Abstract
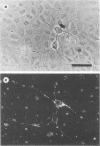
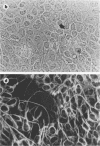
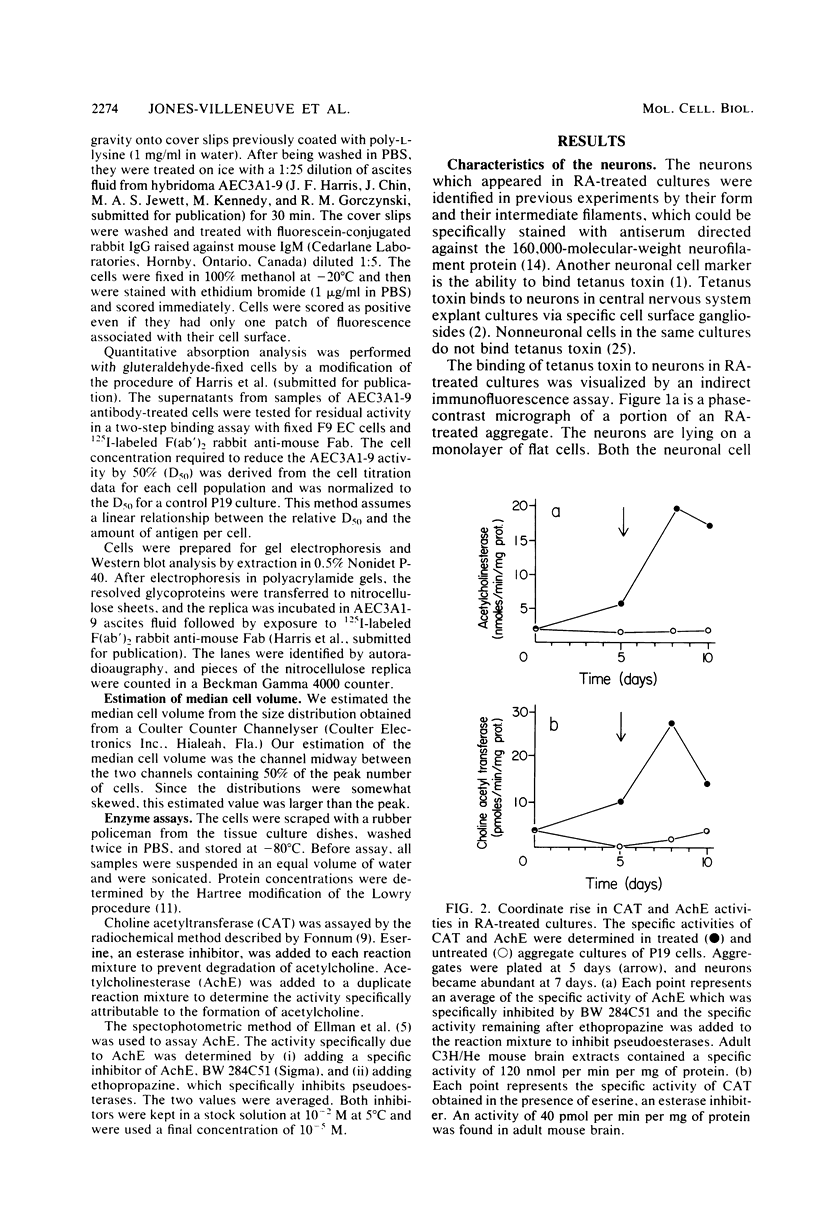
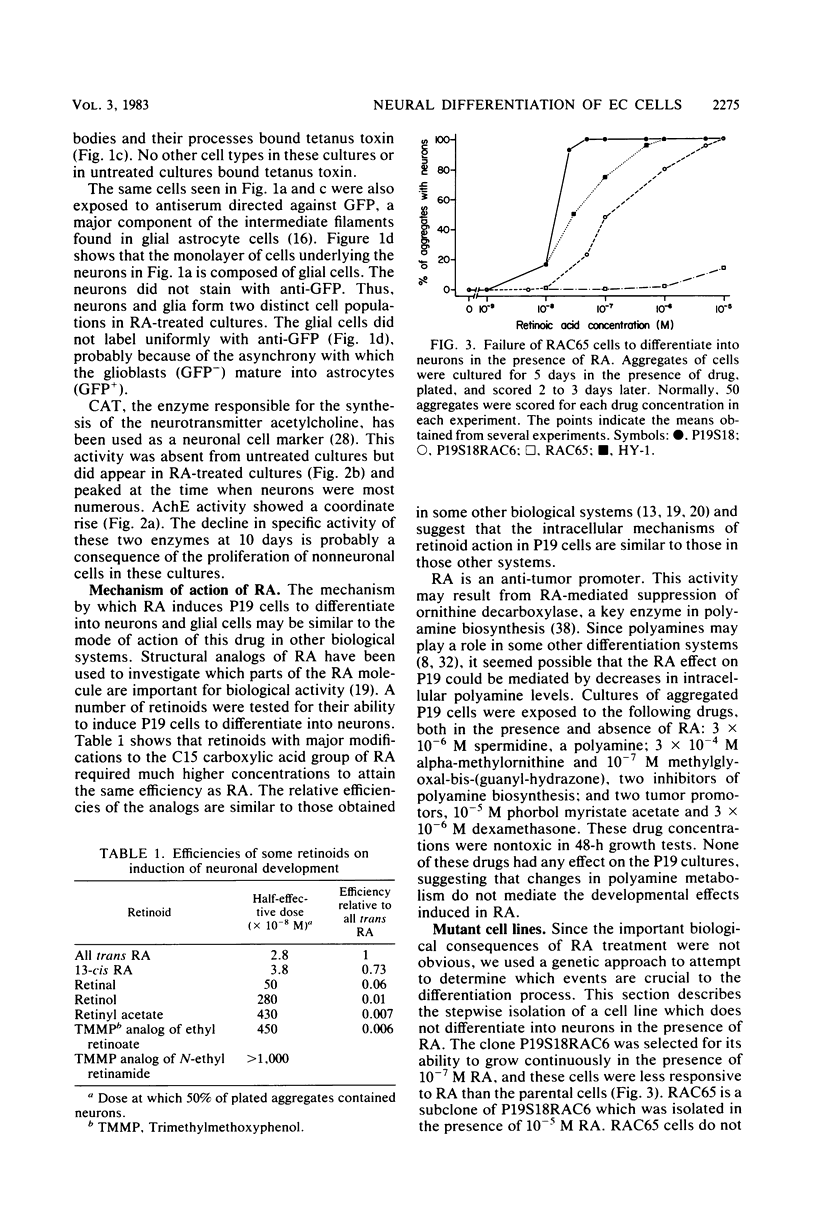
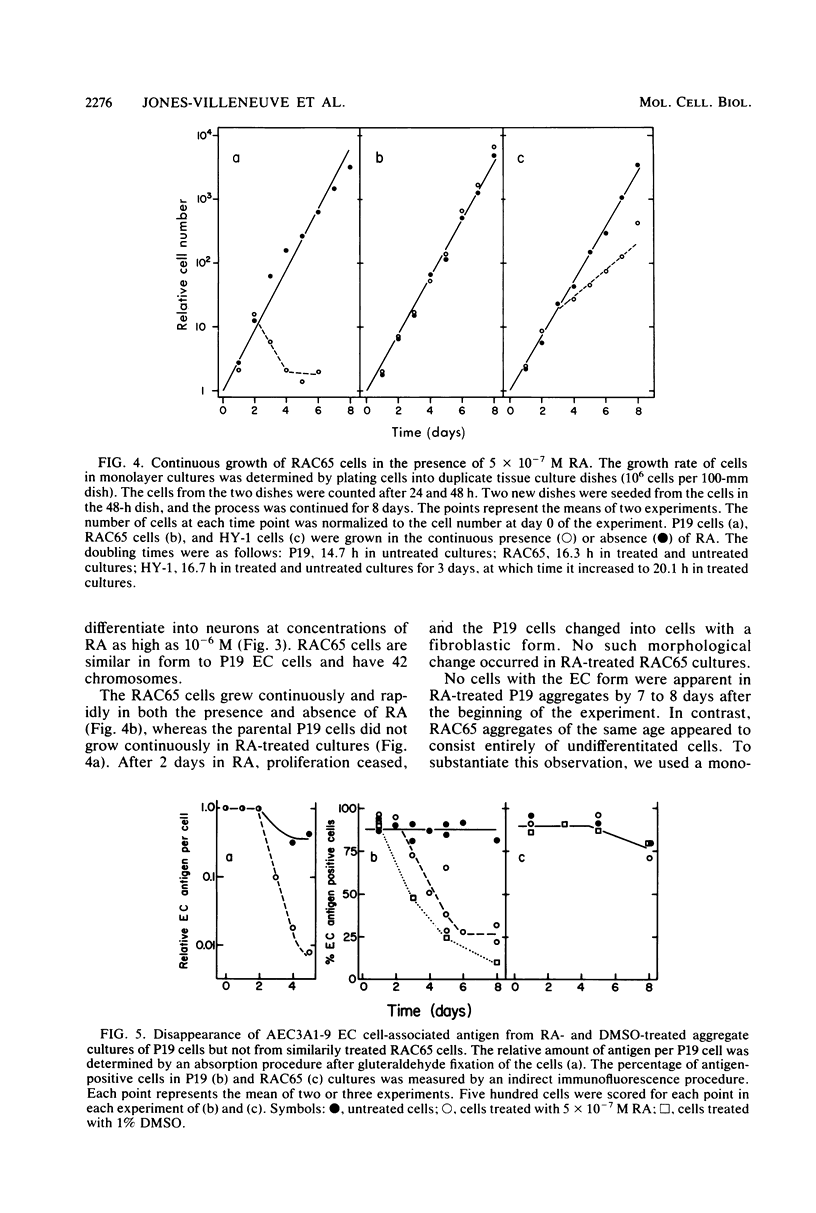
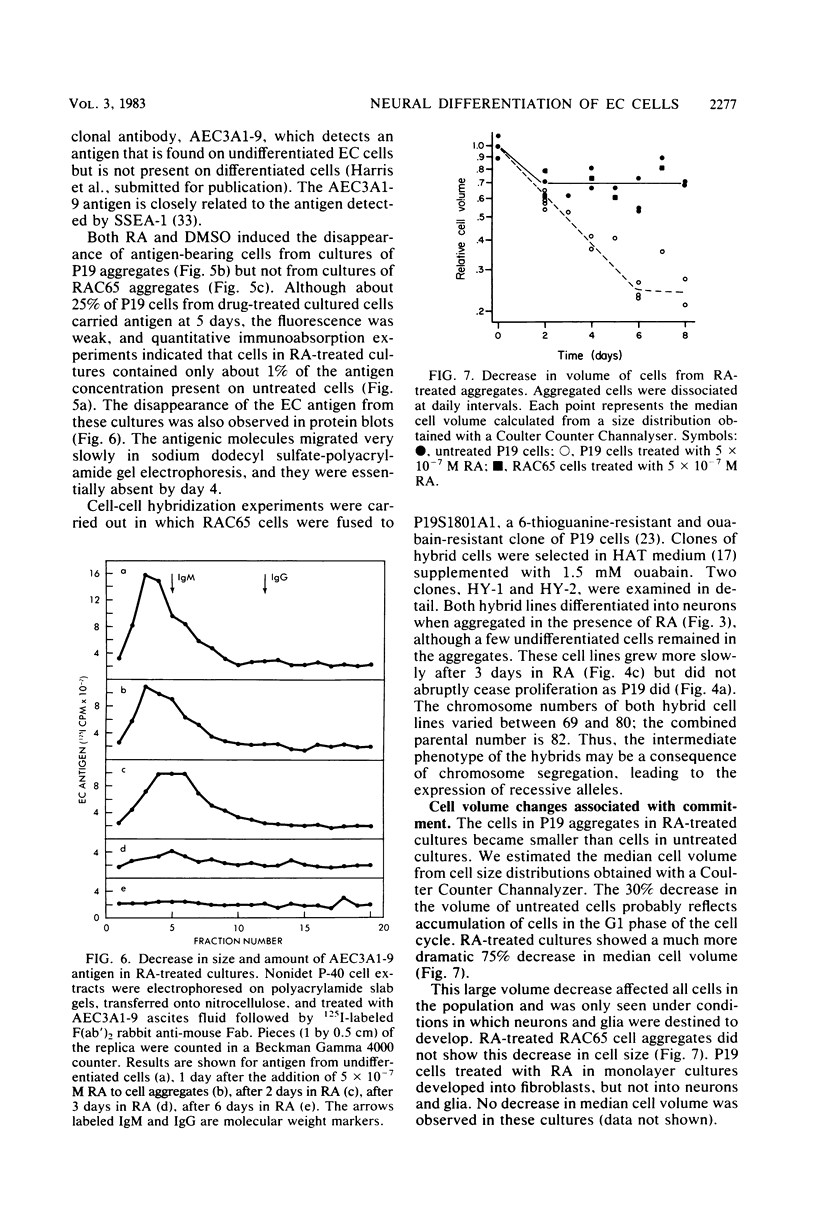
We have previously shown that the P19 line of embryonal carcinoma cells develops into neurons, astroglia, and fibroblasts after aggregation and exposure to retinoic acid. The neurons were initially identified by their morphology and by the presence of neurofilaments within their cytoplasm. We have more fully documented the neuronal nature of these cells by showing that their cell surfaces display tetanus toxin receptors, a neuronal cell marker, and that choline acetyl-transferase and acetyl cholinesterase activities appear coordinately in neuron-containing cultures. Several days before the appearance of neurons, there is a marked decrease in the amount of an embryonal carcinoma surface antigen, and at the same time there is a substantial decrease in the volumes of individual cells. Various retinoids were able to induce the development of neurons in cultures of aggregated P19 cells, but it did not appear that polyamine metabolism was involved in the effect. We have isolated a mutant clone which does not differentiate in the presence of any of the drugs which are normally effective in inducing differentiation of P19 cells. This mutant and others may help to elucidate the chain of events triggered by retinoic acid and other differentiation-inducing drugs.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bizzini B. Tetanus toxin. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Jun;43(2):224–240. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.2.224-240.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L., COURTNEY K. D., ANDRES V., Jr, FEATHER-STONE R. M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1961 Jul;7:88–95. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(61)90145-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards M. K., Harris J. F., McBurney M. W. Induced muscle differentiation in an embryonal carcinoma cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2280–2286. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards M. K., McBurney M. W. The concentration of retinoic acid determines the differentiated cell types formed by a teratocarcinoma cell line. Dev Biol. 1983 Jul;98(1):187–191. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90348-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields K. L. Cell type-specific antigens of cells of the central and peripheral nervous system. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1979;13(Pt 1):237–257. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60697-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch B. W., Ephrussi B. RETENTION OF MULTIPLE DEVELOPMENTAL POTENTIALITIES BY CELLS OF A MOUSE TESTICULAR TERATOCARCINOMA DURING PROLONGED CULTURE in vitro AND THEIR EXTINCTION UPON HYBRIDIZATION WITH CELLS OF PERMANENT LINES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Mar;57(3):615–621. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.3.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish L. A., Baxter C. S., Bash J. A. Murine lymphocyte comitogenesis by phorbol esters, and its inhibition by retinoic acid and inhibitors of polyamine biosynthesis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1981 Mar 30;58(1):39–47. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(81)90113-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonnum F. A rapid radiochemical method for the determination of choline acetyltransferase. J Neurochem. 1975 Feb;24(2):407–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1975.tb11895.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartree E. F. Determination of protein: a modification of the Lowry method that gives a linear photometric response. Anal Biochem. 1972 Aug;48(2):422–427. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90094-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan B. L., Taylor A., Adamson E. Cell interactions modulate embryonal carcinoma cell differentiation into parietal or visceral endoderm. Nature. 1981 May 21;291(5812):235–237. doi: 10.1038/291235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jetten A. M., Jetten M. E. Possible role of retinoic acid binding protein in retinoid stimulation of embryonal carcinoma cell differentiation. Nature. 1979 Mar 8;278(5700):180–182. doi: 10.1038/278180a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones-Villeneuve E. M., McBurney M. W., Rogers K. A., Kalnins V. I. Retinoic acid induces embryonal carcinoma cells to differentiate into neurons and glial cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;94(2):253–262. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.2.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahan B. W., Ephrussi B. Developmental potentialities of clonal in vitro cultures of mouse testicular teratoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1970 May;44(5):1015–1036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLEFIELD J. W. SELECTION OF HYBRIDS FROM MATINGS OF FIBROBLASTS IN VITRO AND THEIR PRESUMED RECOMBINANTS. Science. 1964 Aug 14;145(3633):709–710. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3633.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loritz F., Bernstein A., Miller R. G. Early and late volume changes during erythroid differentiation of cultured Friend leukemic cells. J Cell Physiol. 1977 Mar;90(3):423–437. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040900306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotan R. Effects of vitamin A and its analogs (retinoids) on normal and neoplastic cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Mar 12;605(1):33–91. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(80)90021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotan R., Neumann G., Lotan D. Relationships among retinoid structure, inhibition of growth, and cellular retinoic acid-binding protein in cultured S91 melanoma cells. Cancer Res. 1980 Apr;40(4):1097–1102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. R., Evans M. J. Differentiation of clonal lines of teratocarcinoma cells: formation of embryoid bodies in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1441–1445. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBurney M. W., Jones-Villeneuve E. M., Edwards M. K., Anderson P. J. Control of muscle and neuronal differentiation in a cultured embryonal carcinoma cell line. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):165–167. doi: 10.1038/299165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBurney M. W., Rogers B. J. Isolation of male embryonal carcinoma cells and their chromosome replication patterns. Dev Biol. 1982 Feb;89(2):503–508. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90338-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirsky R., Wendon L. M., Black P., Stolkin C., Bray D. Tetanus toxin: a cell surface marker for neurones in culture. Brain Res. 1978 Jun 9;148(1):251–259. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90399-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore B. W., Perez V. J., Gehring M. Assay and regional distribution of a soluble protein characteristic of the nervous system. J Neurochem. 1968 Apr;15(4):265–272. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1968.tb11610.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolas J. F., Dubois P., Jakob H., Gaillard J., Jacob F. Tératocarcinome de la souris: différenciation en culture d'une lignée de cellules primitives a potentialités multiples. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1975 Jan;126(1):3–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer S. E., Jakob H., Mikoshiba K., Dubois P., Guenet J. L., Nicolas J. F., Gaillard J., Chevance G., Jacob F. Differentiation of a teratocarcinoma line: preferential development of cholinergic neurons. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jan;88(1):57–66. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.1.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal M. D., Wishnow R. M., Sato G. H. In vitro growth and differetiation of clonal populations of multipotential mouse clls derived from a transplantable testicular teratocarcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1970 May;44(5):1001–1014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossant J., McBurney M. W. The developmental potential of a euploid male teratocarcinoma cell line after blastocyst injection. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1982 Aug;70:99–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler J., Matthaei K. I., Sherman M. I. Isolation and characterization of mouse mutant embryonal carcinoma cells which fail to differentiate in response to retinoic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1077–1080. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott K. F., Meyskens F. L., Jr, Russell D. H. Retinoids increase transglutaminase activity and inhibit ornithine decarboxylase activity in Chinese hamster ovary cells and in melanoma cells stimulated to differentiate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4093–4097. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solter D., Knowles B. B. Monoclonal antibody defining a stage-specific mouse embryonic antigen (SSEA-1). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5565–5569. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speers W. C., Birdwell C. R., Dixon F. J. Chemically induced bidirectional differentiation of embryonal carcinoma cells in vitro. Am J Pathol. 1979 Dec;97(3):563–584. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanners C. P., Eliceiri G. L., Green H. Two types of ribosome in mouse-hamster hybrid cells. Nat New Biol. 1971 Mar 10;230(10):52–54. doi: 10.1038/newbio230052a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland S., Smith K. K., Marotti K. R. Hormonal induction of differentiation in teratocarcinoma stem cells: generation of parietal endoderm by retinoic acid and dibutyryl cAMP. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):347–355. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90471-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma A. K., Rice H. M., Shapas B. G., Boutwell R. K. Inhibition of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced ornithine decarboxylase activity in mouse epidermis by vitamin A analogs (retinoids). Cancer Res. 1978 Mar;38(3):793–801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]