Figure 6.
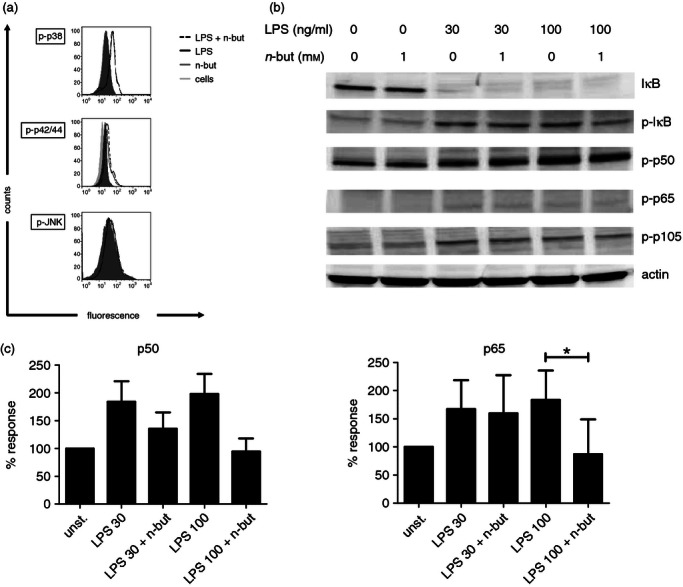
Impact of n-butyrate on mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signalling. (a) Freshly isolated monocytes were stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS; 100 ng/ml) and incubated in the presence or absence of n-butyrate (1 mm). Intracellular staining was performed and the phosphorylated (active) form of the respective MAPK was investigated at 5, 15 (data not shown) and 30 min after LPS stimulation. (b) Monocytes (5 × 106) were pre-treated for 1 hr with or without n-butyrate (1 mm) and then stimulated for 5, 10 (data not shown) and 15 min with LPS (30 and 100 ng/ml). Western blot analysis was performed for the indicated NF-κB signalling molecules. Results are representative of four independent experiments. (c) Monocytes (2 × 106) per probe were pre-treated for 1 hr with or without n-butyrate (1 mm) and then stimulated for 60 min with LPS (30 and 100 ng/ml). DNA binding was assessed for p50 and p65. Results are presented as % binding of nuclear extracts from unstimulated (unst.) monocytes and show mean values ± SEM of four independent experiments. * P ≤ 0·05 (paired Student's t-test)
