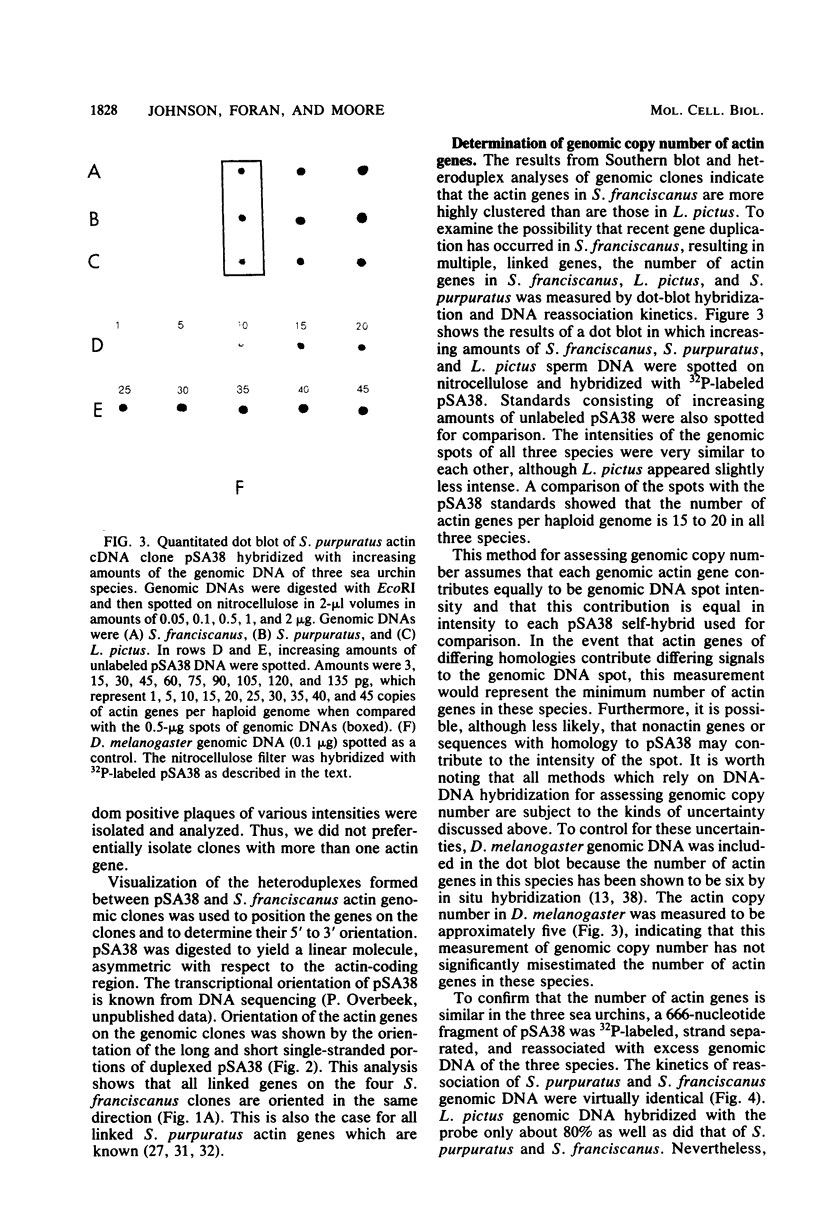
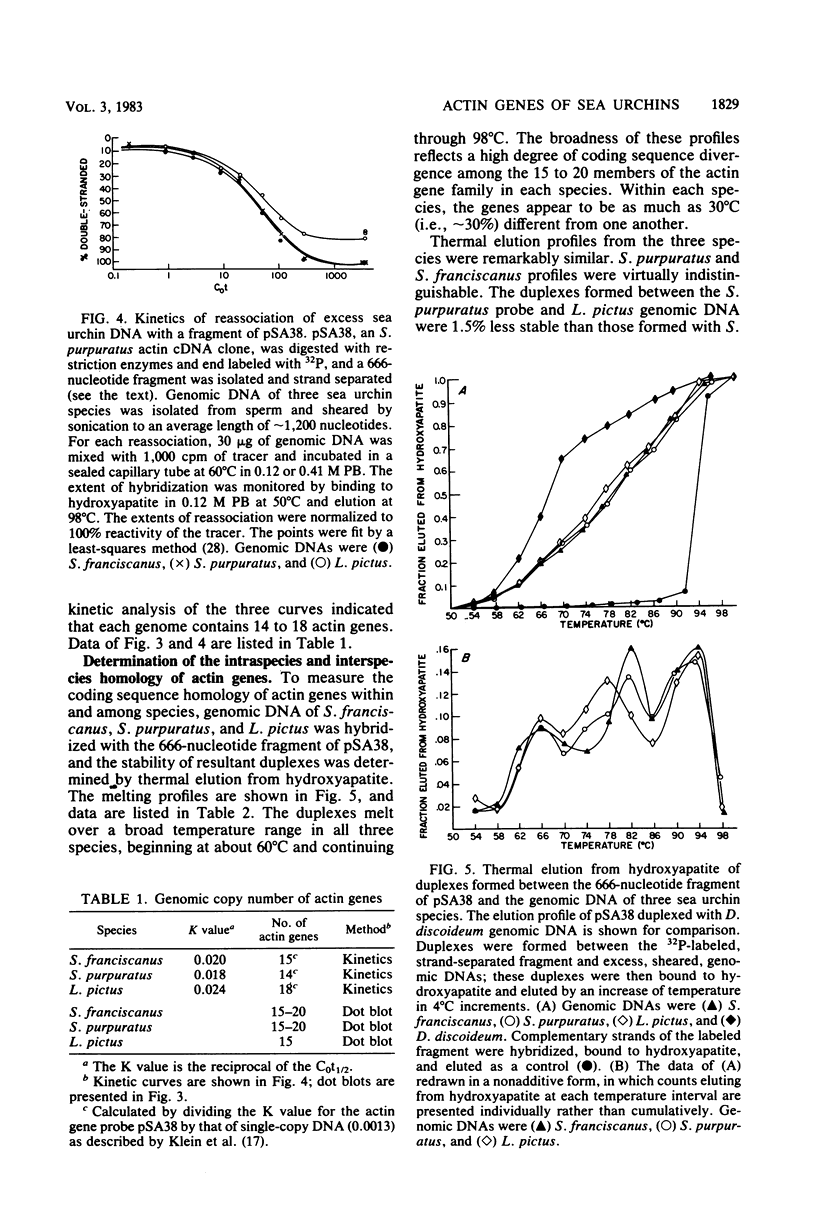
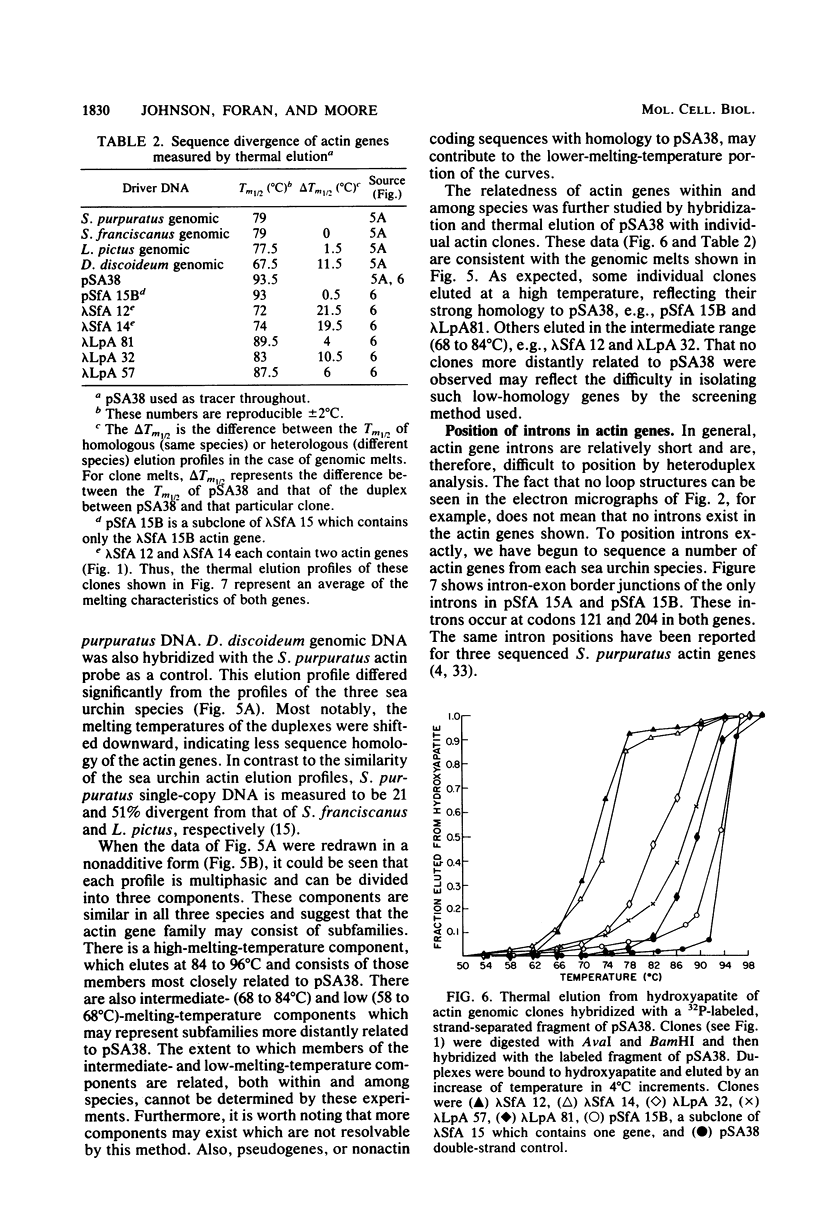
Abstract
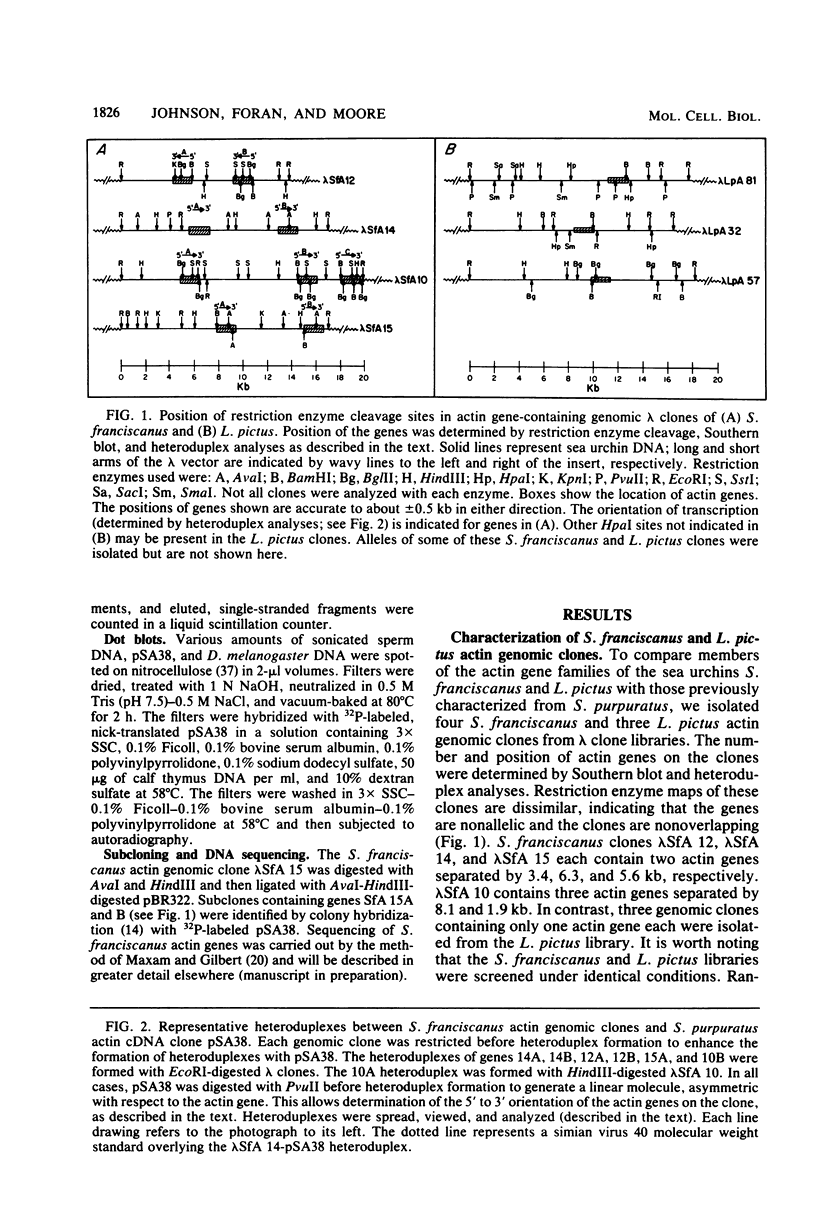
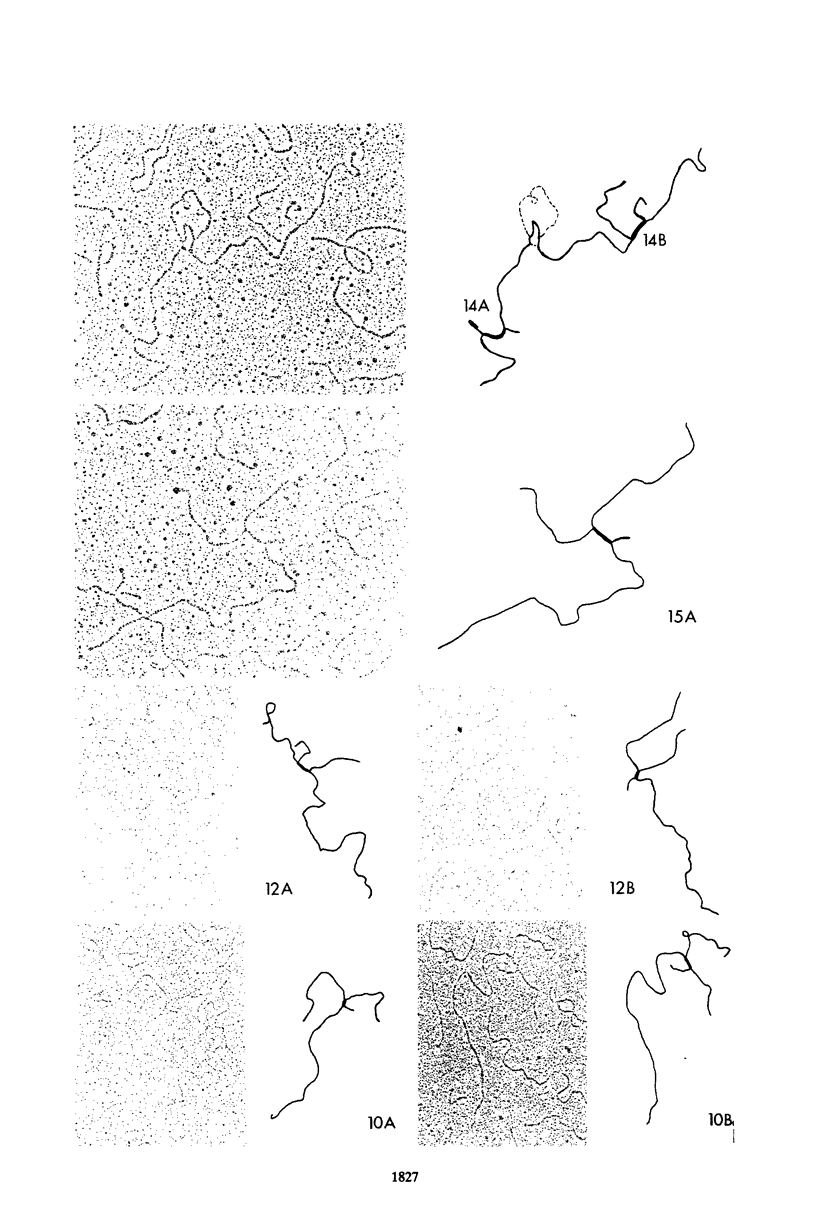
Genomic libraries of the sea urchins Strongylocentrotus franciscanus and Lytechinus pictus were screened with an actin cDNA clone from Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Four nonoverlapping clones were isolated and characterized from the S. franciscanus library; three were isolated and characterized from the L. pictus library. Linked genes having the same transcriptional orientation were found on all S. franciscanus clones. Three clones contained two actin genes each; the other clone contained three. In contrast, the L. pictus clones contained only one actin gene. Comparison of actin genomic clones from these three species indicated a difference in the genomic organization of sea urchin actin genes in that the genes appear to be more highly clustered in S. franciscanus than in S. purpuratus and L. pictus. Genomic dot blots and reassociation kinetics demonstrated that the copy number of actin genes in all three species is 15 to 20. Nucleotide sequence homology of actin genes within and among the species was measured by thermal elution. These experiments indicated that there is a high degree of interspecies actin gene sequence homology but that, within each species, actin gene sequences may differ by as much as 30%. Sequencing of two S. franciscanus actin genes revealed introns at the same amino acid positions, 121 and 204, reported for S. purpuratus actin genes. These data demonstrated that the genomic copy number, the transcriptional orientation of linked genes, and, to the extent studied, the intron position of actin genes have evolved similarly in these three species. In contrast, significant change has occurred in the chromosomal arrangement of sea urchin actin genes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angerer R. C., Davidson E. H., Britten R. J. Single copy DNA and structural gene sequence relationships among four sea urchin species. Chromosoma. 1976 Jul 8;56(3):213–226. doi: 10.1007/BF00293186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Williams B. G., Blechl A. E., Denniston-Thompson K., Faber H. E., Furlong L., Grunwald D. J., Kiefer D. O., Moore D. D., Schumm J. W. Charon phages: safer derivatives of bacteriophage lambda for DNA cloning. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):161–169. doi: 10.1126/science.847462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper A. D., Crain W. R., Jr Complete nucleotide sequence of a sea urchin actin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jul 10;10(13):4081–4092. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.13.4081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durica D. S., Schloss J. A., Crain W. R., Jr Organization of actin gene sequences in the sea urchin: molecular cloning of an intron-containing DNA sequence coding for a cytoplasmic actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5683–5687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firtel R. A., Bonner J. Characterization of the genome of the cellular slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum. J Mol Biol. 1972 May 28;66(3):339–361. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90419-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fornwald J. A., Kuncio G., Peng I., Ordahl C. P. The complete nucleotide sequence of the chick a-actin gene and its evolutionary relationship to the actin gene family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jul 10;10(13):3861–3876. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.13.3861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyrberg E. A., Bond B. J., Hershey N. D., Mixter K. S., Davidson N. The actin genes of Drosophila: protein coding regions are highly conserved but intron positions are not. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):107–116. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90506-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyrberg E. A., Kindle K. L., Davidson N., Kindle K. L. The actin genes of Drosophila: a dispersed multigene family. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):365–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90511-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall T. J., Grula J. W., Davidson E. H., Britten R. J. Evolution of sea urchin non-repetitive DNA. J Mol Evol. 1980 Dec;16(2):95–110. doi: 10.1007/BF01731580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaine B. P., Spear B. B. Nucleotide sequence of a macronuclear gene for actin in Oxytricha fallax. Nature. 1982 Feb 4;295(5848):430–432. doi: 10.1038/295430a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein W. H., Thomas T. L., Lai C., Scheller R. H., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Characteristics of individual repetitive sequence families in the sea urchin genome studied with cloned repeats. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):889–900. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90344-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Hardison R. C., Lacy E., Lauer J., O'Connell C., Quon D., Sim G. K., Efstratiadis A. The isolation of structural genes from libraries of eucaryotic DNA. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):687–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeown M., Firtel R. A. Evidence for sub-families of actin genes in Dictyostelium as determined by comparisons of 3' end sequences. J Mol Biol. 1981 Oct 5;151(4):593–606. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90425-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlino G. T., Water R. D., Chamberlain J. P., Jackson D. A., El-Gewely M. R., Kleinsmith L. J. Cloning of sea urchin actin gene sequences for use in studying the regulation of actin gene transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):765–769. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nellen W., Donath C., Moos M., Gallwitz D. The nucleotide sequences of the actin genes from Saccharomyces carlsbergensis and Saccharomyces cerevisiae are identical except for their introns. J Mol Appl Genet. 1981;1(3):239–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nellen W., Gallwitz D. Actin genes and actin messenger RNA in Acanthamoeba castellanii. Nucleotide sequence of the split actin gene I. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jul 25;159(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nudel U., Katcoff D., Zakut R., Shani M., Carmon Y., Finer M., Czosnek H., Ginsburg I., Yaffe D. Isolation and characterization of rat skeletal muscle and cytoplasmic actin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2763–2767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overbeek P. A., Merlino G. T., Peters N. K., Cohn V. H., Moore G. P., Kleinsmith L. J. Characterization of five members of the actin gene family in the sea urchin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Dec 28;656(2):195–205. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(81)90087-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Davidson E. H., Britten R. J. A program for least squares analysis of reassociation and hybridization data. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Jun;4(6):1727–1737. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.6.1727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D. Cytoplasmic contractile proteins. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 2):156s–165s. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.156s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Weihing R. R. Actin and myosin and cell movement. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1974 Jan;2(1):1–65. doi: 10.3109/10409237409105443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheller R. H., McAllister L. B., Crain W. R., Jr, Durica D. S., Posakony J. W., Thomas T. L., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Organization and expression of multiple actin genes in the sea urchin. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Jul;1(7):609–628. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.7.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuler M. A., Keller E. B. The chromosomal arrangement of two linked actin genes in the sea urchin S. purpuratus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 11;9(3):591–604. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.3.591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuler M. A., McOsker P., Keller E. B. DNA sequence of two linked actin genes of sea urchin. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;3(3):448–456. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.3.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah D. M., Hightower R. C., Meagher R. B. Complete nucleotide sequence of a soybean actin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1022–1026. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soriano P., Szabo P., Bernardi G. The scattered distribution of actin genes in the mouse and human genomes. EMBO J. 1982;1(5):579–583. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01211.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin S. L., Zulauf E., Sánchez F., Craig E. A., McCarthy B. J. Multiple actin-related sequences in the Drosophila melanogaster genome. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):121–131. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90393-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]