Abstract
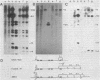
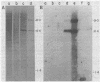
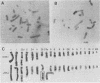
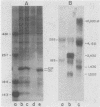
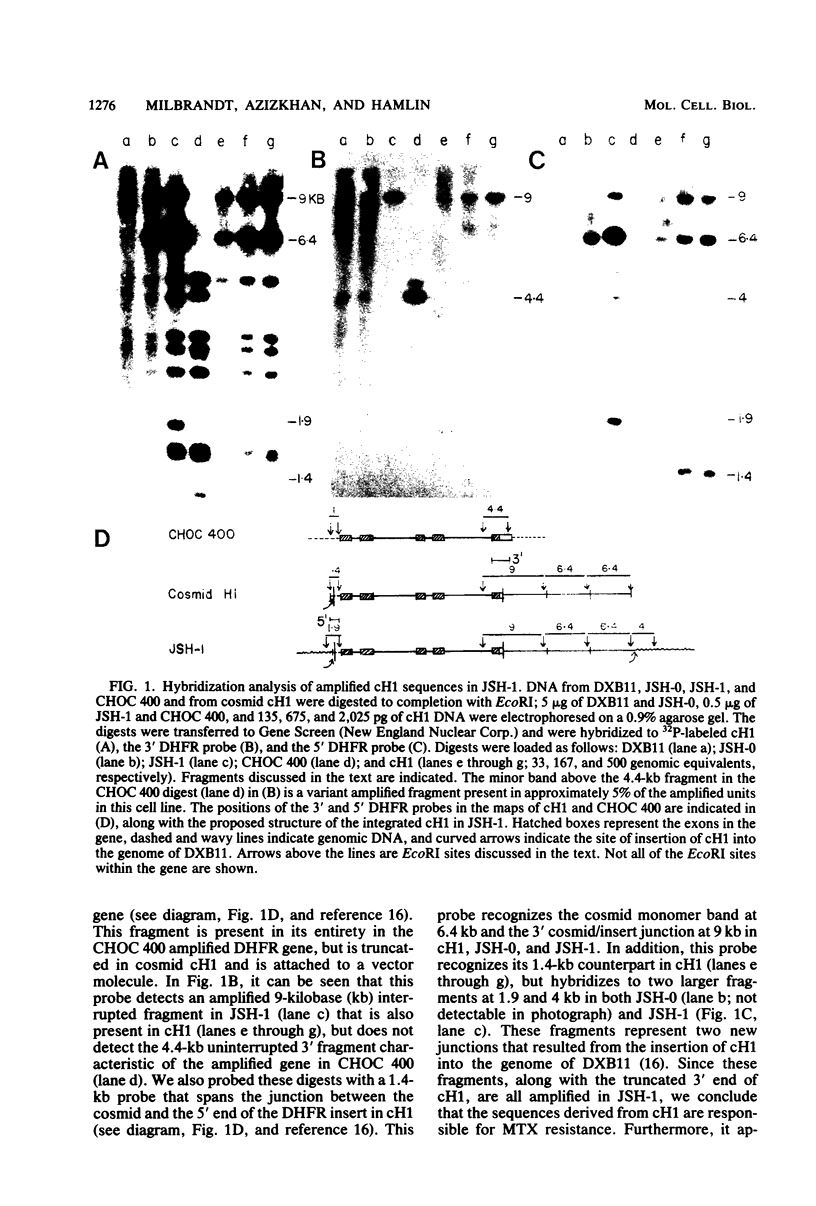
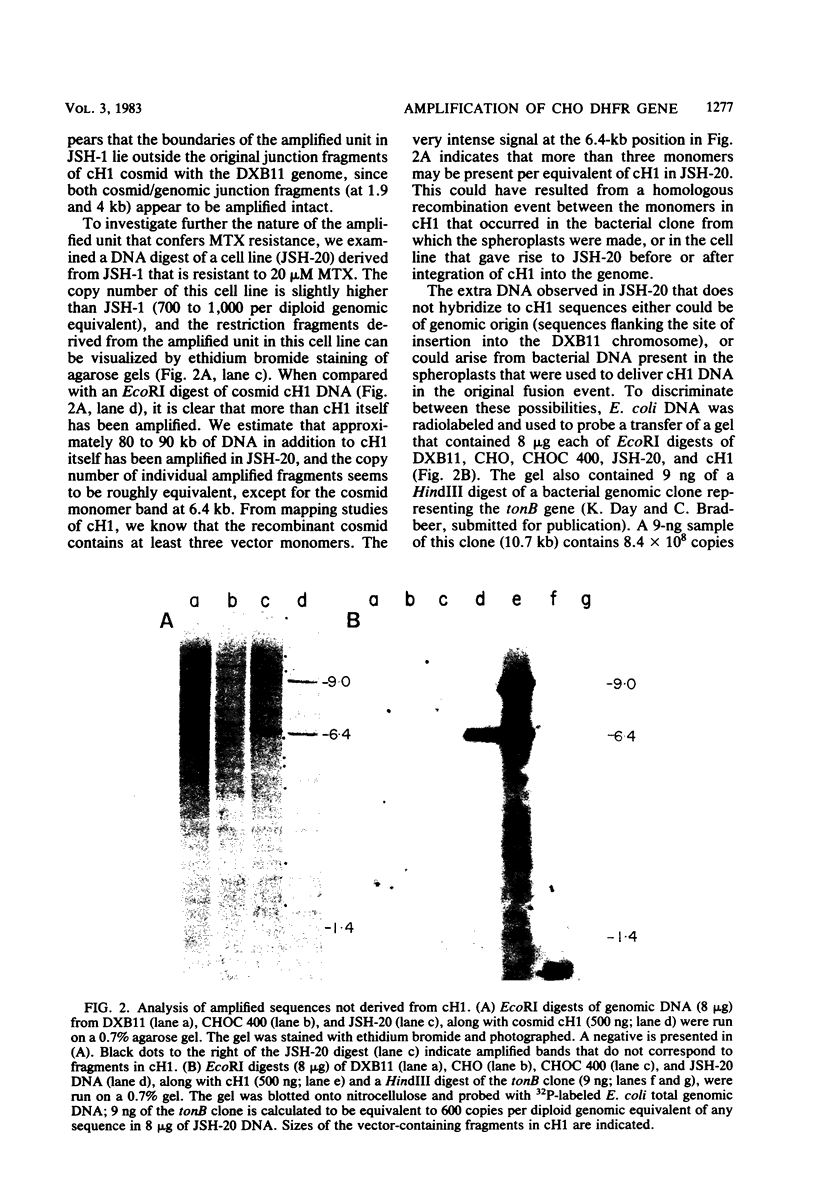
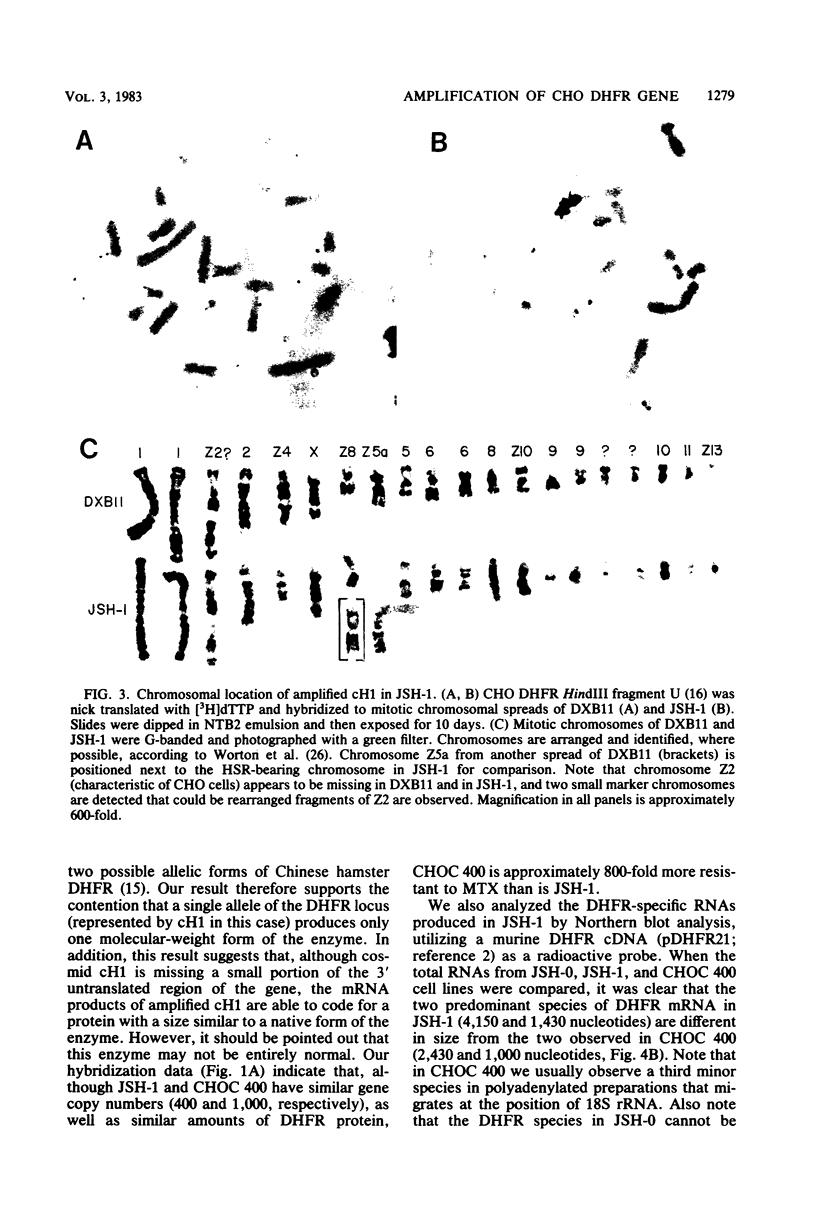
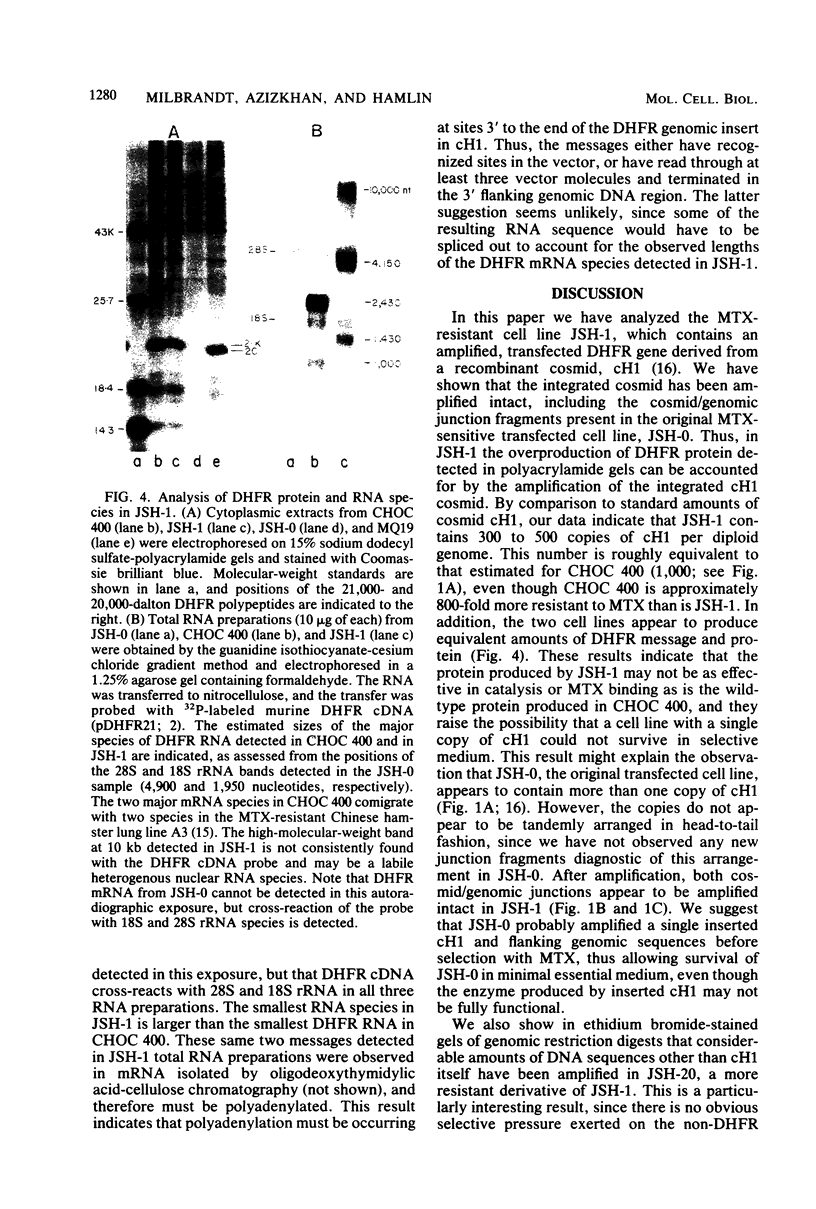
We have transformed a dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR)-deficient Chinese hamster ovary cell line to the DHFR+ phenotype with a recombinant cosmid (cH1) containing a functional Chinese hamster DHFR gene (J.D. Milbrandt et al., Mol. Cell. Biol. 3:1266-1273, 1983). After exposure of cells to successive increases in methotrexate, we have isolated a resistant cell line (JSH-1) that grows in 1 microM methotrexate. We show here that JSH-1 contains 300 to 500 copies of the integrated cosmid and that these copies are located predominantly at one position on a chromosome identified as Z5a. Hybridization analysis of restriction digests of genomic DNA indicates that the cosmid has been integrated intact into the genome and that upon amplification, the original cosmid/genomic junction fragments are also amplified in JSH-1. Furthermore, the pattern of amplified bands observed in ethidium bromide-stained gels indicates that the unit amplified sequence (amplicon) may be as large as 120 to 135 kilobases and therefore includes considerable amounts of flanking DNA in addition to the 45 kilobases of integrated cosmid. We also show that the protein overproduced by the amplified cosmid in JSH-1 comigrates with the 21,000-dalton polypeptide characteristic of the methotrexate-resistant cell line (CHOC 400) from which cH1 was cloned. However, the DHFR mRNA species overproduced in JSH-1 appear to be larger than those detected in CHOC 400, indicating that not all of the normal transcription and processing signals are preserved in the integrated recombinant cosmid.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chang A. C., Nunberg J. H., Kaufman R. J., Erlich H. A., Schimke R. T., Cohen S. N. Phenotypic expression in E. coli of a DNA sequence coding for mouse dihydrofolate reductase. Nature. 1978 Oct 19;275(5681):617–624. doi: 10.1038/275617a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christman J. K., Gerber M., Price P. M., Flordellis C., Edelman J., Acs G. Amplification of expression of hepatitis B surface antigen in 3T3 cells cotransfected with a dominant-acting gene and cloned viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1815–1819. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colbère-Garapin F., Horodniceanu F., Kourilsky P., Garapin A. C. A new dominant hybrid selective marker for higher eukaryotic cells. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 25;150(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90321-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser C. S., Simonsen C. C., Schilling J. W., Schimke R. T. Expression of abbreviated mouse dihydrofolate reductase genes in cultured hamster cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6522–6526. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper M. E., Ullrich A., Saunders G. F. Localization of the human insulin gene to the distal end of the short arm of chromosome 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4458–4460. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kates J. Detection and utilization of poly(A) sequences in messenger RNA. Methods Cell Biol. 1973;7:53–65. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61771-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Sharp P. A. Amplification and expression of sequences cotransfected with a modular dihydrofolate reductase complementary dna gene. J Mol Biol. 1982 Aug 25;159(4):601–621. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90103-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. A., Davide J. P., Melera P. W. Selective amplification of polymorphic dihydrofolate reductase gene loci in Chinese hamster lung cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6961–6965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milbrandt J. D., Azizkhan J. C., Greisen K. S., Hamlin J. L. Organization of a Chinese hamster ovary dihydrofolate reductase gene identified by phenotypic rescue. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;3(7):1266–1273. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.7.1266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milbrandt J. D., Heintz N. H., White W. C., Rothman S. M., Hamlin J. L. Methotrexate-resistant Chinese hamster ovary cells have amplified a 135-kilobase-pair region that includes the dihydrofolate reductase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6043–6047. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan R. C., Berg P. Selection for animal cells that express the Escherichia coli gene coding for xanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2072–2076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W. Direct transfer of cloned genes from bacteria to mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2163–2167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seabright M. A rapid banding technique for human chromosomes. Lancet. 1971 Oct 30;2(7731):971–972. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urlaub G., Chasin L. A. Isolation of Chinese hamster cell mutants deficient in dihydrofolate reductase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4216–4220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Silverstein S., Lee L. S., Pellicer A., Cheng Y. c., Axel R. Transfer of purified herpes virus thymidine kinase gene to cultured mouse cells. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90333-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worton R. G., Ho C. C., Duff C. Chromosome stability in CHO cells. Somatic Cell Genet. 1977 Jan;3(1):27–45. doi: 10.1007/BF01550985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Saint Vincent B. R., Delbrück S., Eckhart W., Meinkoth J., Vitto L., Wahl G. The cloning and reintroduction into animal cells of a functional CAD gene, a dominant amplifiable genetic marker. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):267–277. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90410-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]