to cell age; and (iii) synchronization of cells with the mating pheromone, α-factor. In confirmation of previous studies, we found that the histones H4, H2A, and H2B were synthesized almost exclusively in the late G1 and early S phases. In addition, we identified eight proteins whose rates of synthesis were modulated in the cell cycle, and nine proteins (of which five, which may well be related, were unstable, with half-lives of 10 to 15 min) that might be regulated in the cell cycle by periodic synthesis, modification, or degradation. Based on the time of maximal labeling in the cell cycle and on experiments with α-factor and hydroxyurea, we assigned the cell cycle proteins to two classes: proteins in class I were labeled principally in early G1 phase and at a late stage of the cycle, whereas those in class II were primarily synthesized at times ranging from late G1 to mid S phase. At least one major control point for the cell cycle proteins occurred between “start” and early S phase. A set of stress-responsive proteins was also identified and analyzed. The rates of synthesis of these proteins were affected by certain perturbations that resulted during selection of synchronous cell populations and by heat shock.
Full text
PDF

















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson N. G., Anderson N. L. Analytical techniques for cell fractions. XXI. Two-dimensional analysis of serum and tissue proteins: multiple isoelectric focusing. Anal Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(2):331–340. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90229-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossinger J., Miller M. J., Vo K. P., Geiduschek E. P., Xuong N. H. Quantitative analysis of two-dimensional electrophoretograms. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7986–7998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bostian K. A., Lemire J. M., Cannon L. E., Halvorson H. O. In vitro synthesis of repressible yeast acid phosphatase: identification of multiple mRNAs and products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4504–4508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt W. F., Patterson K., von Holt C. The histones of yeast. The isolation and partial structure of the core histones. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Sep;110(1):67–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04841.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciejek E., Thorner J., Geier M. Solid phase peptide synthesis of alpha-factor, a yeast mating pheromone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Oct 10;78(3):952–961. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90514-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davie J. R., Saunders C. A., Walsh J. M., Weber S. C. Histone modifications in the yeast S. Cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3205–3216. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson D. P. Polypeptide synthesis in cell cycle mutants of fission yeast. J Cell Sci. 1981 Oct;51:203–217. doi: 10.1242/jcs.51.1.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott S. G., McLaughlin C. S. Rate of macromolecular synthesis through the cell cycle of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4384–4388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott S. G., McLaughlin C. S. Synthesis and modification of proteins during the cell cycle of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1979 Mar;137(3):1185–1190. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.3.1185-1190.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott S. G., Warner J. R., McLaughlin C. S. Synthesis of ribosomal proteins during the cell cycle of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1979 Feb;137(2):1048–1050. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.2.1048-1050.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein D. B., McAlister L. alpha-Factor-mediatd modification of a 32P-labeled protein by MATa cells of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 10;256(5):2561–2566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrels J. I. Two dimensional gel electrophoresis and computer analysis of proteins synthesized by clonal cell lines. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7961–7977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halvorson H. O., Carter B. L., Tauro P. Synthesis of enzymes during the cell cycle. Adv Microb Physiol. 1971;6:47–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H. Cell division from a genetic perspective. J Cell Biol. 1978 Jun;77(3):627–637. doi: 10.1083/jcb.77.3.627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H., Culotti J., Reid B. Genetic control of the cell-division cycle in yeast. I. Detection of mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jun;66(2):352–359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.2.352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H., Mortimer R. K., Culotti J., Culotti M. Genetic Control of the Cell Division Cycle in Yeast: V. Genetic Analysis of cdc Mutants. Genetics. 1973 Jun;74(2):267–286. doi: 10.1093/genetics/74.2.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H. Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell cycle. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Jun;38(2):164–198. doi: 10.1128/br.38.2.164-198.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hereford L. M., Hartwell L. H. Sequential gene function in the initiation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae DNA synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1974 Apr 15;84(3):445–461. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90451-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hereford L. M., Osley M. A., Ludwig T. R., 2nd, McLaughlin C. S. Cell-cycle regulation of yeast histone mRNA. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):367–375. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90326-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochhauser S. J., Stein J. L., Stein G. S. Gene expression and cell cycle regulation. Int Rev Cytol. 1981;71:95–243. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61183-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig J. R., 2nd, Foy J. J., Elliott S. G., McLaughlin C. S. Synthesis of specific identified, phosphorylated, heat shock, and heat stroke proteins through the cell cycle of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;2(2):117–126. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.2.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. J., Vo P. K., Nielsen C., Geiduschek E. P., Xuong N. H. Computer analysis of two-dimensional gels: semi-automatic matching. Clin Chem. 1982 Apr;28(4 Pt 2):867–875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. J., Xuong N. H., Geiduschek E. P. A response of protein synthesis to temperature shift in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5222–5225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. J., Xuong N. H., Geiduschek E. P. Quantitative analysis of the heat shock response of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):311–327. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.311-327.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll R., Wintersberger E. Synthesis of yeast histones in the cell cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1863–1867. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumaker M. F. A program which automatically quantitates gel electrophoretic autoradiograms. Anal Biochem. 1978 Dec;91(2):375–393. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90523-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebastian J., Carter B. L., Halvorson H. O. Use of yeast populations fractionated by zonal centrifugation to study the cell cycle. J Bacteriol. 1971 Dec;108(3):1045–1050. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.3.1045-1050.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater M. L. Effect of reversible inhibition of deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis on the yeast cell cycle. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jan;113(1):263–270. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.1.263-270.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vo K. P., Miller M. J., Geiduschek E. P., Nielsen C., Olson A., Xuong N. H. Computer analysis of two-dimensional gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):258–271. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90291-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMSON D. H., SCOPES A. W. The behaviour of nucleic acids in synchronously dividing cultures of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Exp Cell Res. 1960 Aug;20:338–349. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(60)90162-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis J. W., Hereford L., Grunstein M. Histone H2B genes of yeast encode two different proteins. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):799–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90556-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitney P. A., Cooper T. G. Urea carboxylase and allophanate hydrolase. Two components of adenosine triphosphate:urea amido-lyase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1972 Mar 10;247(5):1349–1353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]