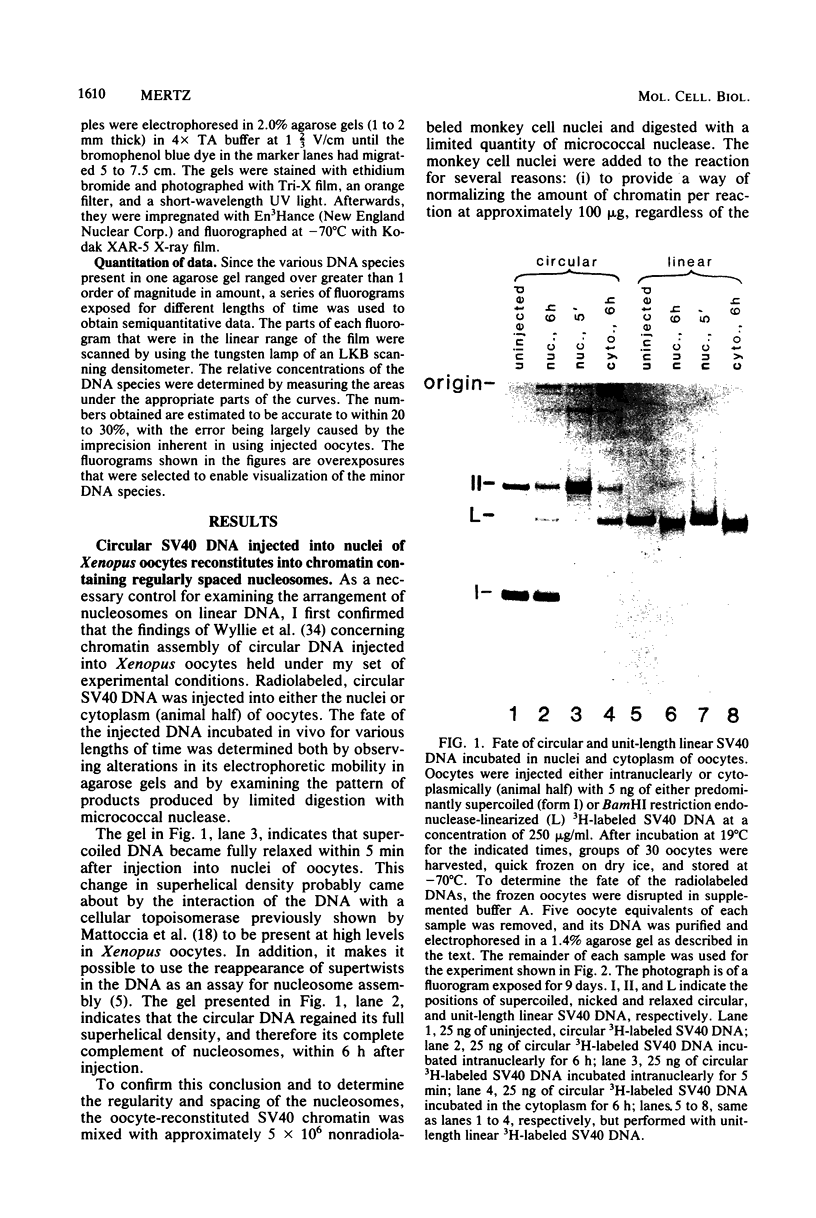
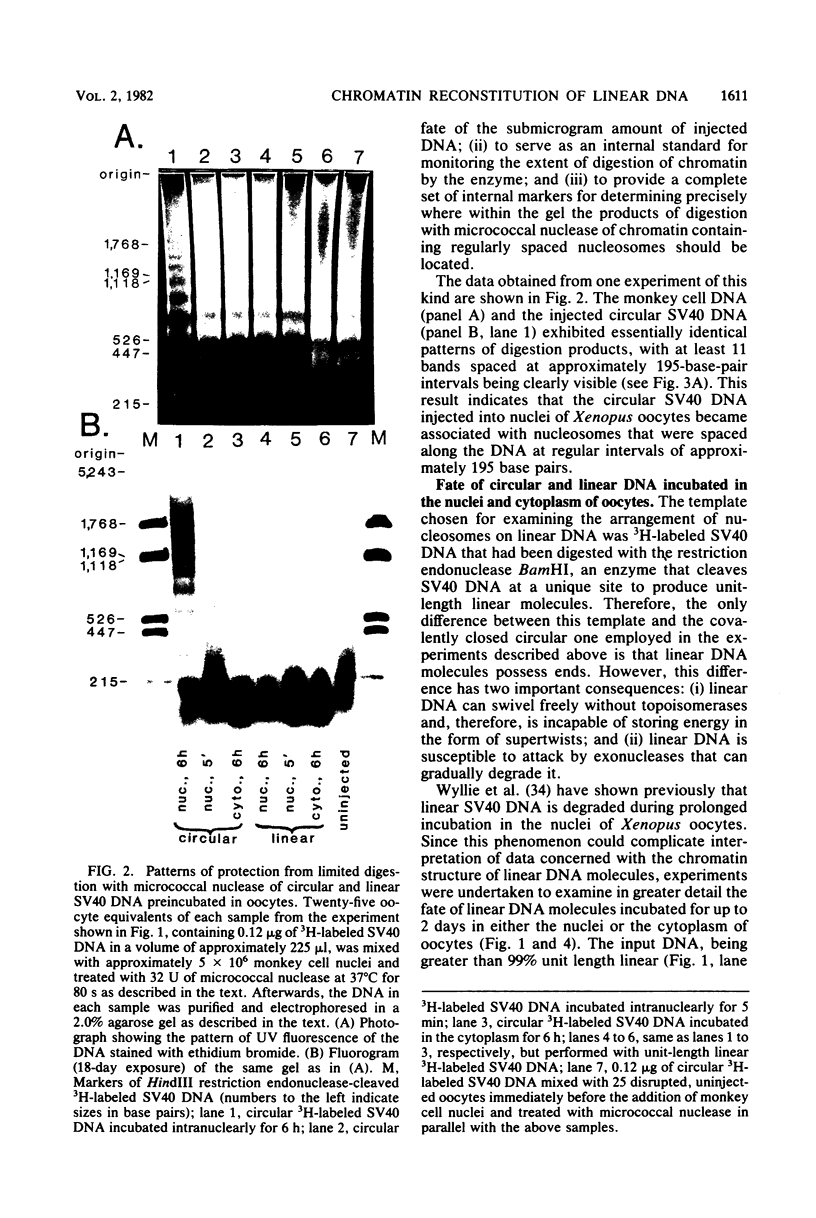
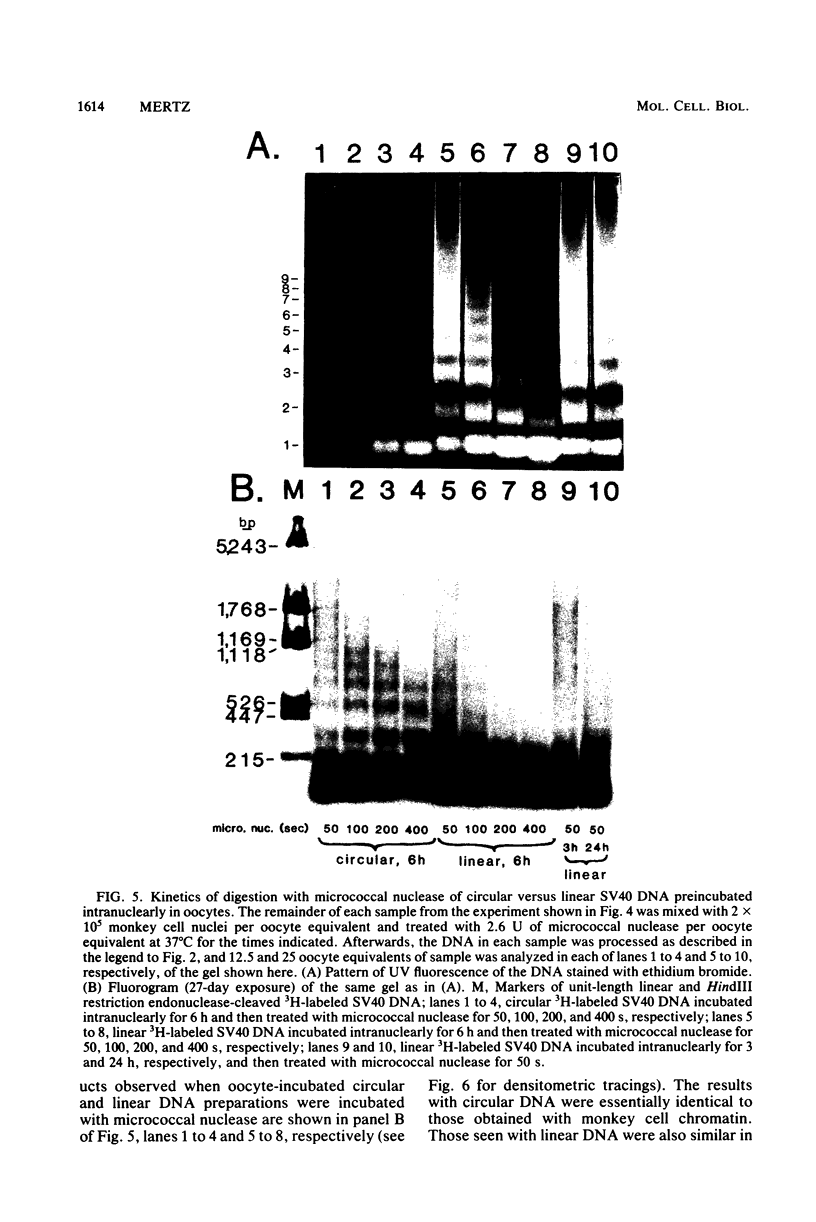
Abstract
The topological state of DNA may play a role in regulating chromatin structure and gene expression in eucaryotes. To test this hypothesis, the arrangements of nucleosomes on circular and unit-length linear simian virus 40 (SV40) DNAs incubated in nuclei of Xenopus oocytes were determined by (i) analyzing changes in the electrophoretic properties of the DNAs and (ii) examining the patterns of DNA fragments resulting from digestions with micrococcal nuclease. Whereas circular DNA became associated with nucleosomes that were arranged along the DNA at regular intervals of approximately 195 base pairs, linear DNA failed to reconstitute into chromatin containing regularly spaced nucleosomes. DNA that failed to form proper chromatin was gradually degraded, indicating that histone proteins in proper association with DNA may be the cellular component that normally protects chromosomal DNA from endonucleolytic attack. When either circular or linear DNA was incubated in an in vitro transcription system made from a whole-cell extract of HeLa cells, most of the molecules did not associate with histone proteins to form regularly spaced nucleosomes. Furthermore, linearization of mRNA-encoding DNAs, including SV40, reduces their transcriptional activity in Xenopus oocytes to a level comparable to that obtained with the in vitro transcription system employed here. Therefore, proper association of DNA with appropriate cellular chromosomal factors may be a prerequisite for proper transcription by RNA polymerase II.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benoist C., Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):304–310. doi: 10.1038/290304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H., Chiou S. S. Non-nucleosomal packaging of a tandemly repeated DNA sequence at termini of extrachromosomal DNA coding for rRNA in Tetrahymena. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2263–2267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandini Attardi D., Mattoccia E., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Formation of branched DNA structures by Xenopus laevis oocyte extract. Nature. 1977 Dec 22;270(5639):754–756. doi: 10.1038/270754a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M. DNA topoisomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:879–910. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.004311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germond J. E., Hirt B., Oudet P., Gross-Bellark M., Chambon P. Folding of the DNA double helix in chromatin-like structures from simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1843–1847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Delimitation of far upstream sequences required for maximal in vitro transcription of an H2A histone gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):297–301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Spacer DNA sequences upstream of the T-A-T-A-A-A-T-A sequence are essential for promotion of H2A histone gene transcription in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7102–7106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B., Melton D. A. Gene transfer in amphibian eggs and oocytes. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:189–218. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.001201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewish D. R., Burgoyne L. A. Chromatin sub-structure. The digestion of chromatin DNA at regularly spaced sites by a nuclear deoxyribonuclease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 May 15;52(2):504–510. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90740-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura G., Dulbecco R. Isolation and characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of simian virus 40. Virology. 1972 Aug;49(2):394–403. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90492-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D. Structure of chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:931–954. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.004435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kressmann A., Clarkson S. G., Telford J. L., Birnstiel M. L. Transcription of xenopus tDNAmet1 and sea urchin histone DNA injected into the Xenopus oocyte nucleus. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):1077–1082. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Earnshaw W. C. Nucleosome assembly. Nature. 1980 Aug 21;286(5775):763–767. doi: 10.1038/286763a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Honda B. M., Mills A. D., Morris N. R., Wyllie A. H., Mertz J. E., De Roberts E. M., Gurdon J. B. Chromatin assembly and transcription in eggs and oocytes of Xenopus laevis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 1):171–178. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D., Morris N. R. Assembly of SV40 chromatin in a cell-free system from Xenopus eggs. Cell. 1977 Feb;10(2):237–243. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90217-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis D. J., Chambon P. The SV40 early region TATA box is required for accurate in vitro initiation of transcription. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):310–315. doi: 10.1038/290310a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattoccia E., Attardi D. G., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. DNA-relaxing activity and endonuclease activity in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4551–4554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertz J. E., Berg P. Defective simian virus 40 genomes: isolation and growth of individual clones. Virology. 1974 Nov;62(1):112–124. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90307-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertz J. E., Davis R. W. Cleavage of DNA by R 1 restriction endonuclease generates cohesive ends. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3370–3374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertz J. E., Gurdon J. B. Purified DNAs are transcribed after microinjection into Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1502–1506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. J., Mertz J. E. Template structural requirements for transcription in vivo by RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;2(12):1595–1607. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.12.1595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. J., Stephens D. L., Mertz J. E. Kinetics of accumulation and processing of simian virus 40 RNA in Xenopus laevis oocytes injected with simian virus 40 DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;2(12):1581–1594. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.12.1581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson T., Hsieh T. S., Brutlag D. Extracts of Drosophila embryos mediate chromatin assembly in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5510–5514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probst E., Kressmann A., Birnstiel M. L. Expression of sea urchin histone genes in the oocyte of Xenopus laevis. J Mol Biol. 1979 Dec 15;135(3):709–732. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90173-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinden R. R., Carlson J. O., Pettijohn D. E. Torsional tension in the DNA double helix measured with trimethylpsoralen in living E. coli cells: analogous measurements in insect and human cells. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):773–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90440-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. R. DNA supercoiling: another level for regulating gene expression. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):599–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90085-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens D. L., Miller T. J., Silver L., Zipser D., Mertz J. E. Easy-to-use equipment for the accurate microinjection of nanoliter volumes into the nuclei of amphibian oocytes. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jul 1;114(2):299–309. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90485-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden B., Keller W. Mammalian deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerases. I. Purification and properties of an -amanitin-sensitive ribonucleic acid polymerase and stimulatory factors from HeLa and KB cells. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3777–3788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voellmy R., Rungger D. Transcription of a Drosophila heat shock gene is heat-induced in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1776–1780. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil P. A., Luse D. S., Segall J., Roeder R. G. Selective and accurate initiation of transcription at the Ad2 major late promotor in a soluble system dependent on purified RNA polymerase II and DNA. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):469–484. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weingärtner B., Keller W. Transcription and processing of adenoviral RNA by extracts from HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4092–4096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H., Gurdon J. B., Price J. Nuclear localisation of an oocyte component required for the stability of injected DNA. Nature. 1977 Jul 14;268(5616):150–152. doi: 10.1038/268150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H., Laskey R. A., Finch J., Gurdon J. B. Selective DNA conservation and chromatin assembly after injection of SV40 DNA into Xenopus oocytes. Dev Biol. 1978 May;64(1):178–188. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]