Abstract
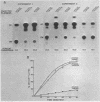
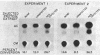
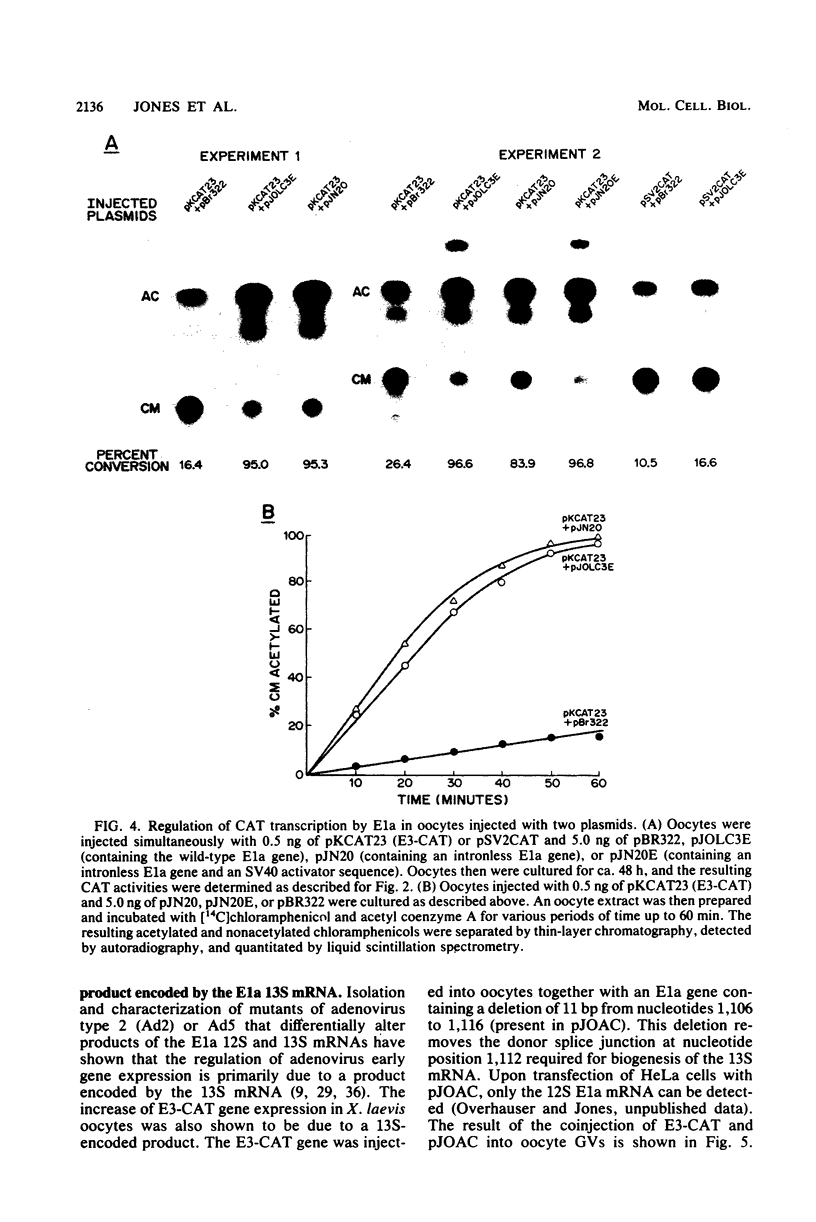
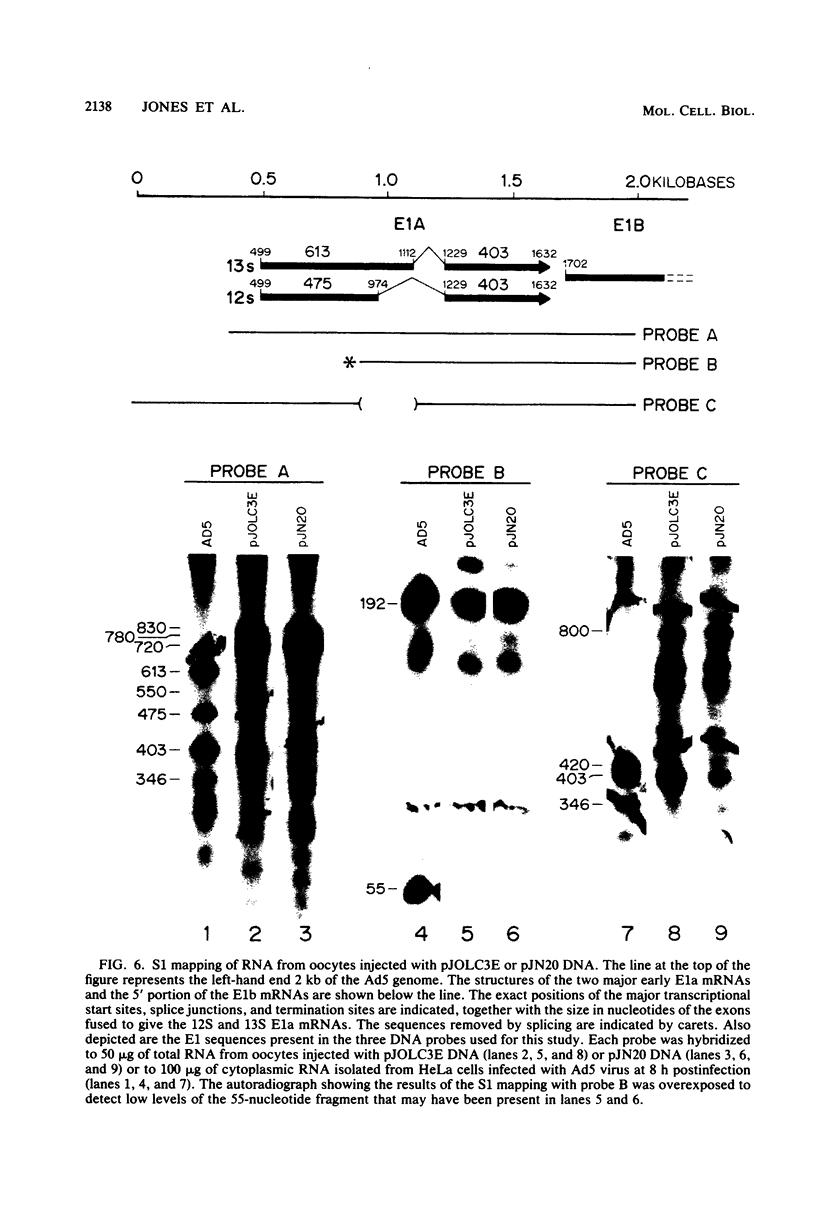
The regulation of adenovirus type 5 gene expression by the E1a gene product was examined in microinjected Xenopus laevis oocytes. Chimeric genes were constructed which included the promoter region of early adenovirus type 5 gene 3 and the structural sequence which codes for the bacterial enzyme chloramphenicol-3-O-acetyltransferase (CAT). A plasmid containing this chimeric gene as well as plasmids containing the E1a gene were coinjected into oocyte nuclei. The presence of the E1a gene was shown to increase CAT activity by up to 8.5-fold over basal levels. Synthesis of the functional product from the E1a gene requires the removal of intron sequences by RNA splicing. The E1a gene and a derivative that precisely lacks the intron were equally effective in increasing CAT activity, suggesting that splicing of the primary E1a transcript is efficiently accomplished in the oocyte nucleus. This was confirmed by directly examining the E1a mRNAs by the S1 mapping procedure. A protein extract from adenovirus type 5-infected HeLa cells enriched for the E1a protein may supplant the E1a plasmid in enhancing CAT activity. Synthesis of the CAT enzyme after gene injection is invariant in oocytes from the same frog, but oocytes from different frogs show a high degree of variability in their ability to synthesize the CAT enzyme. Microinjected X. laevis oocytes appear to be an extremely useful system to study the effects of protein elements on transcription.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asselbergs F. A., Smart J. E., Mathews M. B. Analysis of expression of adenovirus DNA (fragments) by microinjection in Xenopus oocytes. Independent synthesis of minor early region 2 proteins. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jan 15;163(2):209–238. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. C., Ziff E. B. Promoters and heterogeneous 5' termini of the messenger RNAs of adenovirus serotype 2. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 25;149(2):189–221. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90298-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji J., Rusconi S., Schaffner W. Expression of a beta-globin gene is enhanced by remote SV40 DNA sequences. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):299–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90413-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Lee F., Harrison T., Williams J., Sharp P. A. Pre-early adenovirus 5 gene product regulates synthesis of early viral messenger RNAs. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):935–944. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90333-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Structure of the adenovirus 2 early mRNAs. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):695–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90252-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Wormington W. M., Brown D. D. Stable transcription complexes of Xenopus 5S RNA genes: a means to maintain the differentiated state. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):413–421. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90359-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. D., Gurdon J. B. High-fidelity transcription of 5S DNA injected into Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2064–2068. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlock L. R., Jones N. C. Transformation-defective mutant of adenovirus type 5 containing a single altered E1a mRNA species. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):657–664. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.657-664.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Broker T. R., Lewis J. B. Complex splicing patterns of RNAs from the early regions of adenovirus-2. J Mol Biol. 1979 Oct 25;134(2):265–303. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Robertis E. M., Mertz J. E. Coupled transcription-translation of DNA injected into Xenopus oocytes. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90195-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolecki G. J., Smith L. D. Poly(A)+ RNA metabolism during oogenesis in Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1979 Mar;69(1):217–236. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90287-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont J. N. Oogenesis in Xenopus laevis (Daudin). I. Stages of oocyte development in laboratory maintained animals. J Morphol. 1972 Feb;136(2):153–179. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051360203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eppig J. J., Jr, Dumont J. N. Amino acid pools in developing oocytes of Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1972 Jul;28(3):531–536. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(72)90036-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etkin L. D., Maxson R. E., Jr The synthesis of authentic sea urchin transcriptional and translational products by sea urchin histone genes injected into Xenopus laevis oocytes. Dev Biol. 1980 Mar;75(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90140-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaynor R. B., Tsukamoto A., Montell C., Berk A. J. Enhanced expression of adenovirus transforming proteins. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):276–285. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.276-285.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Harrison T., Williams J. Defective transforming capacity of adenovirus type 5 host-range mutants. Virology. 1978 May 1;86(1):10–21. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss P., Dhar R., Khoury G. Simian virus 40 tandem repeated sequences as an element of the early promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):943–947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B., Lane C. D., Woodland H. R., Marbaix G. Use of frog eggs and oocytes for the study of messenger RNA and its translation in living cells. Nature. 1971 Sep 17;233(5316):177–182. doi: 10.1038/233177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N., Shenk T. An adenovirus type 5 early gene function regulates expression of other early viral genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3665–3669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N., Shenk T. Isolation of adenovirus type 5 host range deletion mutants defective for transformation of rat embryo cells. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):683–689. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90275-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn L. J., Gurdon J. B., Price J. Oocyte extracts reactivate developmentally inert Xenopus 5S genes in somatic nuclei. Nature. 1982 Nov 25;300(5890):354–355. doi: 10.1038/300354a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane C. D., Colman A., Mohun T., Morser J., Champion J., Kourides I., Craig R., Higgins S., James T. C., Applebaum S. W. The Xenopus oocyte as a surrogate secretory system. The specificity of protein export. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Oct;111(1):225–235. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06097.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L. Functional relationships between transcriptional control signals of the thymidine kinase gene of herpes simplex virus. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):355–365. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90129-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Gavis E. R. Expression of the herpes thymidine kinase gene in Xenopus laevis oocytes: an assay for the study of deletion mutants constructed in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):5931–5948. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.5931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertz J. E. Linear DNA does not form chromatin containing regularly spaced nucleosomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;2(12):1608–1618. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.12.1608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. J., Stephens D. L., Mertz J. E. Kinetics of accumulation and processing of simian virus 40 RNA in Xenopus laevis oocytes injected with simian virus 40 DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;2(12):1581–1594. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.12.1581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Fisher E. F., Caruthers M. H., Berk A. J. Resolving the functions of overlapping viral genes by site-specific mutagenesis at a mRNA splice site. Nature. 1982 Feb 4;295(5848):380–384. doi: 10.1038/295380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau P., Hen R., Wasylyk B., Everett R., Gaub M. P., Chambon P. The SV40 72 base repair repeat has a striking effect on gene expression both in SV40 and other chimeric recombinants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):6047–6068. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.6047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Mechanism of activation of early viral transcription by the adenovirus E1A gene product. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):213–220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90304-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura N., Ray D. S. Expression of a DNA strand initiation sequence of ColE1 plasmid in a single-stranded DNA phage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6566–6570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne T. F., Berk A. J. Far upstream initiation sites for adenovirus early region 1A transcription are utilized after the onset of viral DNA replication. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):594–599. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.594-599.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perricaudet M., Akusjärvi G., Virtanen A., Pettersson U. Structure of two spliced mRNAs from the transforming region of human subgroup C adenoviruses. Nature. 1979 Oct 25;281(5733):694–696. doi: 10.1038/281694a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probst E., Kressmann A., Birnstiel M. L. Expression of sea urchin histone genes in the oocyte of Xenopus laevis. J Mol Biol. 1979 Dec 15;135(3):709–732. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90173-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi R. P., Jones R. L., Cepko C. L., Sharp P. A., Roberts B. E. Expression of early adenovirus genes requires a viral encoded acidic polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6121–6125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter J. D., Evers D. C., Smith L. D. The recruitment of membrane-bound mRNAs for translation in microinjected Xenopus oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2614–2620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter J. D., Jones N. C., Smith L. D. Stimulation of Xenopus oocyte protein synthesis by microinjected adenovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3789–3793. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter J. D., Smith L. D. Differential capacity for translation and lack of competition between mRNAs that segregate to free and membrane-bound polysomes. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):183–191. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90372-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rungger D., Türler H. DNAs of simian virus 40 and polyoma direct the synthesis of viral tumor antigens and capsid proteins in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6073–6077. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stunnenberg H. G., Birnstiel M. L. Bioassay for components regulating eukaryotic gene expression: a chromosomal factor involved in the generation of histone mRNA 3' termini. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6201–6204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman W. J., Richter J. D., Smith L. D. Protein synthesis during maturation promoting factor- and progesterone-induced maturation in Xenopus oocytes. Dev Biol. 1982 Jan;89(1):152–158. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90303-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks D. L., Jones N. C. E1A control of gene expression is mediated by sequences 5' to the transcriptional starts of the early viral genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;3(7):1222–1234. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.7.1222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickens M. P., Gurdon J. B. Post-transcriptional processing of simian virus 40 late transcripts in injected frog oocytes. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jan 5;163(1):1–26. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90027-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickens M. P., Woo S., O'Malley B. W., Gurdon J. B. Expression of a chicken chromosomal ovalbumin gene injected into frog oocyte nuclei. Nature. 1980 Jun 26;285(5767):628–634. doi: 10.1038/285628a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H., Laskey R. A., Finch J., Gurdon J. B. Selective DNA conservation and chromatin assembly after injection of SV40 DNA into Xenopus oocytes. Dev Biol. 1978 May;64(1):178–188. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]