Figure 4.
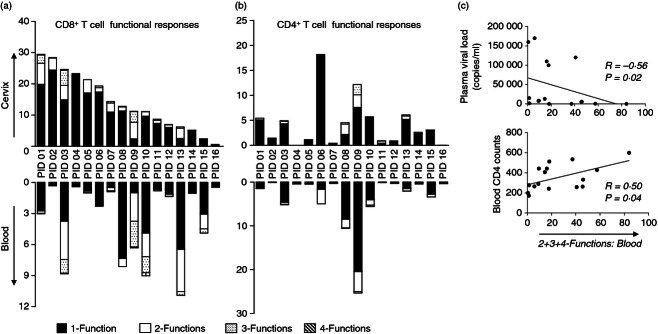
Comparison of HIV-specific T-cell responses between cervix and blood from HIV-infected women and impact of HIV clinical status. (a) Frequency of CD8+ responses within each functional category at the cervix (top graph) were compared with those found in blood (bottom graph). Polyfunctional responses were defined as the total of 2+, 3+ and 4+ functions in blood and at the cervix of CD8+ T cells. (b) Frequency of CD4+ T-cell responses within each functional category at the cervix (top graph) were compared with those found in blood (bottom graph). Responses were considered four-functional (grey) if all four of the markers included in the polyfunctional panel were detected: interferon-γ (IFN-γ), macrophage inflammatory protein 1β (MIP-1β), tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and CD107a. Responses were considered three (dotted), two (open bar) or one functional if any combinations of three, two or one of the four functions investigated were detected, respectively. The bars on the plots represent median functional response after background subtraction. (c) Relationship between polyfunctional (two or more functions) CD8+ T-cell responses to Gag and markers of HIV clinical status. (top graph) Plasma viral load and (bottom graph) blood CD4 T-cell counts associated with polyfunctional CD8+ T-cell responses (defined as two or more responses). Spearman Rank Test was applied to test correlations and P-values < 0·05 were considered significant. Spearman Rho scores are shown on each plot.
