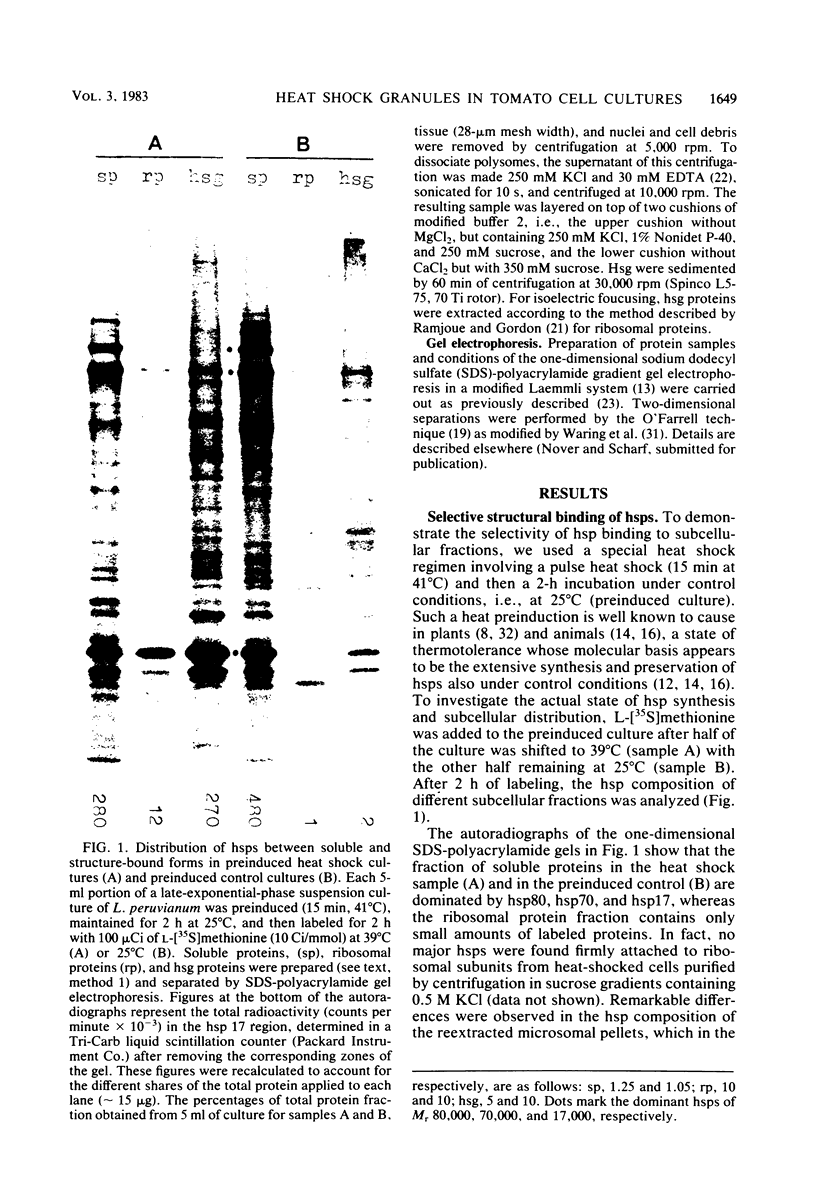
Abstract
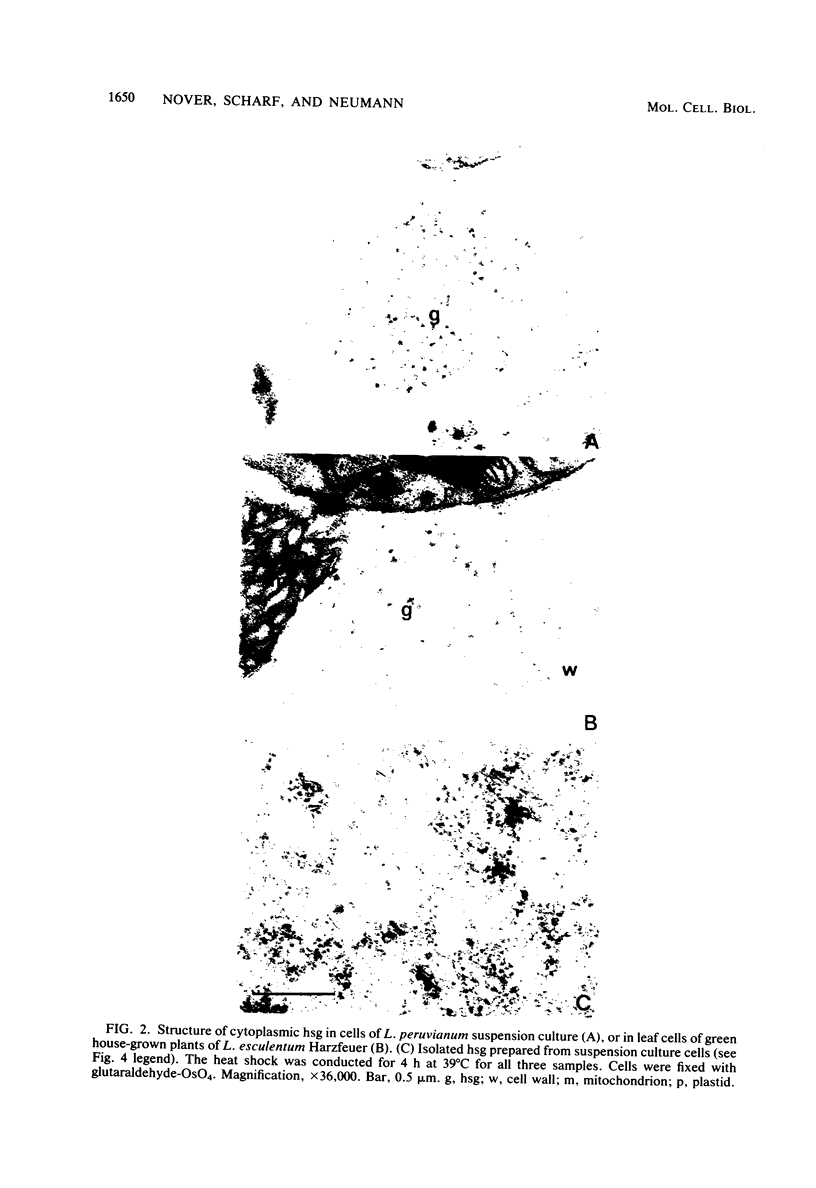
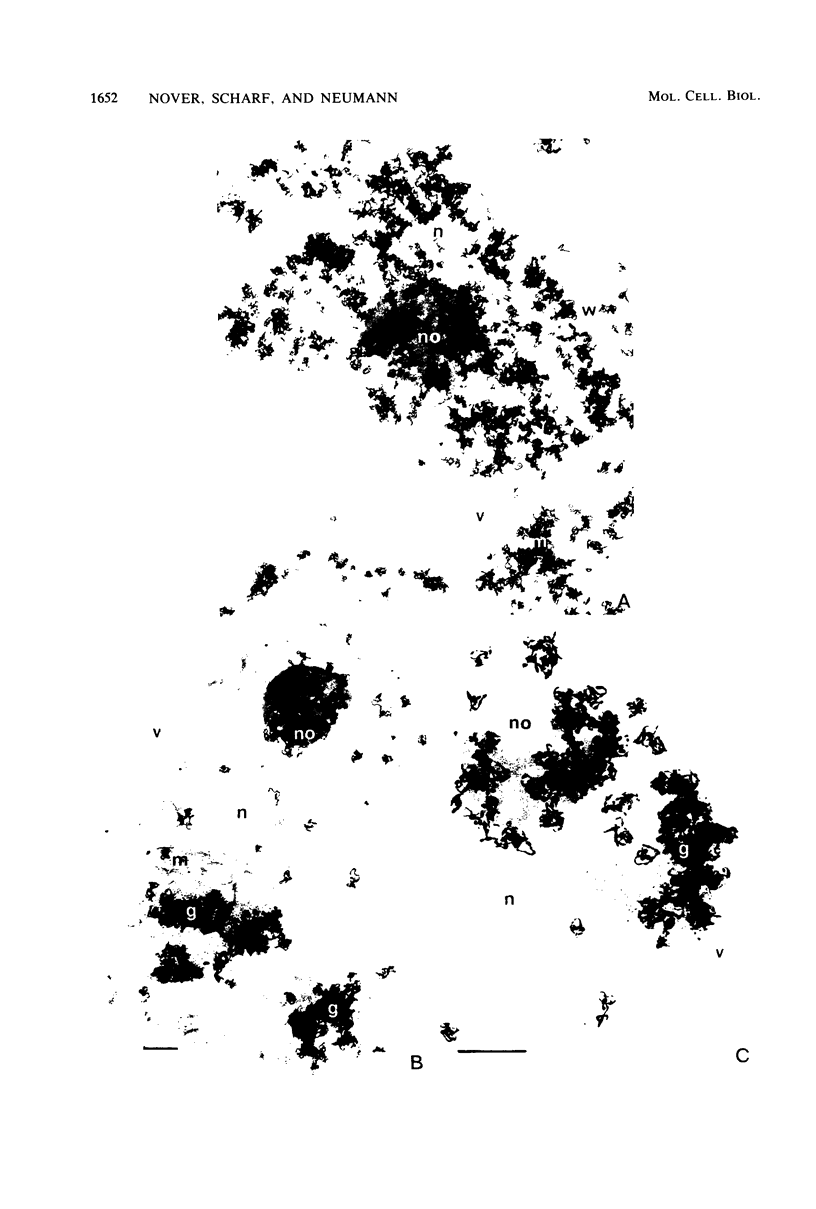
Biochemical and electron microscopic analyses of heat-shocked suspension cultures of Peruvian tomato (Lycopersicon peruvianum) revealed that a considerable part of the dominant small heat shock proteins (hsps) with an Mr of approximately 17,000 are structural proteins of newly forming granular aggregates in the cytoplasm (heat shock granules), whose formation strictly depends on heat shock conditions (37 to 40 degrees C) and the presence or simultaneous synthesis of hsps. However, under certain conditions, e.g., in preinduced cultures maintained at 25 degrees C, hsps also accumulate as soluble proteins without concomitant assembly of heat shock granules. Similar heat shock-induced cytoplasmic aggregates were also observed in other cell cultures and heat-shocked tomato leaves and corn coleoptiles.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arrigo A. P., Ahmad-Zadeh C. Immunofluorescence localization of a small heat shock protein (hsp 23) in salivary gland cells of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(1):73–79. doi: 10.1007/BF00271198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrigo A. P., Fakan S., Tissières A. Localization of the heat shock-induced proteins in Drosophila melanogaster tissue culture cells. Dev Biol. 1980 Jul;78(1):86–103. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90320-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrigo A. P. Investigation of the function of the heat shock proteins in Drosophila melanogaster tissue culture cells. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;178(3):517–524. doi: 10.1007/BF00337856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M., Bonner J. J. The induction of gene activity in drosophilia by heat shock. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):241–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90150-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craine B. L., Kornberg T. Activation of the major drosophila heat-shock genes in vitro. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):671–681. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90174-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiDomenico B. J., Bugaisky G. E., Lindquist S. Heat shock and recovery are mediated by different translational mechanisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6181–6185. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes E. N., August J. T. Coprecipitation of heat shock proteins with a cell surface glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2305–2309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley P. M., Schlesinger M. J. Antibodies to two major chicken heat shock proteins cross-react with similar proteins in widely divergent species. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;2(3):267–274. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.3.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kioussis J., Cato A. C., Slater A., Burdon R. H. Polypeptides encoded by polyadenylated and non-polyadenylated messenger RNAs from normal and heat shocked HeLa cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5203–5214. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landry J., Bernier D., Chrétien P., Nicole L. M., Tanguay R. M., Marceau N. Synthesis and degradation of heat shock proteins during development and decay of thermotolerance. Cancer Res. 1982 Jun;42(6):2457–2461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinger L., Varshavsky A. Heat-shock proteins of Drosophila are associated with nuclease-resistant, high-salt-resistant nuclear structures. J Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;90(3):793–796. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.3.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G. C., Werb Z. Correlation between synthesis of heat shock proteins and development of thermotolerance in Chinese hamster fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3218–3222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loomis W. F., Wheeler S. A. Chromatin-associated heat shock proteins of Dictyostelium. Dev Biol. 1982 Apr;90(2):412–418. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90390-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen N. S., Mitchell H. K. Recovery of protein synthesis after heat shock: prior heat treatment affects the ability of cells to translate mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1708–1711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramjoué H. P., Gordon J. Evolutionary microdivergence of chick and rat liver ribosomal proteins. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 25;252(24):9065–9070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabatini D. D., Tashiro Y., Palade G. E. On the attachment of ribosomes to microsomal membranes. J Mol Biol. 1966 Aug;19(2):503–524. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80019-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharf K. D., Nover L. Heat-shock-induced alterations of ribosomal protein phosphorylation in plant cell cultures. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):427–437. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90240-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinibaldi R. M., Morris P. W. Putative function of Drosophila melanogaster heat shock proteins in the nucleoskeleton. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):10735–10738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storti R. V., Scott M. P., Rich A., Pardue M. L. Translational control of protein synthesis in response to heat shock in D. melanogaster cells. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):825–834. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90559-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanguay R. M., Vincent M. Intracellular translocation of cellular and heat shock induced proteins upon heat shock in Drosophila Kc cells. Can J Biochem. 1982 Mar;60(3):306–315. doi: 10.1139/o82-037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velazquez J. M., DiDomenico B. J., Lindquist S. Intracellular localization of heat shock proteins in Drosophila. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):679–689. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90314-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C., Asai D. J., Lazarides E. The 68,000-dalton neurofilament-associated polypeptide is a component of nonneuronal cells and of skeletal myofibrils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1541–1545. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C., Gomer R. H., Lazarides E. Heat shock proteins are methylated in avian and mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3531–3535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring G. L., Allis C. D., Mahowald A. P. Isolation of polar granules and the identification of polar granule-specific protein. Dev Biol. 1978 Sep;66(1):197–206. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90284-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarwood C. E. Acquired Tolerance of Leaves to Heat. Science. 1961 Sep 29;134(3483):941–942. doi: 10.1126/science.134.3483.941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







